Risky Biz News: Russia wants to absolve patriotic hackers from any criminal liability
In other news: Reddit got hacked; Oakland hit by ransomware; MonkeyDrainer gang made $13mil from stealing NFTs.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The Russian government is exploring the possibility of absolving Russian patriotic hackers from criminal liability for attacks carried out "in the interests of the Russian Federation."
The head of the State Duma Committee on Information Policy, Alexander Khinshtein, told reporters at a press conference on Friday the exemption would be granted to individuals located abroad and within Russia's borders alike.
"We will talk in more detail when it receives more of a clear wording," Khinshtein said, as quoted by RIA and TASS.
Currently, the creation, use, and distribution of malicious computer software is punishable in Russia with up to seven years in prison. There are no exemptions to this law, so many of the current pro-Kremlin hacktivist groups are actually breaking Russian law and could technically face prosecution, especially in the aftermath of a possible regime change.
The exemption would allow pro-Kremlin hacktivists to carry out attacks with a legal carte blanche and would most likely apply to the likes of Killnet, XakNet, NoName057(16), CyberArmyRussia, FRwL Team, and the rest of their ilk.
Breaches and hacks
Reddit security breach: Social network Reddit says that earlier this month, a sophisticated phishing campaign targeted its staff and successfully breached the account of one of its employees. The company says the attackers only gained access to some internal dashboards and business systems that contained internal documents and some of its source code. The intruders did not gain access to primary production systems nor to any user passwords and accounts. Reddit says the incident was quickly dealt with after the phished employee self-reported the issue to its security team. This marks Reddit's second breach after another threat actor gained access to its internal systems back in 2018 in an incident that also exposed some old user passwords.
Oakland ransomware attack: The city of Oakland, California, was hit by a ransomware attack that encrypted some of its IT systems. Officials say they detected the attack on Wednesday and have shut down all the city's IT systems to prevent the attack from spreading and to restore systems safely. Officials say the incident did not affect the activity of its 911, fire, and emergency services. The ransomware gang behind the attack has yet to be identified.
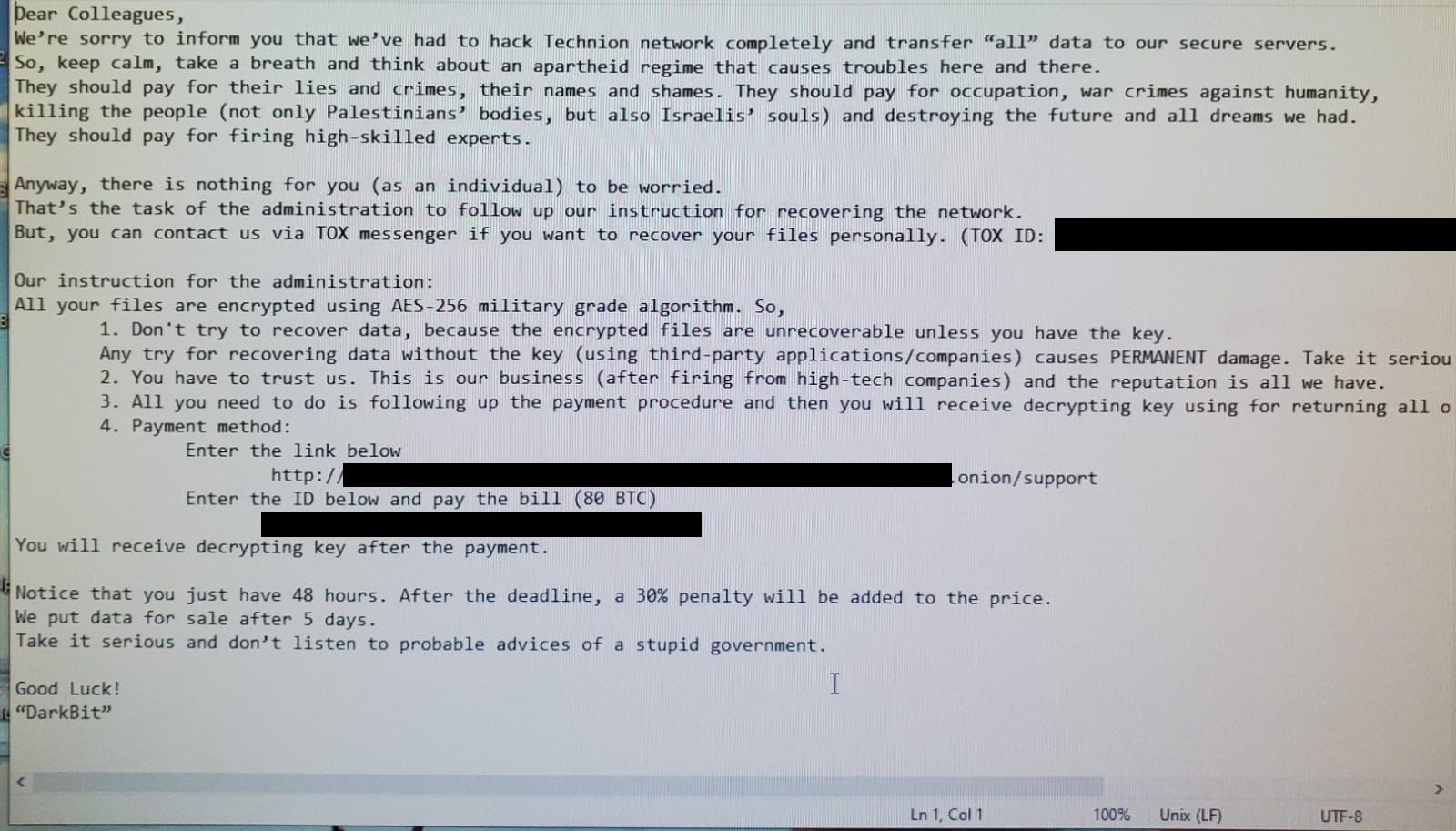
Technion ransomware attack: A ransomware gang named DarkBit has hacked and encrypted the IT systems of Israel's Institute of Technology, Technion, a public research university based in Haifa. The hackers are requesting 80 bitcoin ($1.7 million) to decrypt the organization's network, according to a ransom note shared by Israeli threat intel firm HudsonRock.
New Ali's Justice (Edalat-e Ali) hack: Iranian hacktivist group Ali's Justice (Edalat-e Ali) has hijacked the signal of Iran's state television channel IRIB on the 44th anniversary of the Iranian Revolution, which took place on Saturday, February 11. The hacktivist group interrupted a speech from Iran President Ebrahim Raisi and replaced it with a call to the Iranian people to withdraw money from government banks and to assemble in new anti-government protests to take place on February 16. The interruption only lasted one minute and was also accompanied by a "Death to Khamenei" slogan.
Iranian hacktivist group Edalat-e Ali on Saturday hacked the Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting (IRIB) while the state-run TV was broadcasting President Ebrahim Raisi's speech at the regime’s Revolution Anniversary, displaying images with the slogan "Death to Khamenei”.
— Iran International English (@IranIntl_En) 9:36 AM ∙ Feb 11, 2023
General tech and privacy
MSDT EOL: Microsoft has announced the end-of-life for its Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool, a built-in tool that shipped with many previous Windows versions and would work by launching automatically to diagnose and correct common problems for a variety of Windows features. Microsoft says that starting this year, MSDT will start redirecting users to the Get Help troubleshooting platform, and the MSDT platform will be removed completely in 2025.
CHERIoT: Microsoft has open-sourced CHERIoT, a security-first real-time operating system (RTOS) and software stack for running on embedded devices with under 256 KiB of SRAM. The name stands for Capability Hardware Extension to RISC-V for Internet of Things.
Telemetry comes to Go: Automated built-in telemetry gathering is coming to the Go toolchain.
Brave goes HTTPS-by-default: Starting with the upcoming v1.50, the Brave browser will go HTTPS-by-default.
1Password adopts passkeys: Password management utility 1Password has announced support for passkeys as a way for users to unlock their password vaults without needing to type in a master password. Passkeys support is expected to roll out to all users later this summer.
Meta fined in South Korea: South Korea's privacy watchdog has fined Meta with 6.6 million won for privacy violations. That would actually be a good thing if the fine wouldn't be $5,000, or what Meta makes in one second. The fine was for Meta not giving users the option to refuse tracking when using Meta services like Facebook and Instagram, something for which the company was also fined hundreds of millions of euros in the EU.
Government, politics, and policy
ANSSI yearly report: Back in January, France's cybersecurity agency ANSSI published its yearly activity and threat report for the year 2022. The report is now also available in English.
Another Pegasus case in El Salvador: Paula Patricia Velásquez, a judge on El Salvador's Supreme Court, says Apple notified her last year that her iPhone was infected with Pegasus, a spyware strain developed by the Israel-based firm NSO Group. Velásquez becomes the first member of the Salvadoran judiciary branch to confirm she was targeted with Pegasus. The spyware was heavily used in the country, with Citizen Lab reporting on at least 35 cases where journalists and members of civil society were targeted and infected between July 2020 and November 2021. Last December, several Salvadoran journalists filed a lawsuit in a US court against NSO Group in connection to the hacks.
White House memorandum: The Biden administration has ordered federal agencies to use only .gov and .mil domains for official updates as a way to bolster trust and improve the security of official government communications. The White House has ordered that all federal agencies get an official domain and start using it by May 8. [Press coverage in FederalNewsNetwork / Official White House memo PDF]
Sponsor section
Airlock Digital is one of this newsletter's four main supporters and this week's featured sponsor. Earlier this year, in May, Airlock Digital CEO David Cottingham held a product demo with Patrick Gray, the host of the main Risky Business podcast, showing how Airlock's allow-listing product works.
Cybercrime and threat intel
F*** around and find out story in the making: North Korean state-sponsored hacking groups have laundered almost $25 million worth of cryptocurrency through a new Bitcoin mixing service called Sinbad. According to blockchain analysis firm Chainalysis, those funds also include portions stolen from cryptocurrency service Harmony Bridge in June last year. In an interview with Wired, Sinbad's administrator described their service as a "legitimate privacy-preserving technology project"—using the same stupid and childish arguments the Tornado Cash developer used before he was detained by authorities for helping hackers launder their money.
Infinity Forum: Security researchers have discovered a new cybercrime portal for Russian-speaking users that goes under the name of Infinity Forum. The site is currently used for advertising various cybercrime services, such as hacking tools, hacking services, and DDoS-for-hire botnets. Security firm Radware says the threat actor behind the forum is a group named the Infinity Team, which they described as a collaboration between Deanon Club and Killnet, two pro-Kremlin hacktivist groups that have historically launched DDoS attacks against western targets. More in Radware's security advisory [PDF].
MonkeyDrainer: Blockchain security company SlowMist says that a threat actor named MonkeyDrainer has stolen almost $13 million worth of NFTs since August last year. SlowMist says the gang has stolen more than 7,000 NFTs using techniques like classic phishing and ERC20 token phishing.
Redirection campaign: GoDaddy's Sucuri team has identified more than 2,600 hacked websites that contain links to fake URL shortening services that, in reality, redirect users to a network of bogus cryptocurrency-related Q&A websites. The campaign appears to be related to a campaign Sucuri spotted last November meant to generate and boost ad revenues on the Q&A site network. Seems like a super complicated and convoluted way to perform ad fraud, tbh.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with three new vulnerabilities that are currently being actively exploited. The first is CVE-2023-0669, the zero-day in Fortra GoAnywhere MFT servers we reported on last week. The second is a 2015 bug in one of Intel's ethernet drivers. And the third is CVE-2022-24990, a vulnerability disclosed last March in TerraMaster NAS devices.
ESXiArgs attack surface: Security firm Rapid7 says that almost 19,000 VMWare ESXi servers are currently connected to the internet without a patch for CVE-2021-21974, the vulnerability that was recently exploited to deploy the ESXiArgs ransomware. Rapid7 based its estimate on telemetry data gathered via its Project Sonar.
450+ PyPI malicious libraries: Security researchers from DevSecOps companies Phylum and Checkmarx have discovered a batch of 451 malicious Python libraries that were hosted on the official PyPI website. Researchers say the libraries contained malware that would load an extension in the user's browser that acted as a clipboard clipper, replacing cryptocurrency addresses in the victim's clipboard. The purpose of this attack was most likely to hijack cryptocurrency transactions and send funds to addresses controlled by the attacker. A day after the libraries were spotted and removed, the threat actor came back to flood the PyPI portal with new packages, according to Chris Partridge, a security researcher at Amazon, who discovered another batch of 16 malicious libraries. There was also a different malware campaign on PyPI that deployed the W4SP Stealer.
New npm malware: Fourteen new malicious npm packages were identified on the official npm portal last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for more details. On top of this, ReversingLabs have also identified another package named "aabquerys" used as a downloader to install additional malware on infected systems.
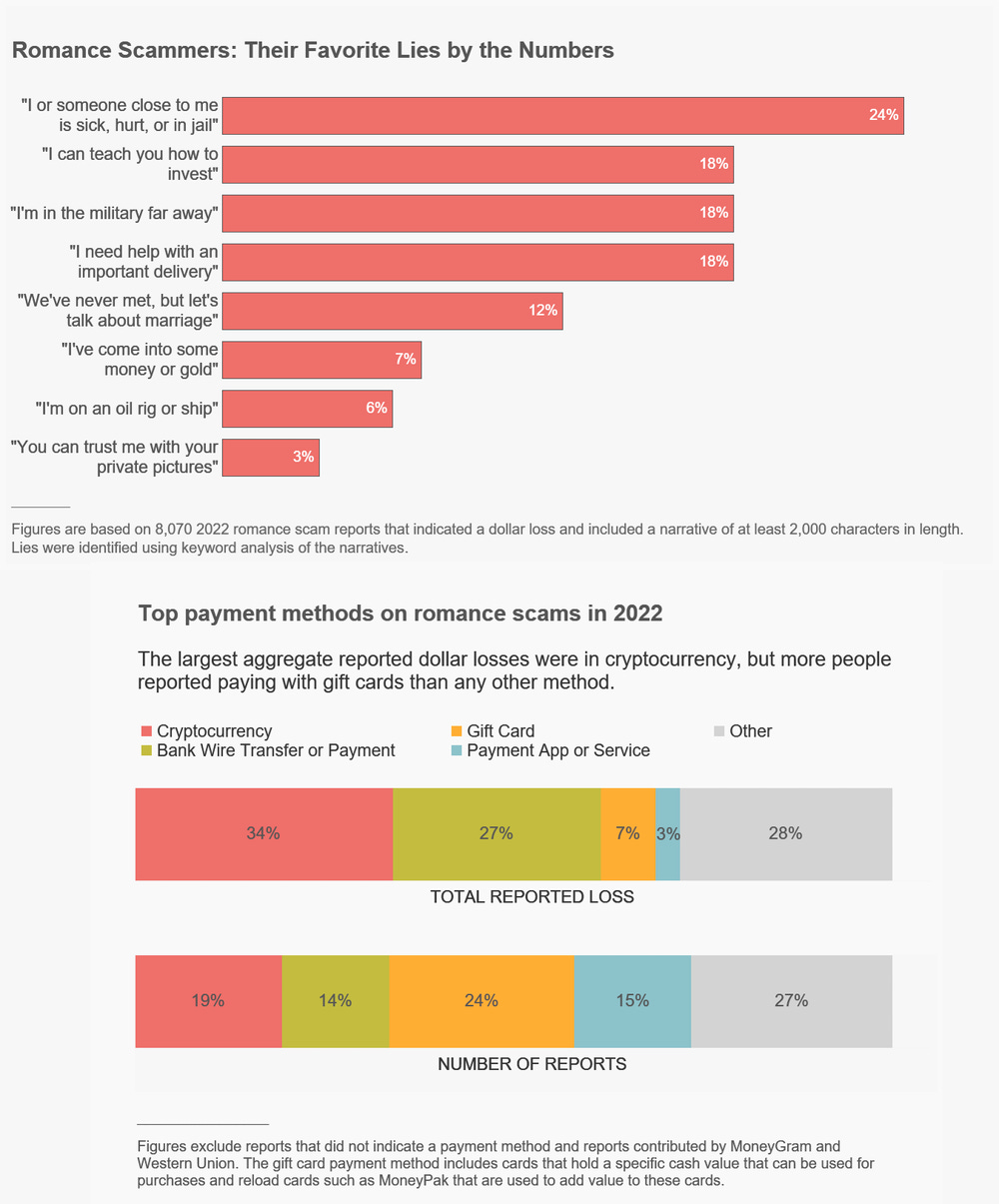
Romance scams in 2022: The US Federal Trade Commission says that more than 70,000 people reported losing money to a romance scam last year. In total, victims lost more than $1.3 billion, with $4,400 the median reported loss. Victims said they were usually approached on dating apps or via unexpected messages on social media. The scammers moved conversations to a private instant messaging service, where they asked victims to transfer money on various pretenses, either to a cryptocurrency wallet or via a bank wire transfer—the same technique they have been using for the past five years, but which still works with spectacular results. The $1.3 billion figure reported by the FTC is 35% higher compared to $956 million, the losses to romance scams reported to the FBI in the previous year, in 2021 [PDF].
Malware technical reports
GooberBot: A new malware strain named GooberBot is infecting Zyxel routers and VPN devices. The attacks are exploiting a vulnerability (CVE-2022-30525) that Zyxel patched last May. According to Chinese security firm QiAnXin, the malware appears to have been developed by the operators of Scar, a DDoS-for-hire service available for only $15/month.
GootLoader: Cybereason has a report on a recent GootLoader distribution campaign that used SEO results poisoning to spread the malware. The campaign primarily targeted English-speaking users and ended up deploying additional payloads like Cobalt Strike and the SystemBC proxy malware.
PikaBot/iPikaBot: DCSO has a report on PikaBot/iPikaBot, a new malware strain spotted last week being deployed on systems previously infected with QakBot.
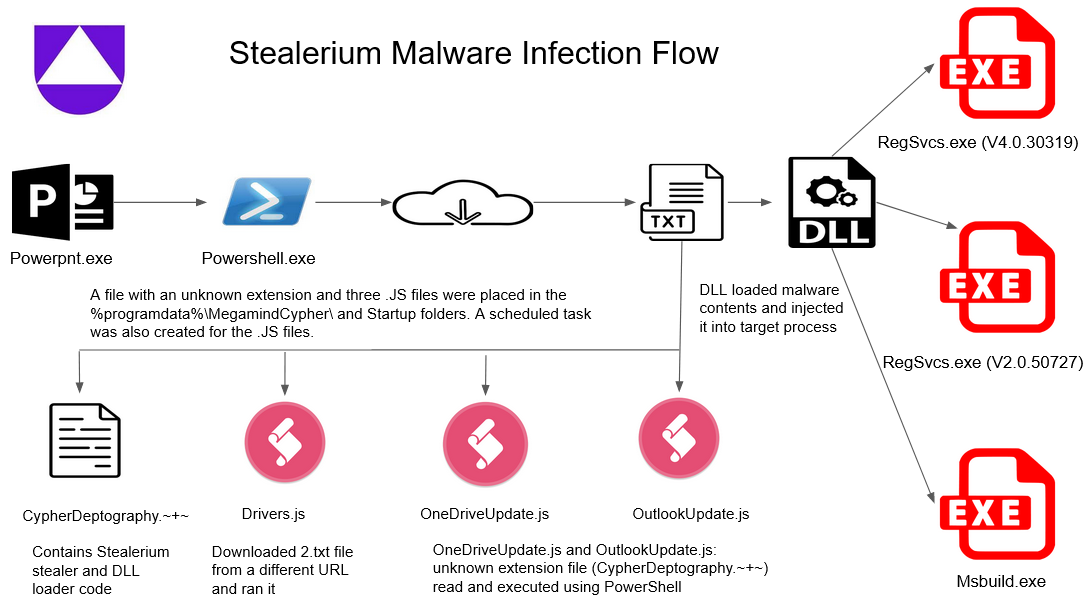
Stealerium: Uptycs researchers have published a technical analysis of Stealerium, an open-source stealer, keylogger, and clipper that was open-sourced on GitHub last year and is currently seeing a wider adoption by various threat actors. A similar report was also published last week by SecurityScorecard.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Bahamut APT: CyFirma researchers have a report out on a November 2022 campaign carried out by the Bahamut APT that targeted an intelligence operative in India using an Android VPN app laced with malware. The attack appears to be part of the same campaign that ESET also previously spotted and documented last year.
NK groups and ransomware: Cybersecurity agencies from the US and South Korea have published a joint security advisory warning that North Korean threat actors are engaging in ransomware attacks against healthcare organizations. Officials say North Korean hackers have developed their own ransomware strains like Maui and H0lyGh0st, but they also used ransomware developed and rented from other cybercrime cartels. This includes ransomware such as BitLocker, Deadbolt, ech0raix, GonnaCry, Hidden Tear, Jigsaw, LockBit 2.0, My Little Ransomware, NxRansomware, Ryuk, and YourRansom. Mandiant has linked this activity to the Andariel APT.
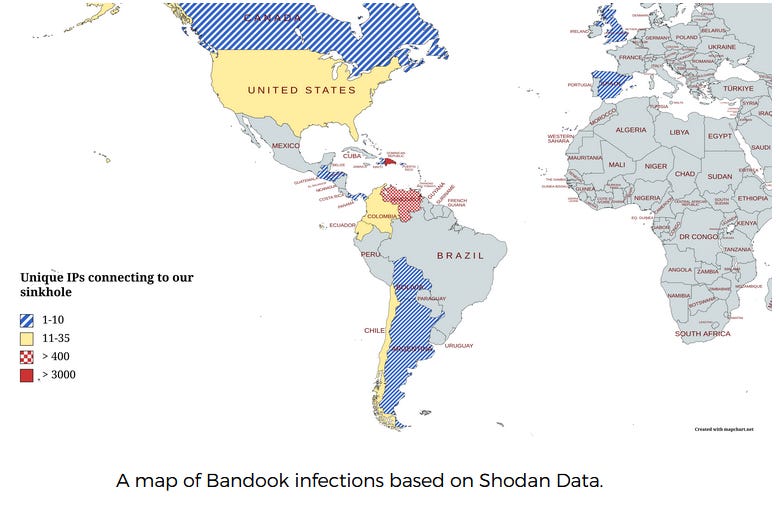
Dark Caracal: Dark Caracal, a cyber mercenary hacker-for-hire group, is still active and targeting individuals in Latin America. Security researchers with the Electronic Frontier Foundation say they discovered the group's Bandook spyware deployed on more than 700 computers in Central and South America. Approximately 75% of the infected computers are located in the Dominican Republic and 20% in Venezuela. The campaign began in March 2022 and is still ongoing. EFF said the Bandook malware was also updated and now supports 148 commands to interact with infected hosts, compared to the 132 commands older versions supported.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
World premiere: Austin Hackers Anonymous, an informal group of hackers and security professionals from the Austin, Texas area, has become an official CVE Numbering Authority (CNA) for the Mitre Corporation. AHA is the world's first hacker collective to be recognized as a CNA, a designation usually granted to product vendors only.
Vulnerability drama: A disgruntled security researcher has published a zero-day vulnerability in the Avalanche blockchain after the company behind the technology refused to pay him for a previous bug report. Ava Labs told the researcher the zero-day was a non-issue, a misconfiguration, but still patched it within 24h anyway. Lots of salt all over that blog post.
LocalPotato attack: Security researchers Andrea Pierini & Antonio Cocomazzi have published details on LocalPotato, a new Windows privilege escalation vulnerability that relies on a new variation of the *potato attack technique. The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2023-21746 and was patched in the January 2022 Patch Tuesday security updates.
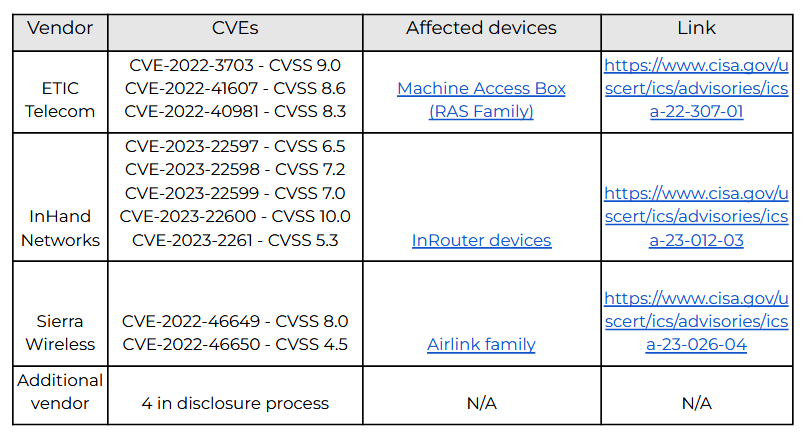
OT vulnerabilities: Otorio researchers have identified 38 vulnerabilities in the products of four vendors of WiFi equipment with industrial OT networks. Findings include vulnerabilities in the web interface and the firmware of these devices alike. Some of the vulnerabilities have been patched already, while some are still in the disclosure process. Many vulnerabilities allow RCE attacks. Affected vendors include Sierra Wireless, InHand Networks, ETIC Telecom, and a fourth still-unnamed vendor. The company plans to reveal more at the S4x23 security conference in Miami on Wednesday, February 15. More in the company's security advisory [PDF].
Infosec industry
New tool—BokuLoader: IBM's X-Force Red team has released BokuLoader, a Cobalt Strike user-defined reflective loader written in Assembly & C for advanced evasion capabilities. Another clever project we missed last year from the same team was SCMKit, a toolkit that can be used to attack source code management systems, such as GitHub Enterprise, GitLab Enterprise, and Bitbucket Server.
Risky Business podcast host Patrick Gray recorded this video with Okta, which shows users how to enable phishing-resistant authentication. It also goes into how enabling phishing-resistant auth for some users can benefit the whole org, even if it's not turned on everywhere.




