Risky Bulletin: Looking at Biden's last cyber executive order
In other news: Threat actor leaks 15k Fortinet firewall configs; US Treasury sanctions company behind Salt Typhoon; FTC settles with GoDaddy over cybersecurity failures.

This newsletter is brought to you by Resourcely, the company that can help you manage Terraform securely. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
In its last days in office last week, the Biden administration signed an executive order (EO 14144) with new requirements and standards for strengthening the US' cybersecurity defenses and ecosystem.
This is the administration's second cyber executive order after EO 14028 from May 2021.
Below, we're gonna go over all the main points included in last week's release. The list is going through the EO from top to bottom. Items are not listed based on "importance."
- All government contractors must submit their software for attestation for use on government systems via the CISA Repository for Software Attestation and Artifacts (RSAA) portal. This measure is designed to improve software supply chains for contracted government software and make sure vendors are using secure development patterns and patching old vulnerabilities in their code, including for smaller components.
- There's one paragraph about open-source software in there too. This one directs the DHS to work with other relevant agencies to publish recommendations for federal agencies "on the use of security assessments and patching of open source software and best practices for contributing to open source software projects."
- Agencies will need to integrate cybersecurity supply chain risk management programs into enterprise-wide risk management activities.
- The White House has ordered agencies to start testing and even mass-deploying "commercial phishing-resistant standards such as WebAuthn."
- The White House has ordered the DHS and DOD to work together on new threat intel-sharing procedures. This one provision likely comes after several GAO reports have found that current inter-agency threat-sharing procedures were slow and ineffective, and information coming out of the DOD being extremely gatekept and hindered because of overzealous classification levels.
- The new threat intel-sharing program will aggregate data from the EDR and SOC platforms of all federal agencies so CISA can detect coordinated campaigns and other threats.
- New FedRAMP baselines to improve the security of government-contracted cloud systems.
- New cybersecurity contracting requirements for any government-procured space systems. These requirements cover the use of secure software and hardware, the use of encryption to protect incoming ground commands, command source authorization, and various other ways to ensure satellite commands can't be hijacked.
- A review and a yearly assessment of the US government's IP space.
- All agencies and IT service providers must use RPKI ROA and ROV. The White House previously recommended the use of RPKI ROAs last September. See here.
- All agencies and contractors must use in-transit encrypted DNS.
- All agencies must "encrypt email messages in transport and, where practical, use end-to-end encryption in order to protect messages from compromise."
- All agencies will have to use "transport encryption" for IM, voice, and video conferencing apps. If clients support it, E2EE must also be enabled by default.
- CISA will have to produce a list of software with post-quantum cryptography (PQC) protections, and agencies must start using and contracting software that's protected against future quantum computer attacks.
- The EO urges agencies to look into using hardware security modules, trusted execution environments, and other isolation technologies to protect their most sensitive encryption keys. FedRAMP, the OMB, and other agencies will have to put out new guidelines to encourage the new practice.
- In a move to address fraud gangs targeting government funds, the White House has directed the OMB to encourage the development of software solutions and government portals that accept "digital identity documents" to access public benefits programs.
- The EO directs agencies to run pilot programs with the private sector and test if AI can be used for cyber defense. From the EO, this should cover vulnerability detection and management, intel-sharing, threat detection, and IR.
- The White House has ordered a fresh batch of new NIST cybersecurity standards and best practices. Yey!
- Government contractors would have to follow any of NIST's new applicable and minimum cybersecurity practices.
- All IoT gear acquired by the government must have a US Cyber Trust Mark.
- All agencies will have to inventory all major information systems and provide the inventory to CISA.
- And, finally, the White House has made it easier for the Treasury to sanction foreign nationals and companies involved in malicious cyber activity targeting the US. Previously, such sanctions could be imposed only for certain types of activities.
The new Trump administration is being sworn in on the day this newsletter goes live. The new admin can revoke the executive order, but it is highly unlikely to happen since most of the EO deals with technical mumbo jumbo that's usually not at the center of US partisan conversations.
However, some are not sure about that and expect the EO to receive some pushback just because Republicans have this thing of undoing everything Democrats do, regardless of how good or bad it is. Kindergarten politics at its finest!
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
China's Treasury hack: Chinese state-sponsored hackers had direct access to over 400 laptops and desktop computers inside the US Treasury Department in a hack at the end of last year. The agency says the hackers stole over 3,000 unclassified documents outside of normal working hours to avoid detection. The intrusion targeted the agency's sanctions (OFAC) and foreign investment (CFIUS) bureaus. US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen's computer was one of the compromised systems. Intelligence officials attributed the hack to a group tracked as Silk Typhoon. [Additional coverage in Bloomberg]
Salt Typhoon hacks impacted govt first, telcos second: CISA Director Jen Easterly says the agency detected Salt Typhoon activity on federal networks before the group was spotted targeting American telcos. The early detection allowed investigators to seize one of the group's virtual private servers and spot the larger campaign targeting US telcos. Tips from the private sector also helped spot the attacks.
Otelier breach: Hotel management platform Otelier suffered a security breach after a threat actor breached the company's Amazon S3 cloud storage environment in July of last year. The attacker is believed to have stolen the personal data of millions of customers. Otelier's platform is used by over 10,000 hotels to manage reservations. It is used by big hotel chains such as Marriott, Hilton, and the Hyatt. The company has confirmed the breach, which allegedly took place via an employee's stolen Atlassian server credentials. [Additional coverage in Bleeping Computer]
General tech and privacy
FTC settles with GoDaddy over cybersecurity failures: Web hosting company GoDaddy has settled with the FTC in an investigation related to multiple security failures the company has suffered since 2018. The company has agreed to set up a robust security program and is prohibited from misleading customers about its security features. GoDaddy will have to roll out multi-factor authentication for customers and employees, remove outdated gear from its network, and protect its APIs. The agency did not impose a fine.
FTC privacy action against GM: The FTC has imposed a five-year ban on American carmaker General Motors on collecting and selling the private information of its customers. The agency's action comes after reports that GM sold geolocation data and driver behavior to insurance companies. The data was used to spike insurance rates for drivers based on their driving styles despite drivers not causing any accidents.
FTC fines Genshin Impact: The FTC has fined game developer Cognosphere $20 million for selling loot boxes to teens under 16 without parental consent in its Genshin Impact title.
GDPR complaints against Chinese apps: EU privacy group noyb has filed GDPR complaints against six Chinese apps for illegally transferring the personal data of EU citizens to China. The complaint lists TikTok, AliExpress, SHEIN, Temu, WeChat, and Xiaomi. The same agency has a long history of filing complaints against tech giants. Previous complaints have targeted Google, Facebook, Amazon, Mozilla, and Microsoft.
Google Search now requires JavaScript: Google is now requiring users to enable JavaScript in their browsers to access and use its search engine.
Government, politics, and policy
SCOTUS greenlights TikTok ban: The US Supreme Court upheld the US government's TikTok ban in a unanimous decision, ruling that the decision to ban the app on national security grounds does not go against the US Constitution's First Amendment. Incoming President Trump, who set the ban going in the first place, started to play Internet Jesus and promised to postpone the ban three months so TikTok has time to negotiate the sale of over 50% of its US branch to a US business. Good ol' mafia-style shakedown, right here. [Read SCOTUS ruling here/PDF] [Additional coverage in CNBC and Axios]
Calls for smaller CISA: In her nomination hearing, DHS secretary nominee Kristi Noem says she plans to make CISA a smaller and more nimble agency. The plan is to move CISA away from election misinformation and disinformation and refocus it on hunting and securing the country's critical infrastructure only. [Additional coverage in FNN]
FCC orders telcos to secure networks: The FCC has ordered telcos to secure their networks against foreign hacks, citing section 105 of the Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act (CALEA), which they have to abide by.
First FALCON deployment: A ransomware attack that hit Costa Rican oil refinery RECOPE was the first real-world deployment of a new US government IR team named the Foreign Assistance Leveraged for Cybersecurity Operational Needs, or FALCON. [Additional coverage in The Record]
EU healthcare cyber plan: The European Commission has unveiled a plan to strengthen the cybersecurity of hospitals and healthcare providers. Officials plan to build an EU-wide early warning service by 2026 that will deliver near-real-time alerts on potential cyber threats. The EU will also establish a rapid response service from trusted private service providers to help hospitals deal with cyber attacks. EU member states will also introduce Cybersecurity Vouchers to provide financial assistance to micro, small, and medium-sized hospitals and healthcare providers. [Full plan here]
Spyware proliferation: Almost 100 foreign governments have purchased advanced spyware designed to crack into cell phones. The head of the US government's counterintelligence agency says the mobile spyware market has seen a "huge growth" with "dozens of companies" selling various products. US NCSC head Michael Casey says nearly 20 new countries have acquired mobile spyware since April 2023, when the number was around 80 nations. [Additional coverage in BreakingDefense]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Travis McPeak, the CEO and founder of Resourcely, explains that companies are now realising they have a ton of cloud-related technical debt because of the success of cloud posture management products. Travis talks about different approaches he has seen to tackle rampant cloud misconfigurations.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Threat actor leaks 15k Fortinet firewall configs: A threat actor has leaked config files and login credentials for over 15,000 Fortinet firewalls. According to security researcher Kevin Beaumont, the data was collected in October 2022 using what was a zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2022–40684) at the time. Security researchers have extracted the IPs of all affected devices and are notifying affected organizations. The threat actor behind the leak calls itself the Belsen Group.
Ukraine phishing gang detained: Ukrainian police detained nine individuals suspected of running phishing campaigns via social media sites.
Fake hotel review scheme dismantled in Nigeria: Nigerian police have arrested 105 suspects who were part of an online scam group that tricked foreigners into posting fake hotel reviews. Officials say the group was led by four Chinese men who recruited and trained Nigerien men to act as technical representatives in the scheme. The gang tricked victims into posting fake reviews in exchange for money and even making bookings in some of the reviewed hotels, only to stop communications when payment was due.
Cyber fraud arrests in China: The Chinese government says it indicted over 67,000 on cyber fraud-related charges from January to November 2024, up almost 60% from the previous year, per China Daily. Officials have also promised to continue their crackdown, especially in northern Myanmar.
AWS Codefinger response: The AWS security team has published a blog post with advice on how to prevent and deal with Codefinger ransomware attacks that have been targeting AWS S3 buckets for the past weeks.
CISA cloud logs playbook: CISA has published a playbook on how organizations can fully employ the newly introduced logging capabilities in Microsoft Purview Audit (Standard) to better detect threats.
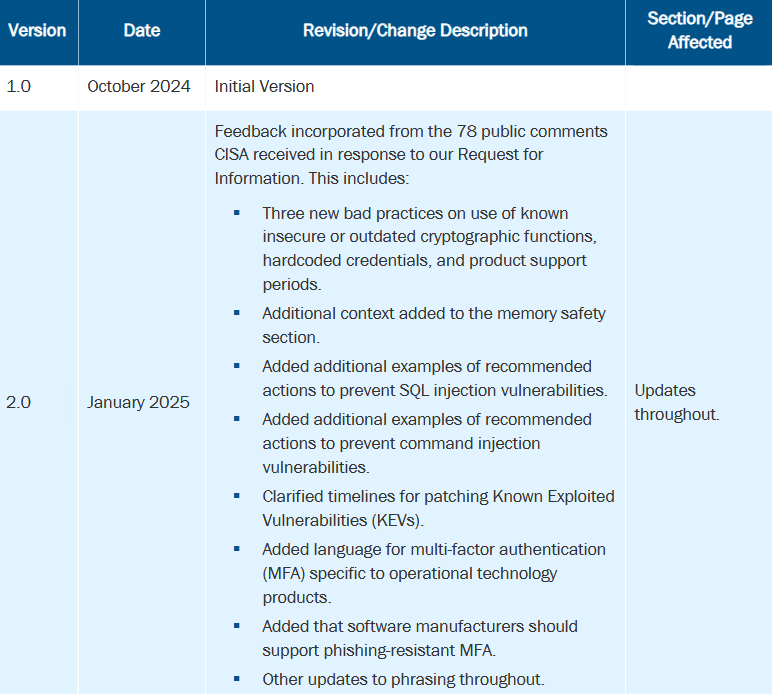
FBI security bad practices: The FBI has released version 2.0 of its Product Security Bad Practices [PDF]. The changes are detailed in the image below.
PyPI malware: Socket Security has discovered new malware on the PyPI repository, this one targeting API developers and Discord bot creators.
New npm malware: Seventy-six malicious npm packages were discovered and taken down last week. Check out the GitHub security advisory portal for more details.
Lumma interview: Threat intelligence analyst g0njxa has published an interview with the creator of the Lumma infostealer.
Truth Social scams: Netcraft looks at the incessant scams that target newly created Truth Social accounts.
CERT-UA AnyDesk alert: Ukraine CERT says an unidentified threat actor is targeting Ukrainian organizations with a social engineering campaign where they're trying to connect to their networks via AnyDesk, posing as a CERT-UA representative.
Toll-themed smishing: Brian Krebs has a report out on a massive SMS phishing wave that has hit the US using toll-themed lures.
Google Ads inception: According to Malwarebytes, a threat actor is using malicious Google ads to target Google Ads users and steal their login credentials.
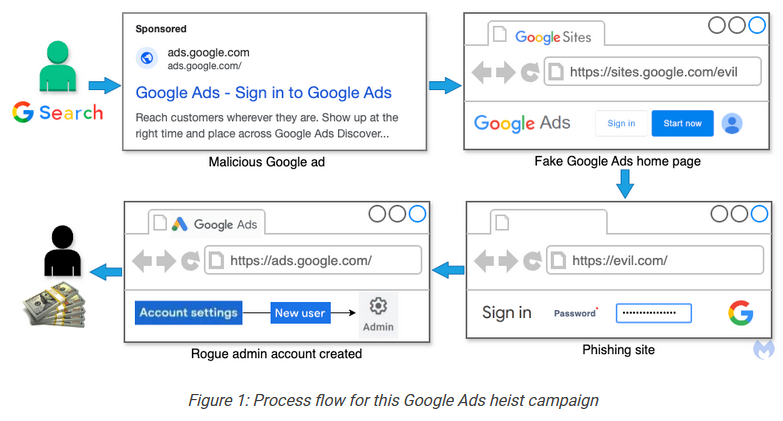
Malware technical reports
Gootloader: Sophos has published a report on Gootloader, a malware family that uses hijacked Google search results to redirect users to compromised, legitimate WordPress websites.
MintsLoader: eSentire has spotted a new campaign this month distributing MinstLoader and the Stealc infostealer.
PNGPlug and ValleyRAT: Intezer looks at a malspam campaign targeting Chinese-speaking companies with the PNGPlug loader. The final payload is a well-known threat known as ValleyRAT.
Purrglar: Kandji has published a report on Purrglar, a new macOS infostealer that was uploaded to VirusTotal this year.
Sneaky 2FA: French security firm Sekoia says it discovered a new AitM phishing kit named Sneaky 2FA that was designed for targeting Microsoft 365 accounts. The kit is sold via a Phishing-as-a-Service model via a Telegram bot.
RansomHub: GuidePoint looks at the tactics of one of RansomHub's affiliates.
"Like ReliaQuest, GuidePoint identified evidence linking SocGholish (FakeUpdate) to the initial access phase of the incident. In the incident GuidePoint investigated, the Python backdoor was dropped roughly 20 minutes after the initial infection. Subsequently, the threat actor dropped Python backdoors on additional systems during lateral movement via RDP sessions."
IoT DDoS botnet: Trend Micro has discovered a new IoT botnet that was used at the end of 2024 to launch large-scale DDoS attacks. The botnet primarily consists of wireless routers and IP cameras that didn't receive security updates and used weak passwords. Once compromised, the devices were infected with a malware strain that combined code from two known strains known as Mirai and Bashlite.
Gambling botnet: Imperva has analyzed a sprawling gambling botnet that uses hacked and backdoored PHP websites to redirect and host its scams. The botnet primarily targets Indonesian users.
Sponsor section
Travis McPeak demonstrates how to set up controls so that deploying cloud infrastructure is secure and repeatable from the get go.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
US sanctions Salt Typhoon company: The US Treasury has imposed sanctions on Sichuan Juxinhe Network Technology, a Chinese cybersecurity company linked to the Salt Typhoon APT group. The US says the company was directly involved in hacking multiple US telcos. Officials say the company is one of many private companies the Chinese Ministry of State Security has used for its hacking operations. The Treasury also imposed additional sanctions on Yin Kecheng, a Shanghai-based individual involved in hacking the Treasury itself at the end of last year. Officials say Yin is an MSS affiliate. The Treasury hack was previously linked to a group tracked as Silk Typhoon.
Volt Typhoon infrastructure: According to new Censys research, the Volt Typhoon Chinese APT group didn't particularly gaf after US law enforcement took down some of their botnets and re-built its infrastructure in the exact same way as before, just changing hosting providers.
Star Blizzard goes after WhatsApp data: A Russian APT group named Star Blizzard has updated its normal tactics and is now targeting victims via WhatsApp messages. According to Microsoft, the group's campaigns are targeting government officials and organizations providing support to Ukraine. The goal is to compromise accounts and steal past messages. The group has been historically linked to Russia's FSB intelligence service. Microsoft claims the group switched to targeting WhatsApp after the FBI seized some of the group's server infrastructure in October.
SDA bypasses sanctions: Check First looks at how Meta has failed to detect and ran politically-themed ads from the Social Design Agency, a Russian disinformation group sanctioned by US authorities.
"Based on 480 screenshots from Facebook Ads Manager included in the leak, combined with prior detection of over eight thousand advertisements, we estimate that SDA-authored propaganda advertisements generated over 123,000 clicks and a minimum earning for Meta of ~$338,000 in the European Union alone, after SDA was sanctioned by the European Union in July 2023."
Russian disinfo targets Canada: Canada NYT Bureau Chief has tracked down a Russian disinformation effort targeting Canadians on Twitter.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Asterisk security update: The Asterisk PBX and telephony server has released security patches to fix a path traversal vulnerability (CVE-2024-53566).
Kubernetes Windows vulnerability: The Kubernetes project has patched a vulnerability in its Windows nodes that could allow threat actors to take over hosts. Tracked as CVE-2024-9042, the vulnerability allows a threat actor who can query a node's "/logs" endpoint to execute commands. Only Windows nodes are impacted.
Planet industrial switch vulnerabilities: Claroty researchers have found three vulnerabilities in Planet Technology WGS-804HPT industrial switches, typically used in critical sector organizations. The bugs can be chained and exploited for remote code execution attacks. The vulnerabilities were privately disclosed and fixed by the vendor.
Mercedes vulnerabilities: Kaspersky researchers have identified 13 vulnerabilities in the MBUX infotainment systems of Mercedes cars.
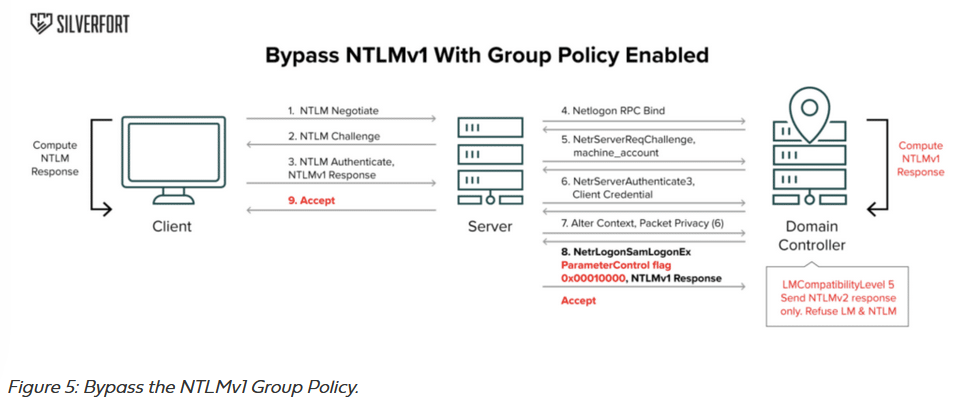
New NTLMv1 GPO bypass: Silverfort researchers have found a way to bypass an Active Directory Group Policy designed to disable the outdated NTLMv1 protocol. The technique abuses scenarios in on-prem networks that allow some applications to continue using NTLMv1 tokens for authentication even if the GPO policy to disable the protocol is active.
Ivanti zero-day PoC: A proof-of-concept is now public for a recent Ivanti zero-day tracked as CVE-2025-0282, exploited in the wild by a suspected Chinese threat actor (UNC5221).
Karmada security audit: The Karmada k8s orchestration cluster has fixed six vulnerabilities found in a recent security audit.
Bitpixie exploit still works: The Bitpixie exploit, which can be used to bypass the Windows BitLocker encryption system without any hardware shenanigans, still works two years after being discovered.
New UEFI Secure Boot bypass: ESET has discovered a new UEFI Secure Boot bypass in a legitimate UEFI application used by several real-time system recovery software suites. The issue was patched this month and was assigned CVE-2024-7344.
"The vulnerability can be mitigated by applying the latest UEFI revocations from Microsoft. Windows systems should be updated automatically."
Thinned-out CVE stats: WordPress-related bugs accounted for almost a quarter of all CVEs issued last year. Le sigh! Also, check out Jerry Gamblinb's breakdown of last year's CVEs.

Infosec industry
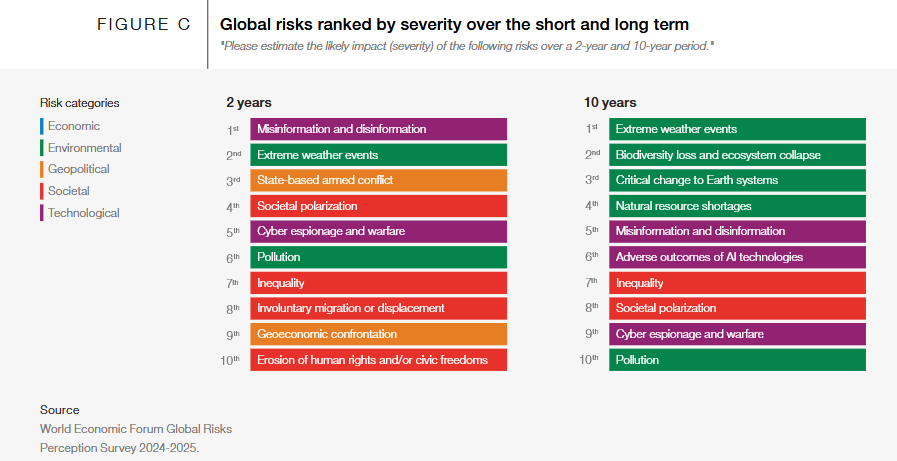
Threat/trend reports: ANY.RUN, GuidePoint Security, ReliaQuest, VMR, and the World Economic Forum have published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
New tool—OSV-SCALIBR: Google has open-sourced OSV-SCALIBR, a library to extract software inventory data, scan files, and detect vulnerabilities.
New tool—LabSync: Cellebrite has released LabSync, an IDA plugin that can be used to partially synchronize IDBs between different users working on reversing the same binaries.
MITRE D3FEND: MITRE has launched v1.0 of D3FEND, a knowledgebase designed to establish a vocabulary and conceptualization of the cyber domain.
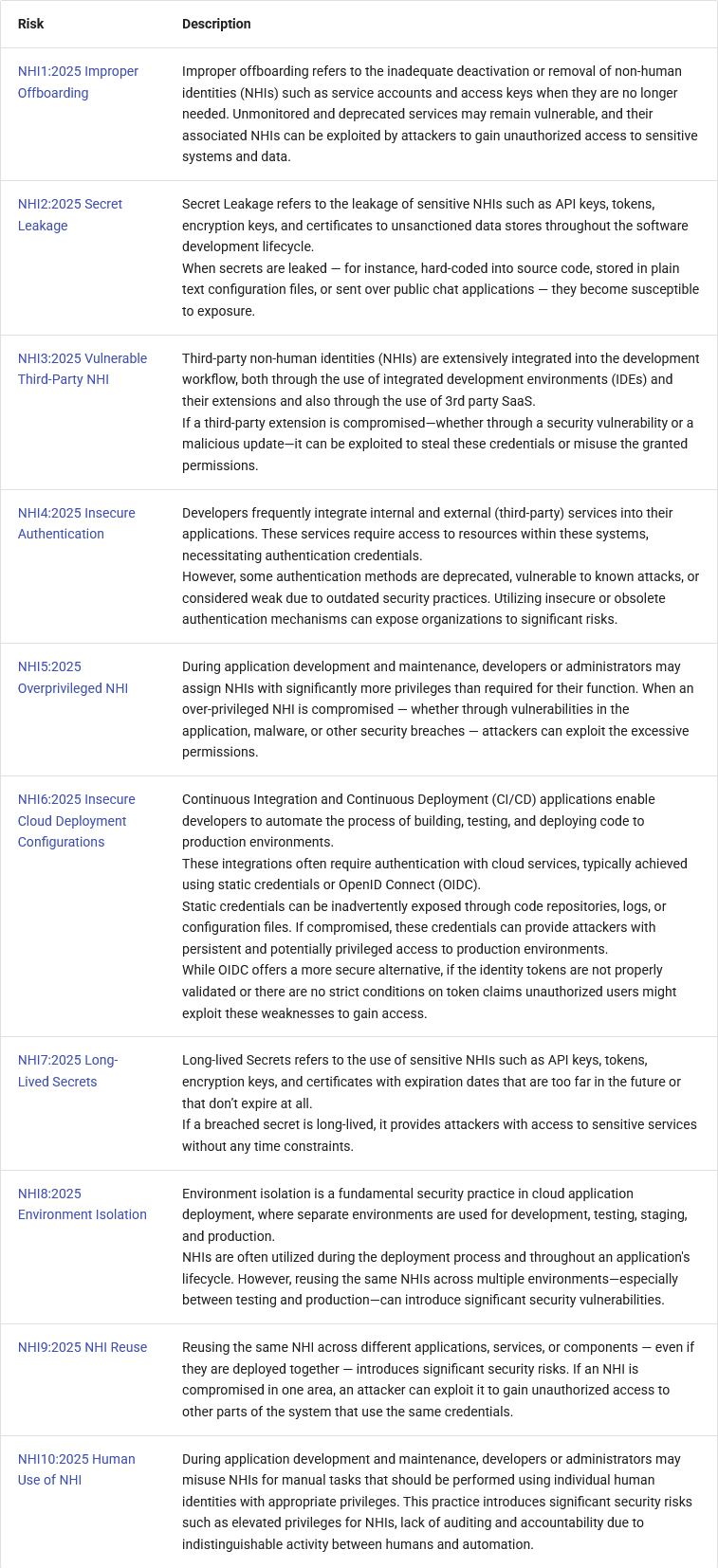
OWASP NHI Top 10: The OWASP Project has published its Top 10 ranking of risks associated with non-human identities (NHIs) for application developers. The organization listed Improper Offboarding as the top risk.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Adam Boileau talk about the continued importance of hack and leak operations. They didn't really affect the recent US presidential election, but they are still a powerful tool for vested interests to influence public policy.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about the evolution of Russian cyber operations during its invasion of Ukraine.




