Risky Biz News: Tor Project removes 1k relays linked to cryptocurrency scheme
In other news: Ukraine fires two cybersecurity officials; NCSC files IoC standard with IETF; and CISA and ACSC launch cybersecurity pilot programs.
This newsletter is brought to you by Yubico. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Spotify:
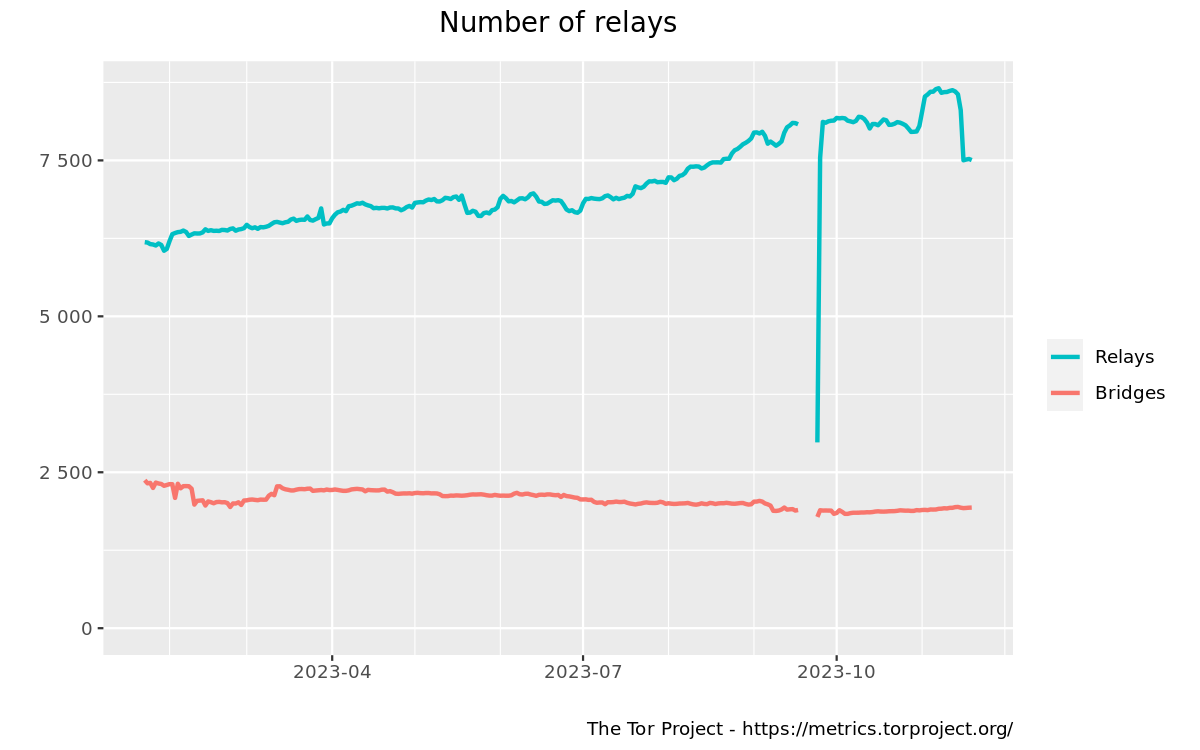
The Tor Project has removed an estimated 1,000 relay servers from its network, citing their involvement with a for-profit cryptocurrency scheme.
The scheme allegedly promised cryptocurrency tokens for users who set up and ran Tor relays.
In a blog post on Monday, Tor admins said they removed participating servers to protect the integrity and reputation of their project. The removal was subject to a community vote that passed last week.
While the number of removed servers was not disclosed, metrics for the Tor network show a drop of almost 1,000 active relays over the past week.
The Tor Project expressed its disapproval of the scheme and warned relay operators of the danger such schemes pose to both node operators and their users.
The project said it had worked on its own in-house monetization schemes in the past to help support its operations and operators, but none have offered an adequate level of protection so far.
The Tor Project did not provide details about the cryptocurrency scheme, but it was most likely referring to the ATOR cryptocurrency project that launched at the end of September. The ATOR token lost 58% of its value after the Tor Project's announcement.
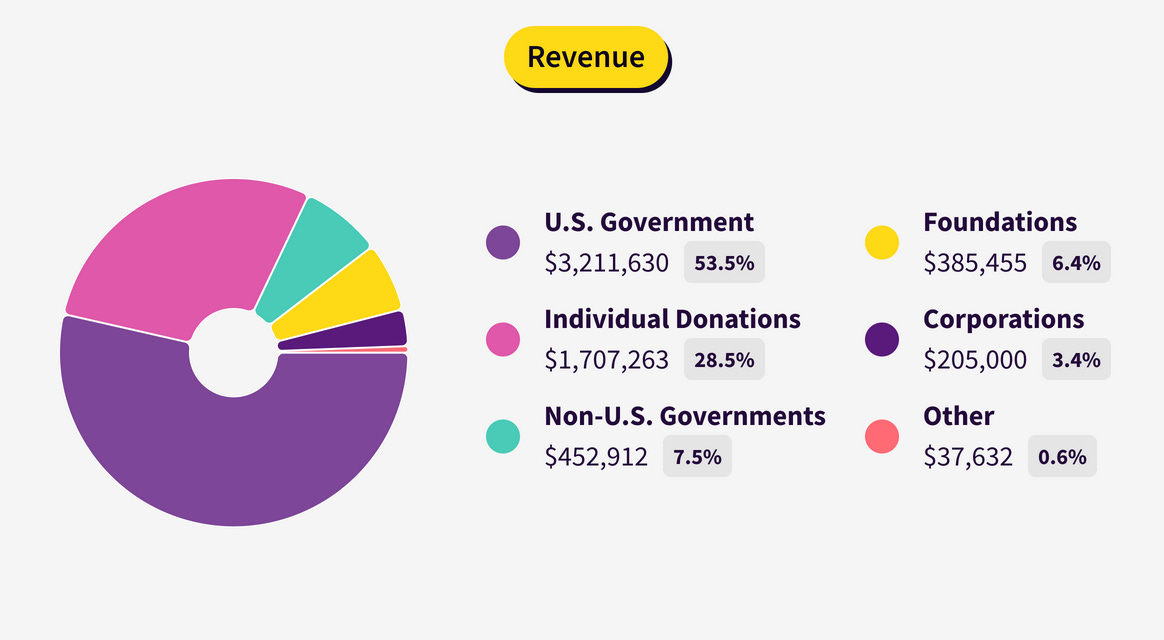
Over the years, the Tor Project has been on a quest to diversify its revenue streams, which have been historically tied to the US Department of Defense.
The project's main financial success has been to reduce the percentage of US government funding from 85% in 2015 to around 50%, a figure Tor has been hanging around since 2018, and going as low as 38% in 2021.
This year, in a financial report released last week, the Tor Project reported that 53% of its funding in fiscal year 2021-2022 came from the US government, a figure larger than usual after a significant fall in user donations last year.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
NTT leak: A former employee of Japanese telco NTT stole and leaked the personal information of 9 million of the company's customers. The employee took the data from an NTT call center server and sold it to local data brokers. The theft took place in April 2022 and remained undetected until July this year, when Japanese police discovered the data as part of its investigations. NTT confirmed the breach in October and blamed it on one of its telemarketing operators. [Additional coverage in The Asahi Shimbun]
AutoZone in the MOVEit zone: Auto parts retail chain AutoZone says the data of almost 185,000 customers was stolen in a cyberattack at the end of May. The data was stolen by the Clop cybercrime group as part of its attacks that targeted MOVEit file-sharing servers. More than 2,600 companies across the world have been impacted by the MOVEit hacks, and the data of 77 million users was stolen in the intrusions.
Call for no more ransom payments: The CEOs of five Canadian hospitals that have been hacked by ransomware gangs are calling for the government to pass a formal ban on ransom payments. The hospital execs are urging the government to follow through on their promise made during the recent International Counter Ransomware summit. Canada and 49 other countries pledged to stop paying ransoms to hackers as a way to cut off their funding. The five CEOs manage five hospitals in the Ontario region that got hit by ransomware at the end of October and decided not to pay to avoid "feeding the monster." [Addition coverage in iHeartRadio] [h/t Brett Callow]
Russian pilot hack: Pro-Ukrainian hacktivist group Cyber Resistance has hacked and leaked data from the email account of a Russian pilot employed by Aviacon Zitotrans, a sanctioned Russian airline. The leaked emails allegedly show how Russian airlines are secretly moving weapons, ammunition, and sanctioned goods from Iran, South Africa, and Mali to Russia. In some cases, the transports are disguised as "humanitarian aid," the group says. The Cyber Resistance group has a history of hacking and exposing Russian operations. They previously doxxed Russian pilots who bombed civilian infrastructure in Ukraine, doxxed the leader of the APT28 cyber-espionage group, and exposed Russia's efforts to recruit Cuban mercenaries. [Additional coverage in InformNapalm]
General tech and privacy
Nothing Chats fiasco: Tech company Nothing has pulled its Nothing Chats instant messaging app from the Google Play Store a day after its launch. Advertised as an E2EE messenger that brings support for iMessage on Android devices, the app was pulled after security researchers discovered egregious privacy issues. Researchers found the app was logging into users' accounts on their behalf and redirecting and logging all messages through its own servers. They also found the app was using HTTP for many of its most sensitive requests. [Additional coverage in The Verge]
Twitter FTC investigation: The FTC is investigating Twitter for running unlabeled ads on its platform. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
YouTube intentionally slows down traffic: Google is intentionally slowing down YouTube page loads for browser users who use an ad-blocker. The delay is not present for Chrome users with an ad-blocker but only for other browsers that use an ad-blocker. Totally not monopolistic behavior. Nope. You're seeing things! [Additional coverage in Android Authority]
FreeBSD 14: Version 14.0 of the FreeBSD operating system is out.
Government, politics, and policy
Ukraine sacks cybersecurity officials: The Ukrainian government has fired two cybersecurity officials amid an investigation into alleged embezzlement. Yurii Shchyhol and Victor Zhora were accused of participating in a scheme to contract software at inflated prices. The two served as the head and deputy of the State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection of Ukraine (SSSCIP). Four other suspects are also under investigation. The group is accused of embezzling $1.7 million from government contracts. [Additional coverage in Cyberscoop]
Europol OSINT task force: Europol has set up a special OSINT task force that will support investigations into war crimes committed in the Russian-Ukrainian war.
Poland to investigate Pegasus cases: The newly elected Polish government will establish a special commission next week to investigate the former government's use of the Pegasus spyware. The commission will look at how the former ruling party PiS used Pegasus to spy on opposition members, journalists, and prosecutors. Reuters reported at the end of October that the government was looking at establishing the commission. [Additional coverage in PAP] [h/t Eva Infeld]
Australia's Cyber Health Check Program: The Australian government is setting up a voluntary cyber health check program for small and medium businesses. The program will allow SMBs to take a free security assessment and access training materials to upskill their employees. SMBs with a higher risk of being targeted by hackers will be able to request a more sophisticated, third-party security assessment. The Australian government is putting $7.2 million into the new program. [Additional coverage in The Canberra Times]
Hemisphere program: US Senator Ron Wyden (D-Ore) has asked the Justice Department to release information about its secret Hemisphere phone surveillance program. The program allows US law enforcement agencies to request searches of US phone records without warrants. The searches are run against an AT&T database of phone records going as far back as 1987. AT&T is allegedly getting paid to provide access to the database and run the Hemisphere platform. The program is not classified, but the DOJ has marked it as "Law Enforcement Sensitive." Sen. Wyden is now asking the DOJ to remove the classification and release Hemisphere documents to the public. [Additional coverage in Wired]
DOD info-op strategy: The US Department of Defence has published its strategy for information operations. On the same note, the US Air Force cyber command also announced plans to devote more time to training airmen in information warfare.
US-ID cyber agreement: The US and Indonesia have signed a defense agreement that includes a significant focus on cyber and space capabilities. [Additional coverage in DefenseOne]
CISA pilot program: CISA has launched a pilot program that will provide what the agency describes as "cutting-edge cybersecurity shared services" to selected US critical sector organizations. The pilot program launched in October with its first phase, with participants from the healthcare, water, and K-12 education sectors. CISA Executive Assistant Director for Cybersecurity Eric Goldstein says the agency plans to enroll up to 100 entities by the end of the year. [Additional coverage in The Record]
GridEx VII: Over 250 organizations take part in GridEx VII, a biennial exercise focusing on the security of the electrical grid in the United States and Canada. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
ICO cookie crackdown: UK privacy watchdog ICO has warned organizations about an impending crackdown if they don't simplify their cookie banners. The agency had previously requested that websites provide an easy way to reject all advertising cookies. The ICO has given the largest visited sites in the UK 30 days to comply with its new rules or face punishment.
IoC RFC: The UK's cybersecurity agency—the NCSC—has filed a formal document with the Internet Engineering Task Force looking to standardize IoC formats. Also known as Indicators of Compromise, IoCs are used by cybersecurity tools and professionals to detect malicious activity and can take the form of domain names, IP addresses, or hashes. The NCSC says the new document introduces a common format for sharing and using IoCs to improve interoperability between different vendors. The agency says it's been working on the IoC standard for the past three years. The IETF has assigned RFC9424 for the proposed standard, which is now entering a public comments period before a voting process.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to Derek Hanson, Yubico VP of Solutions Architecture and Alliances, about the state of authentication and what Passkeys are all about.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Cryptocurrency seizure: The US Department of Justice has seized almost $9 million worth of Tether cryptocurrency from a cybercriminal organization. The DOJ says the group obtained the money after exploiting over 70 victims through romance scams and cryptocurrency confidence scams. Officials did not name or charge any of the group's members.
DraftKings hacker pleads guilty: A 19-year-old from Wisconsin has pleaded guilty to hacking-related charges in connection to a credential-stuffing attack against sports betting website DraftKings. Joseph Garrison admitted to successfully breaching more than 60,000 DraftKings accounts in an attack in November 2022. Officials say Garrison sold access to some accounts online and also stole $600,000 from around 1,600 of the site's users. Garrison is scheduled for sentencing in January 2024.
LockBit has new ransom negotiation rules: The LockBit ransomware operation has announced new rules for its affiliates during the ransom negotiation process. The new rules entered into effect at the start of October. LockBit admins imposed the rules after they saw affiliates requesting small ransoms from victims and giving out generous discounts. According to researchers at Analyst1, affiliates will now be forced to use a tiered percentage-based system for ransom fees, depending on the victim's annual revenue (see below). Affiliates are now also banned from offering discounts greater than 50% of the initial ransom demand.
- companies with revenue up to $100 million pay from 3% to 10%
- companies with revenue up to $1 billion pay from 0.5% to 5%
- companies with revenue of more than $1 billion pay from 0.1% to 3%
vx-underground ransomware: The Phobos RaaS has created a version of their ransomware that poses as vx-underground, a well-known threat intelligence sharing group.
Play goes RaaS: Security firm Adlumin says it found evidence that the Play ransomware gang is now advertising access to its malware via a Ransomware-as-a-Service model.
INC ransomware: Cybereason has published a threat alert on INC, a new ransomware operation that surfaced in August this year.
"All known victims are exclusively from Western countries with the majority of them from the United States and Europe (a single victim was from Singapore)."
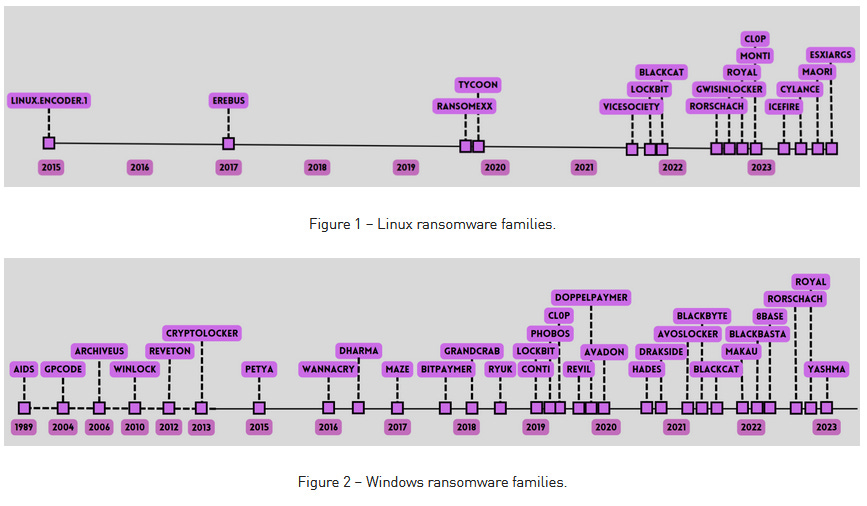
Linux-v-Windows ransomware: Check Point has published a comparative look at the Linux and Windows ransomware scenes, and how ransomware gangs/strains operate on each platform.
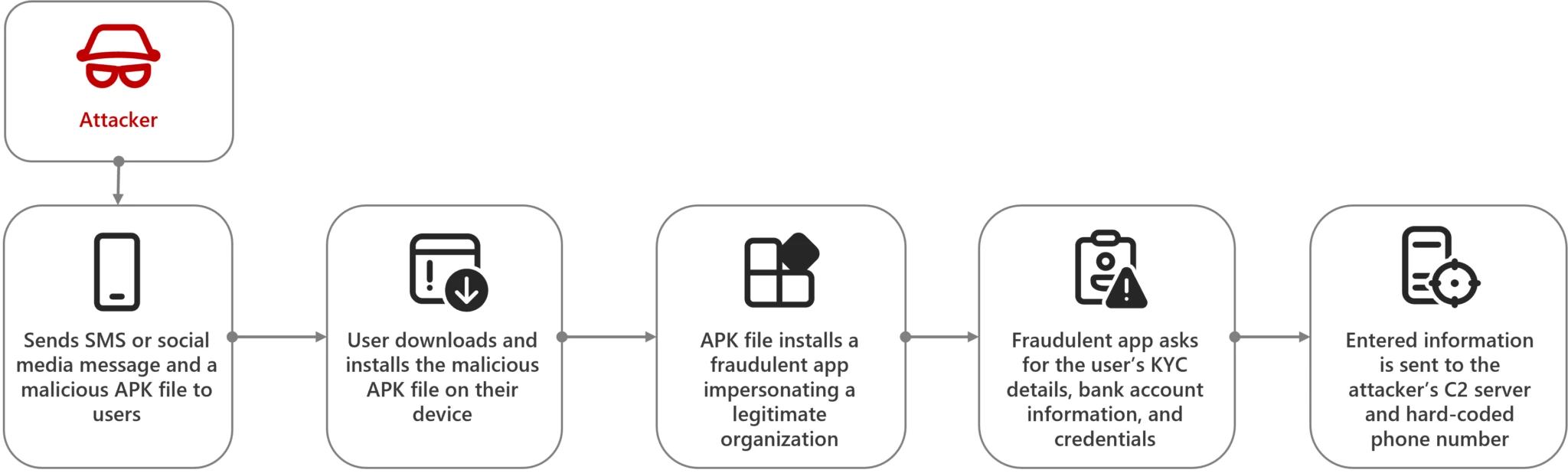
Android bankers in India: Microsoft's threat intel team has published a technical report about the tactics of various cybercrime gangs that use socially-engineered SMS, Telegram, or WhatsApp messages to get victims to install malware-laced Android apps on their devices. The final payload is typically one of the new-age hybrid info-stealing RAT strains that have been growing in popularity in recent years.
Kubernetes leaks: Aqua Security says it found Kubernetes secrets of hundreds of organizations and open-source projects exposed on the internet.
"Among the companies were SAP's Artifacts management system with over 95 million, two top blockchain companies, and various other Fortune-500 companies. These encoded Kubernetes configuration secrets were uploaded to public repositories."
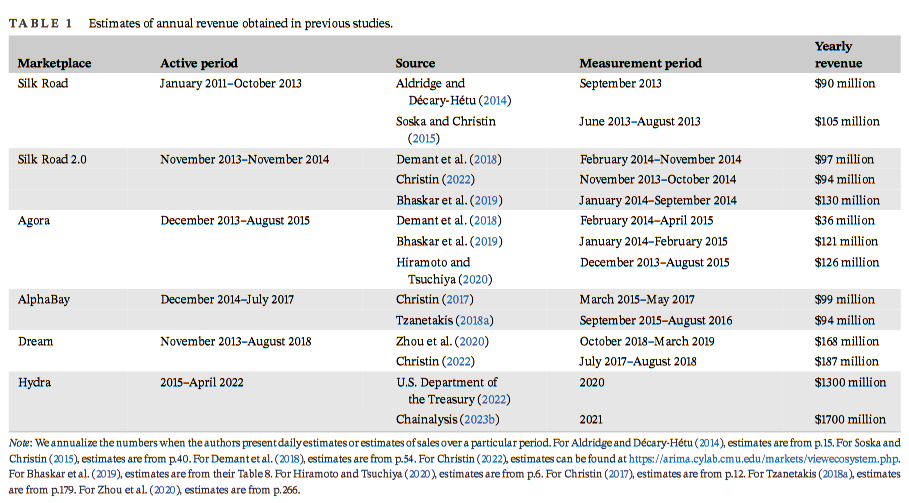
Hydra dark web market analysis: A team of US academics has published a detailed analysis of Hydra, the largest dark web marketplace seen so far. The research comes with this interesting table showing annual revenue estimates for the largest dark web markets of the last decade.
Malware technical reports
NetSupport RAT: Threat actors have repurposed the NetSupport Manager legitimate app into a fully-fledged remote access trojan, currently tracked as NetSupport RAT.
Agent Tesla: A new variant of the Agent Tesla infostealer has been spotted in the wild.
SolarMarker: eSentire researchers have published an analysis of SolarMarker, a .NET infostealer also known as Jupyter.
LummaC2 Stealer: Security firm Outpost24 has found a version of the LummaC2 Stealer that uses an extremely clever way of detecting sandbox environments. The malware records mouse cursor positions and then uses trigonometry functions to detect if the cursor movement is the result of natural human interaction or if the mouse was moved using pre-determined algorithms, typically used by sandboxed environments.
Kinsing: Trend Micro has seen the Kinsing crypto-mining botnet exploit Apache ActiveMQ servers using the recently patched CVE-2023-46604 vulnerability to install their crypto-mining bot.
Crypto-miner: AhnLab looks at a crypto-mining campaign targeting Windows systems running Apache web servers.XWorm: ANY.RUN researchers have published a deep dive into C2 protocol of the XWorm malware.
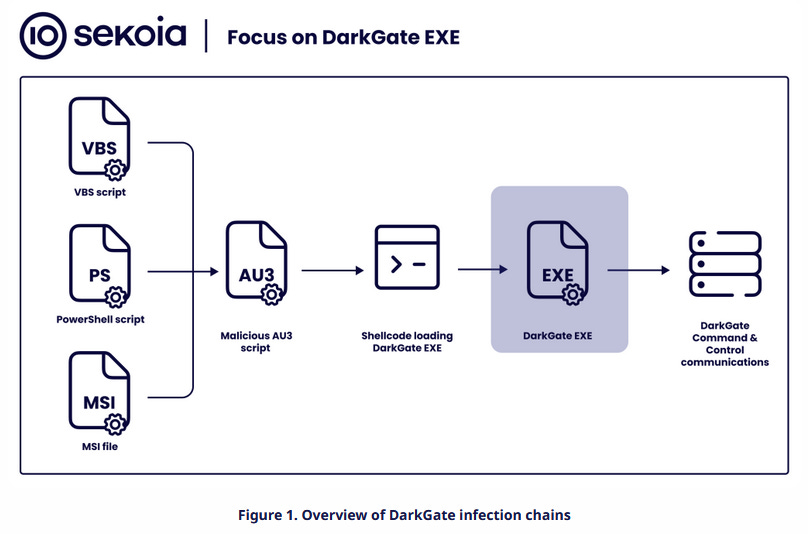
DarkGate: Sekoia researchers have published an analysis of the DarkGate loader, advertised as a go-to replacement for the now defunct QakBot malware—disrupted by the FBI earlier this year.
"After examining the various DarkGate stages (the AutoIT script, its shellcode and also its core), it becomes evident that DarkGate represents a significant threat. Consequently, it is imperative to maintain continuous tracking and monitoring of DarkGate in both the short and long term."
Sponsor Section
Brought to you by Yubico, the inventor of the YubiKey, a security key that provides the gold standard for multi-factor authentication (MFA) and stops account takeovers in their tracks. Find them at yubico.com
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Andariel: Security researchers at AhnLab say the Andariel North Korean hacking group is targeting South Korean organizations through a local asset management program. Hackers are using vulnerabilities in the software to deploy malware on victims' internal networks. AhnLab did not name the vendor. The same group was also seen targeting MSSQL database servers.
Konni: Fortinet's security team looks at a recent Konni campaign targeting Russian entities with malicious Word documents.
North Korean campaigns: PAN's Unit42 has found two job-themed social engineering campaigns that bear the hallmarks of your typical DPRK operation. Unit42 named the campaigns Contagious Interview and Wagemole. Per Unit42, "activity from both campaigns remains an ongoing active threat."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
CitrixBleed reminder: Citrix has published a blog post to remind owners of NetScaler and ADC appliances to not only update its software but also wipe past user sessions. This step is necessary because threat actors who exploit the CitrixBleed vulnerability will steal authentication tokens that they can use later after the device has been patched. A day after the company's blog post, CISA and the FBI also released a security advisory on how the LockBit ransomware gang is exploiting the CitrixBleed vulnerability. The advisory contained IOCs shared by Boeing, one of the LockBit gang's recent victims.
"This CSA provides TTPs and IOCs obtained from FBI, ACSC, and voluntarily shared by Boeing. Boeing observed LockBit 3.0 affiliates exploiting CVE-2023-4966, to obtain initial access to Boeing Distribution Inc., its parts and distribution business that maintains a separate environment. Other trusted third parties have observed similar activity impacting their organization."
Kubernetes security updates: The Kubernetes project has released a security update to fix a privilege escalation on Container-Optimized OS and Ubuntu nodes.
WithSecure Elements vulnerability: Baldur researchers have discovered a DoS vulnerability in the WithSecure Elements cloud-based security solution.
MSFT bug bounty program: Microsoft has awarded more than $63 million in rewards to the security researchers who participated in its bug bounty program over the past decade. Launched in 2013, the Microsoft bug bounty program has turned ten years old this year. Microsoft says the program has grown from less than 100 bug reports in its first year to include 22 different bug bounty programs for various Microsoft platforms, with thousands of submissions each year. The latest of these programs is the Microsoft Defender Bounty Program, which the company launched this week. The program will provide rewards of up to $20,000 for vulnerabilities in the Microsoft Defender line of products.

Infosec industry
SAINTCON 2023 videos: Talks from the SAINTCON 2023 security conference, which took place in October, are available on YouTube.
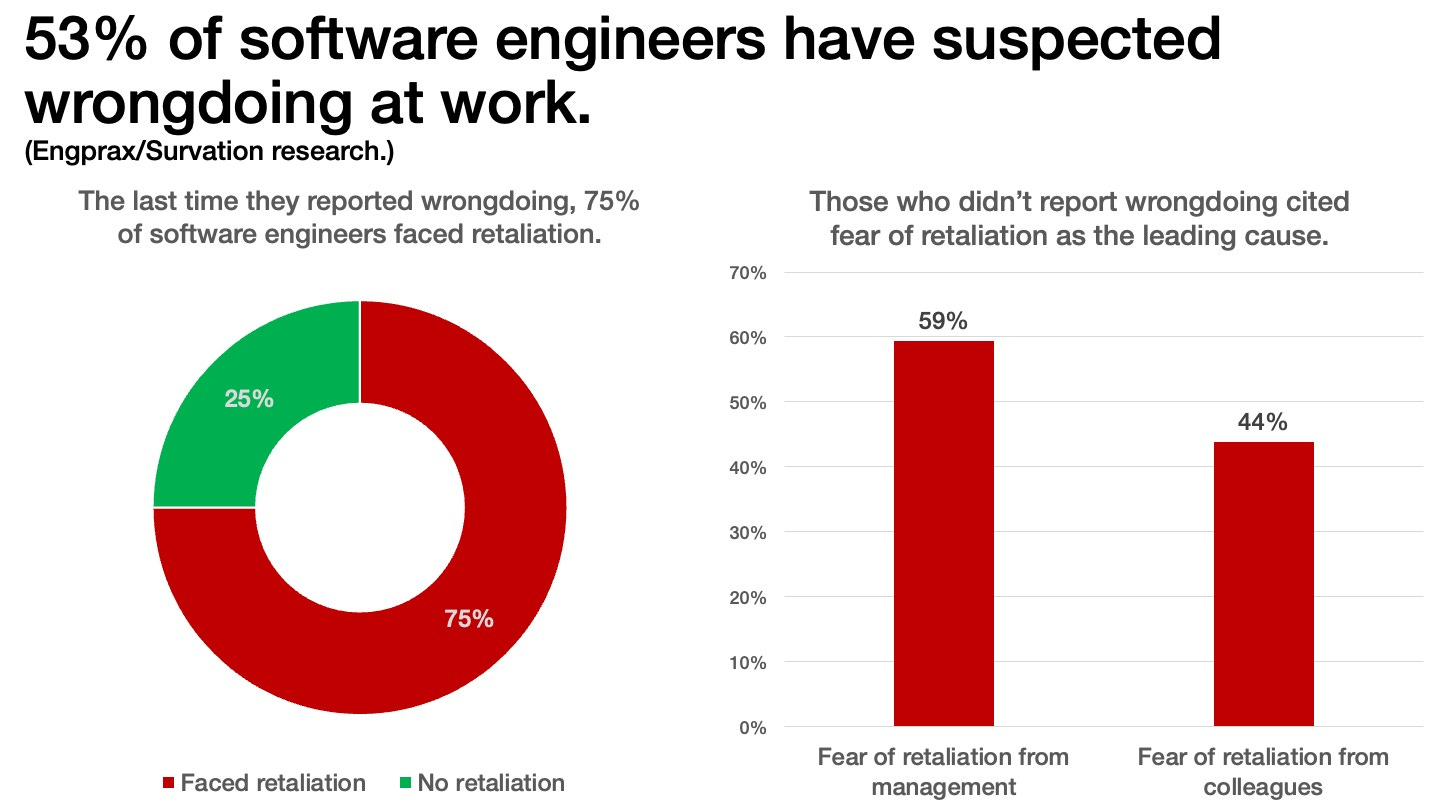
Retaliation at work: A recent Engprax survey of almost 2,000 software engineers found that 53% of respondents witnessed or suspected wrongdoing in their workplace. Of those who spoke up, 75% reported facing retaliation after they reported wrongdoing to their employers. Those who didn't report anything cited fear of retaliation as the primary reason.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how being more open about cybersecurity threats is great for marketing and has also forced cybersecurity companies to pick sides and make value judgements.




