Risky Biz News: UK summons Russian ambassador over hacking campaigns, doxes FSB unit behind APT group
In other news: Former security exec sues Twitter; Reuters temporarily removes Appin hacker-for-hire article; 23AndMe activates the lawyers.
You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
The Risky Biz News newsletter and podcast will be going on hiatus between December 8 and January 8 for our yearly winter holiday.
The UK government has summoned Russia's ambassador to explain a years-long hacking campaign conducted by one of the FSB's cyber units.
Officials say that FSB hackers targeted politicians and government organizations and attempted to use hacked data to influence and interfere in UK politics.
The UK government statement connects—for the first time—an APT group known as Star Blizzard to Center 18, a cybersecurity division inside Russia's FSB intelligence agency.
Also known in infosec nomenclature as Callisto, ColdRiver, Seaborgium, TA446, TAG-53, Gossamer Bear, Iron Frontier, and BlueCharlie, the group has been active since at least 2015.
Officials say Star Blizzard hacked Parliament members from multiple UK political parties, a UK think tank that studies disinformation, and journalists, NGOs, universities, and members of the UK civil society that have played crucial roles in maintaining the UK's democracy.
In addition, the UK says the same hackers also stole secret US-UK trade documents and then attempted to use passages from those documents to sway the UK 2019 General Election in a campaign known as Secondary Infektion.
In a joint technical report [PDF] published with its Five Eyes partners, the UK's cybersecurity agency (NCSC) says the group has recently pivoted to target organizations in other NATO countries and Russia's neighbors.
An additional Microsoft report dives into newer TTPs that the group has been using since 2022.
UK and US authorities also imposed sanctions on two members of the Star Blizzard group, one of whom is an FSB officer. The US has also charged the two for attacks on its government systems and is offering a $10 million reward for information leading to their arrest.
- Ruslan Aleksandrovich PERETYATKO, who is a Russian FSB intelligence officer and a member of Star Blizzard, aka the Callisto Group
- Andrey Stanislavovich KORINETS, aka Alexey DOGUZHIEV, who is a member of Star Blizzard, aka the Callisto Group

This marks the UK government's second action this year against FSB hacking operations. In May, together with its Five Eyes partners, the UK exposed and took down the Snake malware botnet, operated by the FSB's Center 16.
It also marks the second time the US has charged members of the FSB Center 18. In 2017, the US charged another FSB Center 18 officer for his role in hacking Yahoo in 2014.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Nissan breach: Japanese carmaker Nissan has confirmed that hackers breached its financial unit at its Oceania division. The company says it is working to restore affected systems and investigating if user data was accessed. The Nissan Oceania outage is currently impacting other car vendors in Australia that were using the company's financial and loaning services, such as Renault, Mitsubishi, Infiniti, and Ram Trucks.
Austal ransomware incident: Australian shipbuilder and defense contractor Austral has fallen victim to a ransomware attack. [Additional coverage in Maritime Executive]
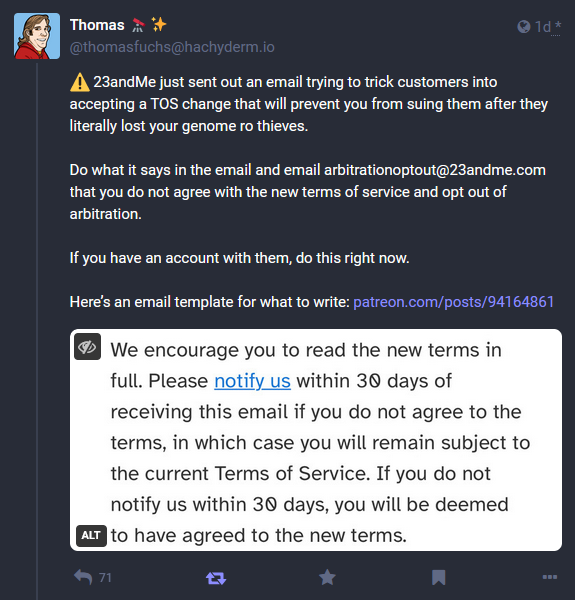
23AndMe breach data: DNA and genetic testing service 23andMe has rolled out an update to its Terms of Service that blocks users from suing the company and forces them into a binding arbitration agreement. The company took this step days after it changed the size of a data breach that took place in October. 23AndMe initially said that hackers stole data on only 1% of the company's users. The company later changed the tally to 6.9 million users, representing almost half of the company's 14 million userbase. [Additional coverage in StackDiary]
General tech and privacy
Push notification surveillance: Law enforcement agencies from the US and abroad have found a new way to track and identify users by requesting mobile push notification metadata from Apple and Google. The technique can reveal a huge amount of information because all mobile push notifications are relayed through Apple and Google servers. According to the Washington Post, the new investigative technique has been used in the US to collect information on January 6 Capital rioters. According to Reuters, the technique has also been used in democracies allied to the United States.
VPN users explode in Russia: The number of VPN users in Russia exploded by 37% this year after authorities increased their internet censorship crackdown. The number of Russian VPN users is estimated to be 11 million users, according to a study of anonymized Internet traffic. The number is 2.5 times higher than in 2021, before Russia's invasion of Ukraine. [Additional coverage in Forbes Russia]
US govt close to dropping Firefox: Because Firefox blocks Google Analytics code, someone at the US government tech department is about to drop support for the Firefox browser from US government websites because they think the browser is not being used by site visitors.
Former security exec sues Twitter: Twitter's former head of information security has sued the company in a New Jersey court for wrongful termination. Alan Rosa claims he was fired after objecting to budget cuts in the aftermath of Elon Musk's takeover. The former exec says he was also asked to shut down software that allowed Twitter to share data with law enforcement. [Additional coverage in Reuters/non-paywall]
Meta rolls out E2EE on Messenger: Meta has started enabling end-to-end encryption (E2EE) conversations for all Facebook Messenger users. The company says the roll-out phase will take a few months to complete, but it will cover all of its one billion Messenger users. Facebook Messenger has supported encrypted conversations since 2016 under a feature named Secret Conversations, but the feature was only optional. Meta says it's been working on default E2EE support since 2019, which now runs on top of its new Labyrinth encrypted storage protocol.
Apple calls for E2EE encryption: Apple Head of Security Engineering and Architecture (SEAR) Ivan Krstić is calling on tech companies to support E2EE encryption as a main defense against data breaches.
YouTube tracking identifier: Something we missed a few months back is that YouTube share links now have a new "SI" tracking identifier appended at the end that you may want to delete when sharing YouTube video links with friends.
Windows 12 release date: According to a report from Taiwanese media citing local laptop and hardware manufacturers Acer and Quanta, Windows 12 is expected to be released in June 2024.
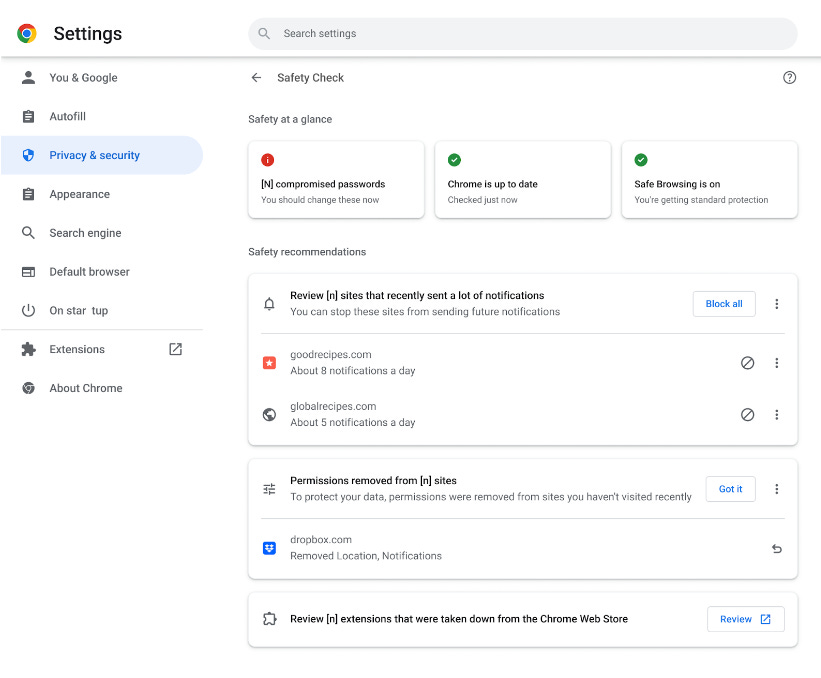
Chrome 120: Google has released version 120 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes include the first stage of deprecating third-party cookies, a password-sharing feature, a revamped look for the new tab page, a new Safety Check feature, a feature to auto-organize tabs, and deprecating support for Android 7. In the EU, Chrome is now also prompting users to choose their default search engine.
Government, politics, and policy
DOD contractor recommendations: The DOD IG has published a document with 24 recommendations for addressing cybersecurity vulnerabilities among DoD contractors.
CISA SbD alert: CISA has published its second Secure by Design alert, with this one urging software developers to transition to memory-safe programming languages.
CyberCommand has to wait for new lead: Republican Sen. Tommy Tuberville has partially ended his hold on US military promotions, but the NSA and CyberCommand still have to wait for a new lead. The US Senate has approved 425 promotions, but Tuberville is still blocking nominations for positions of General four stars and higher. [Additional coverage in CBS]
EU-US cooperation: ENISA and CISA have signed a new cooperation treaty.
Canada's election cyber guidance: Canada's cybersecurity agency has published a series of cybersecurity guides related to its upcoming election cycle. The guides target voters, campaigns, and government officials. The agency warns of online influence operations.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this podcast, Patrick Grey and Tom Uren talk about how threat actors abusing legitimate tools (aka living off the land or LOLbins) is the new normal. Everyone is doing it, from activists to cybercriminals to nation-states. It's a worry because the defender's standard practices really aren't set up to detect and deal with that kind of behavior.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Bitzlate CEO pleads guilty: The CEO of the Bitzlato cryptocurrency exchange has pleaded guilty to money laundering-related charges. Russian national Anatoly Legkodymov was arrested earlier this year together with four of the company's executives. European and US authorities say Bitzlato helped criminal cartels and ransomware gangs launder more than $700 million worth of crypto. Officials say almost half of Bitzlato transactions were linked to criminal activity after the site's leadership failed to implement anti-money laundering controls.
CyberAv3ngers attacks: SecurityScorecard has identified six IP addresses used by Iranian group CyberAv3ngers to scan the internet for unsecured Unitronics PLCs.
New ITAU kit: The IT Army of Ukraine has published a new DDoS toolkit for its members.
DDoS booters: Searchlight Cyber looks at four of the most popular DDoS booters on the market—Nightmare Stresser, Stressthem, Paper Stresser, and Krypton Networks.
Rappler DDoS attacks: An investigation by the Qurium Media Foundation has found that the infrastructure of two proxy providers named FineProxy and RayoByte has been used in a massive DDoS attack targeting Rappler, Indonesia's leading independent news agency. The two proxy providers are operated out of Russia and the US, respectively. Qurium says that when they contacted the two companies, they offered to block outgoing DDoS traffic to Rappler rather than suspend their abusive customers. Researchers are now urging law enforcement authorities to look into the two providers.
"As a way to 'mitigate the problem' both Rayobyte and Fineproxy have asked Qurium to provide a list of our hosted organizations so they can ensure that they will not become victims of DDoS again in the future. Clever isn’t it?, if Qurium’s clients are no longer victims, there will be no more forensics reports revealing their malicious practices!"
"FineProxy even went one step further to silence Qurium. In an email exchange with Ilya Trusov CEO of FineProxy in late October 2023, we were offered to reveal the name of the customer that was responsible for the DDOS attacks. The condition to receive the customer’s information was to remove all articles about their proxy service from Qurium’s website."
"The investigation further reveals the actors behind the Russian proxy provider 'Fineproxy' and how they have managed to obtain hundreds of thousands of IP addresses from regional registrars like RIPE and ARIN and faked geo-location data to make their proxy service more valuable."
DoS classification scheme: ENISA has published a report on the DoS threat landscape, including a DoS classification scheme.
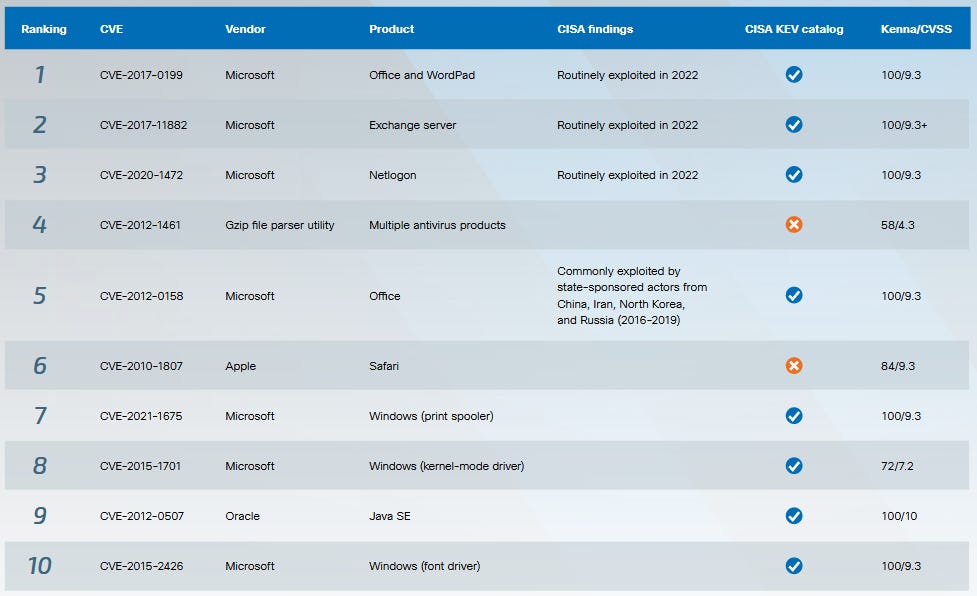
Year in Review: Cisco Talos has published its year-in-review report for 2023. As the company puts it in the introduction, "ransomware, commodity loaders and APTs dominated the threat landscape in 2023." The report has three Microsoft bugs as the top exploited CVEs of the year, per Cisco telemetry.
Malware technical reports
Krasue: Security firm Group-IB has discovered a new Linux malware strain that has been secretly infecting systems since at least 2021. Named Krasue, the malware is primarily used to serve as initial access for other cybercrime operations. Group-IB says the botnet appears to have been created by the author of the infamous XorDDoS malware or at least by someone who had access to its original source code. In addition, Krasue stands out for its use of the RTSP protocol for command-and-control channels and the use of three open-source projects (Diamorphine, Suterusu, and Rooty) to create a powerful Linux rootkit. Most Krasue infections seen so far have been spotted in Thailand.
Csharp-streamer RAT: G DATA's Michael Zimmer looks at the new Csharp-streamer RAT.
Qilin ransomware: ShadowStackRE researchers have published an analysis of the ESXi encrypter used by the Qilin ransomware gang.
Sponsor Section
In this product demo, Senior Sales Engineer Ali Cheikh demonstrates the runZero platform to Risky Business host Patrick Gray.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Lazarus Telegram campaign: North Korean hacking group Lazarus is conducting a large-scale Telegram phishing operation targeting the members of the cryptocurrency industry. The campaign started in early 2022 and is still ongoing, according to blockchain security firm SlowMist. Lazarus operators pose as cryptocurrency investors and typically target DeFi projects. The goal of most campaigns is to lure victims on phishing sites, collect their credentials, and then hack their projects.
UAC-0050: CERT-Ukraine has published an advisory warning of phishing campaigns conducted by Russian group UAC-0050 targeting Ukraine and Poland with the Remcos RAT and the MeduzaStealer.
APT28: PAN's Unit42 looks at APT28 campaigns targeting an Outlook vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-23397. PAN says they've seen the group target 30 organizations across 14 countries over the past 20 months using this vulnerability.
Russian info-op uses celebrities: A Russian threat actor named Doppelgänger has used fake quotes attributed to various celebrities to push anti-Ukraine propaganda. The campaign took place in November and attributed quotes to celebrities like Taylor Swift, Kim Kardashian, Beyonce, Shakira, Justin Bieber, Cristiano Ronaldo, and others. The group also used AI-generated content in a separate campaign, but that one received lesser user engagement. The Doppelgänger group has been previously linked to a unit inside Russia's GRU military intelligence service. [Additional coverage in Wired/non-paywall/Microsoft report]
Teal Kurma's SnappyTCP: PwC's security team has published a report going over SnappyTCP, a Linux reverse shell used in attacks by the Teal Kurma (Sea Turtle) APT. Previous reporting linked the group to Türkiye.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Mozilla VPN security audit: Mozilla has published its most recent security audit of its VPN product.
WordPress RCE: The WordPress team has released a security update to patch a rare remote code execution vulnerability in its CMS. Even if WordPress accounts for 43% of all internet websites, the vulnerability does not have a broad impact. It impacts only two very recent WordPress versions and is not exploitable in default configurations. Websites have to either use certain plugins or be in multisite mode.
Sierra:21 vulnerabilities: Forescout researchers have found 21 vulnerabilities in popular solutions used inside industrial and critical networks. The bugs impact Sierra Wireless Airlink cellular routers and TinyXML and OpenNDS, two open-source components.
Chromecast jailbreak: DirectDefense researchers have developed a three-exploit jailbreak for Chromecast devices. The jailbreak is a secure boot bypass that lets users run their own code on the device.
Syrus4 vulnerability: A team of security researchers says Digital Communications Technologies has not addressed a bug impacting its Syrus4 IoT gateway, leaving vehicle fleets open to attacks that could shut them down. The vendor has been apparently ghosting the researchers. [Additional coverage in CyberScoop]
Zyxel NAS vulnerabilities: BugProve has published details on two vulnerabilities in Zyxel NAS devices.
SonicWall vulnerability: Praetorian researchers have identified an authentication bypass and RCE in SonicWall WXA appliances. Praetorian says the vulnerabilities have a low impact in terms of real-world risk.
Atlassian security updates: Atlassian has released four security updates to patch RCE vulnerabilities across several products. They're all pretty bad, so patch ASAP.
Bluetooth vulnerability: Skysafe security researcher Marc Newlin has found a critical Bluetooth vulnerability (CVE-2023-45866) that can allow threat actors to bypass authentication, hijack Bluetooth connections, and perform keystroke injections. Newlin says attackers can instruct operating systems to install malicious apps or run malicious commands. The attack impacts Android, Linux, iOS, and macOS—and works even if Lockdown Mode is enabled on Apple devices. Only the Android team has patched the vulnerability so far. [Update on Jan 14, 2024: This has now been fixed on Apple devices.]
AutoSpill attack: Three academics from an Indian university have discovered a vulnerability in the Android autofill feature that can be used to spill secrets from password managers. Named AutoSpill, the attack is identical to similar techniques previously seen on desktops, exploiting browser auto-fill operations. Researchers say they successfully tested AutoSpill on password managers from 1Password, LastPass, Keeper, and Enpass. Researchers are also working on replicating the attack on iOS devices. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
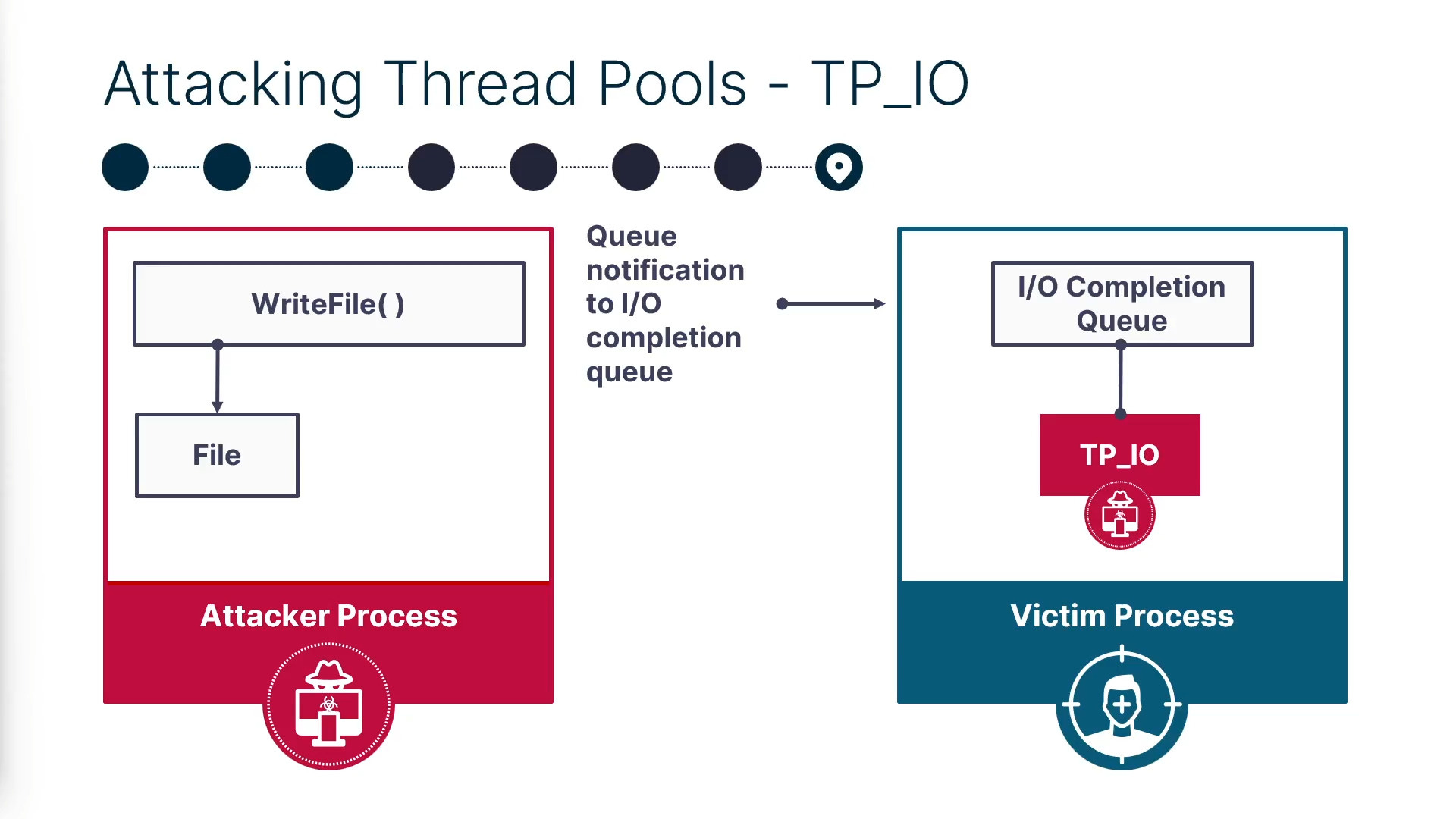
Pool Party technique: SafeBreach researchers have identified eight new process injection techniques they are collectively referring to as Pool Party that can be used to bypass EDR solutions.
Infosec industry
Reuters takes down Appin article: Reuters has taken down an article about an Indian company that has provided hacking-for-hire services for more than a decade. The news agency says it took down the article to comply with a preliminary court order issued in India after Appin sued Reuters last month. Reuters says it stands by its reporting and plans to appeal the court order.
New Microsoft CISO: Microsoft has appointed Igor Tsyganskiy as its new Chief Information Security Officer, Microsoft Executive Vice President for Security Charlie Bell announced on LinkedIn. Tsyganskiy replaces Bret Arsenault, who previously served as Microsoft CISO for 14 years. Arsenault will move to a new role of Chief Security Advisor. Microsoft's executive shuffle comes months after Chinese state hackers compromised the company's internal network. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about recent hints that the Ukrainian government has figured out how to make use of the IT Army.




