Risky Bulletin: Russia spies on foreign embassies using local ISPs
In other news: Google rolls out cryptographically-signed Chrome extension updates; Signal threatens to leave Australia; Russian pharmacies go down after cyberattack.

This newsletter is brought to you by vulnerability management and analysis platform Nucleus Security. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Russian intelligence services are hacking and spying on foreign embassies and their staff by tampering with their internet connections.
Russian espionage units are using the SORM traffic interception system installed at local ISPs to alter traffic and deliver malware payloads to embassy staff.
According to Microsoft, the campaign has been ongoing since at least last year. The company attributed the attacks to a group it tracks as Secret Blizzard, but more widely known as Turla.
Previous reporting has linked the group to Center 16 of the Russian FSB intelligence agency, which manages most of the FSB's signals intelligence units.
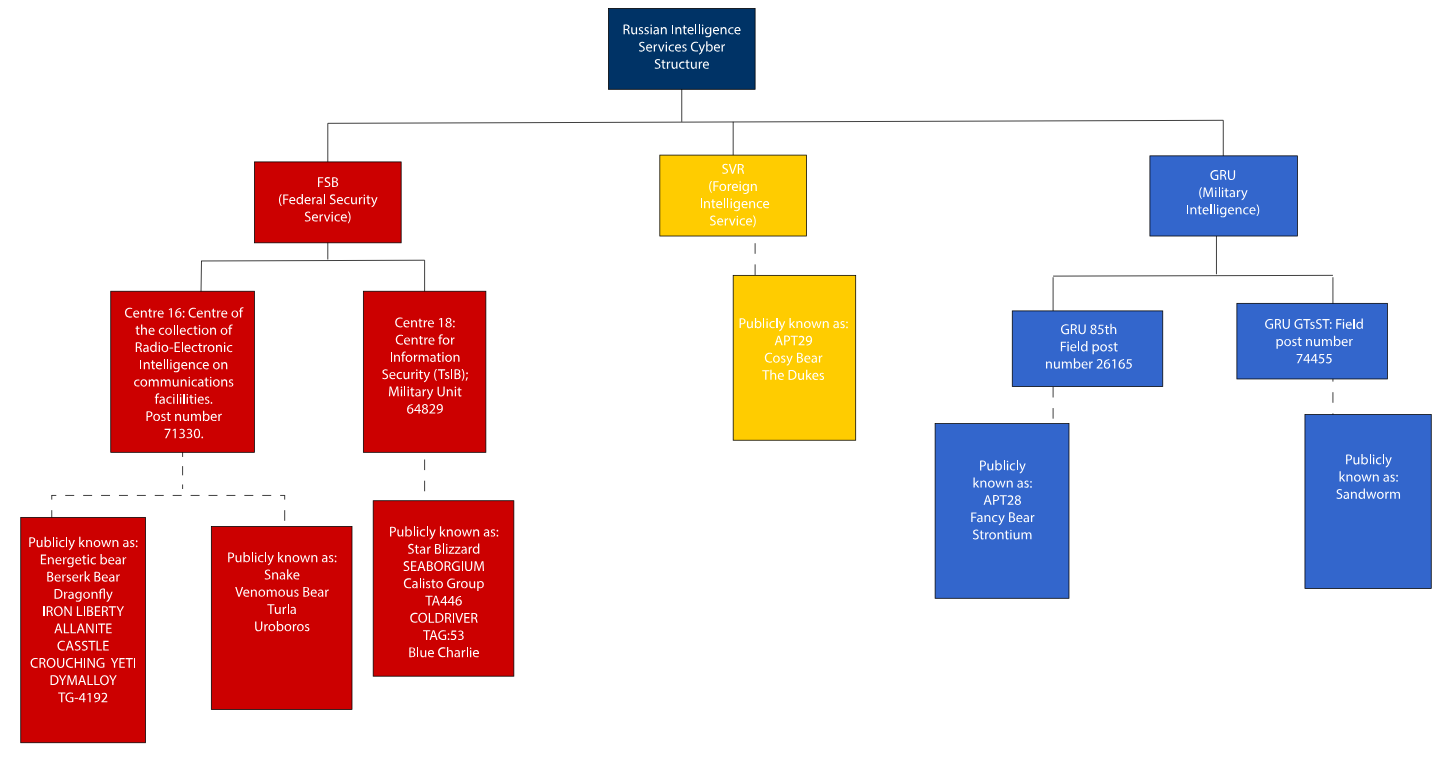
Microsoft says Turla operators are using the ISPs providing internet connectivity to foreign embassies for adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) attacks.
They select specific targets, redirect them to an ISP captive portal, break their HTTPS traffic, and then prompt them to install updated certificates disguised as an update for the Kaspersky antivirus.
The so-called "antivirus update" installs a new root certificate on the victim's computer and a malware strain called ApolloShadow.
The malware relaxes firewalls, and the root certificate legitimizes its malicious traffic.
Microsoft's security team believes Turla uses ApolloShadow to allow further lateral movement into the embassy network from the infected device. It also believes Turla may be performing TLS/SSL stripping at the ISP level to break a victim's browsing encryption and expose traffic and credentials in clear text.

Microsoft didn't say which embassies Turla attacked, but taking into account that Turla used a "fake Kaspersky update" cover, my money is on Russian-friendly countries from Africa, the Middle East, and LATAM that still use the software, mostly banned from official government use across most Western democracies.
The Microsoft report also included loads of recommendations for embassy IT teams on how to secure their internet connections when operating inside rogue or unfriendly states.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
SharePoint hacks targeted 90 US agencies: Chinese hackers have targeted more than 90 US state and local government agencies, per the Center for Internet Security. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Dollar Tree denies ransomware attack: Discount retailer Dollar Tree has denied getting hit by the INC ransomware group. The company said the gang most likely hit 99 Cents Only Stores, a chain that shut down last year. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Hamilton ransomware attack: The city of Hamilton in Canada says that the costs of dealing with and recovering from a ransomware attack last year have now reached CAD$18.3 million, or about $13.2 million. [Additional coverage in CTV News]
Russian pharmacies go down after cyberattack: Hundreds of pharmacies shut down on Tuesday across Russia after a cyberattack. Pharmacy chains Neopharm and Stolichki sent employees home as they dealt with IT outages. No group claimed responsibility for the hacks. [Additional coverage in United24 Media]
General tech and privacy
Dropbox retires password manager: File-sharing service Dropbox will retire its password management component on October 28.
Signal threatens to leave Australia: Signal Foundation president Meredith Whittaker says the secure messaging app will leave Australia if the government forces it to backdoor its encryption or demand encrypted user data. Whittaker made similar threats to pull Signal out of other countries that explored encryption backdoor. This included France, Sweden, and the UK. [Additional coverage in The Australian]
YouTube rolls out age estimation tech: YouTube is rolling out age estimate technology for US users. The new tech will use machine learning to sift through video history and searches and determine a user's approximate age. YouTube will use the technology to automatically move suspected kids into pre-teen and teen supervised accounts.
If 17yos had sufficient imagination they could search for “oral minoxidil” and “dishwasher error code” and get past all age verification
— Ted Underwood (@tedunderwood.me) 2025-07-30T11:42:43.458Z
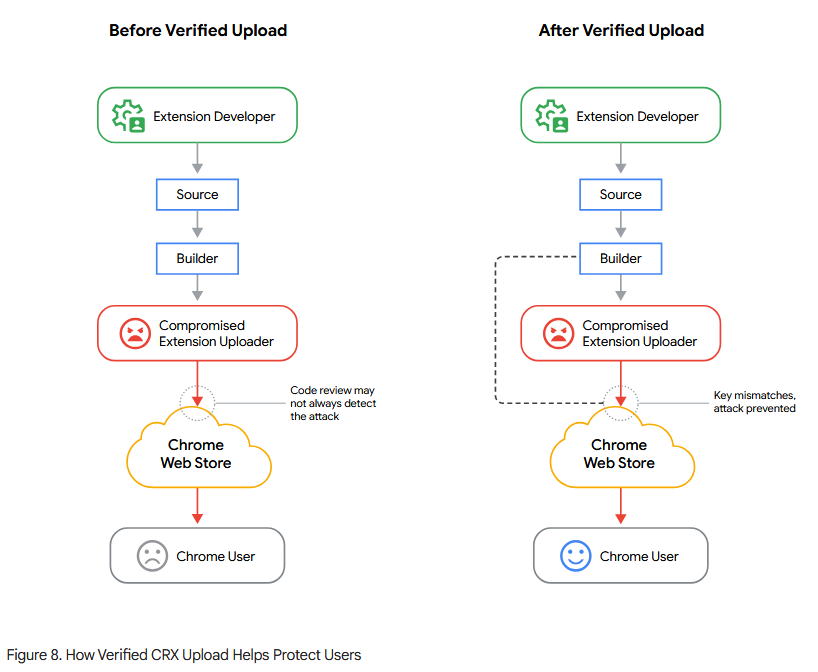
New Verified CRX Upload feature: Google has rolled out a new security feature for Chrome extension developers. The Verified CRX Upload feature enforces cryptographic signatures for all Chrome extension updates. It is designed to stop hackers from compromising developer accounts and publishing malicious updates. The attackers will have to provide a private RSA key before any extension update goes live. The Verified CRX Upload went live in May.
Government, politics, and policy
West Point dismisses Easterly: The US Department of Defense ordered military academy West Point to revoke a teaching position from former CISA Director Jen Easterly. The move comes after criticism from far-right conspiracy theory nutjob Laura Loomer. Easterly is the third major Biden-era figure to be fired after Loomer's criticism. The White House also dismissed former NSA and CyberCom lead Gen. Timothy Haugh and former NSA top lawyer April Falcon Doss. [Additional coverage in Politico/Easterly's response on LinkedIn]
Google didn't receive UK backdoor request: Google says that, unlike Apple, it did not receive any request from the British government to build a secret backdoor. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Support for Chat Control grows: According to former EU MP Patrick Breyer, the number of EU countries in favor of the EU Chat Control legislation is close to going over 50%.

UK Ofcom to investigate porn sites: The UK's communications watchdog launched an investigation into 34 pornography sites regarding their compliance with the UK Online Safety Act. Ofcom says the sites have failed to implement adequate age checks for UK visitors. The sites have over 9 million unique monthly UK visitors.
Australia extends teen social media ban to YouTube: The Australian government has extended its social media minimum age to cover YouTube. Children will have to be at least 16 to be able to register on the site. The government introduced a minimum age to access social media in November of last year. It was initially enforced only for Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, TikTok, and Twitter. [Additional coverage in ABC News]
Russia bans Speedtest: Russia's internet watchdog has banned bandwidth testing service Speedtest. Officials claim the service collects information on the layout and structure of Russia's internet capabilities and shares it with foreign intelligence agencies. The service is owned by American company Ookla. The process to ban the service got underway last October and was backed by Russia's intelligence agency, the FSB. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Russia moves electronic signature system to Max app: Russia will move its electronic document signing system from its official government portal to the new Max national messenger app. The Kremlin established the app through a law in June. The app is a clone of WhatsApp and is being built by Russian tech giant VK. Officials plan to integrate other government services into Max by October and transform it into an everything-app for Russians—in the model of China's WeChat. [Additional coverage in RBC]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Nucleus Security co-founder and COO, Scott Kuffer, joins Casey Ellis to chat about how vulnerability management evolved into quite a lot more than just patch prioritization.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Spain arrests hacker: Spanish and Catalan police have arrested a suspected hacker in the city of Roses. The suspect allegedly hacked Spanish banks, schools, and universities and sold the data on the dark web. The hacks took place last year. [Additional coverage in Diari de Girona]

CoinDCX employee arrested over hack: A 30-year-old software engineer has been arrested in connection with the hack of Indian cryptocurrency exchange CoinDCX. Rahul Agarwal is believed to have sold his work credentials to hackers for $17,000. Authorities say that shortly after the payment, hackers accessed CoinDCX's network through his account and stole $44 million worth of crypto assets. [Additional coverage in The Times of India]
NFT thief sentenced: A Canadian man was sentenced to one year in prison for stealing NFTs. Cameron Albert Redman hacked the Twitter accounts of popular artists in May 2022. Redman lured followers to pages offering NFTs. In reality, the pages contained code that stole cryptocurrency and NFTs from the visitors instead. US officials say Redman stole nearly $800,000 from more than 200 victims.
NZ SMS blaster sentenced: A Chinese national was sentenced to 100 hours of community work for driving with an SMS blaster in his car. Chenwei Zhang was arrested in Auckland last year. He was recruited by a Chinese gang via WeChat and paid $400/day to drive with an SMS blaster around the city. Zhang was the first-ever suspect detained in New Zealand for SMS blasting. [Additional coverage in CommRisk]
Germany confirms BlackSuit seizure: German police (finally) confirmed Operation Checkmate, the seizure of servers and domains operated by the BlackSuit ransomware group.
AI in malware ops: The Safety CLI team looks at how one threat actor has used AI to create a crypto drainer, and at the clues that AI was used.
Gaming-themed phishing: Brian Krebs has a story out on all the gaming-themed phishing campaigns that are currently underway on social media and Discord.
Microsoft OAuth phishing: Threat actors are impersonating various enterprises and delivering fake Microsoft OAuth applications to phish employees and steal credentials. The campaign is capable of bypassing MFA, per Proofpoint.
Pre-exploitation spikes: A GreyNoise report found that in 80% of reconnaissance spikes against enterprise gear, the spikes were followed by the publishing of a new CVE within six weeks, suggesting threat actors or researchers are testing their exploits ahead.
ICANN warns WebNic: ICANN has given the WebNic domain registrar three weeks to deal with security issues. ICANN says the registrar has failed to respond and address DNS abuse reports. The company manages more than half a million domains and primarily operates in the Asian market. If WebNic fails to address the issues, ICANN can terminate its registrar license. [Additional coverage in DomainNameWire/ICANN letter PDF]
Lionishackers profile: Outpost24 has published a profile on Lionishackers, a threat actor known for hacking and then selling enterprise databases on underground forums.
RMMs inside PDFs: WithSecure has documented a pretty smart malspam campaign that hides installation links to rogue RMM software inside PDF files. The campaign has been going on since November last year and also involves a social engineering component.
QR code brushing scams: Threat actors are sending unsolicited packages containing malicious QR codes. The FBI says the QR codes redirect users to sites that collect their financial information. The scheme is a variation of an older technique, adapted to use QR codes instead of written instructions. The FBI calls these "brushing scams."
"Link wrapping" phishing campaign: A threat actor is abusing Proofpoint and Intermedia link wrapping services for phishing campaigns. The attacker cloaks phishing links inside URLs used by the two companies to signal the link has been scanned and deemed safe. According to Cloudflare, the technique works because the malicious link has not been scanned by either company and is not flagged during the early phases of a campaign.
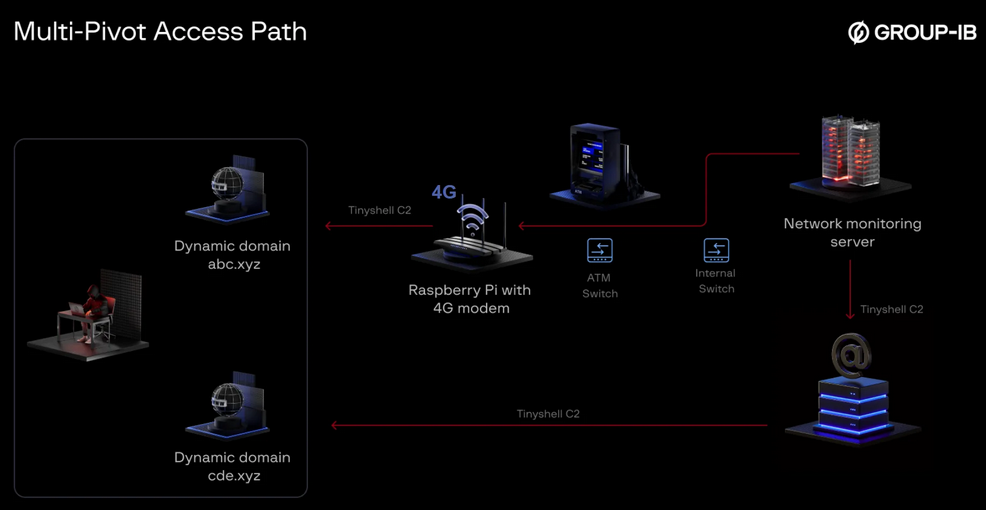
UNC2891 attempts ATM hack: A cybercrime group tried to hack a bank's ATM network using a rogue Raspberry Pi device connected to its internal network. The device was connected to the ATM's networking switch, and the hackers used its 4G modem to connect to the bank's network. Security firm Group-IB says the hackers used the device for lateral movement, but the main objective was to spoof ATM transactions and enable cash withdrawals at the bank's ATMs. Group-IB linked the hack to a group tracked as UNC2891.
Malware technical reports
Pay2Key campaigns hit Russia: Russian security firm F6 says Russian companies have been hit with the Pay2Key ransomware in campaigns that took place between March and May this year. F6 is flabbergasted that while other RaaS platforms ban users from attacking Russian targets, this one allows them.
LockBit ransomware: Broadcom's Symantec division looks at the recent DLL sideloading techniques used by LockBit ransomware clones in the wild.
4L4MD4r ransomware: QiAnXin researchers look at 4L4MD4r, a ransomware strain installed through the exploitation of a recent Microsoft SharePoint zero-day.
DoubleTrouble Android banking trojan: Zimperium has been tracking a new Android banking trojan named DoubleTrouble and targeting European banks.
GOLD BLADE's RedLoader: Sophos has a report on campaigns linked to the Gold Blade group that drop the RedLoader malware.
ArmouryLoader: Chinese security firm Antiy has published a technical report on new versions of the ArmouryLoader, a loader first spotted in 2024.
SilverFox: The Knownsec 404 team has published two reports on the SilverFox group and eponymous malware that's currently being used by cybercrime groups to target Chinese-speaking users.
VIP Keylogger: Seqrite has a report on a phishing campaign delivering the VIP Keylogger.
Raven Stealer: We're continuing our tradition of not putting out a newsletter edition without an infostealer report. Today, it's Raven Stealer, courtesy of CyFirma.
NOVABLIGHT: Another new infostealer is NOVABLIGHT. This one is coded in Node.js, offered as a MaaS, and run by French-speaking individuals.
Sponsor section
July 30 Webinar: Why 71% say reducing risk is hard – and how agentic AI can help. Register now.

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Israel-Iran wartime cyber: The Atlantic Council looks at the role that cyber operations played in the recent Israel-Iran military conflict.
"While these incidents may have caused harm or disruption in the short-term, they failed to provide any decisive military advantage. Instead, the impact was disproportionately felt by ordinary Iranian and Israeli citizens." Basically cyber is good for intel collection and info-ops. That's about it
— Catalin Cimpanu (@campuscodi.risky.biz) 2025-07-31T12:54:54.708Z
Similar to something I commented recently on regarding the use of cyber in Russia/Ukraine - that conflict, and underscored by Israel/Iran - showed how cyber is only a means to an end, or a “combined arm” in military parlance, but not the end itself, and should not be viewed that way.
— Mike Sec (@sudoinit0.bsky.social) 2025-07-30T18:59:23.996Z
The article mentions “power projection” and I think that’s the most important aspect, it gives somewhat symbolic victories or news stories to spin without crossing military red lines. It also gives inspiration to people with similar skills who might take part in current or future conflicts.
— gro.yrotsihkcahlaer@ yrotsihkcahlaer (@bsky.realhackhistory.org) 2025-07-31T13:00:11.455Z
PAN APT naming scheme: Palo Alto Networks has published a blog post on how its APT naming scheme works.
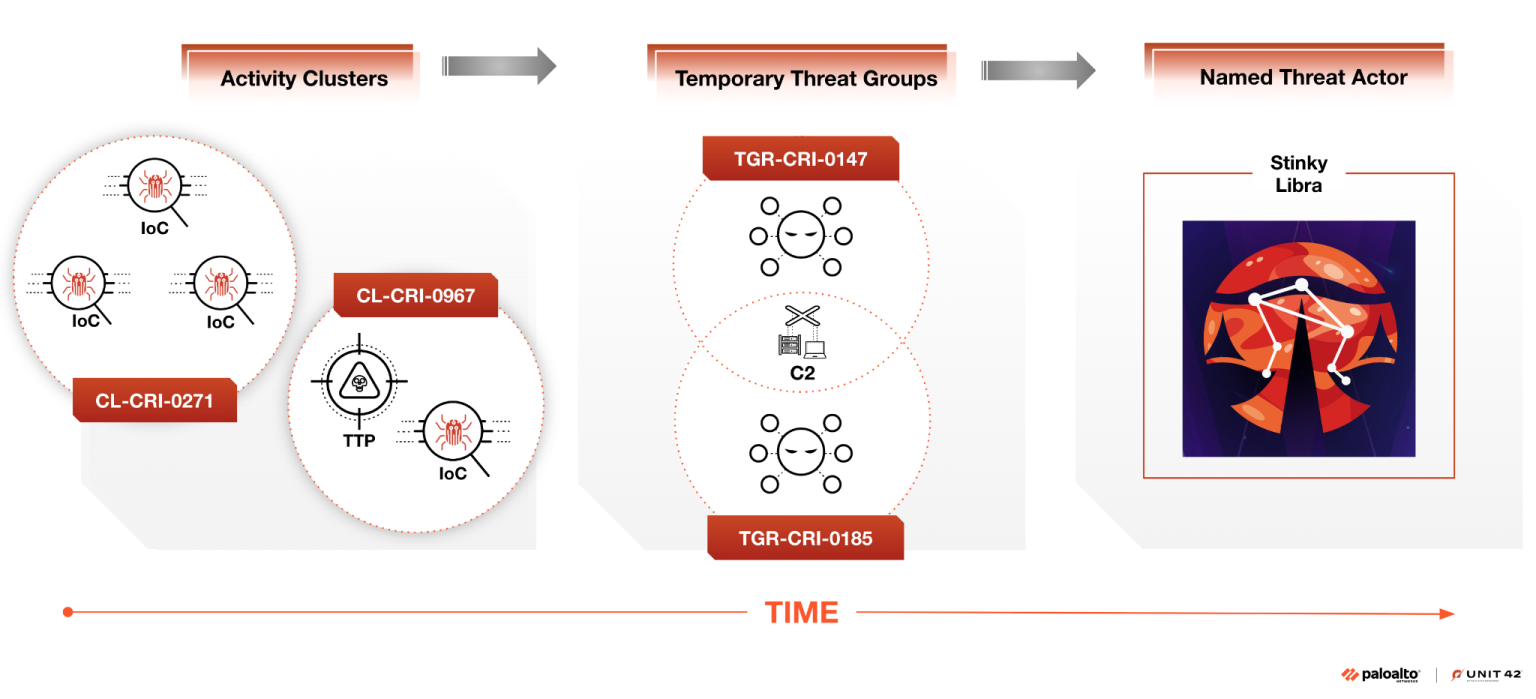
Liminal Panda (CL-STA-0969): A cyber-espionage group is hacking telcos across Southeast Asia to collect location data from mobile devices. Palo Alto Networks says the group maintained a high level of OPSEC and favored stealth over access and exfiltration. Most of the hacks took place last year. The attacks were linked to a group known as Liminal Panda.
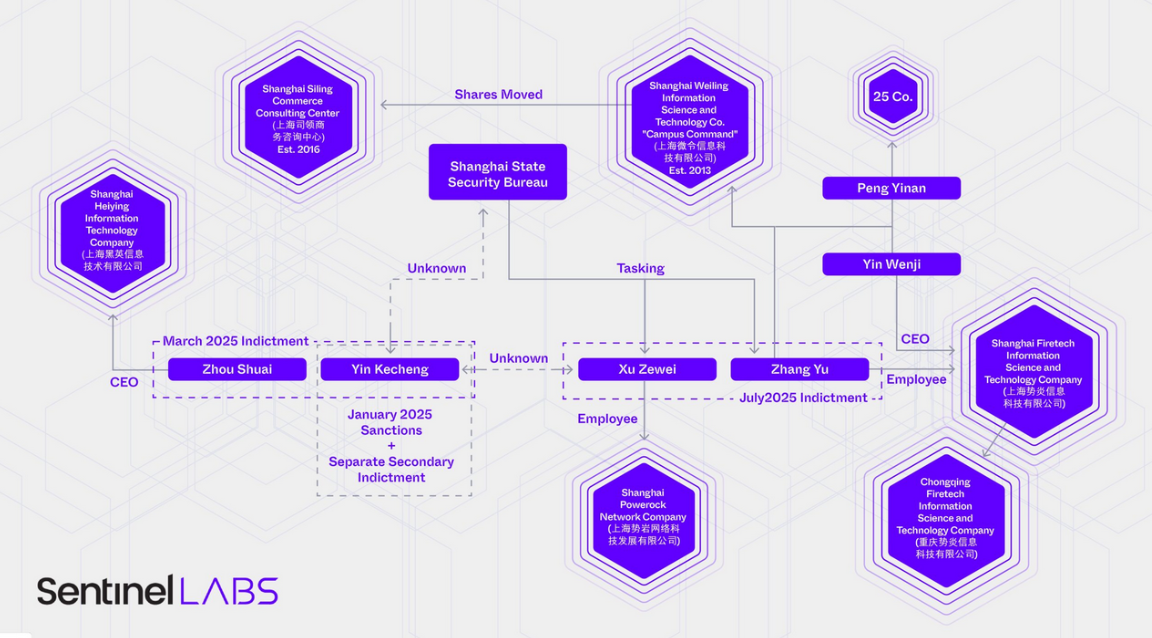
Hafnium patents: Front companies associated with the Hafnium Chinese cyber-espionage group own almost a dozen patents for forensics and data collection technologies. The patents cover the acquisition of encrypted endpoint data, mobile forensics, and the collection of network device traffic. SentinelOne believes the front companies are involved in more than just offensive cyber operations for the MSS.
MAPP leak investigation: The Natto Thoughts team looks at the so-called MAPP leak that led to a recent SharePoint zero-day being exploited in the wild. The report looks at what Chinese vendors are in the program and their respective reporting requirement levels to the Chinese government.
APT28's LAMEHUG: Logpoint researchers have published a technical analysis of LAMEHUG, a new malware strain used by Russian group APT28 in recent attacks against Ukrainian government entities.
Storm-2603 ransomware operations: Check Point has published a report on the previous ransomware attacks carried out by the Storm-2603 APT group. The group is one of the three Chinese APTs that exploited the ToolShell SharePoint zero-day last month. These attacks ended with the deployment of LockBit Black and Warlock/X2anylock ransomware strains.
Remote DPRK worker schemes: The DomainTools security team has a pretty comprehensive report on how North Korea runs its remote IT worker schemes.
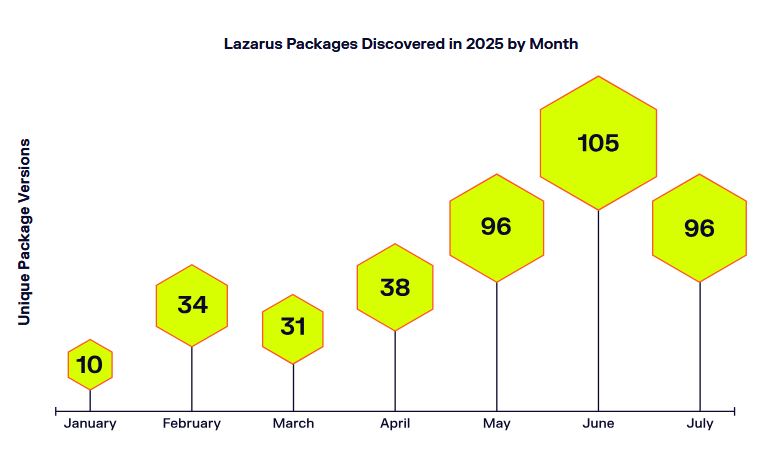
Lazarus FOSS activity: North Korean hackers were linked to 234 malicious packages uploaded on the npm and PyPI portals. Most contained infostealers that were designed to collect credentials from the cryptocurrency developer scene. Sonatype says the campaign could have infected up to 36,000 victims.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
TP-Link tells customers to ditch faulty routers: TP-Link has urged customers to ditch their old Archer C50 routers and upgrade to new devices. The routers are End-of-Life and shipped with hardcoded static encryption keys in their firmware (CVE-2025-6982). The keys can allow attackers to access administrative credentials, Wi-Fi passwords, and other internal settings. This is a known security flaw for many TP-Link models.
Dahua Hero camera vulns: Bitdefender researchers have found two vulnerabilities in Dahua Hero C1 security cameras.
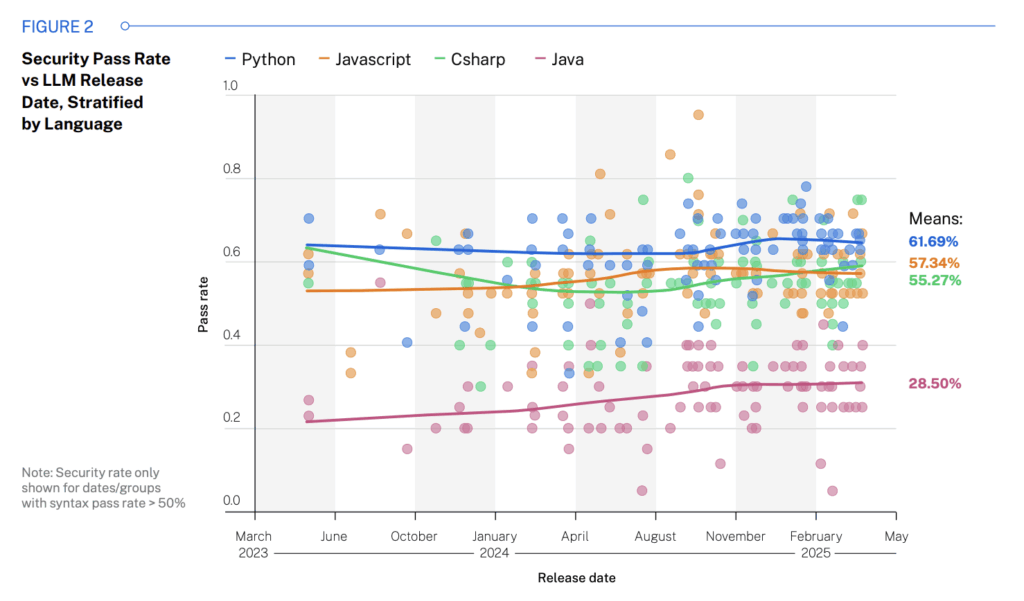
genAIs recommend insecure code: Generative AI models have recommended insecure source code for 45% of tasks. According to Veracode, Java code failed security checks the most, with a 72% failure rate. The Veracode study analyzed outputs from more than 100 LLMs released over the past three years.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: BforeAI, Booz Allen, Center for Internet Security, Check Point, Cisco Talos, Comparitech, Commvault, Gen Digital, Google Cloud, IBM, Malwarebytes, Palo Alto Networks, Radware, Veracode, and VulnCheck have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Acquisition news: Palo Alto Networks has agreed to acquire Israeli security firm CyberArk in a cash-and-stock deal. CyberArk shareholders will receive $45.00 in cash and 2.2 shares of Palo Alto Networks common stock for each CyberArk share. The transaction will close during the second half of next year.
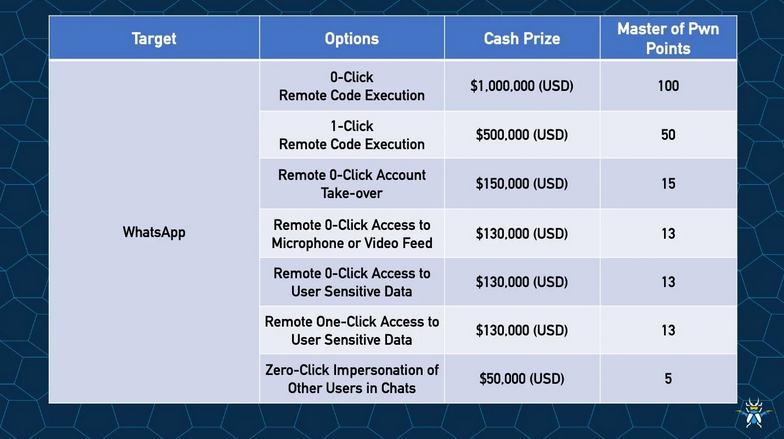
Pwn2Own Ireland returns: The Pwn2Own hacking contest is offering rewards of up to $1 million for zero-click WhatsApp exploits. One-click exploits will be awarded half the reward. The Pwn2Own hacking contest is scheduled to take place in Cork, Ireland, at the end of October.
Zero Trust microsegmentation guide: CISA has released a guide for the microsegmentation of Zero Trust networks.
New tool— Eviction Strategies Tool: CISA has released the Eviction Strategies Tool, a web tool and database to help security teams during the eviction phase of an incident response.
New tool—Thorium: CISA has released Thorium, a malware analysis platform. The platform's code is also on GitHub.
New tool—Censys Chrome extension: The Censys team has released an official Chrome extension for easier interaction with its search engine.
New tool—Autoswagger: Security firm Intruder has released Autoswagger, a command-line tool designed to discover, parse, and test for unauthenticated endpoints.
New tool—machofile: Security researcher Pasquale Stirparo has released machofile, a Python module to parse Mach-O binary files, with a focus on malware analysis and reverse engineering.
Almost 2y ago, finally making public some updates. Current features are: - Parse Mach-O Header, Load Commands, File Segments Dylib Commands, Dylib List - Segment entropy calculation - Extract imported functions and exported Symbols - Extract Entry point, UUID, Version Information 2/3
— Pasquale Stirparo 🇺🇦 🇪🇺 (@pstirparo.bsky.social) 2025-07-30T14:11:38.225Z
Le Tour du Hack 2025 videos: Talks from the Le Tour du Hack 2025 security conference, which took place this May, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about how the recent SharePoint exploitation is a blow-by-blow repeat of the 2021 Microsoft Exchange mass compromise event. The international response to that clearly didn't deter Chinese hackers, so it is time to try something different.




