Risky Biz News: Google addresses JIT security in Chrome 122
In other news: ScreenConnect exploitation starts; Apple adds PQ3 to iMessage; and White House executive order targets cybersecurity at US ports.

This newsletter is brought to you by asset inventory and network visibility company runZero. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Google has released this week version 122 of its Chrome browser, which comes with a new security feature meant to reduce the browser's attack surface.
The feature has no catchy name but can be found in the Chrome settings section and enabled with only a few clicks.
It allows Chrome users to disable performance features for V8, the engine inside Chrome that processes JavaScript and WebAssembly code.
More specifically, they disable Just-In-Time compilation, a type of code compilation that can speed up applications.
V8 and its JIT compiler, in particular, have been the source of many vulnerabilities and zero-days impacting Chrome in the past (here aresome totally random examples).
The new Chrome security feature was inspired by a Microsoft Edge project from 2021 named Super Duper Secure Mode, which tested disabling V8's JIT optimizations for the sake of better security.
That experiment eventually shipped to all Edge users and is now known as Edge's Enhanced Security Mode.
Back in 2021, Johnathan Norman, who was Microsoft Edge's Vulnerability Research Lead at the time, explained the performance-for-security trade-off by pointing out that more than half of all Chrome/Chromium zero-days exploited in the wild at that time were JIT-related issues.
Super Duper Secure Mode was met with praise and high adoption among cybersecurity practitioners at the time. Persons at risk of being targeted with browser exploits were also often told to use Edge in Super Duper Secure Mode while navigating the web for their own personal safety.
The new Chrome V8 security feature is a big win for the browser landscape since its addition to the Chromium core code also allows it to slowly trickle down to all the other related browsers, such as Vivaldi, Opera, and the rest.
The new feature can be enabled from Chrome's security settings section at:
chrome://settings/security
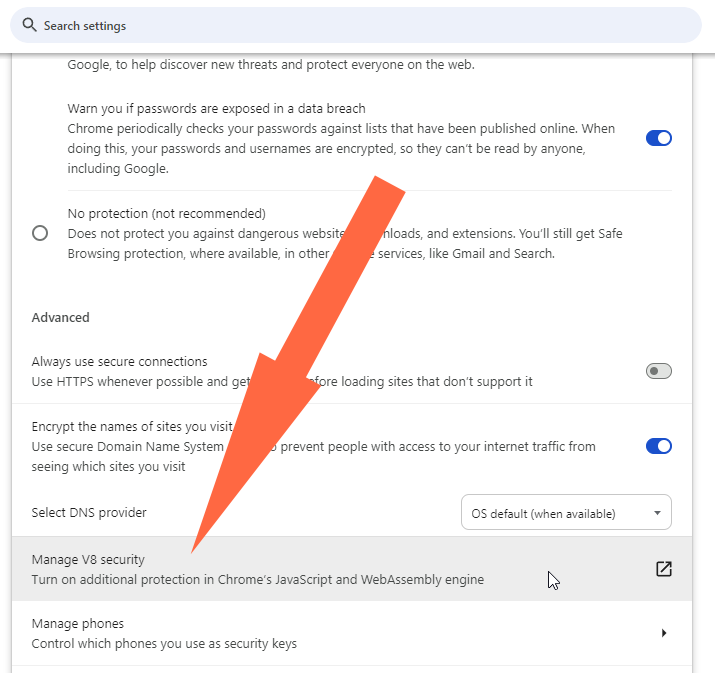
Or by going directly to:
chrome://settings/content/v8
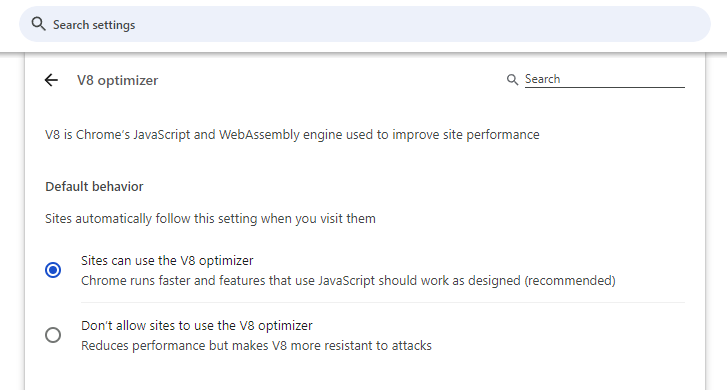
Besides the new V8 engine security management option, Chrome 122 also comes with a revamped Safe Browsing API that will now allow websites to load while it scans them for threats. Previously, the Safe Browsing feature would prevent Chrome from loading sites during a scan.
On top of that, there's also a new UI for the Downloads panel, including new and clearer warnings on dangerous files.
There are also the usual security patches and webdev-related changes, as well as a new Help Me Write AI feature.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Tangerine data breach: Australian internet service provider Tangerine says hackers gained access to the data of 232,000 current and former customers. The breach impacts customers who signed up with Tangerine between June 2019 and July 2023. Tangerine says it discovered the breach on Sunday, February 18, and has already notified affected users.
PSI Software ransomware attack: PSI Software, a German company that develops software for the energy sector, has disclosed a ransomware attack.
Romanian Parliament ransomware attack: The Romanian Parliament was still using Windows XP and Windows 7 computers when it was hit by a ransomware attack at the end of January. Officials said that litigation has prevented the organization from replacing old systems before the breach. Members of the Knight ransomware group stole more than 250GB of data from the Parliament's network. The personal data of multiple Romanian lawmakers was included. Weeks after the attack, the Knight ransomware gang has ceased attacks and is now selling its source code on hacking forums. [Additional coverage in HotNews]
General tech and privacy
DoorDash privacy fine: Home delivery service DoorDash has agreed to pay a $375,000 civil penalty for violating California's privacy laws. California Attorney General Rob Bonta sued DoorDash for selling customer data without notifying users or providing a way to opt out. The company sold customer data such as names, addresses, and transaction histories to a marketing cooperative.
FTC fines Avast: The US Federal Trade Commission has fined cybersecurity firm Avast $16.5 million for selling its users' browsing data. The FTC accused the security firm of using bait-and-switch tactics by offering browser extensions that blocked internet tracking but then selling browsing data behind its users' backs. Between 2014 and 2020, Avast allegedly sold browsing data to more than 100 third parties through its Jumpshot subsidiary. The FTC has banned Avast from engaging in similar practices and has ordered the company to notify all users whose data was sold.
Mastodon security change: Mastodon developers have added a new feature that will close open registration on Mastodon servers if none of an instance's moderators have logged in for more than a week. The change is designed to stop threat actors from abusing abandoned instances to spam the Fediverse.
Microsoft free security logs are now live: Microsoft has officially made a bunch of security logs free to use for its enterprise customers. Thirty-one log categories have been moved from the premium tier of the Microsoft Purview Audit service into the standard offering, something that Microsoft promised last year in the aftermath of its Storm-0558 hack. Microsoft made the move after pressure from CISA and the US government. CISA greeted the company's move.
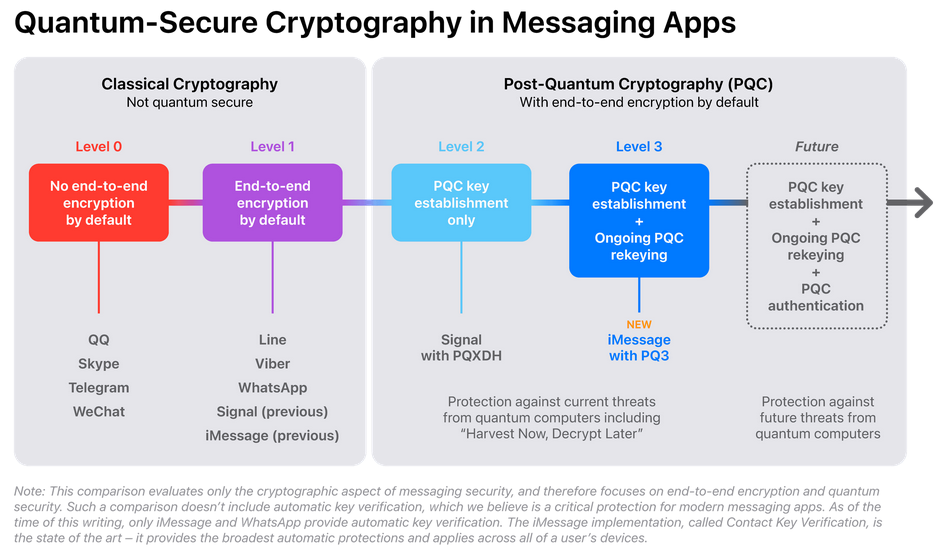
iMessage gets PQ3: Apple has developed a new cryptographic protocol that it plans to incorporate into its iMessage service. The protocol is named PQ3 and incorporates both forward security and post-quantum cryptography protections. It will provide protections against threat actors storing iMessages and using quantum computers to break Apple's current encryption at a later date in the future. The new feature will ship with Apple's upcoming iOS 17.4 and macOS 14.4 releases.
Government, politics, and policy
Spyware in the EU Parliament: The European Parliament's IT service has found traces of spyware on the smartphones of members of its security and defense subcommittee. The infections were discovered after members went in for a routine device check. The EU Parliament has sent a letter this week and has urged members to have their devices scanned by its IT department. EU officials have not confirmed the incident in an official press release. [Additional coverage in Politico Europe]
US port cybersecurity: The Biden Administration has issued an executive order to bolster cybersecurity at US ports. The executive order introduces new cyber regulations. It also comes with a $20 billion investment in US port infrastructure. The White House wants to boost production of US port cranes to replace cheaper Chinese alternatives. US cyber and intelligence agencies have warned that China could use the software on its cranes to spy or sabotage US trades.
US water systems security: CISA, the EPA, and the FBI have published a document with eight basic steps that US water management systems can take to safeguard their systems.
Chinese BESS fears: A CSO Online article goes over recent concerns in the US government that China might use its dominance in the BESS market to sabotage the US power grid. BESS, or battery energy storage system, is a type of industrial battery used by power grids to store large quantities of energy during the day to account for consumption fluctuation.
Mandatory biometrics collection in Vietnam: The Vietnamese government will begin collecting biometric data from citizens in July this year. The collection is mandatory and will take place when citizens replace their ID cards. Authorities plan to collect DNA, voice samples, and iris scans. [Additional coverage in VGP News]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Rob King, runZero's Director of security research. The pair talk about the world of Operational Technology protocols and how Rob dissects these protocols to be sure that active discovery of OT devices is safe.

Cybercrime and threat intel
LockBit reward: The US State Department has announced rewards of up to $15 million for any information on the LockBit ransomware gang. The reward applies to information on both the gang's leaders and its members. Known as affiliates, members are the ones who actually carry out the attacks, while LockBit admins only manage the platform and the ransomware's source code. US officials have offered the reward days after law enforcement from 11 countries took down LockBit's infrastructure.
LockBit father and son duo: Speaking of the LockBit takedown, authorities said they made two arrests, one in Poland and one in Ukraine. The one in Ukraine is a father-son duo from Ternopil.
Medibank hacker detained in Russia: Russian authorities have identified and arrested three members of the SugarLocker ransomware. The group was operating under the guise of a legitimate IT company but was secretly running a Ransomware-as-a-Service platform since at least 2021. Security firm FACCT claims it gained access to the SugarLocker backend in January 2022 after the gang misconfigured one of its web servers. FACCT linked the gang behind the ransomware to a series of phishing and online fraud attacks against Russian organizations. The company identified the gang's leader as a hacker named GustavDore. This is one of the pseudonyms used by Alexander Ermakov, the individual accused by Australia of the Medibank hack.
Russian grid hacker arrested: Russian authorities have arrested a 48-year-old man from Vologda on hacking-related charges. Officials say the suspect allegedly broke into IT systems and cut off power to 38 villages across Vologda. The incident took place in February of last year. If found guilty, the man faces up to eight years in prison. [Additional coverage in VologdaOnline]
Threat reports: IBM X-Force, Cofense, CrowdStrike, S2W, and ArcticWolf have published yearly reports.
Carpet-bombing attacks: Netscout says it's seeing roughly 6000 carpet-bombing DDoS attacks every day. Carpet-bombing is when DDoS attacks target an ISP's entire subnet range. These attacks target individual consumers one be one, in random attacks, and are hard to detect while being extremely disruptive.
PyPI malware: DevSecOps company ReversingLabs has found new malware on the PyPI portal. This time, the attackers tried to pose as the official PyPI account for NP6, a marketing automation tool developed by software company Chapvision.
Operation Synergia: Trend Micro has published details about its work on Interpol's Operation Synergia. As part of this operation, law enforcement agencies detained 30 suspects and took down 1,300+ servers used in malware operations. Trend Micro has linked this to Cobalt Strike, RedLine, and AsyncRAT campaigns.
LockBit-NG-Dev: Trend Micro says that the LockBit ransomware group was in the process of developing a new version of their file encrypter when authorities took down their operation. The new version was allegedly called LockBit-NG-Dev, a temporary name for what would have become LockBit 4.0. Trend Micro described it as "a platform-agnostic malware-in-testing that is different from previous versions."
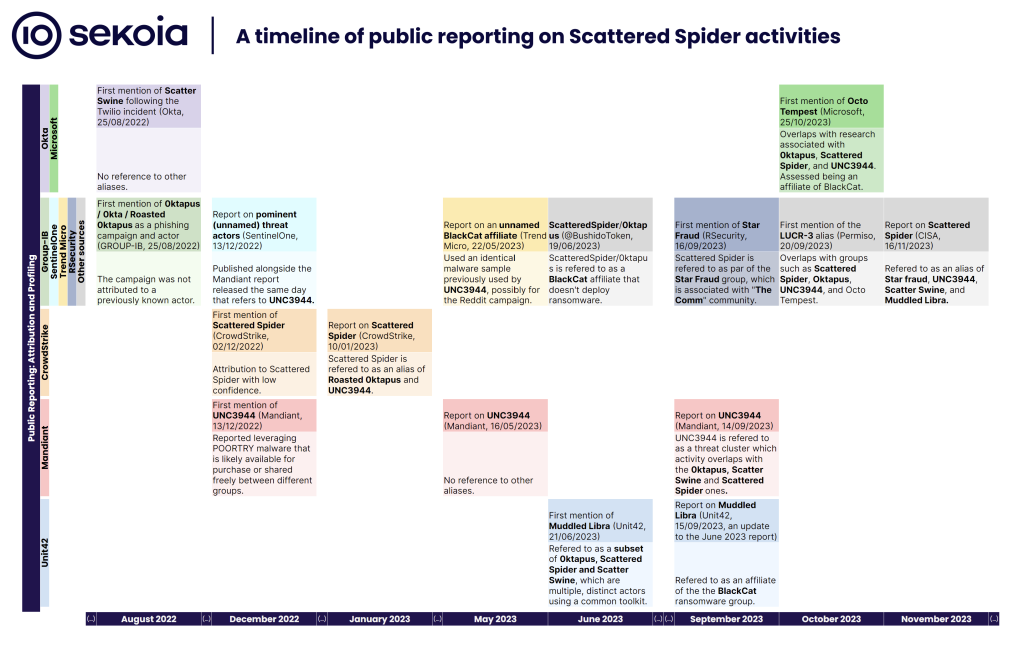
Scattered Spider evolution: French security firm Sekoia has published a report looking at the evolution of the Scattered Spider group and all its connections and infosec codenames—0ktapus (Group-IB), Scatter Swine (Okta), UNC3944 (Mandiant), Octo Tempest (previously Storm-0875, Microsoft), Star Fraud (SentinelOne), Muddled Libra (Unit42) and others.
Malware technical reports
SSH-Snake: Cloud security firm Sysdig says that threat actors have recently adopted an open-source tool to launch attacks against customer systems. The tool is named SSH-Snake and was released by security researcher Joshua Rogers at the start of the year. It works like an SSH worm that gathers local SSH keys and spreads to other systems automatically.
Lucifer: The Lucifer DDoS botnet is now targeting Apache Druid, Apache Flink, and Apache Hadoop servers, according to cloud security firm Aqua. The campaign includes exploiting misconfigurations and vulnerabilities alike. The final payload also includes a cryptominer.
8220 Gang: Uptycs takes a long look at recent tactics used by 8220 Gang, a Chinese cybercrime group focused on cloud cryptomining.
VietCredCare: Group-IB has published a report on VietCredCare, an infostealer sold by a Vietnamese cybercrime group via Telegram channels. The malware has been active since August 2022 and was primarily used in campaigns targeting Vietnamese users.
RansomHouse ransomware: ShadowStackRE has published an analysis of RansomHouse, a ransomware operation that launched at the start of 2022. The group was initially only in data extortion before moving on to actual ransomware attacks.
HomuWitch decrypter: Avast has published a free decrypter for victims who had data locked by the HomuWitch ransomware.
TeaBot: Mobile security firm Cleafy has published a report on the recent spikes in campaigns targeting European users with the TeaBot Android banking trojan. Some of these campaigns managed to sneak the trojan inside apps on the official Google Play Store.
"An interesting aspect concerning the targeted countries is that Russia and CIS regions are typically excluded during the installation phases in multiple malware campaigns. However, in the case of this TeaBot campaign, Russia stands out as one of the targets."
Sponsor Section
Senior Sales Engineer Ali Cheikh demonstrates the runZero platform to Risky Business host Patrick Gray. runZero is a cyber asset management tool that combines active scanning, passive discovery, and API integrations to discover IT, OT, and IoT assets (both managed and unmanaged) across your network, including cloud, mobile, and remote environments.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
KONNI backdoor: DCSO has looked at a backdoored installer that was used by North Korea's KONNI hackers against the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs in January this year.
"In this instance, the backdoored installer appears to be for a tool named 'Statistika KZU' (Cтатистика КЗУ). While we were unable to find any public references to the tool, we suspect on the basis of install paths, file metadata, and user manuals bundled into the installer that the software is intended for internal use within the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MID), specifically for the relaying of annual report files from overseas consular posts (КЗУ — консульские загранучреждения) to the Consular Department of the MID via a secure channel."
TinyTurla-NG: Cisco Talos has published a technical write-up on Turla's latest backdoor, TinyTurla-NG.
Doppelgänger NG: ClearSky and SentinelOne have spotted a new Russian disinformation campaign that originates from the Doppelgänger cluster. The campaign targeted audiences in the US, Germany, Israel, and France with fake websites promoting anti-Ukraine and anti-US rhetoric. The two security firms say the sites were promoted by "a substantial network of X (Twitter) accounts." ClearSky linked the campaign to APT28, a cyber unit inside Russia's military intelligence service GRU.
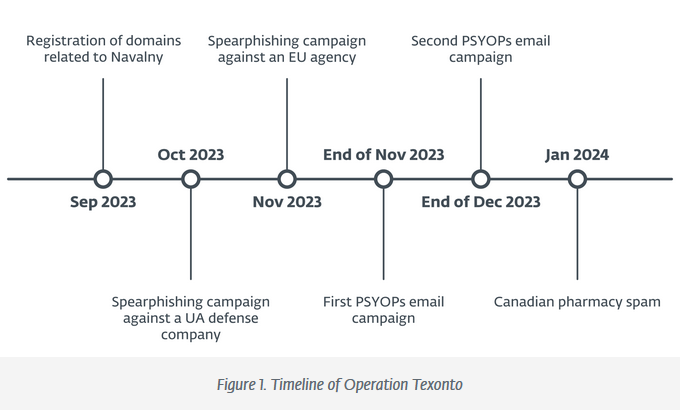
Operation Texonto: ESET researchers say they have spotted a Russia-linked threat actor engaging in a broad range of operations that ranged from spear-phishing to PSYOPS and mundane pharmacy spam. The spear-phishing campaigns targeted an EU agency and a Ukrainian defense company. The PSYOPS operation involved email spam and blasted messages that attempted to demoralize Ukrainian citizens with disinformation about the war. The emails tried to scare Ukrainians by warning of periods of famine and urged men to cut off limbs to avoid military service. ESET did not "formally" attribute the activity to any group, but researchers said they found similarities to past Calisto operations, a group linked to the FSB.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
ScreenConnect exploitation starts: Threat actors are exploiting two vulnerabilities in the ConnectWise ScreenConnect remote access software. Attacks started a day after ConnectWise released patches to address the two vulnerabilities—an authentication bypass and a path traversal. Cybersecurity experts have described both issues as trivial to exploit. Proof-of-concept code is now also broadly available. Exploitation has been seen in the wild and confirmed by the vendor. According to security firm Sophos, one of the groups exploiting the bugs includes remnants of the LockBit ransomware group. ConnectWise has also managed to obtain CVE identifiers for the two issues—tracked now as CVE-2024-1708 and CVE-2024-1709. Technical write-ups on the vulnerability are available from Huntress, Logpoint, and Palo Alto Networks.
Atlassian security updates: Atlassian has published a patch train to address 11 high-severity vulnerabilities across its products.
LoadMaster security update: Kemp Technologies has published a security update for its LoadMaster load balancer appliance. The update fixes a critical security flaw that allows threat actors to access the device's management interface. Kemp says attackers can take over devices via malicious, unauthenticated API commands. The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-1212.
VMware security updates: VMware has advised customers to uninstall its Enhanced Authentication Plug-in (EAP) browser extension. The company says the extension is vulnerable to an authentication relay and session hijacking vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-22245. VMware has rated the vulnerability with a 9.6 out 10 severity score and says the issue can allow threat actors to access a customer's VMware resources. The company has not released a patch since the extension reached end-of-life in 2021. It also patched a second vulnerability across other products.
Zyxel firewall vulnerability update: VulnCheck's Jacob Baines has discovered that a recent vulnerability disclosed in Zyxel firewalls by SSD researchers is actually an older bug tracked as CVE-2023-33012.
"The associated disclosure did not mention any caveats to exploitation, but it turns out only an uncommon configuration is affected. There are currently about 600 internet-facing Zyxel firewalls vulnerable to this issue (out of ~26,000)."
TP-Link vulnerability: The same SSD researchers now say they found a vulnerability in the TP-Link NCXXX family of devices. This one can allow threat actors to access the device without credentials. No CVE, no patch, but there's a PoC.
IBM ODM RCE: watchTowr Labs has published a technical analysis of two vulnerabilities in the IBM Operational Decision Manager (ODM), including a pre-auth RCE.
PrintListener: A team of American and Chinese researchers has devised a theoretical attack that uses the sounds made by users swiping their smartphone screens to partially recreate fingerprints. Named PrintListener, more details on the attack will be presented at the NDSS Symposium next week.
Infosec industry
New tool—LOTP: DevSecOps platform Boost Security has published a new project named LOTP (Living Off the Pipeline). The project lists development tools (typically CLIs), commonly used in CI/CD pipelines, that have lesser-known RCE-by-Design features. The project is similar to other initiatives that track benign tools that can be abused for attacks on Windows (LOLBAS, LOLDrivers, and LOFLCAB), Linux (GTFOBins), and macOS (LOOBins).
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine Russian cyber doctrine and how it was applied in the early days of its invasion of Ukraine. They mention a Human Rights Watch report that examined how international humanitarian law was applied in the 2003 invasion of Iraq.





