Risky Biz News: FTA hacking spree continues with CrushFTP zero-day
In other news: FISA Section 702 renewed for two years; MITRE hacked by state-backed group; China bans Signal, Telegram, WhatsApp.

This newsletter is brought to you by Trail of Bits. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

An unidentified threat actor is exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in CrushFTP, an enterprise file-transfer software solution.
CrushFTP released a patch on Friday, hours after it learned of the attacks from the Airbus CERT team. CrowdStrike also confirmed the zero-day later in the day and described the attacks as "targeted."
The zero-day was assigned CVE-2024-4040.
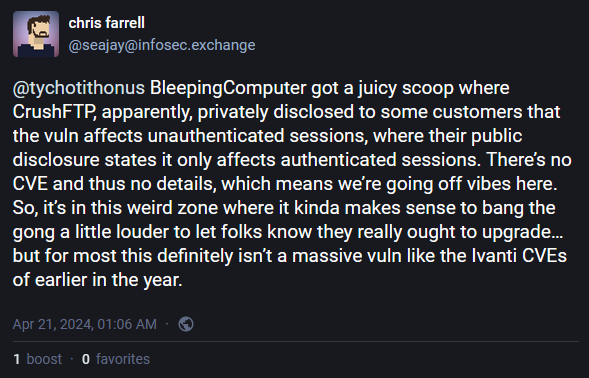
Just like most of these incidents, there is also some sort of misunderstanding and drama about what exactly is taking place. This stems from two conflicting messages that CrushFTP has put out about the issue.
In private messages sent to customers last week, CrushFTP said the vulnerability allowed unauthenticated attackers to escape the virtual file system and download user files,
In a public changelog, the company said that only authenticated attackers can exploit this.
If this is the former, then this is a very big deal. If it's the latter, then there's no threat of mass-exploitation.
The vulnerability does not allow threat actors to take full control over CrushFTP servers, but it can be used to steal user data, which makes it ideal for groups specialized in data extortion, IP theft, or corporate espionage.
According to Censys, more than 7,600 CrushFTP servers have their management panels exposed online and may be vulnerable to attacks.
CrushFTP says servers with the DMZ feature enabled are not affected, so if you can't patch, this might be a good mitigation tactic for the time being.
CrushFTP joins a long list of file-transfer software that has been exploited in attacks over the past 2-3 years. The list includes the likes of Accellion, FileZen, GoAnywhere, and MOVEit.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
MITRE hack: A state-sponsored hacking group has breached the MITRE Corporation at the start of the year. The attackers used two zero-days in Ivanti ConnectSecure VPNs to gain access to the company's R&D network. The company did not attribute the breach to any state. Back in January, security firm Volexity linked the initial zero-day attacks to a Chinese state-sponsored group.
Volkswagen hack: A Chinese state-backed hacking group has breached the Volkswagen Group and stole documents about the company's proprietary technology. According to German broadcaster ZDF, the hack took place between 2010 and 2014. Hackers are believed to have stolen data on the company's gas engines, transmission systems, and electric and hydrogen car technologies. Chinese officials said they were outraged by the accusations.
Grodno Azot hack: Belarusian hacktivist group the Cyber Partisans have hacked and wiped the network of Grodno Azot, Belarus' largest fertilizer plant. The group said it destroyed backups, hacked email servers, and encrypted hundreds of the plant's PCs. The Cyber Partisans say they carried out the hack because the plant's management was involved in political repression against employees who protested the Lukashenko regime. Previously, the group also hacked the BELTA, Belarus' state-owned news agency.
Frontier cyberattack: In an SEC filing last week, Texas-based telecommunications provider Frontier Communications disclosed a security breach of its IT systems.
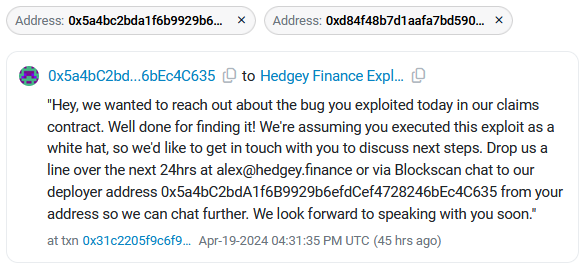
Hedgey Finance crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $44.7 million worth of crypto-assets from DeFi platform Hedgey Finance. The company says the attacker exploited a vulnerability in its Token Claim smart contract to perform a flash loan attack. Hedgey reached out to the hacker to negotiate the return of the stolen funds, but the hacker wasn't interested. [Additional coverage in CoinTelegraph]
General tech and privacy
Android quarantine feature: Google is working on a new feature for the Android OS that will automatically quarantine apps that show signs of malicious behavior. Quarantined apps won't be able to show notifications or interact with other apps. The apps will also have all activity stopped and all windows hidden. Google began working on the feature during Android 14 development last year. The feature is not confirmed to ship with Android 15 later this year. [Additional coverage in AndroidAuthority]
Thunderbird adds Exchange support: The Mozilla Thunderbird email client will add native support for the Microsoft Exchange email protocol in July this year.
"[I]n the entire 20 year lifetime of the Thunderbird project, no one has added support for a new mail protocol before. As such, no one has updated the architecture as mail protocols change and adapt to modern usage patterns, and a great deal of institutional knowledge has been lost."
Banga lists: Dutch officials say Telegram is not responding to requests to remove banga lists on its platforms. Banga lists are files containing the personal info, images, and videos of young women. This is yet another example of Telegram just plain-out refusing to remove offensive content from its platform. Sometimes, I wonder how this site is not blocked and banned everywhere. Apparently, you can host anything on it these days. [Additional coverage in NOS]
WWC shuts down: Women Who Code (WWC), a charity that supports women who work in the technology sector, has announced it is shutting down because of a lack of funding. [Additional coverage in the BBC]
Government, politics, and policy
Congress renews FISA Section 702: President Joe Biden signed on Saturday a bill that extends FISA Section 702 for another two years. The bill passed through the Senate on Friday after it passed through the House a week earlier. According to The Record, the bill passed in the Senate minutes after the statute was set to expire at midnight. FISA Section 702 allows the NSA to collect the electronic communications of foreigners from American companies without a warrant. No major changes were made to Section 702.
China bans four foreign apps: The Chinese government has ordered Apple to remove four foreign apps from the Chinese version of the App Store. Authorities have banned Meta's new Threads social network, as well as secure messaging apps Signal, Telegram, and WhatsApp. The country's internet watchdog cited national security concerns over its decision. Apple said it would conform with Beijing's request. [Additional coverage in the WSJ]
China's new cyber force: The Chinese government has established a new branch of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) dedicated to cyber operations. The new PLA arm is named the Information Support Force. It is China's ninth PLA branch. Officials did not provide additional details about the new force's role, but China already had a dedicated cyberspace force. China also announced its own version of the US Space Force. [Additional coverage from the AFP]
German election security: In a first, Germany's cybersecurity agency, the BSI, will hold training sessions with candidates for the upcoming EU elections on how to secure their TikTok, Twitter, and LinkedIn social media accounts.
UK NCSC CEO: The UK NCSC has named Richard Horne as its new CEO.
Locked Shields exercise: The NATO CCDCOE has invited Ukraine to participate in this year's Locked Shields cyber exercise for the first time.
Georgia state security: The country of Georgia has published its yearly state security report. "The cyber" gets a mention, but I can't tell you what it says because this thing appears to be geo-blocked from almost every IP I tried.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Dan Guido, the CEO of security research company Trail of Bits. Dan and Tom discuss DARPA’s upcoming AI cyber challenge, in which Trail of Bits will compete to solve very difficult bug discovery challenges. They also talk about Trail of Bits’ approach to making some of its own tools available to the community.

Cybercrime and threat intel
German police take down DDoS service: German law enforcement have shut down DDoS-for-hire service Stresser.tech. Police from the German state of Saxony announced the disruption. Officials shut down the service after it was used to launch attacks against its website last September.

Telegram QR phishing campaign: Rostelecom's Solar AURA security division has uncovered a phishing campaign that uses malicious images and QR codes to collect Telegram credentials from Russian users. Solar says the campaign specifically targets Russian users.
New technique for hosting malware on GitHub: Threat actors are using GitHub issue comments to host malicious files on the official repositories of legitimate companies. The technique has been used in the wild for months, according to Sergei Frankoff of OALABS. The trick is to create an issue on an official project and upload the malicious file as a comment but not file the report. The issue is never active or visible to the project owner, but the malicious file remains on GitHub servers. The file's URL will trick users into thinking it's an official file on that project, even if it was uploaded by an attacker. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
New npm malware: Nineteen malicious npm packages were discovered last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for additional details.
Threat/trend reports: GuidePoint, Kroll, and Protect AI have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
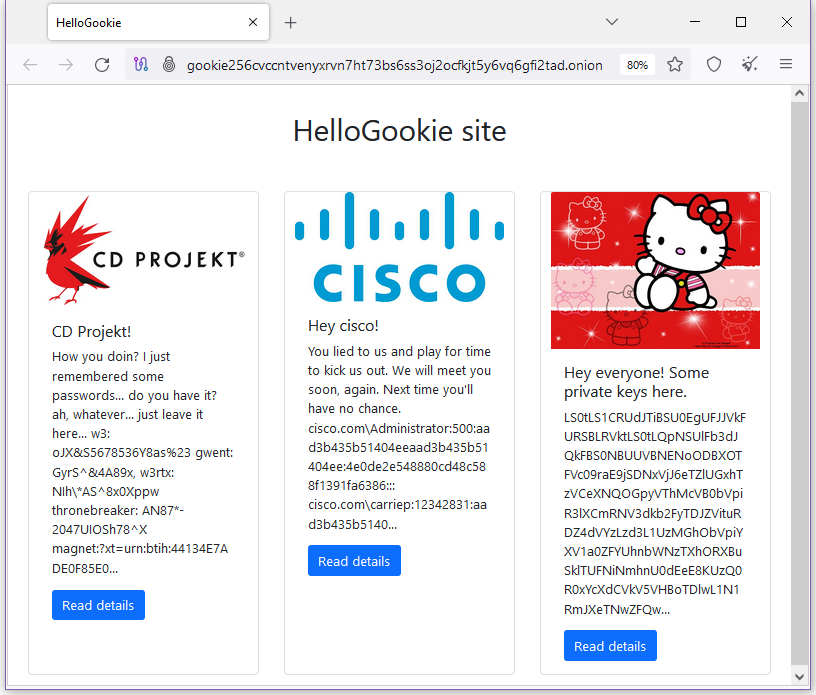
HelloKitty rebrands as HelloGookie: The HelloKitty ransomware gang has rebranded and changed its name to the (more original) HelloGookie. The group released decryption keys for four past victims. It also released passwords to unlock leaked files for two of its most high-profile victims—networking equipment vendor Cisco and Polish gaming studio CD Projekt Red. [h/t @3xp0rt]
Malware technical reports
MadMxShell: Zscaler has published an analysis of MadMxShell, a new backdoor currently distributed via malicious Google ads.
"The newly discovered backdoor uses several techniques such as multiple stages of DLL sideloading, abusing the DNS protocol for communicating with the command-and-control (C2) server, and evading memory forensics security solutions. We named this backdoor “MadMxShell” for its use of DNS MX queries for C2 communication and its very short interval between C2 requests."
Sponsor Section
Trail of Bits has released weAudit, a VSCode extension the company's security engineers use for source code reviews during their security audits. The company also released SARIF Explorer, another VSCode extension for triaging static analysis results.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
UAC-0133 (Sandworm): Ukraine's CERT team says that Russian hacking group Sandworm planned destructive cyberattacks at 20 critical infrastructure facilities across Ukraine. Officials confirmed three supply-chain compromises meant to aid the attacks. Malware infections were found at water, heat, and energy supply facilities in ten regions of Ukraine. The CERT team released IOCs for some of the group's malware with the advisory.
UAC-0149: Ukraine's CERT team says that a threat actor it tracks as UAC-0149 has attempted to infect some of the country's military personnel with malware. The attacks began in late 2023 and used Signal spear-phishing. The final payload is a PowerShell-based malware strain tracked as COOKBOX. Consider this report part II of a previous attack first documented by CERT-UA back in February.
Volt Typhoon: In yet another public warning on the topic, FBI Director Christopher Wray has warned again about the danger posed by Chinese APT group Volt Typhoon. Speaking at the Vanderbilt University, Wray said the group is preparing widespread disruptive actions against US critical infrastructure. [Additional coverage in CyberScoop]
APT43 (Kimsuky): South Korean security firm Genians has published a report on a recent APT43 (Kimsuky) campaign abusing Dropbox services to host payloads for the TutorialRAT (TutRAT).
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
PAN GlobalProtect zero-day: Palo Alto Networks has published the results of their investigation and a root cause analysis of the recent attacks using GlobalProtect zero-day CVE-2024-3400.
MagicDot vulnerabilities: SafeBreach researcher Or Yair has published a write-up on a series of vulnerabilities they discovered last year that can be used to install rootkits on Windows systems. The vulnerabilities exploit the Windows DOS-to-NT path conversion process. The research was presented at the Black Hat Asia 2024 security conference last week.
PAN Cortex takeover: The same SafeBreach team has also presented new research at the conference on bugs they found in the Palo Alto Networks Cortex EDR. The bugs could be used to take over the EDR and use it for offensive operations.
Passbolt vulnerability: Password manager Passbolt has fixed a vulnerability in its browser extension. The bug was discovered by Quarkslab.
"This vulnerability would have allowed an attacker capable of observing Passbolt browser extension queries to the Pwned Password API to more easily bruteforce and therefore guess manually entered passwords."
Dreamehome vulnerability: SEC Consult researchers have published details about a broken authorization vulnerability in the Dreamehome smart cleaning products app. Researchers say there is no patch because the vendor was "unresponsive/uncooperative during multiple months of trying to establish a security contact and to send them our findings."
DOOM on Cisco devices: Researchers at Nettitude Labs have published a write-up and PoC for CVE-2024-20356. This is a command injection vulnerability in the web interface of the Cisco IMC servers that can be used by authenticated attackers to gain root privileges on the device. Nettitude used the bug to install and play DOOM on the device. Cisco patched the vulnerability last week.
SolarWinds security updates: SolarWinds has pushed patches for three security flaws last week.
Atlassian security updates: Australian software company Atlassian has published seven security updates last week.
Arm security updates: Chipmaker Arm has released patches to fix two vulnerabilities in its Mali GPU drivers.
RESIP traffic: A team of academics has looked at several ways to identify residential IP (RESIP) traffic. The research comes as threat actors are building more and more RESIP botnets and renting access to these proxy networks to other threat actors to disguise the origin of malicious traffic.
Minecraft RANDAR exploit: Minecraft clan SpawnMason has published details on RANDAR, an exploit it used to get the in-game coordinates of other players on PvP servers. The exploit utilizes a bug in the RNG of Minecraft servers to leak the coordinates of other players. Coordinates are leaked via simple actions, such as breaking a Minecraft block. A YouTube video of the history of the exploit and how SpawnMason used it is embedded below.
Infosec industry
OWASP 20 years: The OWASP Foundation is celebrating its 20th anniversary.
Black Hat Asia 2024 videos: Slides from the Black Hat Asia 2024 security conference, which took place last week, are now available on the conference's site.
Pwnie Awards 2024: You can now submit your nominations for this year's Pwnie Awards ceremony.
New tool—Task-Ninja: Security engineer Rikunj Sindhwad has released Task-Ninja, an automation framework for DevSecOps engineers, hackers, and bug-bounty hunters.
New tool—AppView: The AppView team has released the first stable version of its app, an open-source, runtime-agnostic instrumentation utility for any Linux command or application. The code is on GitHub too.
New tool—Cargo-Unmaintained: Security firm Trail of Bits (coincidentally this edition's sponsor) has open-sourced Cargo-Unmaintained, a tool to find unmaintained packages in Rust projects.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at Google's review of zero-days in 2023. They discuss what this kind of information tells us and how Google's perspective influences the report.




