Risky Biz News: Multi-party approval comes to Google Workspace
In other news: Ukraine suspends SBU cyber chief; hacker dumps data of most Salvadorans; Ukrainian hackers wipe Russian cloud provider.

This newsletter is brought to you by GreyNoise. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

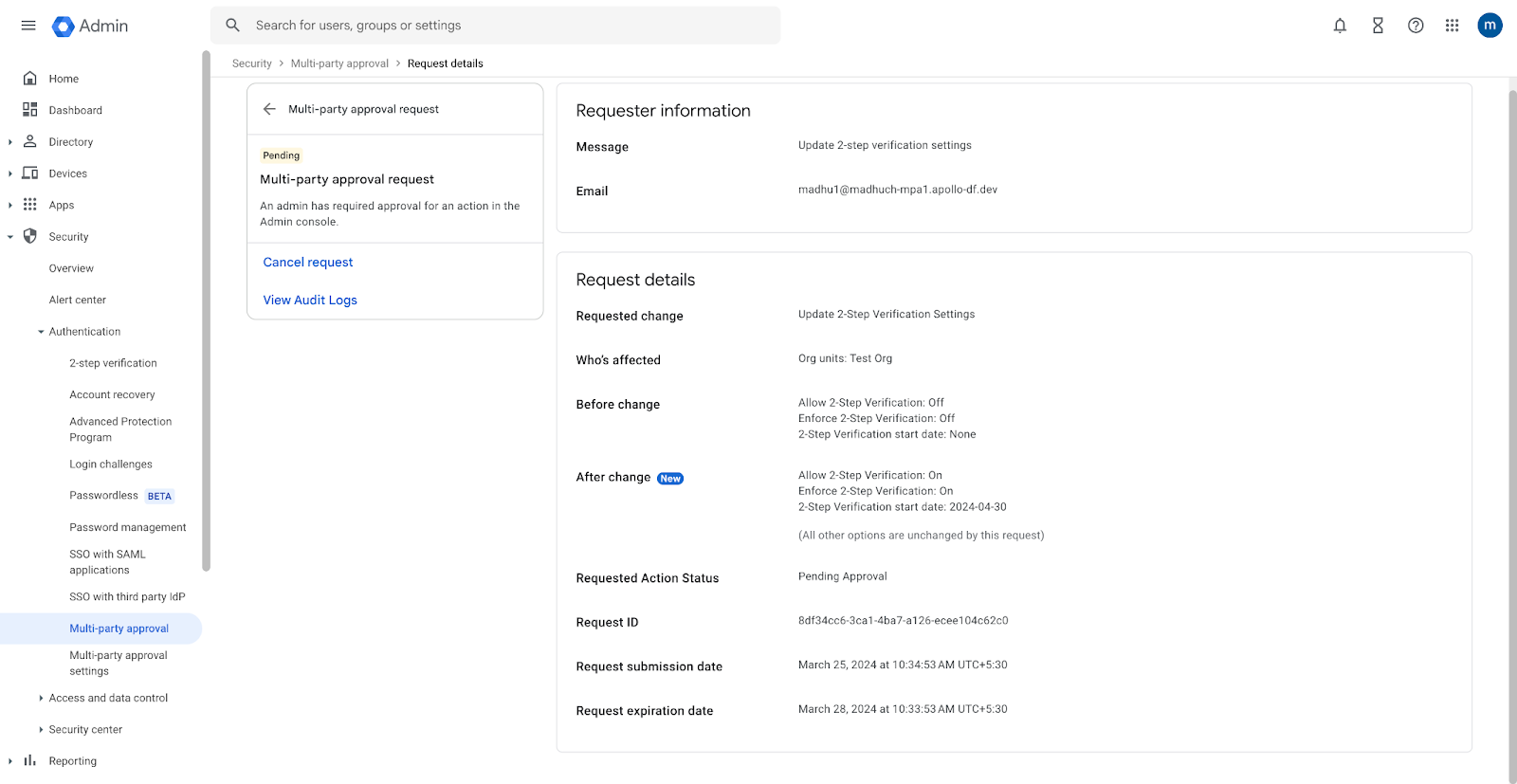
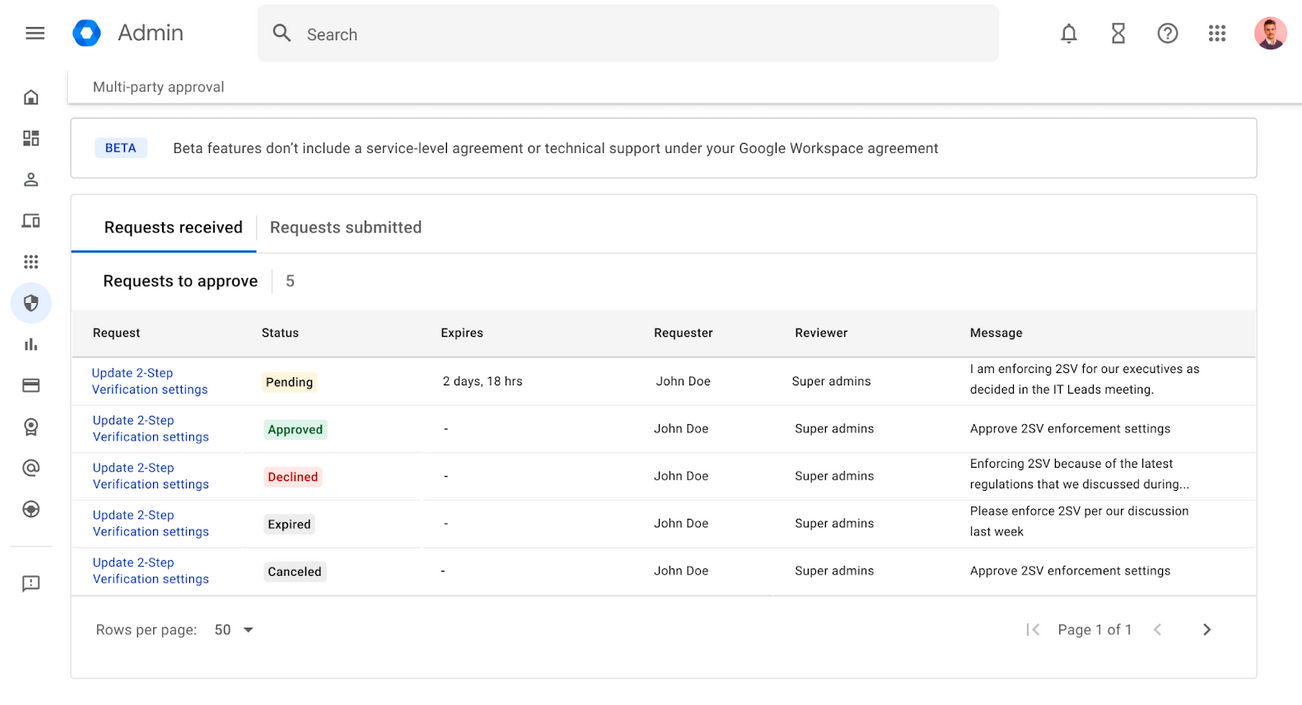
Google has added a new feature for its Workspace enterprise platform that will require multiple administrators to approve changes to an organization's sensitive settings.
The new Multi-Party Approval feature will roll out in the next two weeks and will be available to any Google Workspace customer with two or more super admin accounts.
Once enabled, all super admins will be required to approve changes made to sensitive Workspace environments, such as changing MFA settings, account recovery steps, and login and session controls. The full list of Workspace settings that will trigger a multi-party approval challenge is available below.
- 2-Step verification
- Account recovery
- Advanced Protection
- Google session control
- Login Challenges
- Passwordless
The feature is intended to counter admin account hacks. In the past, threat actors would often compromise an admin account and then silently make changes to an organization's sensitive Workspace settings without the rest of the admin team noticing.
The new Multi-Party Approval will play a dual role of blocking such actions, but also notifying the rest of the admin staff that someone may be messing around in places where they shouldn't.
The new feature was announced at the Google Cloud Next 2024 conference this week. Despite the news that Google Workspace was getting some of those cool and trendy AI-based security tools, this one alone will have more impact on the security posture of organizations across the world than all that AI c**p combined.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Israeli Justice Ministry breach: A hacktivist group named Anonymous for Justice claims to have breached the Israeli Justice Ministry. The group claims to have stolen 300GB of files from the ministry's systems and leaked some of the files online. Israeli officials are investigating but have not confirmed the breach. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Microsoft server leak: Security firm SOCRadar has found an Azure server that leaked Microsoft staff credentials. The server leaked passwords, keys, and source code that could have allowed attackers to pivot to other internal systems. SOCRadar notified Microsoft in February, but the company took a month to secure the server. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
OwenCloud data wipe: Ukrainian hackers have wiped the servers of Russian web hosting provider OwenCloud. Ukrainian media claims the hack was the work of Ukrainian hacktivist group BLACKJACK and the SBU's cyber department. Government sources say the attack wiped more than 400 of the company's servers. OwenCloud claims it has more than 10,000 Russian customers. This includes the biggest companies in Russia's oil and telco sectors. [Additional coverage in UkrInform]
boAt breach: A threat actor has breached and leaked the personal information of more than 7.5 million customers of Indian electronics vendor boAt. The company is investigating the incident, but several customers have confirmed the authenticity of the leaked data. Leaked information includes real names, home addresses, emails, and phone numbers. boAt is India's largest maker of audio products and smartwatches. [Additional coverage in The Economic Times]
PSG cyber incident: French soccer/football club says it was the victim of a cyberattack. Based on the description of the incident, it appears to have been a credential-stuffing attack. [Additional coverage in Le Parisien]
Targus security incident: UK company Targus says it initiated incident response procedures after a threat actor gained access to its systems. The company is one of the largest makers of accessories, cases, and bags for laptops and mobile devices. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
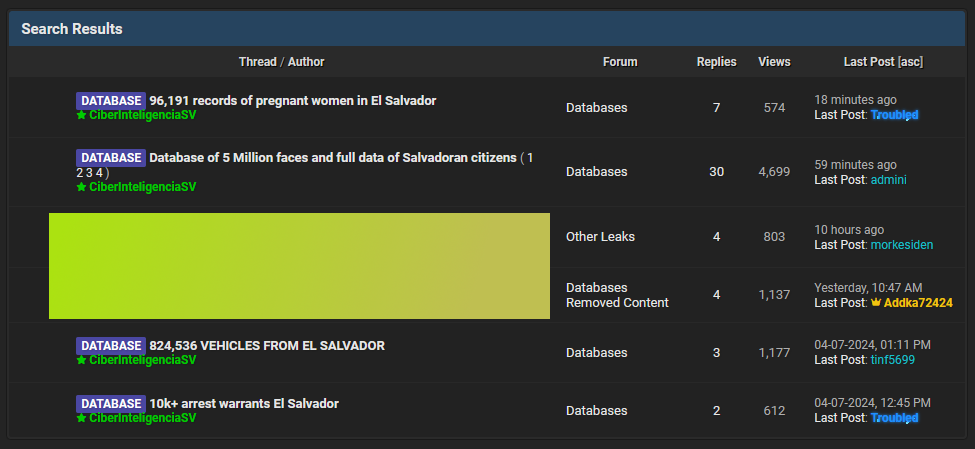
El Salvador breach: A threat actor has leaked several databases containing the personal information of El Salvador citizens. The leak includes the personal data and photos of more than 5 million Salvadorans. The leak covers roughly 80% of the country's population. The hacker claims to have released the data for free after failing to sell it since August of last year. [Additional coverage in La Prensa Grafica]
General tech and privacy
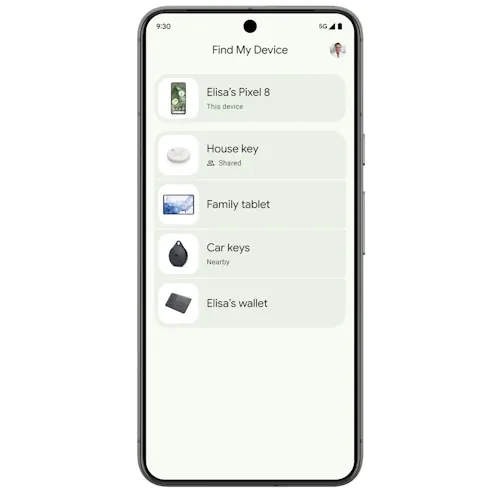
Google Find My Device launches: Google launched its Find My Device service in the US and Canada. The service uses crowdsourced data from over a billion Android devices to find misplaced or stolen devices. The new Find My Device service can also find Bluetooth tracker tags, similar to Apple's AirTags devices. Initial support is included for Chipolo and Pebblebee tracker tags.
Android Private Space: Google is working on a new Android OS feature named Private Space. The new feature works by creating separate profiles where users can install and hide sensitive apps. Private Space is scheduled to ship with Android 15 later this year. [Additional coverage in AndroidAuthority]
Government, politics, and policy
New Polish govt entity: Poland has created the Cyberspace Information Protection Division, a new government agency that will be tasked with countering online disinformation.
Russia does Russia stuff: Russian communications watchdog Roskomnadzor is working on creating a special commission that will have the power to order the deletion of Telegram content without a court order. How very much not so free speech of them, the country with the most free speech bots out there. wink-wink [Additional coverage in TASS]
Ukraine suspends SBU cyber chief: Ukraine has suspended Illia Vitiuk, the head of the SBU's cyber division. Officials say they've reassigned Vitiuk to a unit on the front while they investigate claims of corruption. Journalists from local news outlet Slidstvo claimed that Vitiuk and his wife recently bought expensive real estate despite not having the financial means to do so. Slidstvo reporters also claim they were harassed by SBU staff after publishing their article.
Google accreditation: Google Cloud has been authorized to host classified data for the US military and intelligence community. [Additional coverage in NextGov]
US Treasury & Ukraine memorandum: The US Treasury Department has extended its memorandum of understanding and cooperation on cybersecurity investigations with the National Bank of Ukraine.
American Privacy Rights Act: Two US lawmakers have unveiled a comprehensive data privacy bill for the American market. Named the American Privacy Rights Act, the bill introduces rules for how tech companies should handle the data of US consumers. The bill eliminates the patchwork of state laws and puts forward a GDPR-like system for the US. The chairs of Committees on Energy and Commerce in both the House and Senate are sponsoring the new bill.
Microsoft-aimed legislation: Sen. Ron Wyden has introduced a new bill that would ban the government from using proprietary software that is not interoperable with its competitors. The bill is designed to prevent the US government from getting locked into expensive and insecure walled gardens. The Senator says he crafted the legislation in the aftermath of a long list of Microsoft hacks that exposed US government data. The new bill is named the Secure and Interoperable Government Collaboration Technology Act.
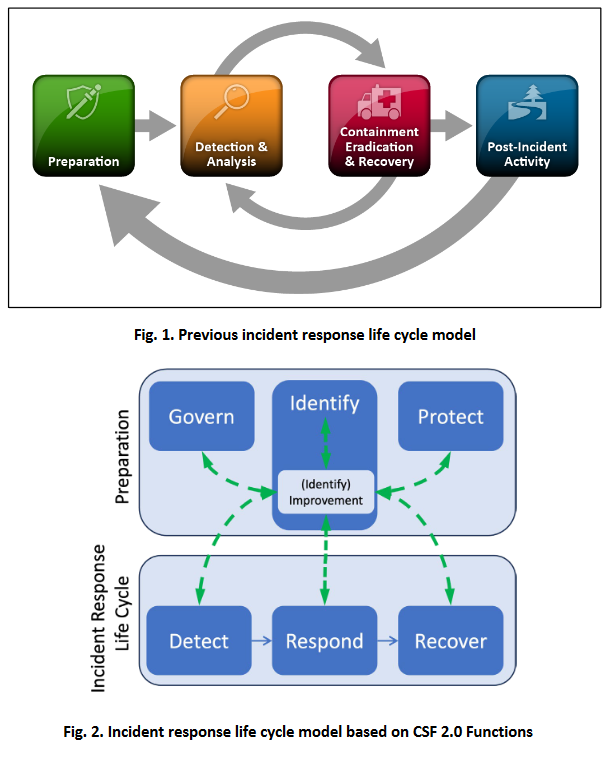
NIST IR recommendations: US NIST has published incident response recommendations and considerations for companies adhering to the recently released NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with GreyNoise founder Andrew Morris about last year's vulnerability exploitation trends, how the company's AI system works, and Catalin makes a fool of himself because he can't pronounce 'abnormalities.'

Cybercrime and threat intel
PasteHub takedown: US law enforcement has seized anonymous text-sharing website PasteHub. The site was previously integrated with the Breach underground hacking forums. It allowed threat actors to exchange anonymous messages and share hacked data. Officials have seized PasteHub more than a year after they seized the BreachForums in March 2023.

BEC scammer pleads guilty: A Nigerian national pleaded guilty to hacking charges related to BEC scams.
Threat/trend reports: CZ.NIC, DTEX, FACCT, the EU EDPS, the UK NCSC, Recorded Future, and S2W Talon have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends. The FACCT report is interesting because it looks at all the ransomware groups that targeted Russia in 2023 and the start of 2024. This includes groups such as Proxima, BlackBit, Zgut, RCRU64, Hardbit, HsHarada, and Muliaka. Also, this is an interesting detail from the NCSC report.
"By far the most common type of breach or attack is phishing (84% of businesses and 83% of charities). This is followed, to a much lesser extent, by others impersonating organisations in emails or online (35% of businesses and 37% of charities) and then viruses or other malware (17% of businesses and 14% of charities)."
Malware-initiated scanning: Palo Alto Networks is seeing an increase in threat actors using malware-infected devices to carry out internet scans instead of using dedicated infrastructure. The benefit of this method is that scans are carried out from clean networks with no history of abuse. Researchers say they've seen scans being conducted from devices previously infected with the Mirai IoT malware.
YouTube malware campaigns: AhnLab warns that threat actors are hacking YouTube accounts to spread infostealers disguised as cracks for popular games and software apps. This is similar to what Proofpoint also reported last week.
Muddled Libra: Palo Alto Networks looks at how Muddled Libra (Scattered Spider) identifies admin users and targets their accounts for access to SaaS services of their targets.
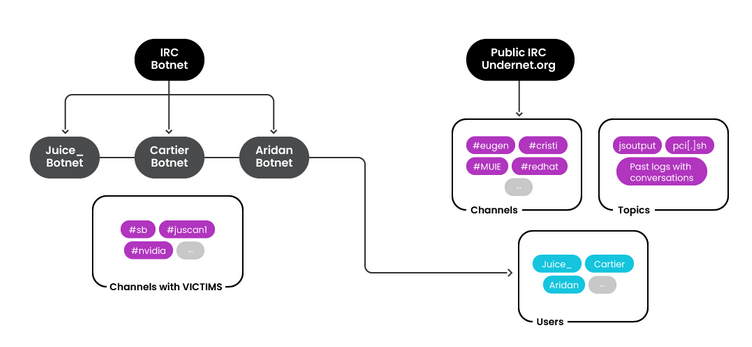
RUBYCARP group: A threat actor named RUBYCARP has operated multiple botnets without being discovered for almost a decade. The group's botnets have engaged in phishing delivery, cryptomining, and DDoS attacks. RUBYCARP has built and run botnets such as Aridan, Cartier, and Juice. Cloud security firm Sysdig believes the group operates out of Romania.
Malware technical reports
Lumma Stealer: OALABS researchers have published a report on the Lumma Stealer obfuscation mechanism.
BianLian ransomware: Chinese security researcher T0daySeeker has published a technical analysis of the BianLian ransomware.
Crypt888 ransomware: Stormshield has published an analysis of the Crypt888 ransomware strain.
Sponsor Section
GreyNoise founder Andrew Morris demonstrates how people use the GreyNoise sensor network.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
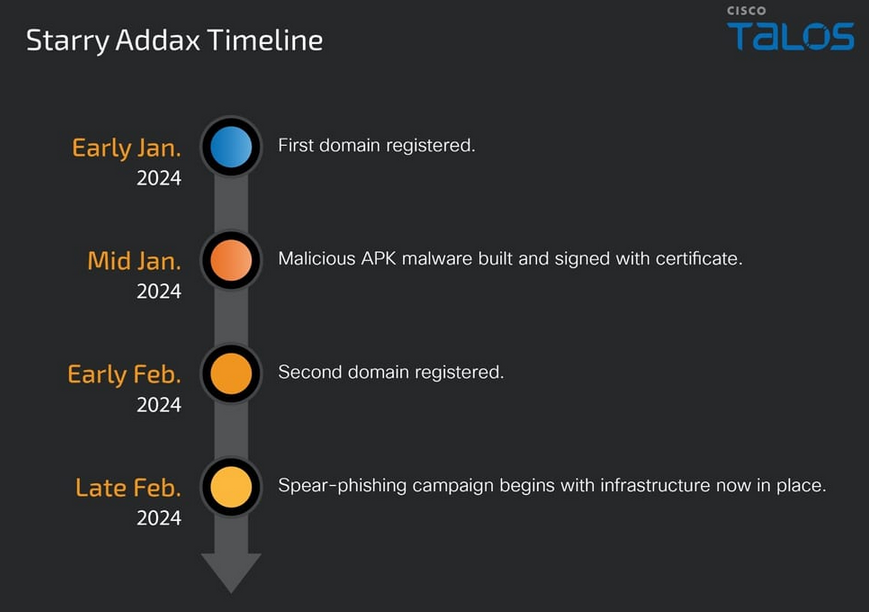
Starry Addax: A new APT group named Starry Addax is targeting human rights defenders in the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, a disputed territory in Western Sahara. The group's first operations took place this year and used Android and Windows malware. The most sophisticated of the two was the Android strain, a never-before-seen malware family named FlexStarling.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the April 2024 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Microsoft, SAP, Fortinet, Zoom, AMD, Siemens, and Schneider Electric. The Android Project,Chrome, Cisco, QNAP, Kubernetes, Kemp, Ivanti, JetBrains, VMWare, and Apache Pulsar released security updates last week as well. This month, Microsoft patched 157 vulnerabilities, and one zero-day (CVE-2024-26234) discovered by Sophos.
Dell security update: Dell has patched a security flaw in the PowerEdge Server BIOS. Dell says an unauthenticated local attacker can exploit the vulnerability (CVE-2024-0172) for privilege escalation attacks.
YubiKey security update: Yubico has fixed a privilege escalation issue in the YubiKey Manager GUI for Windows.
"If a user runs the YubiKey Manager GUI as Administrator, browser windows opened by YubiKey Manager GUI may be opened as Administrator which could be exploited by a local attacker to perform actions as Administrator."
LG WebOS vulnerabilities: LG has released patches to address four vulnerabilities that can be used to hijack the company's smart TVs. The vulnerabilities reside in WebOS, the operating system that runs on LG smart TVs. According to Bitdefender, more than 91,000 LG smart TVs are exposed to the internet and will need to be patched.
D-Link exploitation: Threat actors are exploiting two recently disclosed D-Link vulnerabilities—a backdoor account and a command injection—to take over older unsupported D-Link NAS devices.
Fortinet exploitation: Red Canary publishes details on recent attacks on Fortinet devices using CVE-2023-48788 and where attackers are deploying PowerShell backdoors and remote management and monitoring (RMM) tools.
NIB file technique: Computest Security researcher Thijs Alkemade has published details of a macOS process injection technique utilizing NIB files.
SharePoint exfiltration: Varonis researchers have published details on two new techniques that can be used to bypass data exfiltration detection on Microsoft SharePoint servers.
Native BHI attack: VUSec researchers have discovered a new variation of the old Spectre side-channel attack. The new attack is named Native BHI and impacts Intel CPUs. Academics say the attack can bypass all currently deployed Intel mitigations and leak data from CPU memory.
Infosec industry
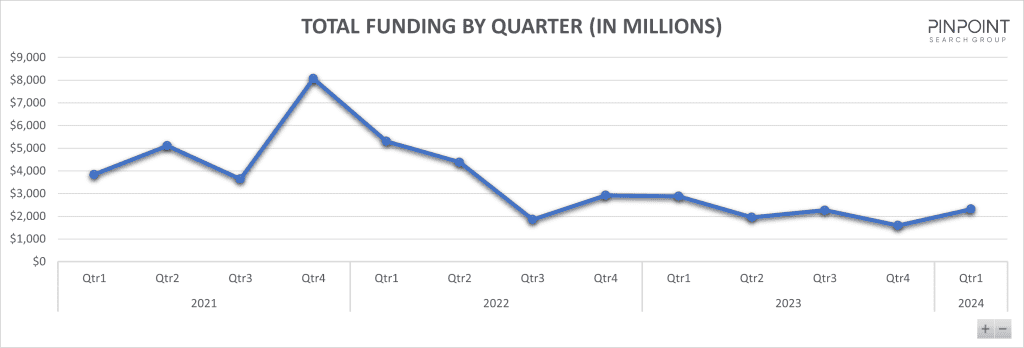
Infosec investments in Q1 2024: The Pinpoint Search Group says cybersecurity firms have raised $2.3 billion in funding in the first quarter of the year. Seed funding for new companies represented 42% of all raised funds. The numbers are still low compared to the all-time peak of 2021, when security firms were raising over $4 billion each quarter.
New tool—PILOT: Echelon Cyber's Dahvid Schloss has released PILOT, a toolkit designed for the stealthy transfer of files across networks using ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets.
New tool—APK Downloader: Kiber.io has released APK Downloader, a tool to download APK files from multiple lesser-known Android app stores.
New tool—Genzai: CS student Umair Nehri has published Genzai, a toolkit to help identify IoT-related dashboards and scan them for default passwords and vulnerabilities.
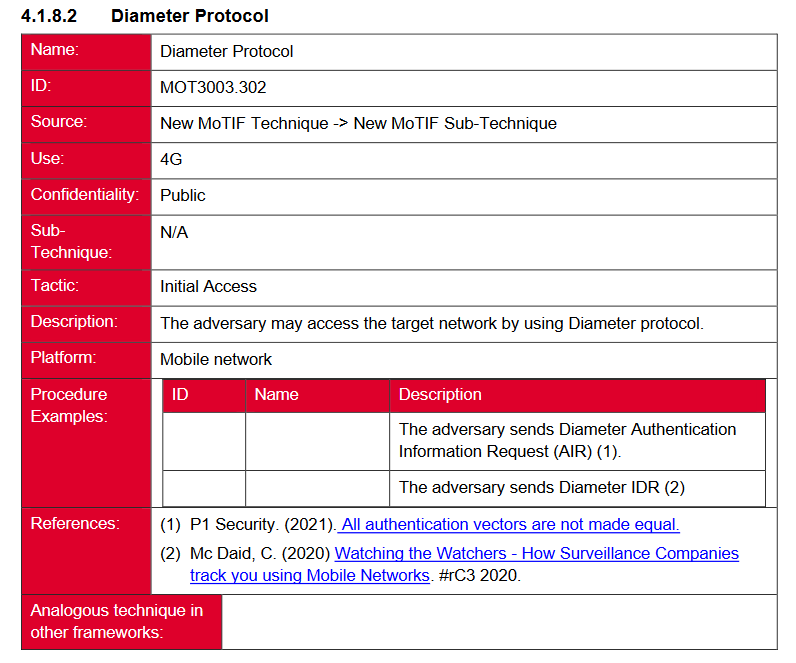
New tool—GSMA MoTIF: The GSM Association (GSMA) has published MoTIF, a framework for assessing threats for the mobile ecosystem. It is inspired by MITRE's ATT&CK and MITRE FiGHT frameworks and covers threats specific to the telco sector.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at the tradecraft used in the compromise of the XZ open-source data compression project.




