Risky Biz News: LockBit leader unmasked, charged, and sanctioned
In other news: UK accuses China of hacking Ministry of Defense; new TunnelVision attack leaks VPN traffic; Microsoft teases new secure DNS client.

This newsletter is brought to you by Thinkst, the makers of the much-loved Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Law enforcement agencies have doxed, charged, and sanctioned the administrator of the LockBit ransomware operation.
Officials say the LockBit admin—known as LockBitSupp—is a 31-year-old Russian national named Dimitry Yuryevich Khoroshev from the city of Voronezh in Southwest Russia.
On Tuesday, the US Justice Department unveiled a 26-count indictment in Khoroshev's name, claiming he personally pocketed more than $100 million from LockBit ransom payments. That's about a fifth of all LockBit ransom payments.
Authorities in Australia, the UK, and the US have also imposed sanctions in what appears to be a new common modus operandi for the three countries—to immediately sanction any indicted ransomware suspect.
In a hacking forum post, LockBitSupp claimed police misidentified him. Too bad nobody believes him.

The LockBitSupp charges and sanctions come two months after law enforcement agencies took down LockBit server infrastructure in February this year.
In a press release on Tuesday, Europol says it has now extracted more than 2,500 decryption keys from LockBit servers, which are now being sent to past victims—7,000 in total.
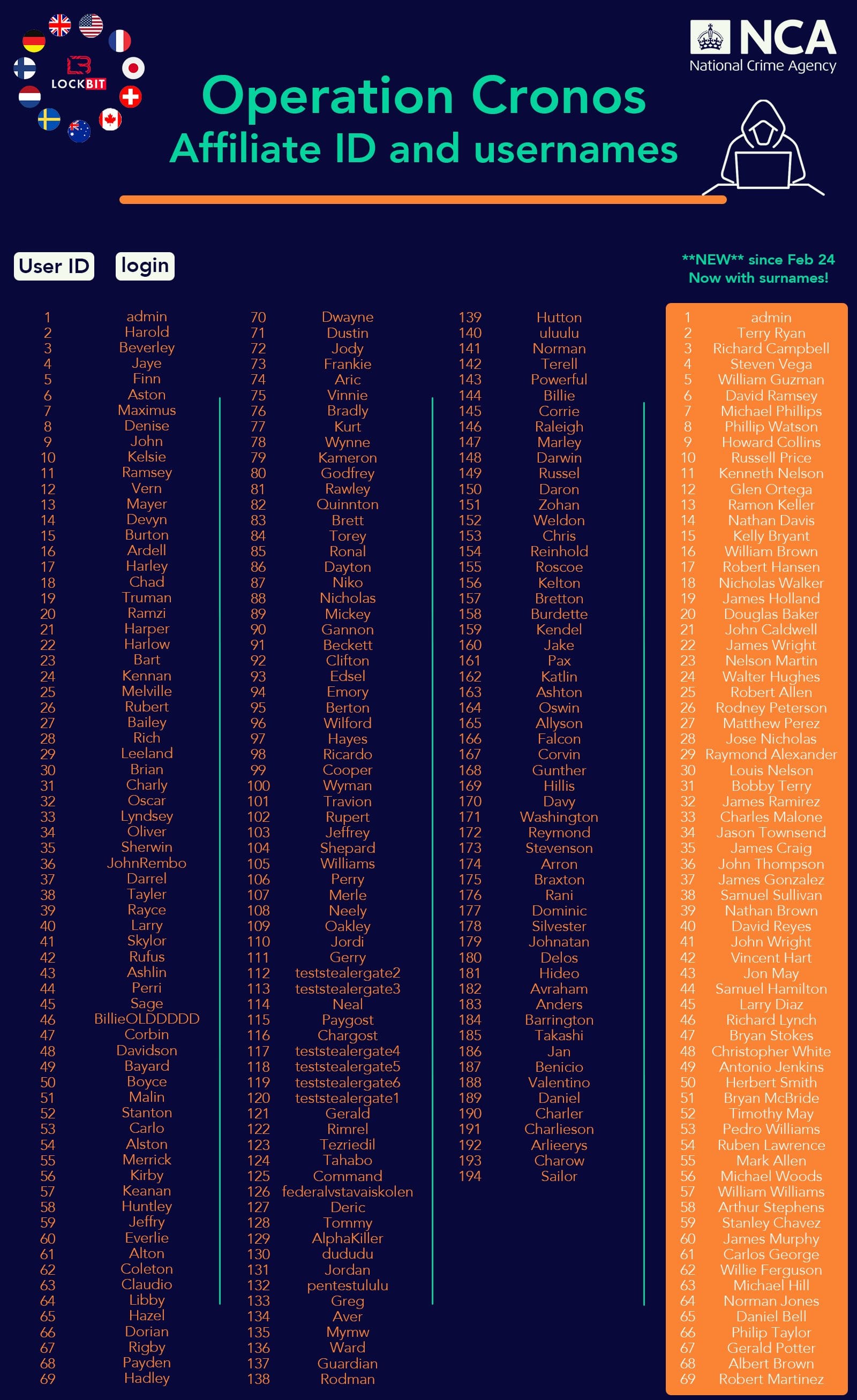
The UK NCA, which led the operation to take down LockBit, also said it has now identified 194 individuals who signed up to work as LockBit affiliates and carry out attacks and extortions with the gang's ransomware tools. Some of the NCA's stats are below:
- 148 affiliates built attacks.
- 119 engaged in negotiations with victims, meaning they definitely deployed attacks.
- Of the 119 who began negotiations, there are 39 who appear not to have ever received a ransom payment.
- 75 did not engage in any negotiation, so also appear not to have received any ransom payments.
Despite a pretty high-profile takedown, Khoroshev has tried to rebuild LockBit but without success.
The NCA echoed a Trend Micro report from April, which found that the LockBit gang ceased almost all activity in the aftermath of the February takedown.
The report found that almost two months after Operation Cronos, the LockBit gang was rarely launching attacks and adding new victims to its leak site. Trend Micro said LockBit was banned and became a pariah on most major hacking forums, and the gang was often relisting old victims on their leak site as a way to simulate new activity.
The NCA says the new LockBit RaaS had only 69 affiliates, compared to the 194 from before the takedown, and the gang's operations started to degrade in operational quality.
The LockBitSupp dox and charges didn't come out of the blue. Over the weekend, law enforcement agencies reactivated the old LockBit dark web portal just to tease Tuesday's announcement.
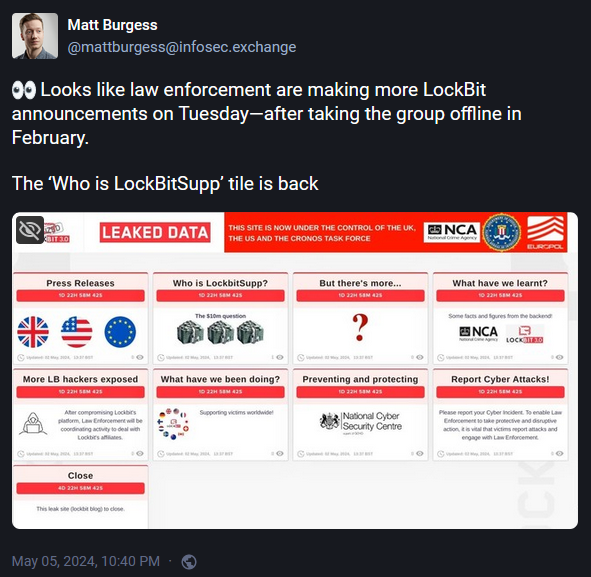
With LockBitSupp now doxed, charged, and sanctioned, the NCA hinted that it is turning its focus on discovering the real-world identities of past LockBit affiliates.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
UK MOD hack: The UK government says that a foreign threat actor hacked a payroll system for the Ministry of Defence. The hackers stole the personal data of 272,000 current and former military personnel. Officials blamed the hack on a contractor's failure to maintain the payroll system but said the incident won't impact monthly salary payments. UK media cited sources and linked the breach to Chinese state-sponsored hackers. Privately, officials fear China will use the stolen data to identify MoD employees with financial problems and use them for intelligence operations. The US and UK governments imposed sanctions on Chinese group APT31 at the end of March for hacking Members of Parliament and the UK Electoral Commission, although it's unclear who's behind this breach. [Additional coverage in the Associated Press]
MITRE hack: The MITRE Corporation has linked its recent security breach to a Chinese APT known as UNC5221 (UTA0178). This is the same APT group that found and exploited an Ivanti Connect Secure zero-day at the end of last year. MITRE says the group breached its R&D network in December of last year, two weeks before its hacking spree came to light. MITRE says the group used unique malware that was not seen in other intrusions.
GNUS crypto-heist: A threat actor has hacked the GNUS.ai cryptocurrency project. The attacker hacked the project's Discord, stole a private key, minted new tokens, and then sold them for a $1.27 million profit. GNUS has launched a token buy-back scheme to reimburse impacted users. [Additional coverage in CCN]
Crypto-whale scammed: The owner of a whale crypto-wallet lost $71 million in a phishing incident. [Additional coverage in Binance Square]
"When attempting to transfer WBTC to the new address, the whale inadvertently copied the fraudster's address, resulting in the loss of all their WBTC to the hacker."
Van Gogh Museum incident: At least 50 people entered their payment card details on a fake website for the Van Gogh Museum that was sitting at top of Google search results. [Additional coverage in Parool]
Enstar incident: US insurance provider Enstar has joined the list of MOVEit victims. The company disclosed the breach last week.
KOR data leak: The South Korean government leaked the data of 1,200 individuals by accidentally issuing the wrong documents to some users. [Additional coverage in The Readable]
UFG ransomware attack: The University of French Guiana has fallen victim to a ransomware attack. The incident took place on April 30 and the university's website is still down following the incident. [Additional coverage in FranceGuyane]
Final Fantasy XIV DDoS: Final Fantasy XIV servers were taken out on Monday by a pretty vicious DDoS attack. [Additional coverage in Siliconera]
General tech and privacy
BetterHelp fine: The US FTC has fined BetterHelp $7.8 million for sharing the health data of 800,000 customers with online advertisers.
Apple M4: Apple has introduced its new M4 chip.
"Built using second-generation 3-nanometer technology, M4 is a system on a chip (SoC) that advances the industry-leading power efficiency of Apple silicon and enables the incredibly thin design of iPad Pro."
SecureDrop protocol: The Freedom of the Press Foundation has released the first preview version of its new SecureDrop protocol. The protocol will be used to support the end-to-end encryption on the upcoming version of the SecureDrop whistleblowing platform.
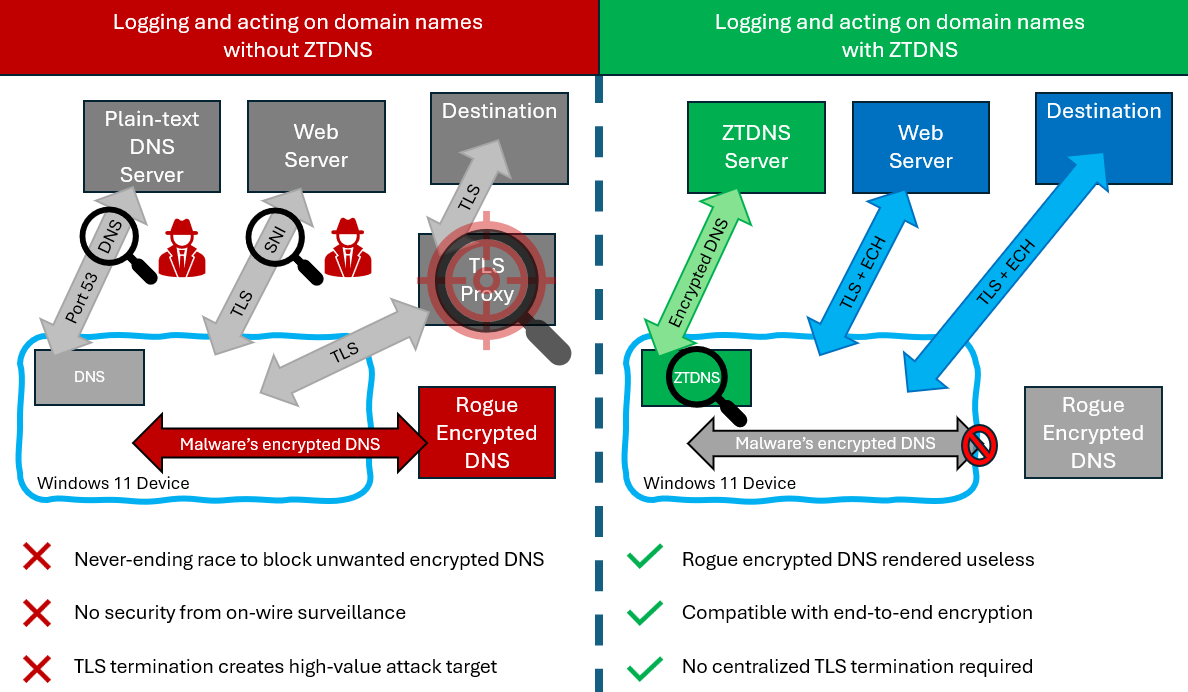
Microsoft ZTDNS: Microsoft has announced a new Windows feature designed to improve the security of DNS connections. The feature is called Zero Trust Domain Name System (ZTDNS) and will run inside its own Windows client. The client handles all DNS queries and will block any outbound internet traffic that was not resolved by a pre-approved DNS server. ZTNDS is currently in private preview and is expected to ship with Windows 11 in the coming years.
Government, politics, and policy
New CSRB members: The DHS and CISA have added four new members to the Cyber Safety Review Board (CSRB). Former CISA Director Chris Krebs and NSA Cybersecurity Director David Luber are part of a group replacing four outgoing members. Ten past members are returning to their roles. The Board will maintain its past leadership. DHS Under Secretary for Policy Robert Silvers will remain CSRB Chair, while Heather Adkins, Vice President for Security Engineering at Google, will return as Deputy Chair.
New CSRB members:
- Jamil Jaffer, Venture Partner Paladin Capital Group and Founder and Executive Director, National Security Institute, George Mason University Scalia Law School
- David Luber, Director, Cybersecurity Directorate, NSA
- Katie Nickels, Senior Director of Intelligence Operations, Red Canary
- Chris Krebs, Chief Intelligence and Public Policy Officer, Sentinel One
Departing members include:
- Katie Moussouris, Founder and CEO, Luta Security
- Chris Novak, Co-Founder and Managing Director, Verizon Threat Research Advisory Center
- Tony Sager, Senior Vice President and Chief Evangelist, Center for Internet Security, and
- Wendi Whitmore, Senior Vice President, Unit 42, Palo Alto Networks
Returning members include:
- Dmitri Alperovitch, Co-Founder and Chairman, Silverado Policy Accelerator and Co-Founder and former CTO of CrowdStrike, Inc.
- Harry Coker, Jr., National Cyber Director, Office of the National Cyber Director
- Jerry Davis, Founder, Gryphon X
- Chris DeRusha, Federal Chief Information Security Officer, Office of Management and Budget
- Eric Goldstein, Executive Assistant Director for Cybersecurity, Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
- Marshall Miller, Principal Associate Deputy Attorney General, Department of Justice
- John Sherman, Chief Information Officer, Department of Defense
- Bryan Vorndran, Assistant Director, Cyber Division, Federal Bureau of Investigation
CSRB Chair:
- Robert Silvers, DHS Under Secretary for Policy
CSRB Deputy Chair:
- Heather Adkins, Vice President for Security Engineering at Google
New CyberCom #3: US Cyber Command has appointed Morgan Adamski as its next Executive Director. She previously served as Director of the NSA Cybersecurity Collaboration Center. Adamski will assume her new position in early June 2024. The Executive Director chair is the third highest role at Cyber Command. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
New US international cyberspace strategy: First teased last week, the US has unveiled a new international cyberspace strategy.
Smaller BIPA fines in Illinois: Lobby groups rejoice! The Illinois legislature seems poised to pass a law that will severely cut the fines that companies pay for violations of the state's Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA). [Additional coverage in The Record]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Thinkst CTO Marco Slaveiro about staying current with modern attack trends and not falling for the trap of optimizing to catch red teams.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Threat/trend reports: AT&T, Forescout, Fortinet, Kaspersky, Kaspersky (again), Trend Micro, XM Cyber, and Zscaler have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
Cryptomining campaign: Netresec has analyzed a cryptomining campaign that targeted a Kubernetes cluster.
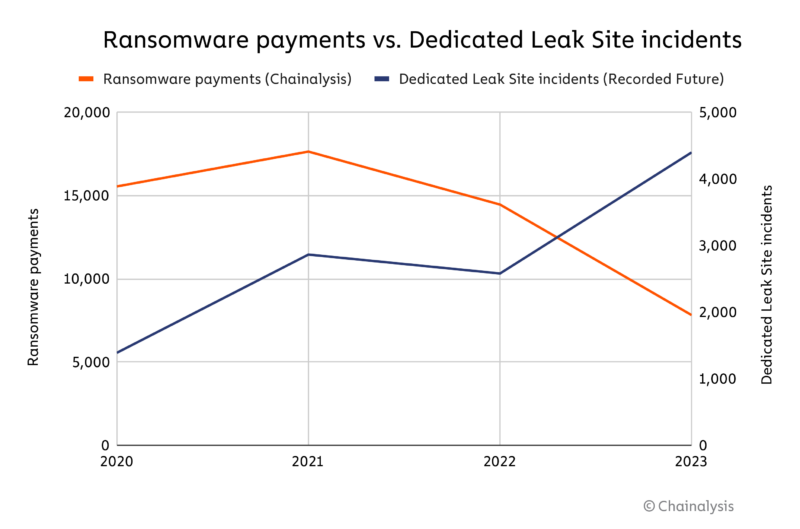
Ransomware payments go down: The number of victims who paid ransomware gangs fell by 46% last year despite a 70% increase in the number of victims. Blockchain analysis firm Chainalysis says the trend suggests that ransomware is getting easier to deploy but harder to monetize and profit from. The company's observations line up with a similar Coveware report, which reported paid ransoms in only 28% of incident response cases in the first three months of 2024.
Scaly Wolf campaigns: Security firm BI.ZONE has published details on a recent malspam campaign linked to Scaly Wolf, a financially motivated threat actor targeting Belarus and Russia.
STORM-0539 alert: The FBI warns that a financially motivated threat actor named STORM-0539 is targeting the gift card departments at US retail corporations. The group uses phishing and smishing to gain access to internal networks and create fraudulent gift cards. Microsoft first spotted the group last December and has the ability to bypass MFA protections. [Full FBI advisory here/PDF]
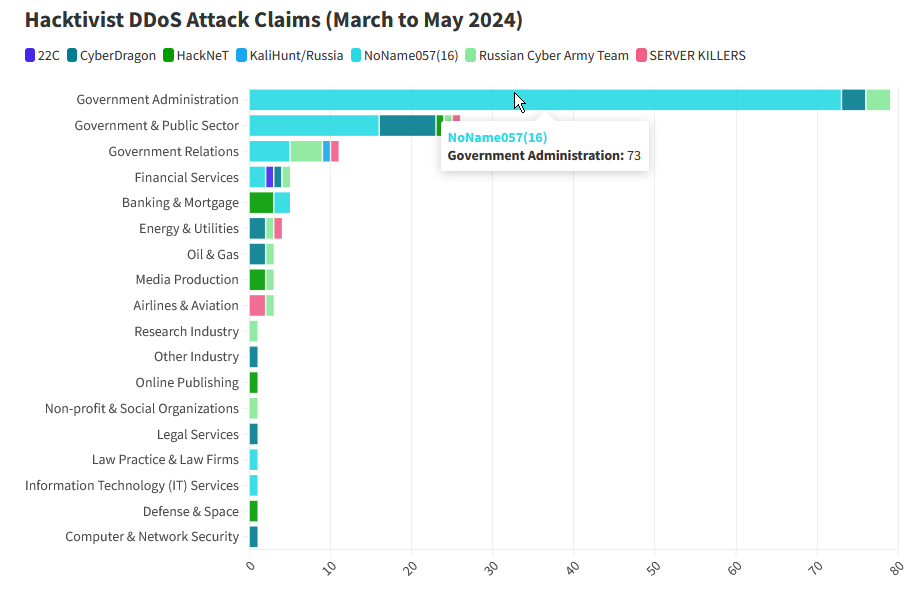
DDoS attacks on Moldova: A pro-Kremlin hacktivist group linked to the Russian military is targeting Moldovan government sites with DDoS attacks. According to Netscout, the attacks have hit more than 50 government sites since the start of March. The campaign is the work of NoName057(16), a group previously linked to Russia's military. Moldovan officials have said the DDoS attacks are part of Russia's hybrid warfare campaign [archived] meant to destabilize its government. Previous elements of the campaign involved attempted coups, assassinations, leaks, and info-ops. Netscout says NoName057(16) is currently the most active geopolitical hacktivist group.
Malware technical reports
Guntior bootkit: Russian security researcher Artem Baranov has published an analysis of the old Guntior bootkit.
zEus Stealer: Fortinet looks at the new zEus Stealer, currently distributed via malicious Minecraft source packs.
Formbook: CyberForensics has published a technical deep dive of the good ol' Formbook malware.
Matanbuchus: Intrinsec researchers have published a report on the server infrastructure used by the Matanbuchus MaaS. The report shows how to use current infrastructure to predict future campaigns. Researchers have also discovered that TA577 is currently either a Matanbuchus client or testing the service.
HijackLoader: Zscaler has published a report on recent changes to what it calls HijackLoader, also known as IDAT Loader.
MorLock ransomware: Russian security firm FACCT has discovered a new ransomware gang named MorLock. The group launched this year and has carried out attacks against at least nine Russian companies so far. MorLock intrusions were linked to stolen credentials and exploitation of known vulnerabilities. The gang's ransomware is based on leaked versions of the Babuk and LockBit code. FACCT says MorLock members appear to be based in Ukraine.
Sponsor Section
This newsletter is brought to you by Thinkst, the makers of the much-loved Thinkst Canary.
We will be in SF for #RSAC next week. Pop by¹ for a demo, to grab a t-shirt, to see Canary in action, or just to talk detection that works.
— Thinkst Canary (@ThinkstCanary) April 29, 2024
It’s totally geeky, but we can’t wait 💪💚
__
¹ North Hall 6445
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Disinformation coordination: The Atlantic has a fantastic piece on how authoritarian regimes like China, Russia, Iran, and others are coordinating with MAGA Republicans to discredit the concepts of democracy and liberalism around the world in the hopes of installing a ruling untouchable political class focused on self-enrichment.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
RIOT OS vulnerabilities: HN Security researcher Marco Ivaldi has discovered 10 vulnerabilities in the RIOT real-time operating system. The researcher discovered all the bugs during a short 16-hour security audit in January this year. RIOT OS has released patches for all bugs over the past few weeks. The project says it will also review why its security team took weeks to respond to Ivaldi's reports.

GitLab vulnerability: GitLab's own security team has published a technical analysis of CVE-2024-0402, a vulnerability they patched back in January. The bug is a file write that can be abused to run arbitrary commands on a GitLab server.
GitHub Enterprise Server vulnerability: StarLabs has published a technical analysis of CVE-2024-0200, a one-line vulnerability that could have compromised GitHub Enterprise Servers.
Android security updates: The monthly security updates for Android smartphones are out. No zero-days, neither in Android nor the Pixel updates.
TunnelVision attack: Security researchers have discovered a new attack that can decloack VPN traffic. The attack is named TunnelVision (CVE-2024-3661) and impacts VPN software installed on user PCs and not enterprise VPN servers. All VPN software released since 2002 is believed to be affected. The attack requires users to connect to a malicious DHCP server. Attackers can use the DHCP server to overwrite users' internet routing and send traffic meant for the VPN via the normal network. This bypasses VPN encapsulation and allows threat actors to intercept and track the victim's traffic.
"It is not feasible to fix the issue by simply removing support for the DHCP feature because this could break Internet connectivity in some legitimate cases. The strongest recommendation we have is for VPN providers to implement network namespaces on operating systems that support them, similar to the method described in WireGuard's documentation. Network namespaces are a Linux feature that can segment interfaces and routing tables away from the local network’s control, and other operating system maintainers should consider whether namespaces are feasible to implement."
Infosec industry
Black Hat Asia 2024 slides: Slides from the Black Hat Asia 2024 security conference, which took place in April, are available on the conference's site.
Industry moves: AT&T has divested its cybersecurity business into LevelBlue, a new company founded together with WillJam Ventures.
Acquisition news: Akamai has agreed to buy API security company Noname Security for $450 million.
New tool—Okta Terrify: Security researcher Ceri Coburn has released Okta Terrify, a tool to demonstrate how passwordless solutions such as Okta Verify's FastPass or other FIDO2/WebAuthn type solutions can be abused once an authenticator endpoint has been compromised.
New CSA tools: The Cloud Security Alliance has published four guides [1, 2, 3, 4] on the proper implementation and use of AI on cloud platforms.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at how different types of secrecy-obsessed organizations learn.




