Risky Bulletin: Threat actor impersonates FSB APT for months to target Russian orgs
In other news: HPE investigates breach; Trump guts the CSRB; malicious Chrome extensions found on the Web Store.

This newsletter is brought to you by Resourcely, the company that can help you manage Terraform securely. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
A cyber-espionage group has mimicked the tactics of an FSB-linked APT to target Russian organizations for months.
Named GamaCopy (or Core Werewolf), the group emulated the tactics of Gamaredon (or Armageddon), a cyber-espionage group operated by the Russian FSB intelligence agency from the occupied region of Crimea.
The group's false flag attacks have been taking place since June of last year. The campaign has tricked several security vendors who misattributed attacks to Gamaredon, according to a report from Chinese security firm Knownsec 404.
The spear-phishing campaigns have used military-related lures to target individuals in Russia's defense and critical infrastructure sectors and trick them into extracting malicious 7zip archive files.
"Obviously, this is a successful false flag operation by the organization that has deceived some vendors who have not conducted in-depth analysis."
Knownsec 404 has not made a formal attribution for GamaCopy, and neither have the Russian security vendors who previously covered past campaigns, such as BI.ZONE, FACCT, and Kaspersky.
While Ukraine would seem an easy source of origin for the attacks, both China and North Korea have been just as active in spying on Russian defense orgs over the past two years as the Ukrainians, so it's not as clear as it may look.
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Rostelecom attack: The Russian government says that a threat actor has hacked one of Rostelecom's contractors but that the incident did not impact the activity of the government's Gosuslugi e-portal. A hacking group named Silent Crow has breached and leaked data from several of Rostelecom's online portals. The Russian company and the Russian government have confirmed the hack and blamed the breach on one of Rostelecom's contractors. Rostelecom manages Russia's e-government portal known as the Gosuslugi. Rostelecom says the leaked data is not sensitive in nature and did not impact Gosuslugi in any way. This is Silent Crow's second major hack this year after it also breached Russia's State Registration, Cadastre, and Cartography agency, the Rosreestr.
HPE investigates breach: American tech giant HPE is investigating a possible security breach after a threat actor started advertising a batch of data allegedly stolen from its servers. The hacker claims to have stolen old user data and source code for the Zerto & iLO products. The threat actor is named IntelBroker, the same individual who breached Cisco's DevHub portal at the end of last year. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Carrefour leak: On the same note, a threat actor is also claiming to have breached French retail giant Carrefour. This one's unconfirmed at the time of writing.
General tech and privacy
Douyin takes down restrictions: Douyin, the name of the Chinese version of TikTok, has removed restrictions on the use of foreign phone numbers to register accounts. This means that international users can now apply and browse the Chinese version of TikTok. [Additional coverage in Tech In Asia]
CoDCW anti-cheat: A reverse engineer known as ssno has reverse-engineered the anti-cheat system used by the Call of Duty: Cold War game.
RPKI ROA coverage: According to RIPE Labs, more than half of both the IPv4 and IPv6 routes in the global routing system are covered by RPKI ROAs (~ 54%).
Government, politics, and policy
Trump revokes Biden's AI executive order: Hours after being sworn in, US President Donald Trump has revoked a 2023 executive order signed by his predecessor that required AI companies to limit the risks that artificial intelligence poses to consumers, workers, and national security. [Additional coverage in Reuters and Lawfare Media]
"Large AI labs, such as Google and OpenAI, faced reporting requirements under the EO. The Biden administration intended for the US AI Safety Institute—also a product of the EO—to ensure that leading AI models did not pose excessive societal risks. [...] In line with the GOP platform, which called for accelerating AI research and deployment, any forthcoming AI EO by the Trump Administration will likely omit safeguards related to privacy, misinformation, and bias."
Trump ousts CSRB members: The Trump administration has removed all non-government members from all DHS committees, including the Cyber Safety Review Board. Six CSRB members representing private sector entities were removed, such as Heather Adkins, Dmitri Alperovitch, and Rob Joyce. The CSRB was founded in February 2022 and had a 14-member panel. [Additional coverage in Politico] [Post-publication update: We removed Chris Krebs of SentinelOne from the list. The company told us Krebs resigned on Saturday, two days before Trump was sworn in.]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Travis McPeak, the CEO and founder of Resourcely, explains that companies are now realising they have a ton of cloud-related technical debt because of the success of cloud posture management products. Travis talks about different approaches he has seen to tackle rampant cloud misconfigurations.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Fraudster pleads guilty: A Washington man has pleaded guilty to his role in running multiple smishing campaigns that resulted in losses of almost $600,000 to victims.
DrugHub leaks real IP addresses: The DrugHub has leaked the real-world IP address on which it hosts its dark web drugs marketplace. The IP address is 186.2.171.6, owned by UAE ISP IQWeb FZ-LLC.
Fake Fortinet leak installs malware: Last week, a threat actor leaked the configuration files and login credentials of over 15,000 Fortinet firewalls. Now, a threat actor is using the said leak to distribute a malware-laced ZIP file via GitHub.
Malicious Chrome extensions: Security researcher Wladimir Palant has discovered 35 Chrome extensions that circumvent a Google ban and retrieve and execute code from remote servers. The extensions pose as VPN and ad-block-related tools but spy on users and engage in affiliate link fraud. All the extensions are still available through the official Chrome Web Store.
"As noted last week I consider it highly problematic that Google for a long time allowed extensions to run code they downloaded from some web server, an approach that Mozilla prohibited long before Google even introduced extensions to their browser."
Zendesk abuse: CloudSEK has spotted a threat actor abusing Zendesk SaaS infrastructure to mimic popular brands for phishing and online fraud operations.
Spam bomb campaigns: Threat actors are adopting spam bombs to overwhelm workers at large corporations and then contact the target posing as their IT help desk. Attackers usually contact workers via Microsoft Teams by exploiting a misconfiguration in the Teams platform that allows remote parties to call and text individuals inside private workspaces. The technique was first used last year by a Black Basta ransomware affiliate [Rapid7, Red Canary, Microsoft] and has now spread to other groups.
Malware technical reports
Infostealer hunting guide: Israel's National Cyber Directorate has published a guide [PDF] for hunting infostealer malware.
ApateWeb: Validin has published new IOCs on ApateWeb, a botnet of hacked websites that redirects users to PUP and scareware.
Qbot: Walmart's security team is raising the alarm that the Qbot (Qakbot, Pinkslipbot) botnet is slowly rebuilding its infrastructure and mounting new operations following a law enforcement takedown in May 2024.
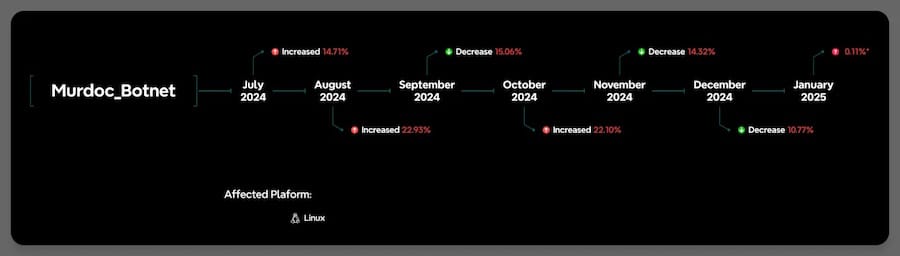
Murdoc botnet: Qualys researchers have discovered a new IoT botnet used to carry out large-scale DDoS attacks. Named Murdoc, the botnet began operating in July of last year. Qualys says the botnet was assembled by exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities in AVTECH cameras and Huawei routers. Based on open-source intelligence, the botnet is currently running on around 1,300 devices.
Sponsor section
Resourcely is releasing Campaigns, a tool for identifying and remediating vulnerabilities in your existing infrastructure. Want to burn down your CSPM findings? Try out Campaigns today!

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Lazarus' InvisibleFerret: ANY.RUN has published a report on InvisibleFerret, a Python-based backdoor distributed as an npm package. The malware was linked to the Lazarus Group last year by Hauri, PAN, and Group-IB.
Operation 99: SecurityScorecard has spotted a new "fake interview" campaign linked to North Korean hackers. This one targeted freelance Web3 and cryptocurrency developers.
Donot Android malware: Security firm CyFirma has published a report on a piece of Android malware it found in the Tanzeem Android app. The company says the malware appears to be the work of the Donot APT group.
FakeTicketer: A new cyber-espionage group named FakeTicketer has targeted Russian government officials in a clever campaign that used fake tickets for sporting events. The campaign has been going on since June of last year and used tickets for Russian football matches and rowing competitions to trick victims into infecting themselves with malware. The final payload was a new malware family named Zagrebator, consisting of a loader, RAT, and infostealer.
OceanLotus comeback: Chinese security firm QiAnXin reports seeing new attacks from Vietnamese APT group OceanLotus after a period of inactivity. The new attacks targeted China's military, energy, and aerospace sectors.
More on the US-hacks-China report: Back in December, the Chinese CERT accused the US government of hacking two Chinese organizations. CERTCN has now published a tad more details and IOCs, including some of the attacking IPs—if you can call entire /16 subnets that. The organization claims the attacks took place during a 10:00 to 20:00 time window, from Monday to Friday on an Eastern US timezone. They also claim no attacks took place during US holidays.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
7zip patches: The 7zip team has patched a bug that allowed threat actors to bypass the Mark-of-the-Web protection mechanism and drop "safe-looking" files from malicious archives.
Elastic security updates: Elastic has released security updates for the Elasticsearch database, the Defend security system, and the Kibana UI.
Intel TDX vulnerabilities: A team of academics from the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur has discovered several vulnerabilities in the Intel Trust Domain Extensions (TDX) trusted execution environment (TEE) technology. The vulnerabilities can be used to breach the isolation between the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) and Trust Domains (TDs).
"In this work for the first time, we show through a series of experiments that these performance counters can also be exploited by the VMM to differentiate between activities of an idle and active TD. The root cause of this leakage is core contention. This occurs when the VMM itself, or a process executed by the VMM, runs on the same core as the TD. Due to resource contention on the core, the effects of the TD's computations become observable in the performance monitors collected by the VMM. This finding underscore the critical need for enhanced protections to bridge these gaps within these advanced virtualized environments."
Infosec industry
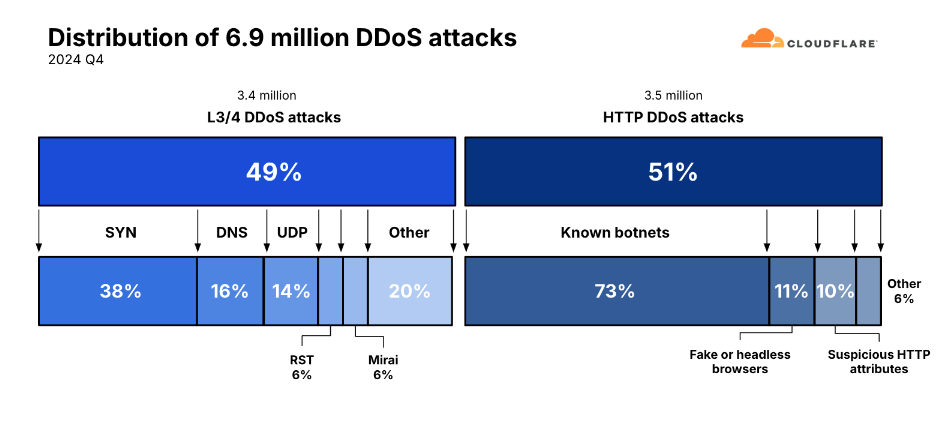
Threat/trend reports: Cloudflare, CyberInt, Omdia, Recorded Future, RIPE Labs, SentinelOne, and Trustwave have published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
New infosec book: VirusTotal founder Bernardo Quintero has published a book on the company's launch, growth, and up until its Google acquisition.
New tool—BaitRoute: Security researcher Utku Sen has released BaitRoute, a web honeypot library to create vulnerable-looking endpoints to detect and mislead attackers.
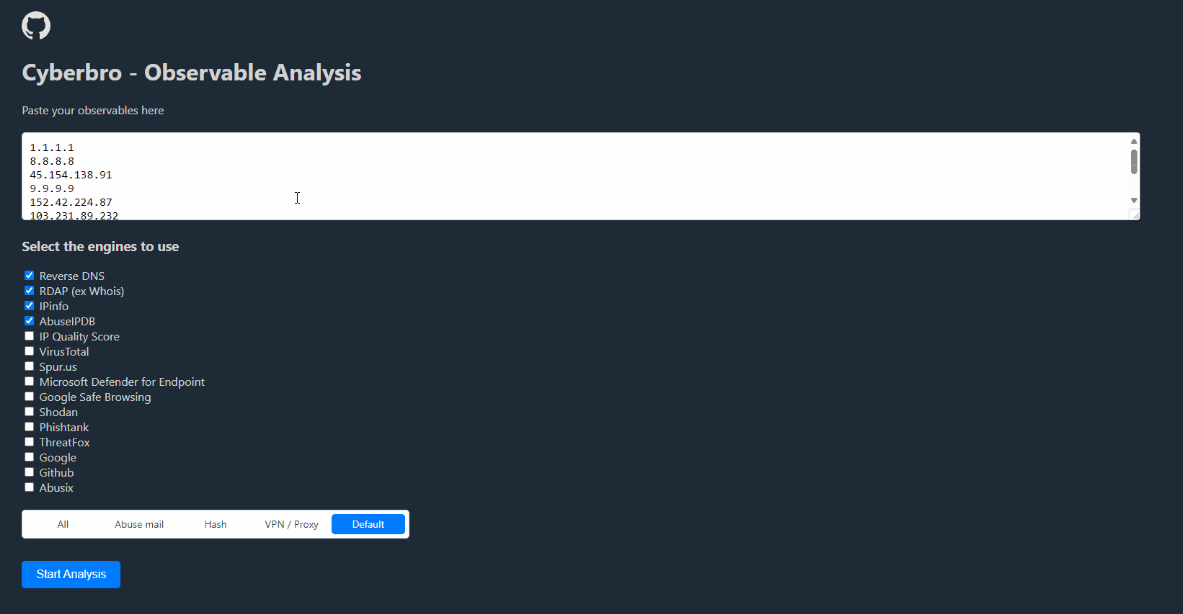
New tool—Cyberbro: Cybersecurity engineer Stanislas M. has released Cyberbro, a tool to extract IoCs from garbage input and check their reputation using multiple CTI services.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Adam Boileau talk about the continued importance of hack and leak operations. They didn't really affect the recent US presidential election, but they are still a powerful tool for vested interests to influence public policy.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about the evolution of Russian cyber operations during its invasion of Ukraine.




