Risky Bulletin: Six-years-old backdoor comes to life to hijack Magento stores
In other news: US to destigmatize and normalize offensive cyber operations; Darcula PhaaS admin identified as 24-year-old Chinese man; Ireland fines TikTok for secret user data transfers to China.

This newsletter is brought to you by Stairwell. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Hackers activated secret backdoors they planted six years ago inside Magento plugins to hijack almost 1,000 Magento online stores.
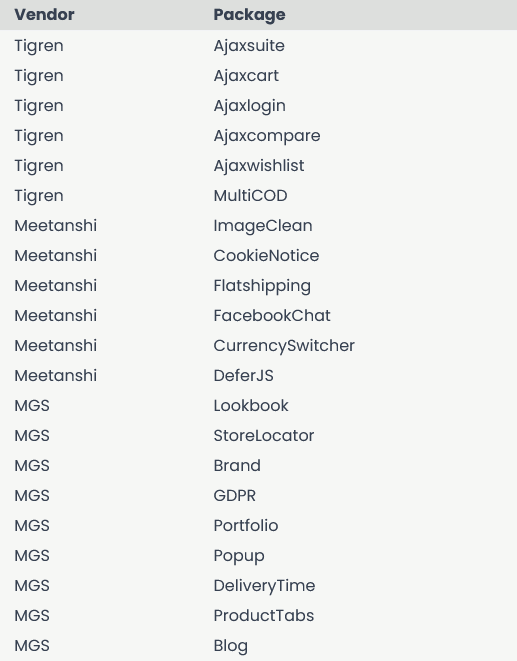
The initial compromises took place in 2019 when the attackers allegedly gained access to the servers of three Magento software developers—Magesolution, Meetanshi, and Tigren.
According to security firm Sansec, the hackers modified the source code of 21 plugins. The backdoor was hidden in the License.php file, which is typically included in most plugins to check if the user holds a valid license.
Sansec says the malicious code was left dormant for six years until April when the attackers started exploiting it to deploy malicious code on Magento stores that installed the plugins.
The backdoor code checked for a secret key in incoming requests and allowed the key holder to run commands on the server.
While removing the malicious plugins, listed below, will remove the initial entry for the attackers, stores will need a thorough check to ensure the hackers didn't leave additional web shells for secondary access.
So far, the attacks seem to have hit some big sites, and Sansec says one of the victims is a "$40 billion multinational."
The company also notified the plugin developers, but all three seem to be in denial mode right now:
- Magesolution did not respond, but the backdoored packages can still be downloaded from their site as of Apr 30th.
- Tigren denies to have been hacked, but the backdoored packages are still available on their site as of Apr 30th.
- Meetanshi claims that their software has not been tampered with but confirmed that their server got hacked.
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
TeleMessage hacked: A hacker has breached and stolen customer data from TeleMessage, an Israeli company that sells modified versions of secure messaging apps. According to 404 Media, the TeleMessage backend contained messages logged by customers and their contact details. The company's customers include several US government agencies and a modified version of Signal, named TM SGNL, is also used by multiple members of the White House to log Signal conversations. According to privacy activist Micah Lee, the Android version of the app contained hardcoded credentials and other vulnerabilities.
I don’t know who made the choice to use TM SGNL instead of Signal, or why. I doubt it’s to comply with record laws. I think a real possibility is that they wanted a record for themselves, the same reason Nixon taped all his own conversations
— Micah Lee (@micahflee.com) 2025-05-03T23:09:22.193Z
SK suspends new customer sign-ups after hack: South Korea's largest carrier, SK Telecom, has suspended new user registrations as it struggles to grapple with a major security breach. The company will focus all efforts and resources on replacing all customer SIMs. It will also stop porting numbers in and out of its network to prevent hackers from using the stolen SIM card data. [Additional coverage in The Korea Herald]
Failed DDoS attacks on Romania's election: Several pro-Kremlin hacking groups claimed they launched DDoS attacks on key Romanian government websites on the country's election day. None of the websites were down, and some agencies claimed they saw no such attacks in the first place. Props to Romania's cybersecurity agency for an unexpected May the Fourth meme! [Additional coverage in Hotnews.ro]
Raw data leak: Mobile dating app Raw fixed a data leak that exposed the personal information of all its users. The company's API server allowed anyone to query personal user information without proper credentials. Attackers could retrieve sensitive data such as names, dates of birth, geolocation data, dating, and sexual preferences. According to TechCrunch, the company also didn't run end-to-end encryption despite marketing claims.
xAI leak: Congratulations to the xAI developer who leaked a private API key on GitHub that could have granted access to internal LLMs developed for Elon Musk's companies—Tesla, Twitter, and SpaceX. [Additional coverage in KrebsOnSecurity]
DragonForce takes credit for UK retail attacks: A ransomware group named DragonForce has taken credit for the cyberattacks against UK retailers Marks & Spencer, Co-Op, and Harrods. The group confirmed one of the attacks by sending a sample of Co-op's user data to the BBC last week. It claims other intrusions will be revealed in the future. The attacks are part of an extortion scheme targeting the UK retail sector. [Additional coverage in Bloomberg]
Peru denies cyberattack: The Peru government deflected claims that its official government portal was hacked, claiming that the "supposed" breach only impacted a small portal. Rumors of a hack arose last week after the Rhysida ransomware group claimed it stole official government data and asked for a 5 BTC (~$500,000) ransom. The incident is still in its early phase, and this whole thing may turn out to be a massive breach or a nothinburger.
General tech and privacy
Ireland fines TikTok: Ireland's data protection agency has fined TikTok €530 million for transferring the data of EU citizens to China without disclosing it to its users. The agency says TikTok failed to meet transparency obligations under the GDPR—by blatantly lying about its data storage practices. TikTok has six months to become compliant.
EoL/EoS format: The OASIS Open Consortium has proposed a machine-readable format that could be used by device makers to disclose End-of-Support and End-of-Life dates for their products. The new format was designed to be used with emerging cybersecurity formats such as Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs) and the Common Security Advisory Framework (CSAF). The OASIS Open Consortium was founded by IBM and includes some of the world's largest tech companies, such as Cisco, Microsoft, Google, Intel, and others.
Redis returns to FOSS license: The Redis database has returned to its old AGPL license after a brief foray into the dual open-commercial licensing space that managed to alienate and scare away a bunch of core contributors and customers.
Chrome 136: Google has released version 136 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes in this release are a feature to prevent inactive tabs from being purged and a fix for an old tracking technique that abused visited links.
Firefox 138: Mozilla has released Firefox 138. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest feature in this release is support for browser profiles.
Government, politics, and policy
ICC publishes cyber-enabled crimes draft: The International Criminal Court has published the first draft of a new policy that adds cyber-enabled crimes to the court's jurisdiction. The draft amends the Rome Statute, an international treaty that recognizes the ICC's international judicial power. Previously, the Rome Statute covered four main types of international crimes—genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity, and international military aggression. The ICC Prosecutor's Office looked into expanding its mandate after Russia's use of cyber against civilian targets in Ukraine.
Russian lawmaker proposes military strikes on Ukrainian hackers: One Russian lawmaker has proposed designating Ukrainian hackers and scam call centers as valid military targets, an idea that has kept popping in and out of the Russian propaganda space for two years now, inspired by Israeli missile strikes against Hamas cyber units in 2019.
US to normalize offensive cyber operations: The Trump administration plans to use offensive cyber operations as a tool of national power. Senior director for cyber on the National Security Council, Alexei Bulazel, says the White House will work to destigmatize and normalize cyber operations going forward. Bulazel says the US will eventually respond with its own cyberattacks against foreign adversaries attacking the US, a departure from the policies of previous administrations. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Trump admin proposes CISA budget cuts: The Trump administration wants to cut $491 million from CISA's budget for next year. The cuts target CISA programs focused on international affairs and programs focused on misinformation and propaganda. The Trump administration claims CISA was weaponized and involved in a "Censorship Industrial Complex" that targeted Americans and current President Donald Trump. According to CybersecurityDive, the White House budget cut proposal repeated debunked and false right-wing talking points. [White House document PDF]

Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview Mike Wiaceck, CEO and founder of Stairwell, explains why he believes security is really a data storage and retrieval problem. He demonstrates how that pays off with in the analysis of new malware.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
US charges Black Kingdom ransomware dev: The US Justice Department charged a Yemeni national for hacking and extorting US companies with the Black Kingdom ransomware. Rami Khaled Ahmed allegedly exploited the ProxyLogon vulnerability to hack Microsoft Exchange email servers and deploy his ransomware. He allegedly hacked over 1,500 systems and asked for $10,000 paid in Bitcoin to decrypt servers.
Swatter sentenced to prison: US authorities have sentenced a Wisconsin man to 44 months in prison for participating in a one-week-long swatting spree. Kya Christian Nelson hacked Ring door cameras, called the police, and streamed the swatting on social media. The swattings took place in November 2020. One of Nelson's co-conspirators was also sentenced to seven years in prison.
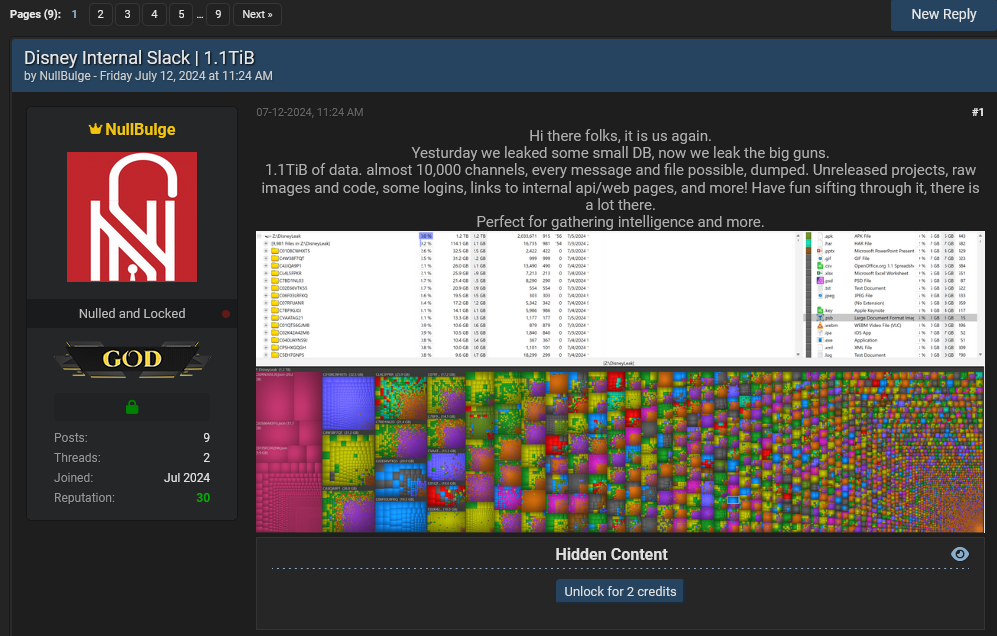
Disney hacker pleads guilty: A California man pleaded guilty to hacking The Walt Disney Company after he infected one of their employees with malware. Ryan Mitchell Kramer used the employee's credentials to access Disney's Slack channel and steal internal data. Kramer later leaked the data on a hacking forum, where he posed as a fake Russian hacktivist group named NullBulge.
Hong Kong arrests scam ring: Hong Kong police detained eight members of a scam ring that opened accounts at local banks using forged documents. Authorities say the group used deepfake technology to replace photos on lost identity cards. The group opened 30 bank accounts after the modified documents passed ID checks on online banking portals. [Additional coverage in the South China Morning Post]
US sanctions Huione Group: The US Treasury Department has sanctioned and designated Cambodian financial company Huione Group as a money laundering hub. Officials say the company laundered funds from North Korean crypto heists and funds linked to investment scams coming from Southeast Asian scam compounds. Huione and its subsidiaries helped criminal groups launder over $4 billion over the past four years. The company's illegal dealings were first exposed by blockchain security firm Elliptic last July.
South Korean crime groups adopt cyber crimes: New recruits in long-lived South Korean criminal gangs are moving the groups towards the realms of cyber and cryptocurrency scams. [Additional coverage in the OCCRP]
DragonForce profile: SentinelOne has published a profile on the DragonForce ransomware group that recently wrecked three of the UK's biggest telcos.
Darcula operator identified as Chinese man: A joint investigation between German, French, and Norwegian journalists has identified the administrator of a phishing service named Darcula (actually called Magic Cat) as a 24-year-old Chinese national named Yucheng C. The service launched in late 2023 and has grown to become one of the largest and most popular Phishing-as-a-Service platforms today. It's been linked to over 20,000 phishing domains, most of which mimic package delivery services to trick users into entering their credit card details.
MyGov phishing campaign: CyberKnow looks at a two-month-old MyGov phishing campaign targeting Australians.
BreachForums clones and scams: DataBreaches.net looks at two clones of BreachForums that have recently popped up online after the main site was hacked last month. In the meantime, BreachForums is back online after almost three weeks, formally admitting it got hacked.
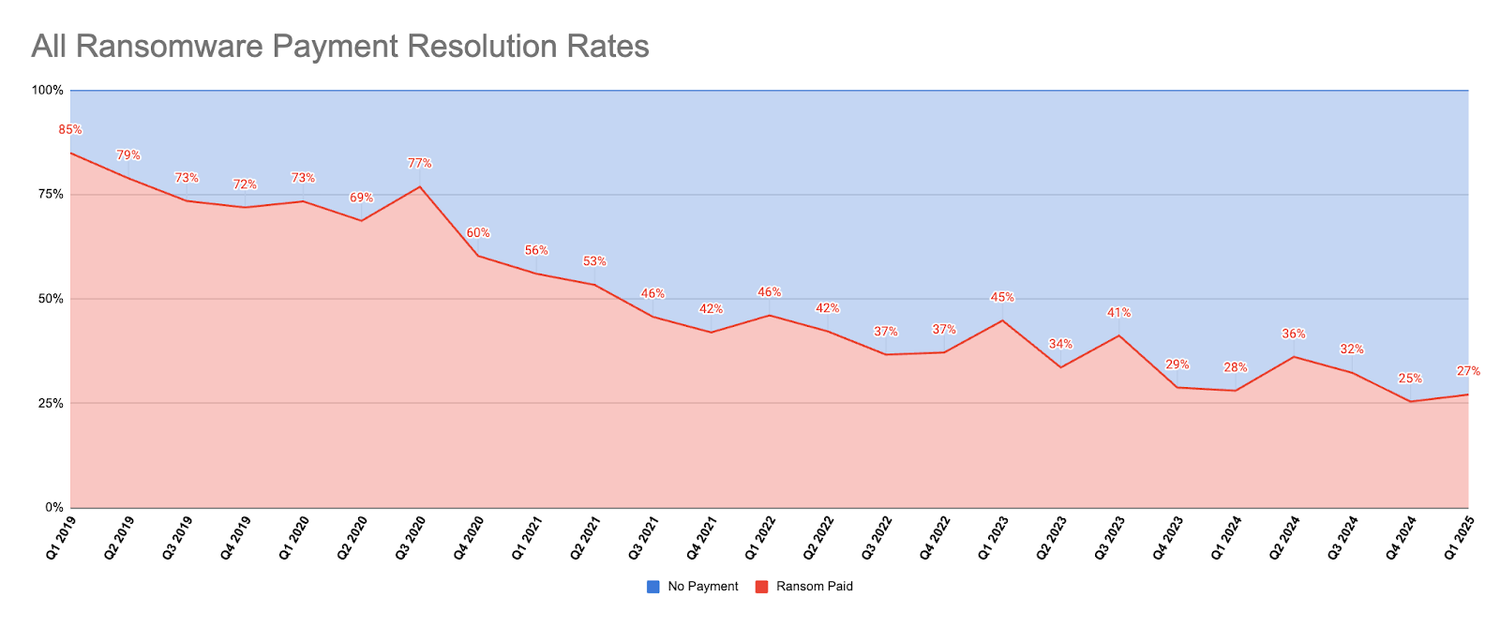
Decrypter reliability is going down: Coveware's quarterly assessment of the ransomware market draws attention to the rising problem of faulty ransomware decrypters as one of the main reasons why ransomware payments have been going down and why it may not be a good idea to pay these ransoms in the first place.
New ransomware groups: Three new ransomware gangs popped up on the dark web this past week—AzzaSec, J Group, and Nova.
Larva-25003 attacks on IIS servers: South Korean security firm AhnLab has spotted a Chinese-speaking threat actor (Larva-25003) planting web shells on unsecured IIS servers.
New npm malware: One hundred seventeen malicious npm packages were discovered and taken down last week. Check out the GitHub security advisory portal for more details.
Go packages deliver data wiper: Socket Security has discovered three malicious Go packages that delete all data on Linux development environments. The data-wiping commands are hidden in a shell script that zeros out the primary hard drive. The commands run immediately after installation and give almost no chance to prevent or react to the attack.
Scam compounds are also big polluters: Two scam compounds operating in Cambodia were named as some of the country's biggest polluters.
CAMBODIA: Ministry of Environment report 5 locations found polluting public waterways. 2 of them are large and expanding scam compounds. www.facebook.com/MinistryOfEn...
— Cyber Scam Monitor (@cyberscammonitor.bsky.social) 2025-05-04T08:01:39.138Z
Kraken almost hired DPRK IT worker: Cryptocurrency exchange Kraken says it almost hired a North Korean IT worker for one of its US operations. On the other side, congrats to the Oregon congressional campaign that hired one of these workers last year, although, through an intermediary.
Malware technical reports
Gunra ransomware: CyFirma researchers have identified a new ransomware operation named Gunra, currently targeting Windows environments with double-extortion schemes.
Formbook campaign updates: Forcepoint looks at a new malspam campaign spreading the Formbook malware, but this time crypted via the Horus Protector.
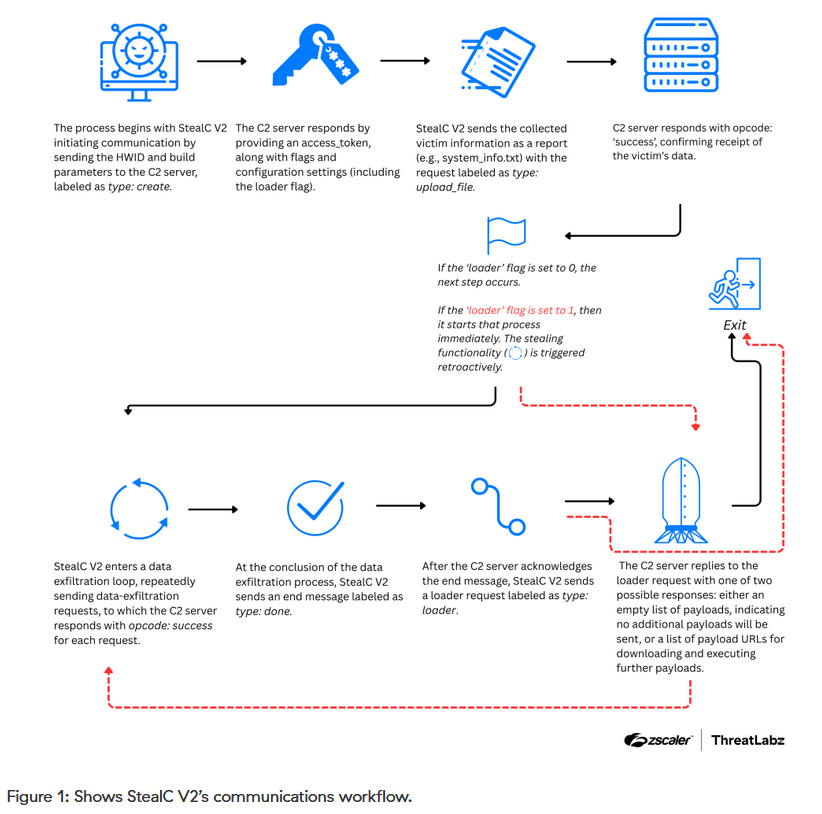
StealC: Zscaler has published a report on version 2.0 of StealC, an infostealer and malware downloader sold online since January 2023.
Sponsor section
Learn why traditional security falls short and how Stairwell gives you the edge to outpace tomorrow's threats and uplevel your security team.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Iranian APT intrusion at Middle East CNI: Fortinet has published a 57-page report [PDF] on an intrusion at a Middle East critical infrastructure operator that lasted from May 2023 to February 2025. The company attributed the attack to an unnamed Iranian APT, with some TTPs overlapping older Lemon Sandstorm activity.
Transparent Tribe Pahalgam phishing: Pakistani APT group Transparent Tribe is using the recent Pahalgam terrorist attack as a phishing lure to target Indian government officials. Qihoo 360 also has a report on the same group but focusing on some of its new Android malware, used in a separate campaign.
Lazarus Tsunami: HiSolutions has published a technical analysis of Tsunami, a malware framework used by the Lazarus APT as a malware loader in operations against the cryptocurrency community.
TikTok info-ops summary: TikTok has published its monthly report on covert influence operations the company has spotted on its platform in March this year. The company took down influence networks targeting French-speaking audiences in West Africa and France (from Togo), Russian audiences (from Ukraine), and anti-Israel US audiences (from the US).
Russian disinfo efforts masquerade as Anonymous: Russian disinformation group Matryoshka has weaponized the Anonymous hacker collective brand to release fake leaks meant to discredit and spread lies about Moldova's pro-EU president Maia Sandu and pro-EU parties. The campaign targets Moldova's parliamentary election set to take place in September. The campaign is of note because the Matryoshka group tried to pass some of its leaks as the work of French anti-disinformation agency VIGINUM. The Matryoshka group has been targeting Moldova's pro-EU political scene for several months now with the same tune.
Doppelganger activates ahead of Romania's elections: Romania's communications watchdog has identified a network of websites and social media accounts impersonating Romanian news outlets and government agencies. The agency says the sites are peddling disinformation ahead of the country's presidential election, which were held over the weekend. ANCOM linked the sites to a Russian disinformation group tracked as Doppelganger. Romanian canceled its elections last year after previous Russian meddling in support of one of the candidates.

Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
PoC published for unpatched WDS bug: Security researcher Zhiniang Peng has published proof-of-concept code and details about a pre-auth denial of service bug in the Windows Deployment Services. The bug can allow unauthenticated attackers to crash Windows systems via malformed FTP requests. The service runs on all major Windows versions and is normally used to remotely install the Windows OS inside managed networks. Zhiniang published the PoC after Microsoft declined to patch the bug earlier this year.
Digigram PYKO-OUT Digigrams don't require authentication: Digigram PYKO-OUT audio streaming devices run without authentication and expose their configuration files. The PYKO-OUT devices are typically used to stream music or live announcements across large building complexes. According to the Carnegie Mellon University CERT team, attackers on the same network can compromise the devices by accessing their web servers. Digigram says the product is now end-of-life, but users can enable a password via the PYKO-OUT admin panels.
SonicWall exploitation: WatchTowr Labs has published a deep dive of two SonicWall bugs (actually one Apache and one SonicWall bug) that have recently come under active exploitation.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database (twice) with four vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. This includes the SonicWall+Apache and Commvault+Yii bugs exploited in campaigns disclosed last week.
Citrix PoC released: Rapid7 has published details and a PoC for Citrix NetScaler info leak tracked as CVE-2024-6235. VulnCheck says there's a high chance this bug gets exploited, seeing how past NetScaler bugs with "free PoCs" have also had the same fate.
IXON VPN vulnerabilities: Security firm Shelltrail has discovered two vulnerabilities in IXON VPN clients that could be used for local privilege escalation. The company found a third bug, but it's not disclosing details because it's still unpatched.
Qwen3 assessment: Lukasz Olejnik looks at three issues in Alibaba's Qwen3 LLM that may lead to prompt injection attacks.
Fortra security updates: Fortra has released two security updates for the GoAnywhere file-sharing server.
Infosec industry
RIP Robert Metzger: Cybersecurity industry veteran Robert Metzger, known for his work on the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), has passed away from cancer. [Additional coverage in Washington Technology]
New tool—DataSig: Security firm Trail of Bits has released DataSig, a tool that detects on what type of data your AI/ML models have been trained on.
New tool—Foundation-sec-8b: Cisco has released Foundation-sec-8b, an open-weight Large Language Model (LLM) purpose-built for security.
Threat/trend reports: Coveware, Fortinet, and Sublime Security have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Risky Business podcasts
Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about a SentinelOne report about how it is constantly targeted by both cybercriminal and state-backed hackers. Security firms are high-value targets, so constant attacks on them are the new normal.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq discuss the Southeast Asian criminal syndicates that run online scam compounds. Should organizations like US Cyber Command or the UK's National Cyber Force target these gangs with disruption operations?




