Risky Biz News: AU, UK, US sanction Russian behind Medibank ransomware attack
In other news: Attacks target Atlassian's latest Confluence vulnerability; crypto-wallet Trezor discloses data breach; and unsuccessful swatting event targets CISA Director Jen Easterly.

This newsletter is brought to you by Material Security, the company that secures the cloud office with unified email security, user behavior analytics, and data loss prevention for Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
Australia, the UK, and the US have sanctioned a Russian national for his role in a ransomware attack on Australian private insurance provider Medibank in October 2022.
Identified as Alexander Ermakov, he is believed to be connected to the REvil ransomware operation, where he allegedly operated under pseudonyms such as GustaveDore, JimJones, Blade_Runner, and aiiis_ermak. Ermakov is believed to be 33 and a resident of Moscow.
Officials say Ermakov was a "pivotal" and "key actor" in REvil's attack on Medibank, considered one of Australia's worst cybersecurity incidents.
The REvil gang breached the private insurer's network, stole data, encrypted systems, and then leaked portions of the data on the dark web in an attempt to pressure the company into paying a $10 million ransom demand.
More than 9.7 million patient records were stolen in the attack, and more than 480,000 health claims were posted on REvil's dark web leak site.
The records contained names, dates of birth, Medicare numbers, and sensitive medical information. Some of the leaked health claims contained information about sensitive procedures, such as abortions and mental health treatment.
Officials say Ermakov was directly involved in breaching and releasing the data.
At the time, the hack and the appalling extortion tactics triggered an aggressive response from the Australian government, which set up a permanent operation to hunt down cybercriminal syndicates.
Named Operation Aquila, the initiative is a joint effort with personnel from both the Australian Federal Police (AFP) and the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD).
Ermakov is the first individual tracked down by Aquila and the first cybercriminal to be sanctioned by the Australia government.
The joint AU-UK-US sanctions include both financial sanctions and travel bans. Australian officials warned that anyone breaking faces up to ten years in an Australian prison.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
DDoS attacks on Romanian govt sites: Pro-Kremlin hacktivist group NoName launched DDoS attacks on several Romanian government websites. The impact was extremely minor, and local authorities barely noticed the downtime.
Trezor breach: Cryptocurrency wallet service Trezor has confirmed that a threat actor gained access to the data of 66,000 customers after gaining access to its support ticketing portal. Trezor says all users who registered an account on its support portal since December 2021 are affected. The company says the hacker used data from the portal to contact 41 customers and attempt to obtain data about their wallet recovery seeds.
Trello leak: A threat actor is selling a list of more than 15 million emails that were scraped from internet-exposed Trello boards.
LoanDepot ransomware aftermath: American mortgage provider LoanDepot has confirmed that the data of almost 16.6 million customers was stolen in a ransomware attack at the start of the year. In an update provided to customers and shareholders, LoanDepot says it made significant progress in restoring loan servicing systems that were impacted by the attack. The company is the fourth major US mortgage and real estate insurance provider that was hit by a cyberattack over the past months. Similar incidents have also affected Mr. Cooper, Fidelity National Financial, and First American Financial.
Jason's Deli cred-stuffing attack: American fast food chain Jason's Deli says that threat actors gained access to more than 344,000 customer accounts on its reward points portal after a successful credential-stuffing attack.
SEC Twitter hack: The SEC has published a final report on how its Twitter account got hacked. It was SIM swapping and a lack of MFA, as initially suspected.
MOAB leak: Security researcher Bob Dyachenko has discovered a database exposed online that contains more than 26 billion user records. The leaky database appears to aggregate data from more than 3,800 past data breaches. Dyachenko was unable to identify the database's owner and named the leak the Mother of all Breaches (MOAB) since it's currently the biggest leak known to date. [Additional coverage in CyberNews]
Concentric Finance cyber-heist: Cryptocurrency platform Concentric Finance lost $1.6 million in assets in a security incident that took place earlier this week. The company says the attacker managed to social-engineer one of its employees and gain access to one of its wallets. Blockchain security firm CertiK linked the attack to the same threat actor who stole $2.7 million worth of crypto-assets from OKX in December of last year.
GMEE cyber-heist: The operators of the GMEE (or Gamee) cryptocurrency token lost $15 million worth of assets after hackers exploited one of its smart contracts. All the stolen tokens were from the project's reserve, and no user-owned tokens were affected. The token lost 40% of its value in the aftermath of the hack. [Additional coverage in the DailyCoin]
Pegasus in Togo: Traces of the Pegasus spyware was found on phones of two independent Togolese journalists. The infections took place throughout 2021 and were discovered by the security team of Reporters Without Borders. The organization was providing assistance to the two journalists after they were arrested in December after reporting on a theft from the home of one of the country's ministers. According to a report from French newspaper Le Monde, the Togo government was a customer of NSO Group at the time of the infections.
General tech and privacy
Meta will let EU users unlink its services: Social media company Meta will let EU users unlink its services from one another.
"People using Instagram and Facebook in the EU, EEA and Switzerland will soon be offered several choices about how they would like to manage their experiences across Meta products. We are offering these choices to address the requirements of the DMA, which enter into force in March 2024."
First IPv4 sunset date: The Czech government has announced that it will stop providing its services via IPv4 on June 2, 2032, making this the first unofficial IPv4 sunset date.
Amazon fined in France: French privacy watchdog CNIL has fined American retail giant Amazon €32 million for using "an excessively intrusive system for monitoring employee activity and performance" at its warehouses across the country. The fine also covers the company's use of video surveillance without warning employees and for not securing the accounts used to access the surveillance system.
Apple fined in Russia: The Russian government has fined Apple $13.5 million for not allowing third-party payment systems on the iOS App Store.
iOS Stolen Device Protection: Apple's new Stolen Device Protection feature is now live in the company's latest iOS 17.3 release.
Chrome 121: Google has released version 121 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes in this release include the addition of an AI-based tab organizer and theme generator, a new side panel, and the start of Chrome's third-party cookie deprecation procedures.
Government, politics, and policy
Russia's emoji ban: A Russian Duma member has proposed a law that will ban roughly two dozen emojis on smartphones sold in Russia. The ban covers LGBTQ-themed emojis that depict same-sex families, pregnant men, bearded women, and men in wedding dresses, among others. The law was proposed by Alexey Zhuravlev, a member of the Rodina party. It comes after a Russian judge outlawed LGBTQ activism, and authorities started a countrywide crackdown on members of the LGBTQ community. This is the second time the Russian Duma is looking at a law to ban same-sex emojis after a similar attempt in 2015. [Additional coverage in Rossiyskaya Gazeta]
CISA Director swatted: CISA Director Jen Easterly was the target of a swatting attempt, according to a report from The Record, citing sources inside CISA. The attacker claimed gunfire was heard from Easterly's house on the night of December 30, last year. The CISA official was unharmed after Arlington County Police arrived on scene and determined no shooting had occurred. The incident comes as a large number of US officials have been swatted over the past weeks, with two incidents targeting the White House itself.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to Ivan Dwyer of Material Security about how it makes sense to view office productivity suites as an organisation's critical infrastructure.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Killnet leader interview: Russian news outlet Gazeta has published an interview with BTC, the new leader of the pro-Kremlin hacktivist group Killnet. The outlet previously doxed the gang's former leader, 30-year-old named Nikolai Nikolaevich Serafimov, known as Killmilk. BTC took credit for the destructive attack that crippled Ukrainian mobile operator Kyivstar. Ukrainian officials previously attributed the attack to Sandworm, a GRU-managed APT group.
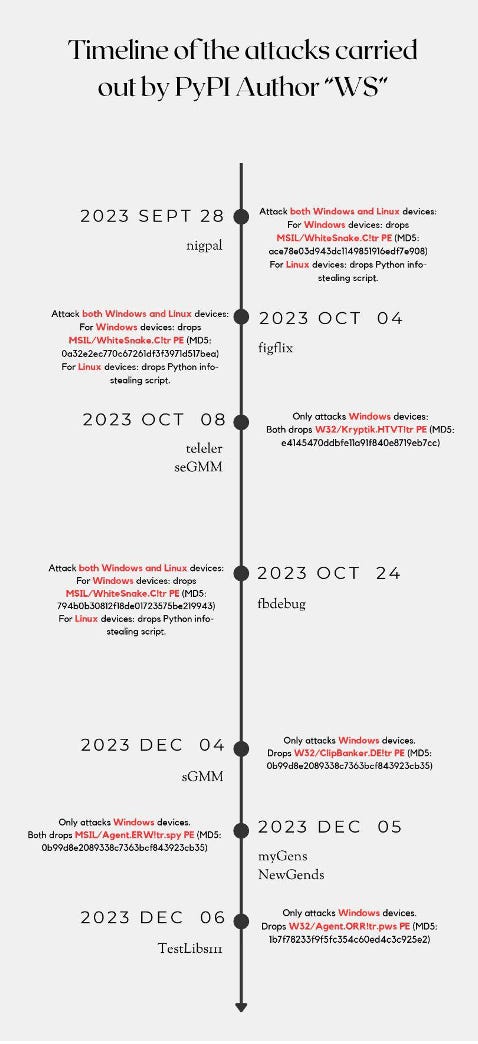
WS: Fortinet has published a profile of WS, a threat actor that has published nine malicious Python libraries via the PyPI portal over the past years.
Fake loan apps: Indian security firm CyFirma looks at a campaign from a Pakistani threat actor targeting Indians with fake loan apps infected with malware.
npm malware caught stealing SSH keys: ReversingLabs researchers have discovered two npm libraries designed to steal SSH keys from infected developer machines and upload the data to a GitHub repository.
"Fortunately, the reach of this campaign was limited. ReversingLabs observed different accounts publishing warbeast2000 and kodiak2k on npm. The warbeast2000 package was downloaded a little less than 400 times, whereas the kodiak2k was downloaded around 950 times."
Ransomware in 2023: The number of ransomware victims listed on dark web leak sites in 2023 was 4,667, a figure 84% higher than the number of victims listed in 2022.
Malware technical reports
BianLian ransomware: Palo Alto Networks researchers have found a shared tool used by the BianLian and the Makop ransomware gangs.
Cactus ransomware: ShadowStackRE has published an analysis of Cactus, a ransomware operation that launched in May of last year.
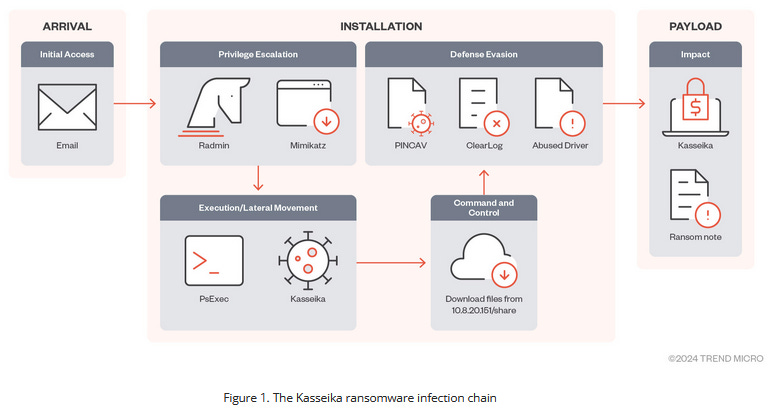
Kasseika ransomware: Trend Micro researchers have discovered a new ransomware operation named Kasseika. The ransomware was first spotted in 2023 and is one of the rare groups that uses the Bring-Your-Own-Vulnerable-Driver (BYOVD) approach for its intrusions. Kasseika becomes the fourth ransomware strain to use BYOVD after the likes of Akira, BlackByte, and AvosLocker. Trend Micro says the group appears to resemble the BlackMatter ransomware operation, which shut down in late 2021.
NS-Stealer: Trellix has published a technical report on a new infostealer written in Java and named NS-Stealer that can steal web browser data and upload it to Discord bot channels.
Godzilla webshell: Trustwave looks at Godzilla, a JSP webshell that the company has recently saw being planted on hacked Apache ActiveMQ hosts.
DarkGate: Kroll's security team has published a report on the DarkGate malware's encoding system.
SystemBC: The same team also published a report on the C2 server system used by the SystemBC malware family.
New macOS malware: Kaspersky has discovered a suite of cracked and pirated macOS apps secretly installing infostealers on user devices.
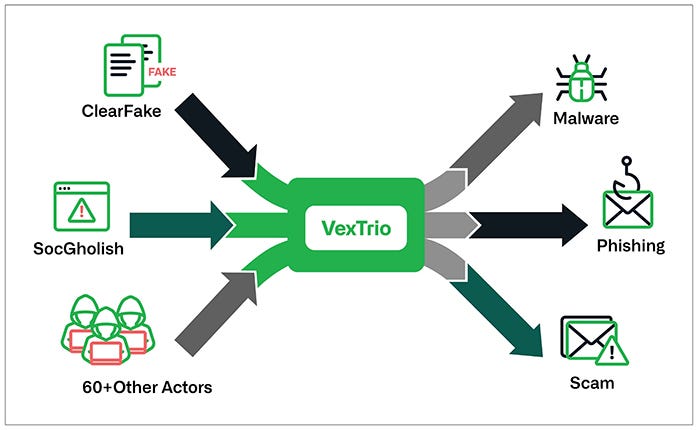
VexTrio: Infoblox has published a report on VexTrio, a TDS platform that launched in 2017 and currently redirects traffic from hacked devices between more than 60 cybercrime operations. Some of its customers include ClearFake and SocGolish, two other TDS platforms, showing how these groups would often collaborate with each other, rather than compete.
Sponsor Section
A deep dive into what's new with Material Security's Phishing Protection product: New detections, response UX boosters, and more actionable reports.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
UAC-0050: CERT-UA has published a report on UAC-0050's latest spear-phishing campaign targeting Ukrainian government agencies. The group has been at it for a year now, with non-stop attacks aimed at Ukrainian agencies. On the same note, AhnLab also spotted a SmokeLoader campaign targeting Ukrainian government organizations as well. Unclear which threat actor was behind this one.
ScarCruft: North Korean hacking group ScarCruft (APT37) has conducted a spear-phishing campaign that targeted members of the South Korean cybersecurity community. Spotted by SentinelOne, the campaign took place throughout November and December of 2023. Besides infosec professionals, the campaign also targeted media organizations and high-profile experts in North Korean affairs. ScarCruft's final payload was the group's typical malware, the RokRAT remote access trojan.
Lazarus: AhnLab analyzes a new DLL side-loading technique used by the Lazarus APT group in attacks targeting South Korean organizations.
OceanLotus: Chinese security firm CrackME looks at recent OceanLotus operations targeting Chinese organizations.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
MavenGate research: More than 6,100 Java libraries listed on the MavenCentral package repository appear to have been abandoned by their authors. The libraries use expired domains for their admin accounts, which can be registered by attackers to hijack the library itself. Security firm Oversecured says some of the libraries are dependencies in some of today's most popular Java projects, including apps from companies like Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Adobe, and Netflix.
Apple patches WebKit zero-day: Apple has released security updates for all its products to patch a new zero-day (CVE-2024-23222) in its WebKit browser engine. Patches were made available for iOS, macOS, iPadOS, tvOS, and Safari. The company also backported fixes for two zero-days (CVE-2023-42916 & CVE-2023-42917) it patched in November of last year to its older generation of devices. This is Apple’s first zero-day this year after having patched 20 zero-days in 2023.
Splunk security updates: Splunk has released security patches to fix five vulnerabilities in its products.
Fortra security update: Fortra has published a patch for its GoAnywhere file-sharing server. The security update fixes an authentication bypass tracked as CVE-2024-0204 discovered by two software engineers from Spark Engineering Consultants. A PoC has been published here.
WifiKey PoC: SSD has published proof-of-concept for a still-unpatched pre-auth RCE vulnerability in WifiKey's AC Gateway product.
Bitcoin ATM vulnerabilities: IOActive researchers have found a series of vulnerabilities that could allow a physical attacker to steal user assets from Lamassu Douro Bitcoin ATMs.
Confluence exploitation: Threat actors are exploiting a recently patched Atlassian Confluence vulnerability. Tracked as CVE-2023-22527, the vulnerability has a severity rating of 10/10 and allows for unauthenticated remote code execution attacks. According to the Shadowserver Foundation, attacks began on January 19, three days after Atlassian released a patch. After the attacks got underway, technical write-ups and proof-of-concept code were published by several Chinese and Vietnamese researchers.
Ivanti exploitation: According to the same Censys, 412 (of more than 26,000) Ivanti Connect Secure VPN appliances are compromised with a backdoor after being recently exploited using two new zero-days (CVE-2023-46805 & CVE-2024-21887).
VMWare vCenter exploitation: Censys researchers say they have seen 3,541 VMWare vCenter servers exposing their web panel on the internet, but only 293 of these were running the DCERPC service. The service contains a vulnerability that has been secretly exploited in the wild by a Chinese APT group since late 2021. VMWare released patches for the vulnerability (CVE-2023-34048) in October of last year.
Infosec industry
Industry moves: F5 has named Samir Sherif as its new Senior VP and CISO. Sherif previously served as CISO at Absolute Software and Imperva. Sherif takes over the CISO role from Gail Coury, who is retiring in March. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Pwn2Own Automotive 2024: The Pwn2Own Automotive 2024 hacking contest is taking place in Tokyo this week. The contest has rewards of up to $1 million. The full schedule is here.
New tool—GraphStrike: Pen-testing company Red Siege has open-sourced a tool named GraphStrike to enable the use of Cobalt Strike Beacons via the Microsoft Graph API for HTTPS C2 communications.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how Stuxnet was an 'inevitability gamechanger,' how much we now know about the operation, and how much the Dutch government should have known at the time.




