Risky Bulletin: Payment card NFC relay attacks spread across Russia
In other news: Hacker Pompompourin to be resentenced; a Chinese APT pulls off another supply chain attack; new cookie sandwich technique.

This newsletter is brought to you by Resourcely, the company that can help you manage Terraform securely. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Russians have lost over 40 million rubles (~$400,000) to a new type of scheme that steals their payment card NFC data and relays it to a remote threat actor, who then empties their accounts.
Russian security firm FACCT says it detected over 400 NFC relay attacks over the past two months alone, suggesting the scheme is gaining popularity with criminal gangs.
NFC cloning and relay attacks were first seen in Czechia in late 2023 and spread to Russian banks in August of last year.
The scheme works by tricking users into installing a malicious Android app on their devices using various lures, such as the need to secure hacked bank or government accounts.
The malicious apps contain a version of NFCGate, an open-source app developed for academic research that can copy and relay a card's NFC data stream to a remote device.
Attackers use the malicious app to prompt users to scan their cards and even enter their PIN codes. The data is then sent to a remote smartphone paired with NFCGate.
Attackers use the data to withdraw funds from ATMs in real time, or they tokenize the NFC stream and use it for online transactions at a later date.
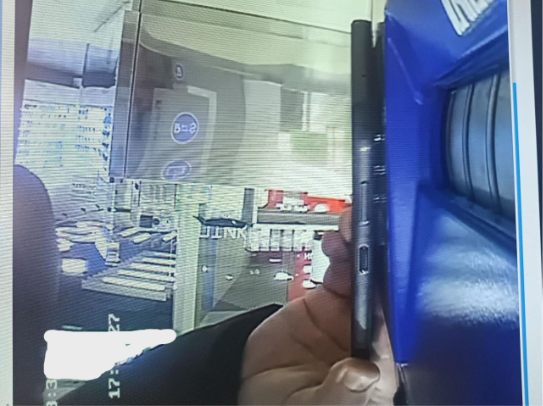

FACCT says its threat intel analysts have detected increased chatter on underground cybercrime forums about the use of NFCGate.
Recent discussions also mention the possibility of setting up Malware-as-a-Service portals designed around the app and its NFC cloning and relaying capabilities.
This confirms ESET's initial fears back in 2024 that the new technique would quickly spread to more regions as cybercriminals would learn and become proficient at using the technique.
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Conduent cyberattack: Government technology contractor Conduent has restored systems after a cyberattack crippled some services at the start of the year. The company services state governments and provides technology for programs involving Medicaid, child support, food assistance, and more. The incident has impacted Conduent services in Oklahoma and Wisconsin. [Additional coverage in The Record]
ScriptAPI hacks: A threat actor has hacked over 500 websites and added malicious scripts that create hidden links for black hat SEO purposes. According to security firm C/Side, the hacking campaign has impacted websites hosted on a wide variety of platforms, such as WordPress, PHP forums, and ASP.NET. Some of the hacked websites belong to national governments and major universities. The campaign's malicious code is loaded from the same ScriptAPI[.]dev domain.
Georgia leak: A mysterious Elasticsearch database containing the personal data for the entire country of Georgia appeared online and was shortly taken down, according to CyberNews.
General tech and privacy
Let's Encrypt stops email notifications: Let's Encrypt will stop sending email notifications for expired domains starting June 4 this year. The organization says sending the emails costs it tens of thousands of US dollars each year. It also wants to stop storing millions of email addresses to improve customer privacy.
Apple Intelligence goes default: Apple is forcibly enabling its kinda inaccurate AI tech (Apple Intelligence) by default for iOS 18.3 and macOS 15.3 users.
Reddit subs are banning Twitter links: Over 50 Reddit communities are now blocking users from posting Twitter links. Some have cited legitimate reasons, while others said the ban is a protest to Musk's Nazi salute during Trump's inauguration ceremony. [Additional coverage in NBC]
LinkedIn sued for training AI on DMs: A group of LinkedIn Premium users filed a lawsuit against Microsoft for using their private messages to train its AI models. The lawsuit alleges Microsoft trained the data without notifying users and providing a way to opt out. Users claim that when the company's actions were revealed, it silently changed its privacy policy to justify its actions. [Additional coverage in the BBC]
UK antitrust body now led by Amazon boss: The indomitable Cory Doctorow has published a report on how a former Amazon UK boss is now the leader of the UK's Competitions and Markets Authority, the antitrust agency with the best investigative team in the world and whose work is at the base of many antitrust cases since its reports are shared with similar authorities in other countries.
"The CMA is the global convener and ringleader in tech antitrust, in other words. Smaller and/or poorer countries that lack the resources to investigate and build a case against US Big Tech companies have been able to copy-paste the work of the CMA and hold these companies to account. The CMA invites (or used to invite) all of these competition regulators to its HQ in Canary Wharf for conferences where they plan global strategy against these monopolists."
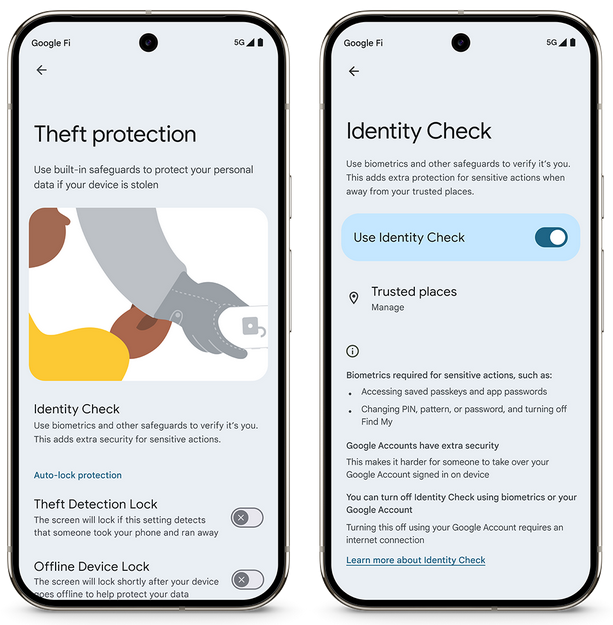
Android Identity Check: Google has announced a new Android security feature named Identity Check that will ask users to authenticate using biometrics when the user's phone travels outside a common trusted location. The new authentication prompt will show up when the user wants to access a phone's settings and account data. Google says the feature is designed to protect the user's data in the case of a device's theft.
Government, politics, and policy
Digital driving license coming to UK: The UK government is launching digital versions of various identity documents for its citizens. Digital driver's licenses and veteran cards will launch later this year, with other documents being in the works. The government is also launching a digital wallet app where the documents can be stored and used to prove a user's age from their phone in shops or online.
EU calls out Russian disinformation: The EU has called out Russia over its disinformation campaigns inside EU democratic countries. Sources told me the Russian government is in tears of fear and shame. </s>
Easterly interview: Wired's Lily Hay Newman has published an interview with former CISA Director Jen Easterly on her legacy and last days in office.
FISA 702 searches need a warrant: A US federal district court ruled that searches in a government database holding data collected under FISA Section 702 require a warrant.
Incoming social media crackdown in Russia: Russia's internet watchdog plans to require social media networks to block access to popular accounts that have not provided their real name to the government. The Roskomnadzor ordered social media personalities with over 10,000 subscribers to register their real names with the agency by the start of this year. Currently, accounts that have failed to do so cannot monetize their channels through ads. The provision covers online bloggers, Telegram channels, and social media accounts. [Additional coverage in TASS]
Pakistan introduces social media bill: Pakistan's government has introduced a bill that would jail individuals who spread misinformation on social media. The new Prevention of Electronic Crimes Act introduces prison sentences of up to three years for offenders. It also forces social media companies to register with the local government or face permanent bans. The bill has already passed through the country's lower house of parliament. [Additional coverage in the Hindustan Times]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Travis McPeak, the CEO and founder of Resourcely, explains that companies now realize they have a ton of cloud-related technical debt because of the success of cloud posture management products. Travis talks about different approaches he has seen to tackle rampant cloud misconfigurations.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Pompompurin to be resentenced: An appeals court has vacated a sentence handed down to the administrator of cybercrime platform BreachForums last year. Brian Connor Fitzpatrick, known online as Pompompurin, was initially sentenced to time served and 20 years of supervised release. The prosecution has appealed the judge's initial decision and his case was now sent back to a lower court for resentencing. DOJ prosecutors claim the judge abused her discretion in handing down a sentence far lower than the 15 years minimum the initial charges required. [Additional coverage in DataBreaches.net]
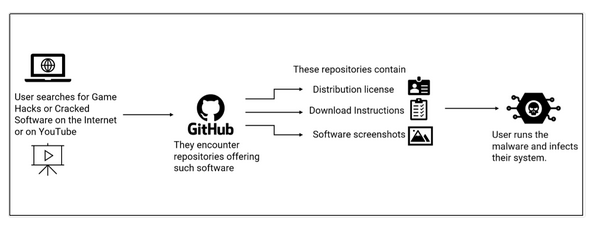
GitHub abused for crack hosting: A McAfee report draws attention to threat actors abusing GitHub to host malware-infested cracks, hacking, and crypto tools.
DPRK workers behind data extortions: The FBI says that North Korean IT workers are abusing their positions inside Western companies to steal data for future extortions. Officials say North Korean workers have released proprietary data in the public domain after ransom requests were not met. Besides extortions, the FBI says North Korean IT workers have also used their inside roles to steal access credentials, facilitate cybercrime activity and even conduct revenue-generating activity.
Fortinet leak data: Security researcher Kevin Beaumont has extracted available emails from the Belsen Group's Fortinet leak. The emails can be used to send notifications to companies that had Fortinet firewall configs and credentials stolen back in 2022.
GhostGPT: Abnormal Security has discovered GhostGPT, a malicious AI chatbot designed to cater to cybercriminals, working on top of a jailbroken ChatGPT wrapper.
Google Cloud Threat Horizons Report #11: In the eleventh edition of its threat and trends report [PDF], the Google Cloud security team looks at UNC2165, a ransomware group that uses the cloud to store payloads, and TRIPLESTRENGTH, a threat actor involved in cryptomining, initial access server brokerage, and ransomware attacks against cloud systems.
FunkSec gets funky: December 2024 was the most active month on record for ransomware groups. Ransomware gangs have published over 570 victims on dark web leak sites, breaking all previous records. A new group named FunkSec was the most active threat actor. The group listed over 100 victims on its own and was responsible for almost a fifth of all attacks.
Dark Gaboon: Russian security firm Positive Technologies has discovered a new financially motivated threat actor that has targeted the financial departments of Russian companies for almost two years. The new DarkGaboon group is believed to have started operations in May 2023. The company says DarkGaboon is well versed in the peculiarities of Russian document names, and is also familiar with the Russian vocabulary. The group's primary tool is an off-the-shelf tool named the Revenge RAT.
Crazy Evil cryptoscam gang: Recorded Future says that a massive cybercrime operation named Crazy Evil is behind a massive network of cryptocurrency scams and phishing sites. The group has been active since 2021 and includes six subteams specialized in targeting victims using different techniques. Their primary targets are cryptocurrency enthusiasts, NFT traders, and online gaming professionals.
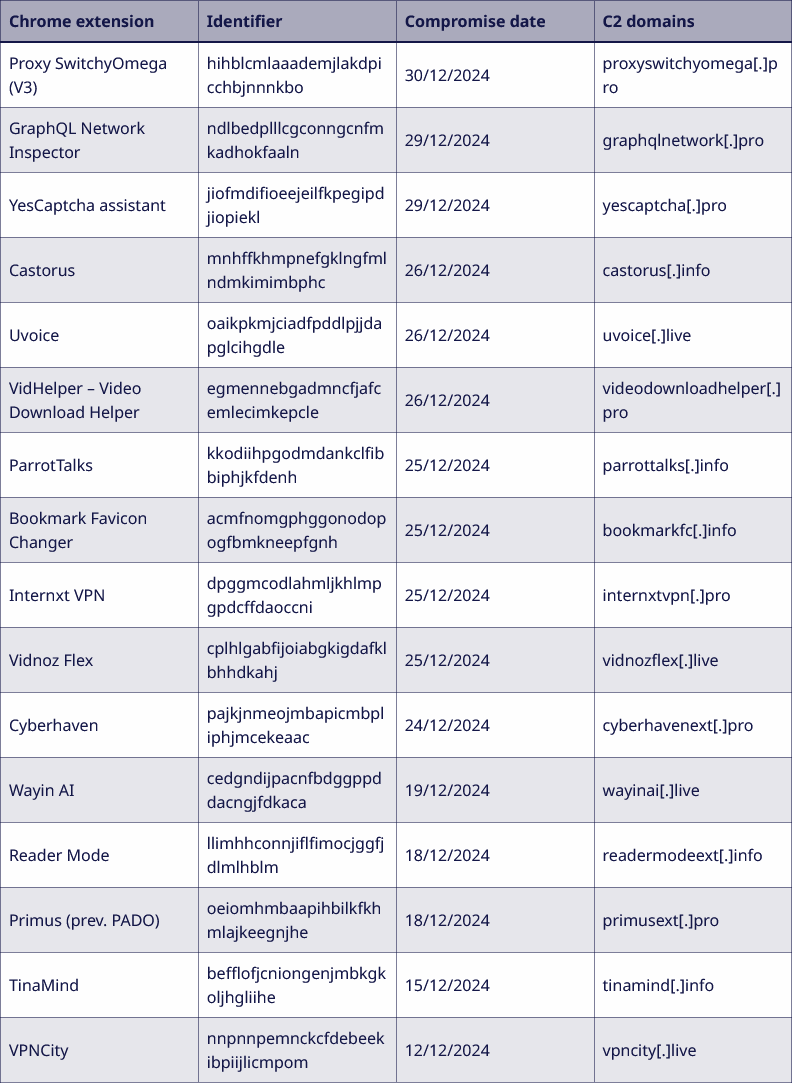
Chrome extension dev phishing campaign: French security firm Sekoia says that a hack of the CyberHaven Chrome extension last year was part of a larger campaign that compromised 15 other extensions as well. The attackers used a malicious OAuth application to harvest the developer's credentials and then push malicious versions of the extensions. The hacked extensions were then used to collect credentials for Facebook for Business and ChatGPT. Sekoia says the threat actor behind the hacks has been going after Chrome extension developers since at least 2023.
Malware technical reports
Nnice ransomware: CyFirma researchers have discovered a new ransomware strain named Nnice. It's primarily used to target end users rather than enterprises.
HellCat and Morpheus: SentinelOne says two RaaS platforms named HellCat and Morpheus are using an identical payload, suggesting their platforms are using a shared codebase or possibly a shared builder.
Lumma Stealer: Netskope researchers look at a recent Lumma Stealer campaign using fake CAPTCHAs to infect users. There's also one of these campaigns impersonating Reddit.
J-magic backdoor: Security researchers have discovered an advanced piece of malware on Juniper enterprise routers and VPN gateways. Named J-magic, the backdoor has been used in attacks since September 2023. Lumen says J-magic uses five different predefined magic packets and a certificate-based challenge before allowing attackers to connect to the compromised devices. The company has not linked the malware to any known threat actor.
AceCryptor adoption goes down: ESET says the AceCryptor malware crypting service is slowly declining in popularity and adoption.
Sponsor section
Resourcely is releasing Campaigns, a tool for identifying and remediating vulnerabilities in your existing infrastructure. Want to burn down your CSPM findings? Try out Campaigns today!

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Seashell Blizzard resumes wiper attacks: Microsoft says that a Russian APT group known as Seashell Blizzard (aka Sandworm) has been observed conducting spear-phishing campaigns against the European energy sector. The group has also returned to deploying wipers in its intrusions, such as WalnutWipe and SharpWipe.
PlushDaemon pulls a supply chain attack: A Chinese APT group has compromised South Korean VPN provider IPany and replaced its installer with malware. The compromise lasted from November 2023 to May 2024. Users who downloaded the VPN client were infected with a feature-rich backdoor named SlowStepper. ESET says the new PlushDaemon group was also involved in operations that hijacked legitimate updates for some Chinese applications.
Sichuan Juxinhe: Natto Thoughts has published a profile on Sichuan Juxinhe, the Chinese MSS front company sanctioned by the US last week for its role in Salt Typhoon operations.

Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Cloudflare CDN vulnerability: A 15-year-old security researcher has found a zero-click vulnerability in the Cloudflare CDN that can allow an attacker to determine in which data center an item was cached and get a general idea of where a user is located. [Additional coverage in 404 Media]
Oracle CPU: The quarterly Oracle security updates are out, with patches for 318 vulnerabilities.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released three security updates, including a patch for a ClamAV bug with a public exploit.
Jenkins update: The Jenkins project has released a security update to fix vulnerabilities in eight plugins.
Mastercard DNS typo: Mastercard had a typo in its DNS records for almost five years until security Philippe Caturegli discovered the issue earlier this year. As a thank you, he received a letter from Mastercard's legal team to take down a LinkedIn post describing the issue. [Additional coverage in KrebsOnSecurity]
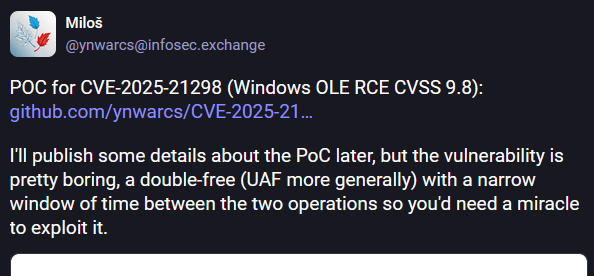
OLE RCE POC: Serbian security researcher Miloš has published a POC for CVE-2025-21298, a zero-click remote code execution in Windows OLE that can be exploited via malicious emails sent to Outlook inboxes. According to the researcher, attackers would "need a miracle to exploit it."
WP plugin and theme unpatched bugs: Patchstack researchers have disclosed details about two unpatched vulnerabilities in the RealHome theme (premium version) and one of its plugins, Easy Real Estate. They're not exploited in the wild for now, but they also don't have a patch coming, so they might need to be nuked from existing sites. Both issues are an unauthenticated elevation of privilege that can allow threat actors to take control of affected sites with a few HTTP requests.
Vulnerabilities in Maven repo managers: The GitHub security team has discovered vulnerabilities that can poison the local artifacts of third-party Maven Central repo managers, such as Reposilite, Sonatype Nexus, and JFrog Artifactory.
"All tested solutions not only store and serve artifacts, but also perform complex parsing and indexing operations on them. Therefore, a specially crafted artifact can be used to attack the repository manager that processes it. This opens a possibility for XSS, XXE, archive expansion, and path traversal attacks."
SkibidiJava vulnerability: Checkmarx's Eilon Cohen has found a vulnerability in Java's core collection objects that can be used for denial of service attacks.
"We named this SkibidiJava as a nod to how Java's automatic method calls can create bizarrely dangerous behaviors in complex environments, turning normal and naive operations into, well, unexpected skibidi chaos."
New AMSI bypass: IBM X-Force researcher Joshua Magri has published details and a POC for a new bypass of the Windows Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI). The new technique uses Common Language Runtime (CLR) customizations.
Next.js cache poisoning attack: Security researcher Allam Rachid has discovered a cache poisoning attack (CVE-2024-46982) in Next.js, one of today's most popular JavaScript frameworks. Rachid says the technique allowed him to mount XSS attacks on web apps built using the framework, such as crypto, e-commerce, and fintech backends. The researchers made a six-figure sum by reporting the issue to multiple bug bounty programs before the issue was patched in Next.js last October.
Cookie sandwich technique: PortSwigger researchers have developed a new technique called the "cookie sandwich" that can be used to trick servers into exposing sensitive cookies to malicious client-side scripts. The attack manipulates how web servers parse and handle cookies that contain special characters. The technique also bypasses HttpOnly, a security flag that blocks local scripts from interacting with cookies. Threat actors can abuse the cookie sandwich technique to exfiltrate cookies from servers, browsers, and various backends.
RANsacked LTE/5G vulnerabilities: A team of academics from two US universities has developed a new telco infrastructure fuzzing engine named RANsacked that discovered 119 vulnerabilities in LTE and 5G RAN-core infrastructure.
"We discover 119 vulnerabilities in LTE/5G core infrastructure, each of which can result in persistent denial of cell service to an entire metropolitan area or city and some of which can be used to remotely compromise and access the cellular core. Our research covers seven LTE implementations (Open5GS, Magma, OpenAirInterface, Athonet, SD-Core, NextEPC, srsRAN) and three 5G implementations (Open5GS, Magma, OpenAirInterface); we find vulnerabilities in every single LTE/5G implementation tested."
Subaru vulnerabilities: Two security researchers have found a vulnerability in Subaru's STARLINK component that allowed them to track, steal PII data, and interact with affected vehicles across the US, Canada, and Japan. Researchers say they could start and stop any vehicle, lock or unlock its doors, and even retrieve the car's position with an accuracy of up to 5 meters. Exploiting the vulnerability required only minimal data, such as an email address, phone number, or license plate. The issue was patched last year. Subaru says it did not find evidence it was ever exploited.
jQuery exploitation: CISA says that a 2020 XSS vulnerability in the jQuery framework tracked as CVE-2010-11023 is now being exploited in the wild.
Invanti attacks: CISA has published a report on four Ivanti vulnerabilities that were exploited in the wild last September as part of two exploit chains.
"According to CISA and trusted third-party incident response data, threat actors chained the listed vulnerabilities to gain initial access, conduct remote code execution (RCE), obtain credentials, and implant webshells on victim networks. The actors' primary exploit paths were two vulnerability chains. One exploit chain leveraged CVE-2024-8963 in conjunction with CVE-2024-8190 and CVE-2024-9380 and the other exploited CVE-2024-8963 and CVE-2024-9379. In one confirmed compromise, the actors moved laterally to two servers."
SonicWall VPN auth bypass: BishopFox has published a detailed write-up on CVE-2024-53704, an authentication bypass affecting the SSL VPN component of SonicWall firewalls.
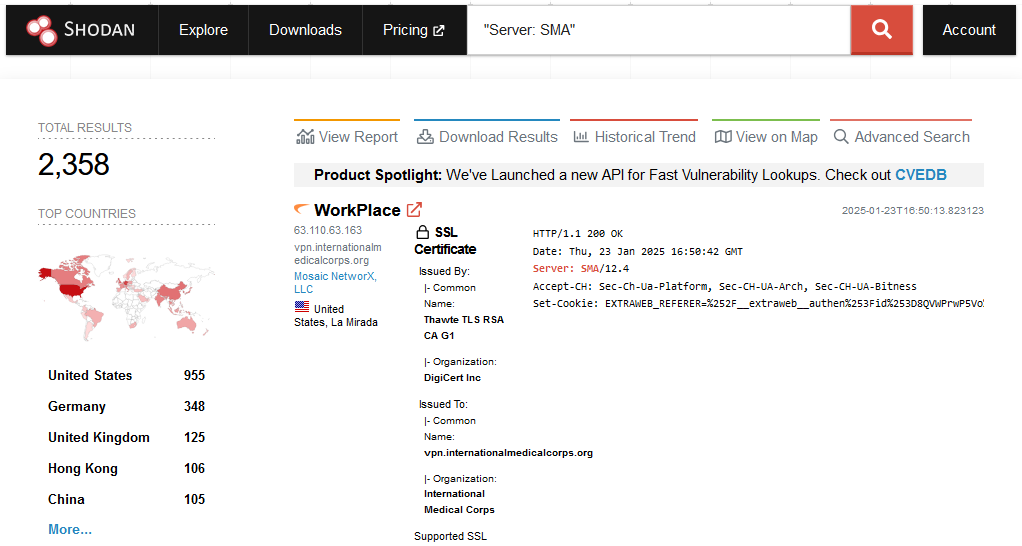
New SonicWall SMA zero-day: SonicWall has released a security update to patch an actively exploited zero-day in its SMA1000 security gateways. Tracked as CVE-2025-23006, the zero-day is a pre-authentication deserialization attack that can run malicious commands on the device's underlying OS. The zero-day has a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10. Over 2,300 SonicWall SMA appliances are currently exposed on the internet and vulnerable to attacks.
Infosec industry
New tool—convoC2: Security researcher Fabio Cinicolo has released convoC2, a C&C server to allow red teamers to execute system commands on compromised hosts through Microsoft Teams.
Threat/trend reports: Black Kite, Check Point, Google Cloud [PDF], Legit Security, NCC Group, Nisos, and Trustwave have published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.

Risky Business Podcasts
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Adam Boileau talk about the continued importance of hack and leak operations. They didn't really affect the recent US presidential election, but they are still a powerful tool for vested interests to influence public policy.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about the evolution of Russian cyber operations during its invasion of Ukraine.




