Risky Bulletin: Supply chain attack plants backdoor on Android tablets
In other news: EU blocks AI tools on lawmaker devices; Cellebrite used against a Kenyan activist and politician; Chinese APT exploits a Dell zero-day.

This newsletter is brought to you by runZero, the Total Attack Surface & Exposure Management platform. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
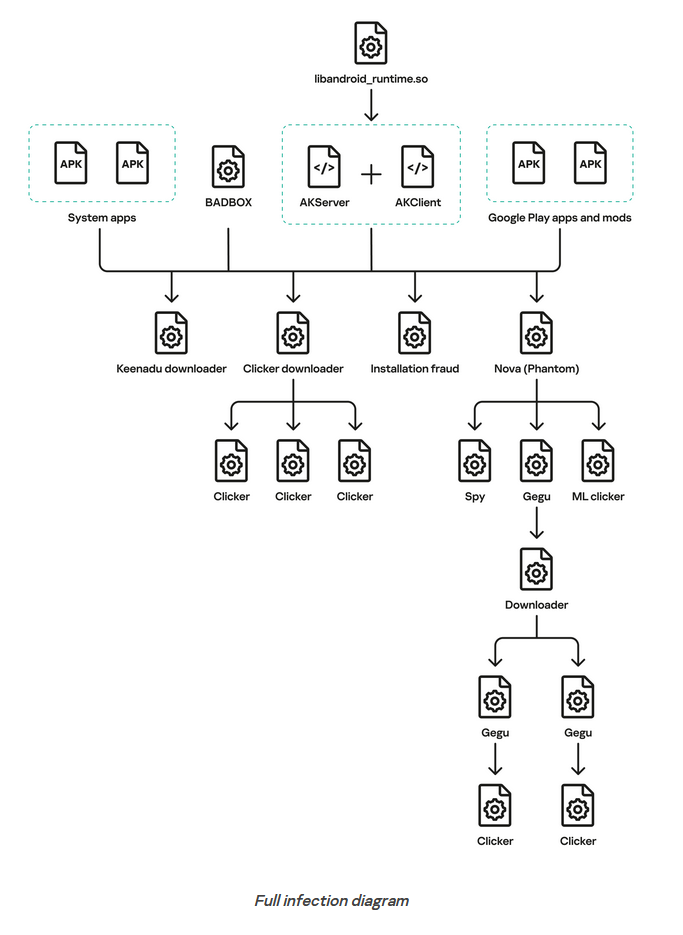
A supply chain attack has planted backdoors inside the firmware of multiple Android tablet makers. Incidents of tainted firmware updates have been traced back to as far as August 2023.
The firmware images were infected with a new backdoor named Keenadu.
Spotted and analyzed by Kaspersky in a report released on Tuesday, the backdoor is injected in Zygote, the central core process of the Android operating system from where it cannot be removed without a full device flash and reinstall.
Keenadu stays hidden for two and a half months before triggering any malicious behavior. Once this interval passes, Keenadu pings its command and control infrastructure from where it downloads and runs additional modules.
So far, the malware has been spotted deploying components that click on ads inside a hidden container, hijack browser search settings, or deploy unwanted apps in pay-per-install schemes.
According to Kaspersky, the malware works in a very similar way to Triada, another Android backdoor that has been seen preinstalled on low-cost Android tablets and smartphones for the past 3-4 years.
The company's researchers say they found multiple code and infrastructure similarities between Keenadu and Triada, but also Vo1d and BADBOX, two botnets that also made a name for themselves by shipping preinstalled on some low-cost smart TVs.
While Kaspersky has not linked the four operations, there is likely a major connection here and likely a threat actor cluster specialized in hacking developer tools and planting malicious code that later makes its way into Android device firmware and apps. Targeting a developer or a shared library seems to be the source, since some of the tainted firmware updates were also signed and delivered via over-the-air updates coming directly from the vendor's servers.
The Kaspersky report says multiple tablet makers have been impacted, but they only named Alldocube by name.
Telemetry indicates the backdoor is on more than 13,000 devices, but the number of infections is likely an order of magnitude higher. Both Vo1D and BADBOX are known to have infected more than 1 million devices each.
Kaspersky warned that while Keenadu has not seen stealing credentials from infected devices this will likely happen in the near future. Triada also gained this ability as it matured across the years.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Data leak at the Abu Dhabi Finance Week: The organizers of the Abu Dhabi Finance Week event have leaked passport and ID scans for more than 700 conference attendees. The leak has allegedly exposed the personal details of billionaires and political figures. Conference attendees included former British Prime Minister David Cameron, hedge fund billionaire Alan Howard, and former White House communications director Anthony Scaramucci. The exposed cloud server has now been secured. [Reuters]
Australian court data exposed: Workers at an Indian company have accessed highly sensitive Australian court documents. The leak occurred after a contractor subcontracted voice-to-text transcription to a company in India. Canadian company VIQ Solutions was authorized to transcribe court proceedings using Australian employees only. According to the ABC, VIQ tried to hide the contract breach by claiming that Indian company e24 was using workers based in Sydney.
Land Bank ransomware attack: The Land and Agricultural Development Bank of South Africa has been the victim of a ransomware attack. The incident took place last month. The bank shut down some IT systems and issued new laptops to employees. The attackers allegedly asked for a $3 million ransom. No known ransomware group has taken credit for the attack. [IOL]
Tulsa airport hack: The Tulsa International Airport has fallen victim to a ransomware attack. The incident took place on January 17 but the airport recovered after three days. The airport authority says staff personal data was exposed, including ID and Social Security numbers, and banking data. [Tulsa World]
Canada Goose breach: Almost 582,000 customers of clothing and outerwear retailer Canada Goose have had their data stolen last year and released online last week. [BleepingComputer]
DIIA hack claims: Multiple Russian news outlets are running a claim made on Telegram that a Russian hacktivist group known as PalachPro has hacked DIIA, the Ukrainian government's administrative platform. The platform is currently used by Ukrainians to register Starlink terminals inside Ukraine's territory. The Telegram post in question only contains two screenshots and no other proof.
General tech and privacy
Notepad++ rolls out new update system: The Notepad++ text editor has rolled out a new update and more secure update system. The app now uses a "double lock" system that verifies the update information received from Notepad++ servers but also the installer itself. The changes come after a Chinese APT hijacked the app's update servers last year to launch targeted attacks against some of its users.
Ireland launches Twitter inquiry: Ireland's data protection agency has launched its own investigation into Twitter (X) over its Grok AI producing sexualized images of children.
Bitchat adds device-to-device installs: Jack Dorsey's decentralized IM app Bitchat is adding support for device-to-device installation for situations where a country's internet has been shut down. [h/t Katya]
Samsung Privacy Display: Samsung has developed a feature that reduces the viewing angle of phone displays. The new Privacy Display uses a new type of OLED panel to prevent people nearby from reading the screen at off angles. The new feature will be available in the company's upcoming S26 models. [SamMobile // The Verge]
Apple to enable Stolen Device Protection by default: Apple will enable by default for all users a security feature to protect against device thefts. The Stolen Device Protection feature requires users to authenticate using Face ID or Touch ID before making changes to sensitive device settings. Any settings are also applied with a one-hour delay. Apple added the feature to iOS in 2023 and will be enabled for all users with the next version of iOS, version 26.4. [AppleInsider]
MySQL 30th anniversary: As MySQL is getting close to its 30th anniversary, Oracle promised in a blog post not to abandon the open-source version of the project, likely a result of the MySQL community's massive exodus to MariaDB over the past few years.
Government, politics, and policy
EU blocks AI tools on lawmakers devices: The European Parliament has disabled AI features on the work devices of lawmakers and their staff. Members of Parliament were notified of the change in an email on Monday. The Parliament IT staff cited cybersecurity and data safety concerns over the change. They said AI tools sent data to cloud servers outside of their control. [Politico Europe]
EU DPAs support digital rules simplification: The EU's top data protection authorities will support the Commission's effort to simplify the bloc's tech rules. While the EDPB and EDPS showed support for the digital regulatory framework, they warned against weakening the GDPR. The EU's Digital Omnibus Regulation is set to narrow down the definition of personal data and also remove pseudonymized data from the personal data category. The two agencies approved of the idea of incorporating user consent inside browser settings to reduce the current consent and popup fatigue. [h/t misspurple]
UK promises tech crackdown: The UK government has announced a crackdown on tech firms to protect children from online harms. Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer says no platform will get a free pass, including AI companies that have been the driver behind some of the recent abuses. [Sky News]
Odessa Triangle cyber cooperation: Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine have signed a treaty of cooperation on cybersecurity at the recently concluded Munich Security Conference. [Calea Europeana]
CISA threat-hunting leader departs: The head of CISA's threat-hunting unit is leaving the agency. Jermaine Roebuck notified staff of his decision in an all-hands meeting last week. Roebuck is leaving voluntarily to take a job in the private sector. [NextGov]
Australia signs with Palantir: The Australian Department of Defence has signed an AUD $7.6 million contract with Palantir to provide intelligence to its Cyber Warfare Division. [Crikey]
FSB gets the power to cut connections at will: The Russian Duma has passed a law that grants the FSB intelligence service the power to cut mobile and internet connections at will, even when there's no threat to national security. The law passed after its third reading, after the threat to national security requirement was removed. The law was proposed in November to counter Ukrainian drone attacks by cutting mobile communications in a region but has now turned into another instrument of state control and oppression. [Meduza // Svoboda]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Casey Ellis chats to Todd Beardsley, VP of Security at RunZero about Kevology, the company’s analysis of CISA’s KEV list. Kevology lets you easily identify and fix vulnerabilities from the list that are urgent and relevant to you.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Phobos affiliate detained in Poland: Polish authorities have arrested a 47-year-old man for attacks with the Phobos ransomware. The suspect was in possession of hacked credentials and was in contact with the Phobos group via an encrypted messenger. The arrest is part of Operation Aether, an Europol operation targeting the Phobos group and its affiliates.
Man loses $800,000 to romance scammers: An Australian man has lost AUD$800,000 (USD$565,000) to a romance scammer. According to Australia's Federal Police, Australians lost AUD$28 million (USD$19.75 million) to romance scams last year, with most victims being over 55.
Cellebrite used in Kenya against activist: Kenyan authorities used Cellebrite's phone-cracking software against the personal device of an activist and political rival. Boniface Mwangi says his device was exploited when police took his phone following his arrest in July of last year. Researchers at Citizen Lab said they found traces of Cellebrite's software on Mwangi's Samsung phone. Mwangi plans to run for president in Kenya's 2027 elections.
WhatsApp account takeovers spike in Armenia: Almost 4,000 WhatsApp accounts have been hacked across Armenia. Attackers are using the hacked accounts to register WhatsApp Business profiles and then send large volumes of spam before they get blocked. CyberHUB-AM, a non-profit that works as a CERT for the Armenian civil society, claims attackers have exploited vulnerabilities in the WhatsApp SMS two-factor authentication delivery chain.
Cyber threats to marine sector: Canada's cybersecurity agency has published an assessment of current cyber threats to the marine sector.
Cyber Essentials reminder: The UK NCSC is urging small and medium enterprises to adopt its Cyber Essentials playbook and protect their networks from the damages caused by cyberattacks.
Matryoshka ClickFix: macOS security company Intego has spotted a new variant of ClickFix attacks that uses a nested Matryoshka-style obfuscation technique to hide its malicious payloads.
Telegram ban abused for malware distribution: Threat actors are using Russia's recent Telegram crackdown to distribute malware. Kaspersky has spotted malicious apps that offer to speed up Telegram but instead deploy an Android banking trojan named Mammoth. The malware emerged in 2024 and has been exclusively used to target Russian users.
Fraud evolves in Russia: Banking fraud in Russia is evolving from card-related operations to online banking and the fast payment system. According to the Bank of Russia, all three categories experienced a record number of incidents last year, but carding incidents are going down. Experts attributed the trend to banks shoring up their card defenses, forcing threat actors to adopt social engineering and target online accounts. [Kommersant]
Infostealers target OpenClaw instances: Hudson Rock has spotted the first case of an infostealer targeting OpenClaw installations and stealing their config files. The data extracted from these files can be used to access the instance remotely.
Kimwolf accidentally DDoSes I2P: The Kimwolf IoT botnet has accidentally swamped the I2P anonymity network with junk traffic. The disruptions started two weeks ago and are preventing legitimate users from connecting to I2P resources. The issues started after Kimwolf started using I2P to host some of its command and control servers, flooding the anonymity network with connections from millions of hacked routers andTV set-top boxes. [KrebsOnSecurity]
GS7's Operation DoppelBrand: A financially motivated threat actor has deployed over the past two months phishing portals targeting multiple Fortune 500 brands. SOC Radar has linked more than 150 domains to a group known as GS7.
The shame of romance scams: A survey of 2,000+ Americans found that more than half would be ashamed to talk about falling victim to a romance scam compared to other types of scams. The survey also found that men are more frequently targeted by scammers.
SilverFox adopts BYOVD: The SilverFox cybercrime group has adopted BYOVD for its operations and is installing and then exploiting a bug in the STProcessMonitor Windows kernel driver to elevate privileges on infected hosts.
Rise of the CARINT domain: A Haaretz report looks at the rising category of CARINT (car intelligence) service providers, companies that provide car hacking and auto surveillance technologies. The report claims most providers are based in Israel and are part of the country's expansive surveillance and spyware market.
New PBaaS infrastructure: Infoblox has found new server infrastructure linked to online scams and Pig-Butchering-as-a-Service providers. This particular cluster blended malvertising with fake investment portals.
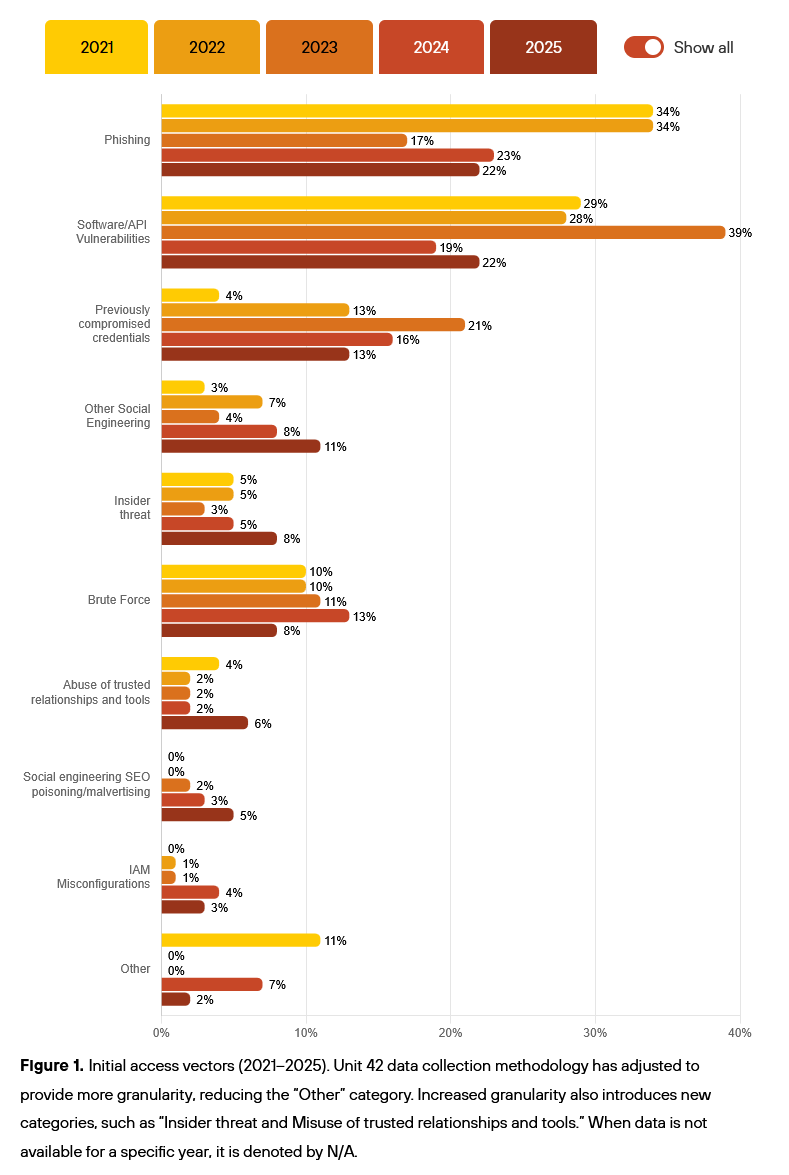
Identity abuse is a main entry point: Palo Alto Networks says that two-thirds of the 750 incident response engagements it had last year were traced back to the abuse of user identities. The most common entry points were social engineering, phishing, leaked credentials, brute-force attacks, and IAM misconfigurations. Last year, the company also saw a spike in supply chain attacks, which are now impacting SaaS providers on a regular basis.
Malware technical reports
DigitStealer: Security researchers have tracked new infrastructure linked to the DigitStealer macOS infostealer, which they claim is run by one single developer or at least a very small team.
Aeternum Loader: Ctrl-Alt-Int3l has published a two-part series on the new Aeternum Loader. It covers the malware's control panel, its flawed C&C encryption scheme, and the malware's main binary.
XWorm: ANY.RUN has published a write-up on the XWorm variant hitting LATAM.
0APT ransomware: After multiple security firms called out the 0APT ransomware group for listing fake victims on its dark web leak site, Cyderes has managed to get its hands on the group's actual ransomware, and it's apparently a legit encrypter.
Sponsor section
In this product demo Patrick Gray hosts Ali Cheikh while he shows off how you can use runZero to scan for and manage vulnerabilities in your environment.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
CRESCENTHARVEST: Iranian citizens domestically and abroad are being targeted with a new Windows backdoor named CRESCENTHARVEST. The campaign began shortly after anti-government protests started in Iran at the start of the year. It targets individuals who attended protests in Iran, but also in Western cities. Security firm Acronis has not attributed the attacks, but this is likely the work of Iranian authorities. According to multiple reports, the Iranian government is also using mobile telephony data to track down people who attended protests or those who posted online about them.
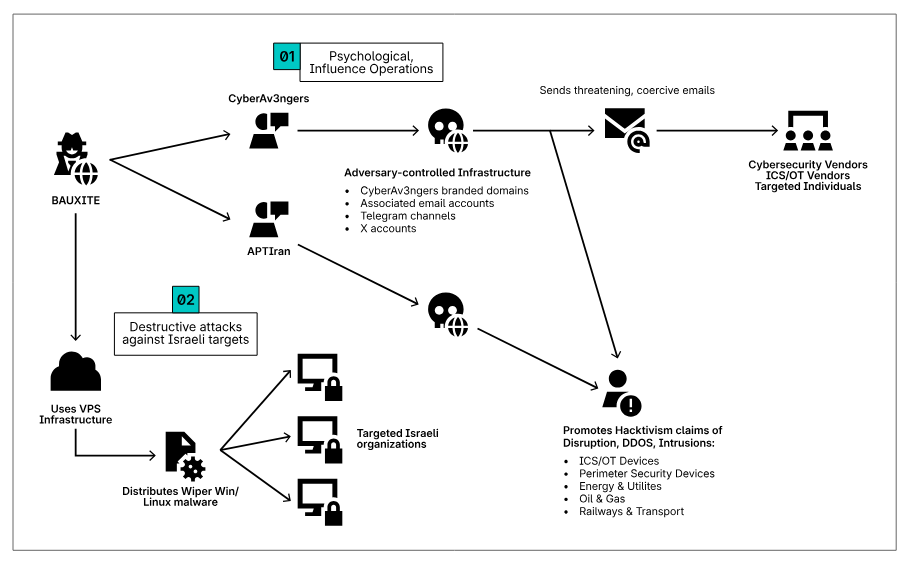
Iranian groups deployed wipers against Israel's ICS orgs: At least two Iranian cyber groups deployed data-wiping malware against Israeli critical sector organizations during the two country's armed conflict last June. Security firm Dragos didn't specify if the attacks were successful. The company tracks the groups as Bauxite and Pyroxene, but they are more broadly known as CyberAv3ngers and APT35. Pyroxene is one of three new groups Dragos has spotted targeting the ICS and OT sector last year. The other two are Azurite and Sylvanite.
Poisonous Mars: Positive Technologies has detected a new campaign targeting telecommunications companies in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan with the LuciDoor and MarsSnake backdoors. The company believes this may be a Chinese APT related to what ESET tracks as UnsolicitedBooker.
UNC6201 exploits Dell zero-day: A suspected Chinese APT group is exploiting a zero-day in the Dell RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines software. Google has linked the attacks to a group it tracks as UNC6201. Tracked as CVE-2026-22769, the zero-day is a set of hardcoded admin credentials for the app's integrated Tomcat server. Google says UNC6201 is using the credentials to upload a malicious WAR file, and access it to run commands as root on the appliance.
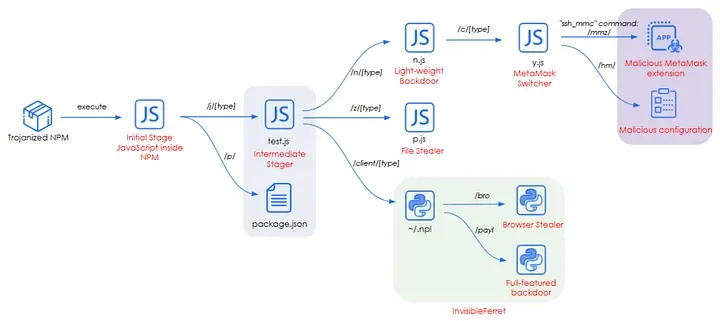
Contagious Interview expands to Metamask: Zscaler security researcher Seongsu Park says that North Korean hackers who conduct attacks against Web3 developers—commonly referred to as Contagious Interview—have updated the BeaverTail and InvisibleFerret backdoors with the ability to steal data from the Metamask cryptowallet.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Chrome zero-day: Google has released a security update to patch a Chrome zero-day exploited in the wild. Tracked as CVE-2026-2441, the zero-day is a memory corruption issue in how Chrome processes a CSS feature that lets users customize font names. The vulnerability can be used to run malicious code inside the Chrome sandbox via an HTML page.
Pre-auth vulns in TRUfusion Enterprise: RCE Security has found two pre-auth vulnerabilities in TRUfusion Enterprise, a system for sharing CAD and PLM data inside companies. The company found four similar flaws last year too.
OpenClaw log poisoning vulnerability: The OpenClaw personal AI agent project has patched a log poisoning vulnerability. The bug allowed remote attackers to write malicious content to OpenClaw log files via WebSocket requests. Since the agent reads its own logs to troubleshoot certain tasks, the issue could have led to indirect prompt injection scenarios. The vulnerability mainly impacted only OpenClaw instances left connected to the internet. [Eye Security]
Nanobot WhatsApp hijack bug: And speaking of dumb AI agents exposing connected apps, Nanobot had a similar bug where it bound WhatsApp to all network interfaces and allowed WebSocket connections to it with no authentication. [Tenable]
CheckSum aftermath: Silverfort looks at the aftermath from its CheckSum (CVE-2025-60704) vulnerability research, a Kerberos delegation attack.
"While defenders commonly restrict delegation for user accounts, Dor found that sensitive computer accounts (Tier 0 / machine identities) can remain delegable by default, because the protection exists under the hood but is not exposed in standard AD UI tooling for computer accounts, creating a blind spot where sensitive machines remain delegable even in otherwise hardened environments."
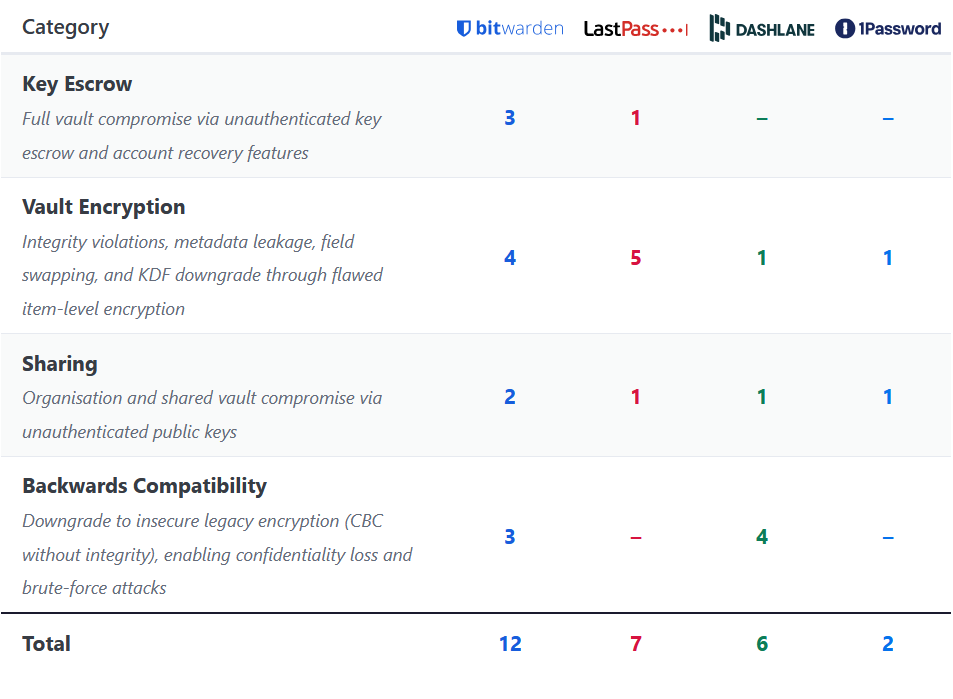
Password manager vulnerabilities: A team of academics has found 27 vulnerabilities in four cloud-based password managers. Some vulnerabilities allowed the attackers to leak metadata, downgrade encryption, or grant access to stored credentials. The research operated from the scenario that a malicious party had taken control of the cloud server and was launching attacks against connected users and the app's encryption techniques. Bitwarden, LastPass, Dashlane, and 1Password have all addressed the researchers' findings.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Arctic Wolf, Bank of Russia, BI.ZONE, DB-Engines, Dragos, Huntress, Intel471, Jamf, Microsoft, NordProtect, Palo Alto Networks, Searchlight Cyber, Securin, and Teleport have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
Acquisition news: Infosec giant Palo Alto Networks is acquiring AI and endpoint security startup Koi Security for $400 million.
Woolworths divides security roles: Australian retail giant Woolworths has split its cyber and physical security roles and will now have dedicated executives for each. [iTnews]
New tool—yt-media-storage: Software engineer Brandon Li has released yt-media-storage, a tool to store files on YouTube by encoding them as lossless video files and then retrieving them when needed. This sounds like a perfect way to store malware on the site, ngl!
New tool—AID: Johann Rehberger has released AID, a tool for detecting invisible Unicode characters in files.
New tool—BloodBash: Anthony Russell has open-sourced BloodBash, a serverless Bloodhound JSON file analyzer.
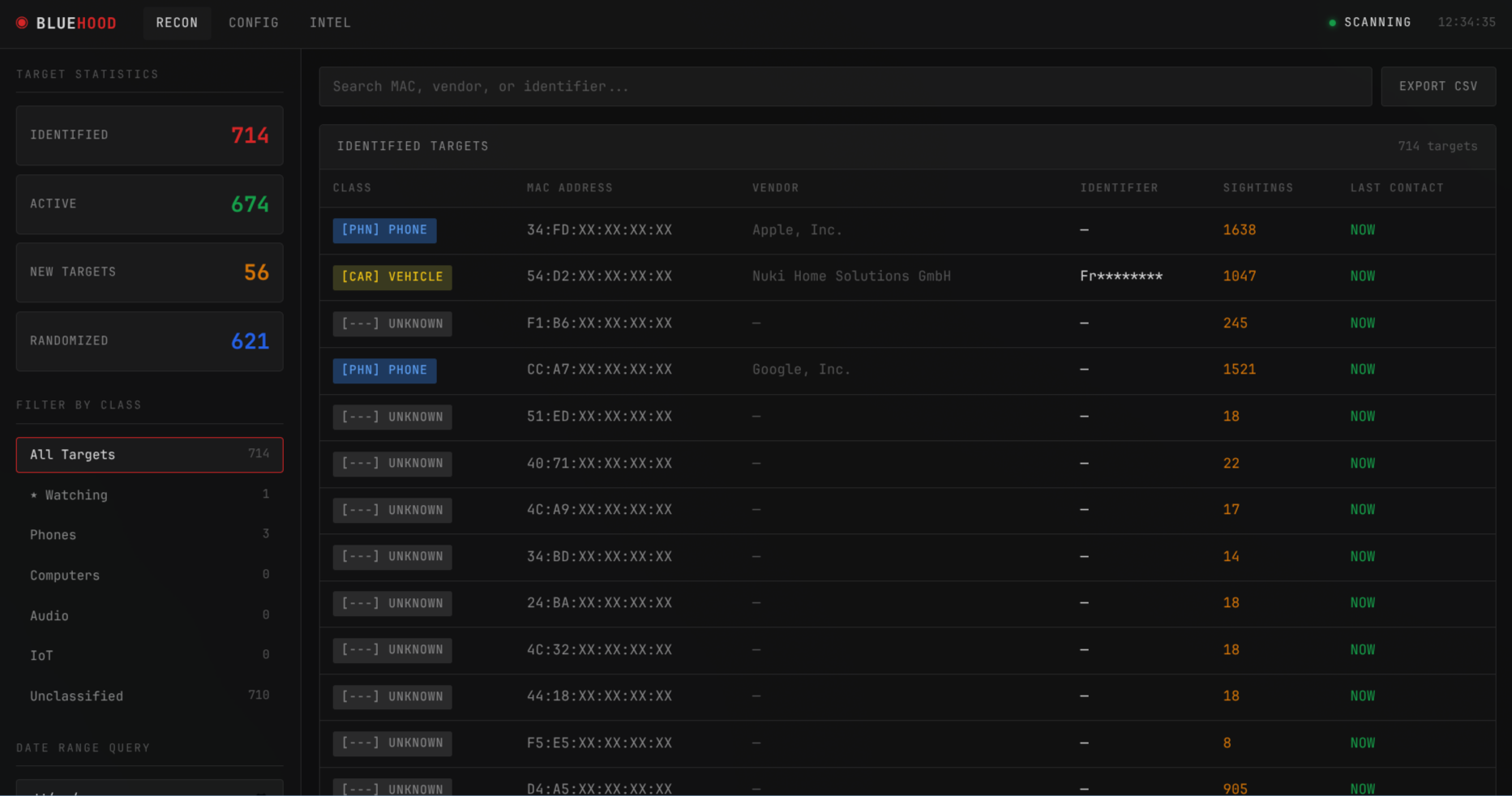
New tool—Bluehood: Danny McClelland has published Bluehood, a Bluetooth scanner that reveals what information leaks from Bluetooth-enabled devices.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq discuss whether middle powers should be investing in military cyber capabilities.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella's messaging around personnel changes at the top of its security organisation. These signal a focus on selling security products rather than on making secure products.




