Risky Biz News: Russia's FSB says NSA hacked iPhones in cyber-espionage campaign
In other news: Backdoor mechanism discovered in Gigabyte motherboard firmware; 18 malicious Chrome extensions spotted on the Web Store; and the FTC goes after Amazon.
This newsletter is brought to you by Nucleus Security. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. Apple Podcasts embed below:
Russia's FSB intelligence service claims to have uncovered a US intelligence operation that hacked the Apple smartphones of "diplomatic missions and embassies in Russia."
The operation allegedly targeted thousands of devices, including the devices of Russian citizens and diplomatic representatives from NATO countries, the post-Soviet bloc, Israel, China, and South Africa.
The attacks exploited a vulnerability in Apple smartphones.
The FSB attributed the hacks to the US National Security Agency (NSA), and claimed Apple cooperated with the NSA for the attacks.
Russian cybersecurity firm Kaspersky says the same attacks—which the company tracks as Operation Triangulation—also targeted its employees.
The company found compromised devices as far back as 2019 and says the attacks are still ongoing.
According to Kaspersky and to a technical report released by FSB's National Coordination Center for Computer Incidents (NKTsKI), the attacks involve an iOS zero-click exploit delivered as a file attachment via iMessage.
The attachment executes without user interaction as soon as it arrives on a device and starts downloading additional files. Kaspersky described the final payload as "a fully-featured APT platform."
Unlike the FSB, the company did not link the activity to the NSA or any other APT group and couldn't say if the attacks targeted other organizations.
News of the attacks come after, in March, the Kremlin's security team instructed presidential staff to dump their iPhones by April 1, 2023.
Employees were told to get an Android device, either from a Chinese vendor or one running Rostelecom's Aurora OS.
Kremlin officials cited security considerations for their decision, claiming iPhones were "more susceptible to hacking and espionage by Western experts compared to other smartphones."
Russian officials asked the Prosecutor General's Office to start a formal investigation into Apple employees and US intelligence officials.
Update: In an email received after this newsletter's publication, Apple has formally denied the FSB's accusations:
We have never worked with any government to insert a backdoor into any Apple product and never will.
Breaches and hacks
New Toyota leaks: Japanese carmaker Toyota has identified new cloud servers that have leaked customer information online. The new findings come after Toyota found last month a database that exposed the personal and vehicle information of its Japanese customers for nearly 12 years. The carmaker says it has now identified two additional servers that also leaked data online since 2015 and 2016, respectively.
EDE crypto-heist: The El Dorado Exchange has been hacked for $580,000 worth of crypto assets. The hacker says they used an intentional backdoor left in the code by the platform's developers. The attacker claimed they were a white-hat researcher and offered to return the funds for a 10% bounty reward.
Discord crypto hacks: Brian Krebs reports that several Discord communities focused on cryptocurrency have been hacked over the past month after their admins were tricked into running malicious Javascript code disguised as a Web browser bookmark. Krebs reports that many of the hacks began with an interview request from someone posing as a reporter for a crypto-focused news outlet online. Hacked communities include the Ocean Protocol, Aura Network, Nahmii, MetrixCoin, among others.
General tech and privacy
Gigabyte motherboard backdoor: Hardware security company Eclypsium has identified a backdoor mechanism in the firmware of hundreds of Gigabyte motherboards models. Researchers say the Gigabyte firmware drops a Windows binary that is executed when the operating system boots up, which then downloads and runs other files from Gigabyte servers. The files are downloaded either via HTTP or via a misconfigured HTTPS connection, exposing users to attacker-in-the-middle (AitM) scenarios. Eclypsium says there's no evidence to suggest the mechanism has been used for malicious purposes as of yet.
RFC 9399: A proposed standard with the IETF seeks comment on including logos in X.509 certificates. Three logo categories are proposed, for the issuer CA, for the subject organization, and for a community (parent org).
FTC Amazon case: The US FTC and DOJ have filed a complaint against Amazon, accusing the company of violating US children's privacy COPPA laws. Officials say the company has misled parents and has kept their children's Alexa voice recordings and personal data for years, even if it claimed parents could request to have the data deleted. The FTC is looking for a court order to have Amazon pay a $25 million civil penalty and force the company to delete children's personal information, geolocation data, and their Alexa voice recordings.
FTC Ring case: The FTC also filed a second complaint against Amazon, this one against the company's Ring home security camera division. Officials say Ring had poor business practices that allowed any employee or contractor to access its users' private videos. In addition, Ring also had poor security practices that allowed hackers to take control of user accounts, cameras, and access videos. The FTC is looking for a court order to have Amazon to pay $5.8 million in consumer refunds and have the company implement a series of cybersecurity measures, such as MFA support for both employee and user accounts and keeping logs of employee access.
"According to the complaint, these failures amounted to egregious violations of users' privacy. For example, one employee over several months viewed thousands of video recordings belonging to female users of Ring cameras that surveilled intimate spaces in their homes such as their bathrooms or bedrooms. The employee wasn't stopped until another employee discovered the misconduct. Even after Ring imposed restrictions on who could access customers' videos, the company wasn't able to determine how many other employees inappropriately accessed private videos because Ring failed to implement basic measures to monitor and detect employees' video access."
Windows 7 Firefox EoL: Mozilla has announced that Firefox 115, set to be released in July, will be the last supported version of the Firefox browser on Windows 7, 8, and 8.1. Although support for new features will stop, Mozilla says it will continue to deliver security updates for Firefox users on these platforms until September 2024. Firefox joins Chrome and Edge, which announced EoL for their browsers on these platforms earlier this year.
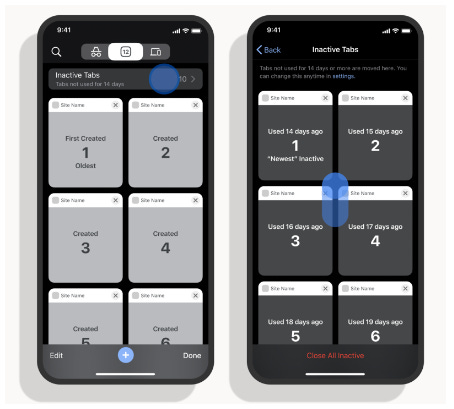
Chrome 114: Google released Chrome v114 to users this week. The update comes with 16 security fixes. Other updates include the new Private State Tokens API, a feature to lock cookie files on disk to prevent their theft, and a feature to group older tabs in a new Inactive Tabs section.
Government, politics, and policy
Krebs firing: Special counsel Jack Smith is investigating former President Donald J. Trump's firing of former CISA Director Chris Krebs. Trump fired the former CISA head in November 2020 after Krebs debunked claims by the former president that the 2020 election was marred by fraud. The special counsel has subpoenaed staff members from the Trump White House who are believed to have pushed Trump to fire the former CISA head for being "disloyal." [Additional coverage in The New York Times]
CyberCommand second-in-command: The White House has nominated Army Maj. Gen. William Hartman to become the next deputy of US Cyber Command. If confirmed, Hartman would replace US Air Force Lt. Gen. Timothy Haugh, who's been nominated to become the next NSA and CyberCommand chief. Hartman is currently the head of the US Cyber Command's Cyber National Mission Force (CNMF). [Additional coverage in The Record]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Patrick Garrity, VP of Marketing and security researcher at Nucleus Security, on how the company has been tapping into CISA's KEV database for insights on vulnerability management and prioritization.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Barracuda zero-day exploitation: A zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2023-2868) patched in Barracuda email gateways has been under active exploitation for nearly eight months since October 2022. In an update on its vulnerability disclosure, Barracuda says the attacks exploited a module that screens incoming email attachments. Attackers placed files with malicious names inside a TAR archive that deployed malware on customers' email gateways. Malware spotted in the attacks includes the SALTWATER and SEASPY backdoors and the SEASIDE reverse shell. Barracuda says it identified evidence of data exfiltration from some impacted appliances.
Apache NiFi exploitation: A threat actor is scanning the internet for unprotected Apache NiFi servers to install a cryptocurrency miner. According to SANS ISC, the attackers are also searching for SSH credentials to move to other systems on the organization's internal network and expand their mining capacity.
IBM ransomware guide: IBM X-Force has published a 32-page guide on recent ransomware tactics and how to defend against it.
RAIDForum leak: KELA has an analysis of the recently-leaked RAIDForum user database.
- 63% of users were inactive in terms of posting
- 70% of users registered using a Gmail address
Terminator: A threat actor named Spyboy is allegedly selling access to a tool named Terminator that they claim can shut down the services of almost all cybersecurity software on the market. The tool is being advertised in the cybercrime underground as a way for threat actors to evade detection by simply shutting down the local security software. The tool is being sold for $3,000. Buyers can also get their hands on a custom and cheaper version that bypasses just one security software for $300. According to Crowdstrike, the tool uses the BYOVD technique for its attacks. Stairwell also has a breakdown of this new tool.
PostalFurious update: Group-IB has an update on PostalFurious, a Chinese cybercrime group that has been running SMS phishing campaigns targeting users in Australia and the APAC region. Per the new report, the group has now expanded operations to the UAE.
XeGroup MO: Menlo Labs published a report on the modus operandi of XeGroup, a Vietnam-based cybercrime group that's involved in web skimmer attacks, phishing operations, and the trade of PII data on the dark web. Researchers have also published the identity of one of the group's members, an individual named Nguyen Huu Tai.
Salesforce ghost sites: Security firm Varonis has identified Salesforce "ghost sites," which are past Salesforce community sites that have been improperly deactivated and are still accessible online and likely leaking corporate and PII data.
Ruby supply chain attack: AppSec company Mend has discovered that a threat actor took over the management of a popular Ruby package after the library had been retired and its name freed up by its original developer. The library is named "gemnasium-gitlab-service" and was previously maintained by software company Gemnasium. After GitLab acquired Gemnasium, GitLab retired the library. Across its lifespan, the library was downloaded almost 2 million times. Mend says the threat actor who re-registered the old library had also uploaded malicious npm packages to the npm portal last year and was most likely to deploy the same code to Ruby projects that were still using the legacy library in their code. The Ruby library was eventually revoked by the Rubygems security team.
New PyPI attack: ReversingLabs says it discovered a malicious Python library available through the official PyPI portal that used Python byte code (PYC) files to evade detection. The incident marks the first known case of a threat actor using PYC files to hide malicious content.
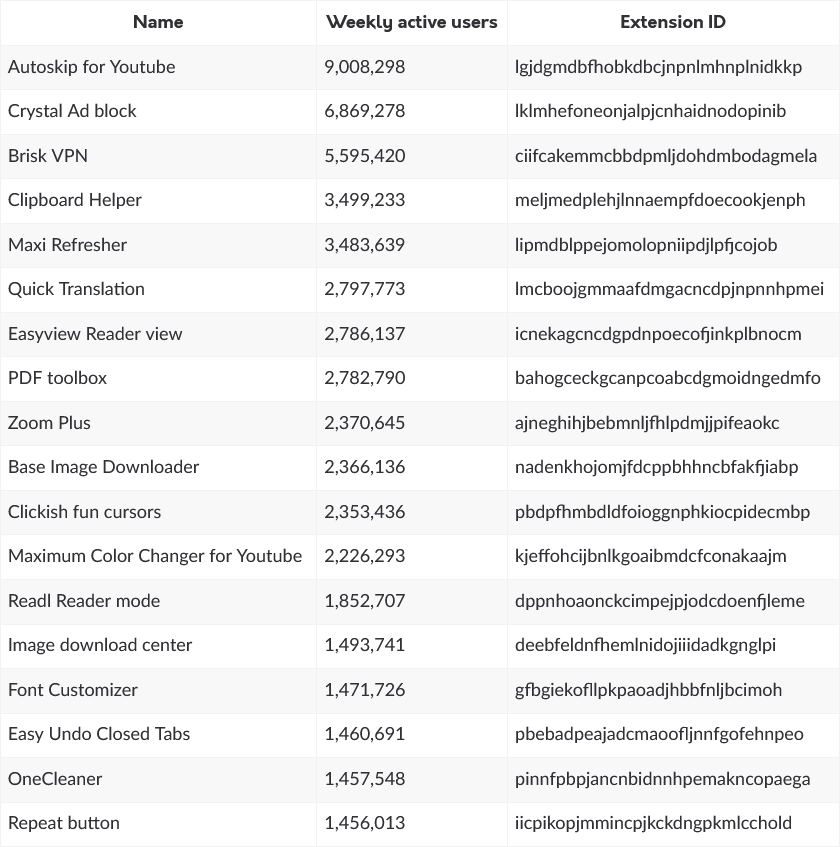
Malicious Chrome extensions: Security researcher Wladimir Palant has discovered 18 malicious Chrome extensions available through the official Chrome Web Store. The extensions have been installed more than 55 million times. They range from PDF viewers to ad blockers and from clipboard managers to VPN clients. Palant says the extensions inject JavaScript code into all websites visited by a user.
"While it is impossible for me to tell what this is being used for, the most likely use is injecting ads. More nefarious uses are also possible however."
Malware technical reports
BlackSuit ransomware: Trend Micro says the new BlackSuit ransomware appears to be a new variant of the Royal ransomware or was at least developed by the same coders.
Sphynx ransomware: According to IBM X-Force, the BlackCat group recently released a new version of their ransomware named Sphynx, with upgraded capabilities meant to thwart defensive measures.
Ramnit and drIBAN: Cleafy researchers have published a report on how the drIBAN web injection toolkit has been integrated into Ramnit.
Qakbot: Lumen's Black Lotus Labs team has published an analysis of the recent techniques used by the Qakbot malware to propagate and evade detection.
Horabot: Cisco Talos has discovered a new botnet named Horabot. The malware has been active since November 2020 and has been deploying banking trojans and a spam tool on infected machines. The threat actor appears to be targeting Spanish-speaking users in the Americas and, according to Cisco, may be located in Brazil.
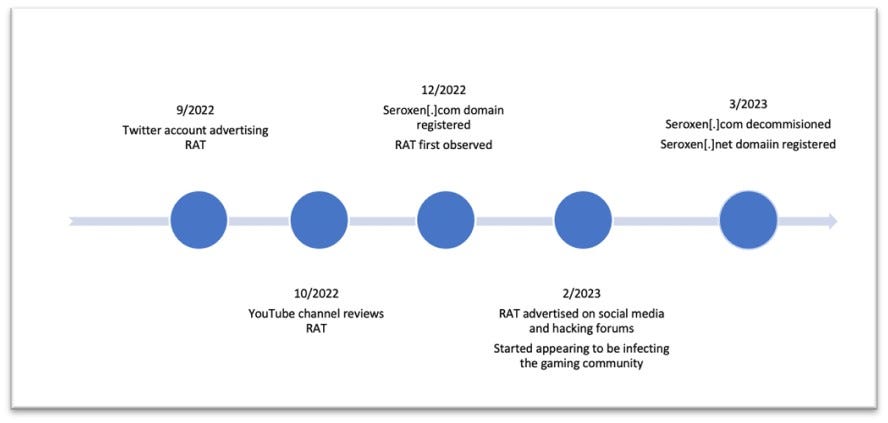
SeroXen RAT: AT&T's security team has spotted a new remote access trojan being advertised on underground hacking forums. Named SeroXen RAT, the malware is being sold for prices ranging from $30 to $60. Researchers say the RAT can function in a fileless mode and is built on top of several open-source projects like the Quasar RAT, the r77 rootkit, and the NirCmd command-line utility. The malware appears to have been created late last year and became very popular this year.
Risky Business Demo
Nucleus Security's COO Scott Kuffer shows Risky Business podcast host Patrick Gray their vulnerability management platform. It ingests scan outputs from a number of vulnerability identification tools, normalizes that information, and then allows vulnerability management teams to do things like assign responsibility for certain types of bugs to the correct people.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Dark Pink: Group-IB researchers have identified new attacks carried out by the Dark Pink APT group. New operations carried out this year targeted organizations in Brunei and Indonesia. Other older attacks carried out last year were also found targeting organizations in Belgium, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Camaro Dragon's TinyNote: Check Point has published a report on TinyNote, a previously unknown Go-based backdoor used by the Camaro Dragon APT, which the company discovered earlier this year.
APT37's RokRAT: ThreatMon has a breakdown of RokRAT, a go-to utility of the APT37 North Korean espionage group.
Influence operations: Google's TAG security team has published a summary of the coordinated influence operation campaigns terminated on Google platforms in Q2 2023 (so far). Google took down campaigns linked to all of today's lovely regimes, such as Russia, Iran, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, and China. The largest batch was from China, and Google says it also received leads from LinkedIn and Graphika about that particular campaign.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
Chrome VRP news: Google has tripled the rewards for valid reports of Chrome sandbox escapes submitted to its bug bounty program. Until December 1, 2023, researchers can earn $180,000 instead of the usual $60,000. The triple reward is only valid for the first report. Subsequent reports get only double the reward ($120,000).
Adobe private bug bounty program: US software company Adobe has launched a private bug bounty program on the HackerOne platform. Qualified researchers can apply here. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Jetpack vulnerability: The WordPress security team has forcibly installed a security update for the Jetpack security plugin on more than five million WordPress websites. The update fixed a critical security flaw that impacts all Jetpack versions released since 2012. The plugin's authors prepared and released 102 different security patches for all the different Jetpack versions that are impacted and are still used online. They say they have seen no active exploitation of the Jetpack flaw so far.
MOVEit Transfer vulnerability: Software company Progress has released a security update for a vulnerability impacting its MOVEit managed file transfer (MFT) utility. According to reports, the vulnerability has already been exploited in the wild to steal data from some organizations. MOVEit now becomes the fourth major MFT product to be exploited in the wild after Accellion, FileZen, and GoAnywhere.
TitanFTP vulnerabilities: And sticking with the MFT bugs, White Oak Security discovered multiple vulnerabilities in the TitanFTP file transfer server. Found bugs include a privilege escalation leading to RCE and multiple instances of directory traversals leading to file inclusions. All bugs have been patched.
STARFACE PBX vulnerability: RedTeam Pentesting has discovered a vulnerability in STARFACE PBX telephony servers where an attacker could authenticate using the SHA512 hash of the password instead of the cleartext password (CVE-2023-33243).
TRON vulnerability: Researchers with dWallet Labs have found a vulnerability in the TRON cryptocurrency.
"This vulnerability allows any signer (with any weight) of a multisig account to completely overcome the multisig security offered by TRON, regardless of the threshold and number of signers defined in the account. This vulnerability impacts over $500M in digital assets that are held in TRON multisig accounts. [...]
An attacker, taking advantage of this vulnerability, can double the weight of every signature in a partially signed multisig transaction and potentially cause the transaction to meet the required threshold. He can do this without any knowledge of the private keys of the valid signers involved."
Infosec industry
New tool—pkilint: Digicert has open-sourced a new tool named pkilint, a linting framework to automate and verify compliance checks for digital certificates.
Acquisition news: Cisco announced plans to acquire Armorblox, a company known for its AI-based security products.




