Risky Bulletin: France runs phishing test on 2.5 million students
In other news: Google fixes Chrome zero-day; China publishes new facial recognition rules; DragonForce ransomware hacks two rivals.

This newsletter is brought to you by Sublime Security, an email security platform that's not a black box. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The French government conducted last week a large-scale phishing test on over 2.5 million middle and high school students.
The test included a link in their school's digital workspace that advertised cheats and cracked games that redirected students to a phishing awareness video.
According to CNIL, France's privacy watchdog, over 210,000 students clicked the link, representing roughly one in twelve students.
Officials conducted the national phishing test after a small pilot last year in the Yvelines department, west of Paris. Students from more than 4,700 schools participated in this year's test.
The phishing test was named Operation Cactus and is—to our knowledge—the largest phishing test conducted to date.
The results are actually more promising than they look, and the kids did way better than expected. With only an 8% click rate, Operation Cactus is far below the ~33% click rate seen in corporate environments, according to a KnowBe4 report.
Risky Business Podcasts
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Belgium govt portal DDoS: Pro-Kremlin group NoName057 has launched DDoS attacks that took down the Belgium government's official portal. The group, allegedly run by people linked to Russia's military cyber units, is mad because Belgium has contributed to Ukraine's defense. [Additional coverage in BelgaNewsAgency]
Abracadabra Finance crypto-heist: A hacker has stolen $13 million worth of crypto-assets from DeFi lending platform Abracadabra Finance. The attack targeted the platform's lending pools, where the company aggregates customer funds. Abracadabra refunded half of the stolen assets back to its users two days after the attack and expects to refund all the assets by mid-year. [Additional coverage in the Crypto Times]
CERT.BY hack: Belarusian hacktivist group the Cyber Partisans have hacked and released the source code and database for the Belarus CERT website. The group leaked the data on Belarus Freedom Day when the organization cut off internet access to Belarusian sites. The shutdown was allegedly part of a government test of its ability to control internet infrastructure.
StreamElements breach: Streaming platform StreamElements has confirmed a security breach after a hacker stole data from one of its old online store partners.
Sydney Tools orders leak: Australian home supplies vendor Sydney Tools left a database exposed online that leaked details on over 34 million orders. Detailed customer information was also included. In addition, the novelty is that the leak came from ClickHouse, a relatively new database system. [Additional coverage in Cybernews]
IT company fined for major 2022 NHS attack: The UK's privacy watchdog has fined a British IT company over £3 million for a 2022 ransomware attack that impacted NHS healthcare services. The attack was conducted by the LockBit group and impacted multiple NHS IT platforms and its 111 non-emergency phone line. The ICO fined British MSP Advanced for failing to secure its systems by not using MFA, not scanning for vulnerabilities, and failing to install patches. The ICO and Advanced agreed to the fine and the company won't appeal.
T-Mobile pays $33 million in SIM swap lawsuit: T-Mobile has agreed to pay $33 million in damages to a man who was SIM-swapped and lost $38 million worth of cryptocurrency. The funds would have now been worth over $165 million. T-Mobile also settled with the FTC last year for $31.5 million in a similar SIM-swapping probe. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Twitter API leak: F12 warriors will be glad to know they can now scrape Twitter profiles via the Developer Tools tab.
General tech and privacy
Google to develop Android behind closed doors: Google will develop the Android operating system in private and will share its source code after each official release. The company says it changed the way it develops Android to simplify development operations. Currently, Google maintains two separate branches of the OS in real-time, an internal version and a public open-source project. The company plans to provide smartphone makers versions of its internal branch in advance for future releases. [Additional coverage in Android Authority]
Google Titan security keys: Google is making its Titan security keys available in 10 more countries.
- Ireland
- Portugal
- The Netherlands
- Denmark
- Norway
- Sweden
- Finland
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Puerto Rico
PQC in OpenSSL: The OpenSSL project has released a beta for its upcoming 3.5 branch that's set to support PQC algorithms that can protect data against quantum computing attacks.
Zoho wins Indian browser competition: Zoho's Ulaa browser has won a public contest organized by the Indian government to create a homegrown web browser. [Additional coverage in SME Channels]
Mozilla asks for donations after losing USAID funds: Mozilla is asking users to donate to Firefox browser development after the organization lost US government funding. Mozilla has lost $2.5 million in USAID funding already and is expected to lose another $1.05 million. The USAID funding is only a small part of its yearly revenue. The organization reported $653 million in revenue in 2023, with almost $500 million coming from its search deals. [Additional coverage in Consumer Affairs]
Firefox gets DLP friendly: Mozilla is adding a new component to its Firefox browser to allow DLP security solutions to easily tap into the browser and monitor user actions. The new SDK will serve as an alternative to DLL injections, which are known to cause browsers to crash. The SDK was initially developed by Google for its enterprise version of Chrome. The component will roll out in Firefox 138, scheduled for release at the end of April.
Vivaldi integrates ProtonVPN: Vivaldi has released a new version of its browser with built-in support for ProtonVPN, now available as a VPN button in the toolbar.
Government, politics, and policy
US puts export restrictions on 80 companies: The US Commerce Department has added 80 foreign companies to its export restrictions list. American companies are forbidden from selling products and services on national security grounds. Fifty of the companies are based in China, while the rest are based in Taiwan, Iran, Pakistan, South Africa, and the UAE. The companies are linked to AI, high-performance computing, and quantum technologies. [Additional coverage in Reuters/Commerce Dept order/PDF]
ODNI annual threat report: The Office of the US Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) has published its annual threat assessment report. There are some mentions of cyber in there, but they're rather superficial and mention generic cyber strategies from US adversaries.
US govt officials' data found online: Der Spiegel reporters have found the personal data, phone numbers, and passwords of US government officials in online repositories of past data breaches. Some of the phone numbers were still valid and used for managing personal online accounts like Dropbox, LinkedIn, and Instagram. Affected officials include National Security Adviser Mike Waltz, Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard, and Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth. The finding comes days after the Signalgate scandal.
China publishes new facial recognition rules: The Chinese government has banned the use of facial recognition technology without consent. The rules take effect from June 1, and ban companies from using facial recognition if other less-intrusive identification alternatives exist. When facial facial recognition is used, companies are required to secure consent, encrypt biometric data, and go through regular security audits. The rules also ban facial recognition in places such as hotels, public bathrooms and store changing rooms. [Additional coverage in Tech In Asia]
Papua New Guinea blocks Facebook: The government of Papua New Guinea has blocked access to Facebook, citing an increase in hate speech, disinformation, and pornography. The government began looking at Facebook after its role in spreading disinformation related to recent tribal killings. Officials say the block is only a test, and no final decision has been made. The country's opposition criticized the move as bordering on autocracy. [Additional coverage in ABC]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Josh Kamdjou, co-founder and CEO of Sublime Security. Josh goes over recent trends in email badness, such as the increase in QR code abuse and the rise of SVG smuggling.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Mamont malware dev arrested in Russia: Russian authorities have arrested three men suspected of developing the Mamont Android banking trojan. The suspects were detained in Russia's Saratov region, near the Kazakhstan border. Officials said they received over 300 complaints linked to infections with the Mamont malware. [Additional coverage in CNews/English coverage in The Record]

BEC scam seizure: The US DOJ recovered $5.3 million stolen in a $6.4 million BEC scam from a workers union based in Dorchester, Massachusetts.
DOGE staffer linked to cybercrime ops: A DOGE staffer named Edward "Big Balls" Coristine operated a company named DiamondCDN that hosted cybercrime operations, with one of them being a group named EGodly. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
npm package hides a downloader: ReversingLabs has discovered two malicious npm packages that patch a legitimate npm package if found on a victim's system and add a reverse shell.
More npm badness: Sonatype has found ten old npm packages that were hijacked and injected with malicious code designed to steal sensitive information such as environment variables.
RedCurl creates its own ransomware: Corporate cyber-espionage group RedCurl has developed and is now using its own ransomware strain. Named QWCrypt, the ransomware can target Windows systems and Hyper-V virtual machines. This is a major shift in the group's operations. RedCurl has been active since 2018 and was usually involved in slow and stealthy data exfiltration.
ZuizhongJS campaign hits 150,000 sites: A web malware campaign tracked as ZuizhongJS has now hijacked over 150,000 websites—and counting—to insert ads and redirect users to Chinese gambling sites. This campaign started last month.
OpIsrael 2025 campaign: Several pro-Palestinian and pro-Muslim hacktivist groups have announced plans to participate in the yearly OpIsrael DDoS campaign. This year, the groups say they're also gonna target US and UK organizations for their support of Israel's war in Gaza—instead of the usual Israeli targets.
Hellcat group: KELA has published a profile on Rey and Pryx, the two main individuals behind the Hellcat hacking group, responsible for several breaches over the past months, such as Schneider Electric, Telefónica, and Orange Romania. They were previously known as the ICA Group.
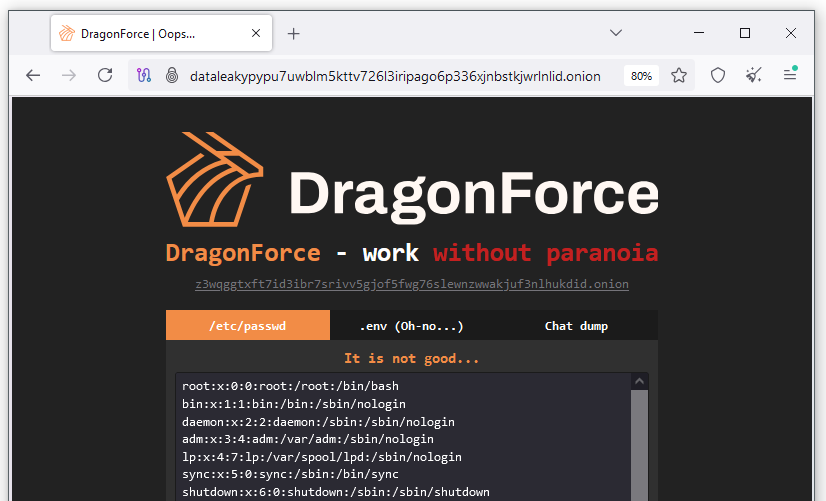
DragonForce hacks BlackLock: The DragonForce ransomware group has hacked and defaced the infrastructure of one of its rivals, the BlackLock ransomware. The group dumped server configuration files for BlackLock's backend and data leak site. BlackLock has not restored its website and has gone dormant. The group was one of today's most active ransomware operations, listing tens of victims over the past few months. Resecurity says BlackLock infrastructure was insecure, and its analyst also managed to gain access to its backend over the previous weeks. BlackLock is the second ransomware gang hacked by DragonForce this month after another rival named Mamona.
Malware technical reports
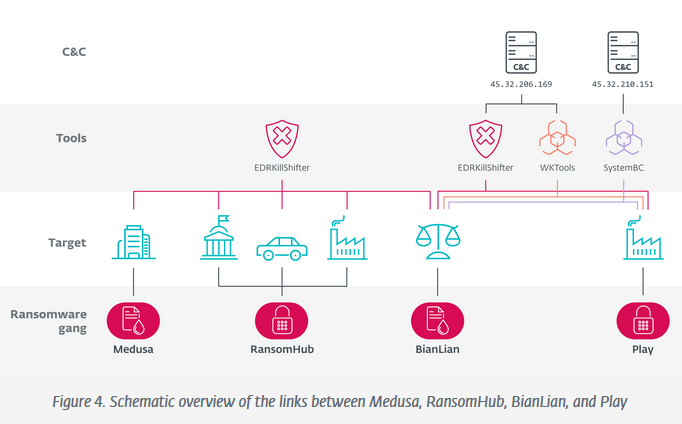
EDRKillShifter: ESET looks at EDRKillShifter, a tool used by RansomHub and other ransomware gangs to shut down EDR products before deploying their payloads.
Triton RAT: Cado Security says an open-source Python-based RAT named Triton is now being used in the wild.
Morphing Meerkat PhaaS: Infoblox takes a look at Morphing Meerkat, a cybercrime group behind a pretty sprawling phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform.
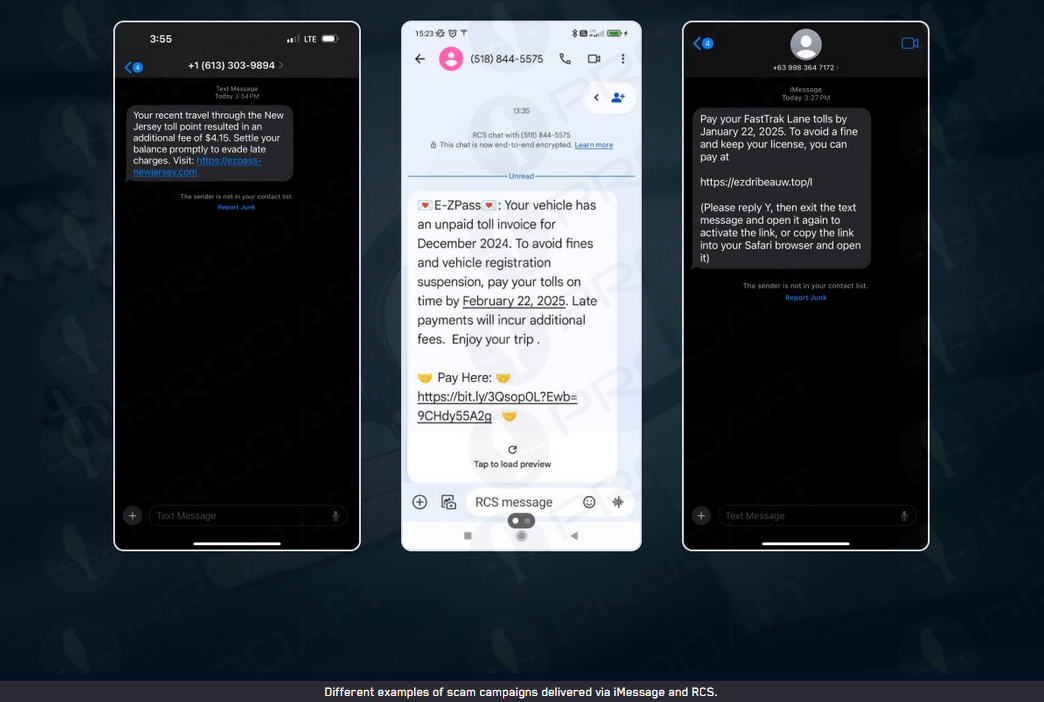
Lucid PhaaS: Security firm Prodaft has linked the Lucid Phishing-as-a-Service platform to a Chinese threat actor named the XinXin Group. The platform allows customers to automate the sending of SMS-based spam. The platform is different from similar competitors because of its ability to target Android users via RCS and iPhone users via iMessage.
Sponsor section
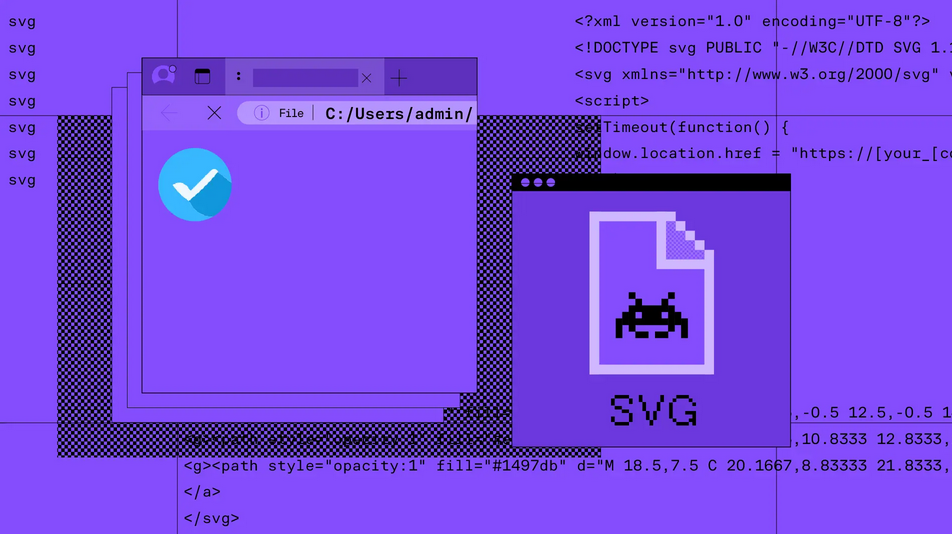
Sublime Security explores a new type of attack observed in the wild—the embedding of malicious JS code within SVGs to deliver adversary-in-the-middle credential phishing attacks.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Russian honeypot network: Russian intelligence services are likely behind a network of honeypot websites that appeal to anti-war supporters and pro-Ukraine sympathizers. The websites mimic the CIA, the Russian Volunteer Corps, the Legion Liberty, and a Ukrainian portal named Hochuzhit. Security firm Silent Push says the fake portals focus on collecting personal information via web forms or Telegram channels. The honeypot sites are buried in Google results but rank first in Russia's Yandex search engine.
FamousSparrow's SparrowDoor backdoor: ESET researchers have discovered two new versions of SparrowDoor, a backdoor used by Chinese APT group FamousSparrow. The report also disputes Microsoft's classification of FamousSparrow as part of the Salt Typhoon group. ESET believes the two APTs may be using a shared digital quartermaster (malware and tools developer).
PJobRAT makes a comeback: Sophos has discovered new campaigns using the PJobRAT Android remote access trojan. The RAT was last time used in 2021 to target Indian military personnel. The latest campaign targeted users in Taiwan. The attacks look to be the work of an APT group.
"While this particular campaign may be over, it's a good illustration of the fact that threat actors will often retool and retarget after an initial campaign – making improvements to their malware and adjusting their approach – before striking again."
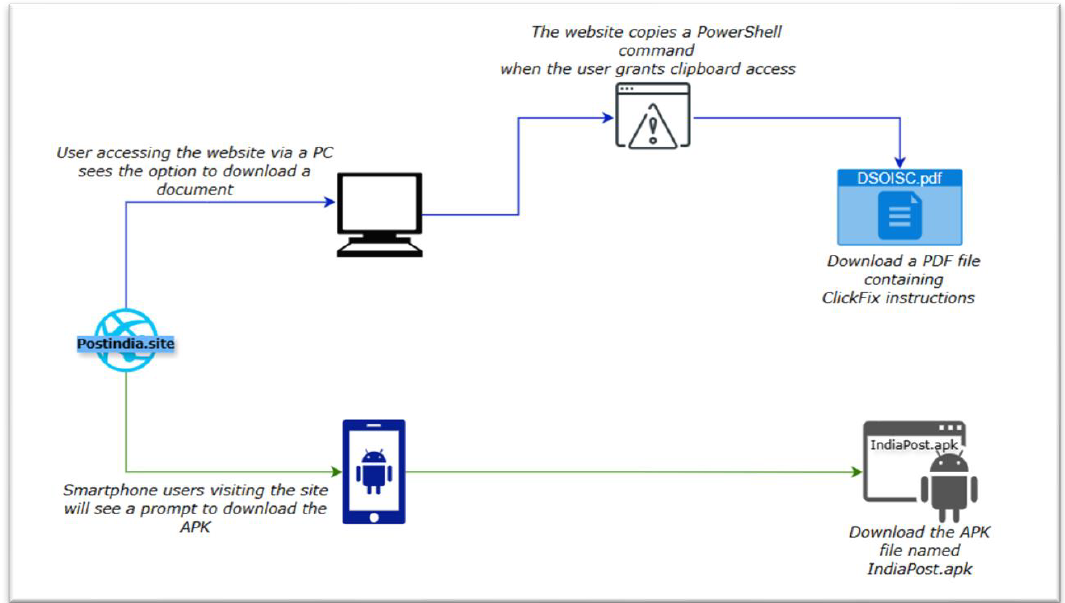
APT36: Indian security firm CyFirma looks at a suspected APT36 campaign using a fake IndiaPost website to target both Windows and Android users.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Chrome zero-day: Google patched a Chrome zero-day used in targeted attacks against Russian media outlets and educational institutions. Kaspersky says the attacks took place this month and are the work of a state-sponsored APT group. The zero-day (CVE-2025-2783) is a Chrome security sandbox escape and was used together with a second exploit to deploy malware on a target's computer. Kaspersky described the malware as "highly sophisticated."
Firefox rolls out pre-emptive patch: Mozilla has also rolled out a fix for the Chrome zero-day after noticing similar patterns in its Windows browser code.
Tomcat exposure: Users downloaded vulnerable versions of Apache Tomcat three times more often than the patched versions over the past 90 days, according to new research released by Sonatype.
ArcGIS auth vuln: American software company Esri has released a patch to fix an authentication vulnerability in its ArcGIS platform. Tracked as CVE-2025-2538, the vulnerability allows unauthorized access to the platform and has a severity rating of 9.8/10. The ArcGIS platform is a geographic information system (GIS) used to manage and visualize topographic data and is widely used by government agencies to manage state resources. There are currently over 1,100 ArcGIS systems exposed on the internet.
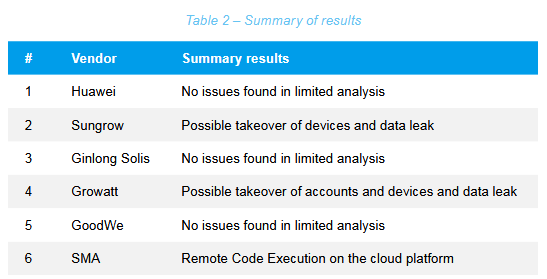
SUN:DOWN vulnerabilities: Forescout researchers have discovered 46 vulnerabilities across three popular solar inverter vendors. Named SUN:DOWN, the vulnerabilities can be used to take over devices or their cloud platform. Impacted vendors include Growatt, SMA, and Sungrown. Academics have warned on multiple occasions over the past years that mass hacks of solar inverters could imperil national power grids.
Splunk security updates: Cisco has patched 12 vulnerabilities in the Splunk SIEM platform.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with two vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. They include two 2019 data deserialization issues in the Sitecore CMS.
X-Wiki exploitation: SANS ISC expert Johannes Ullrich looks at recent attacks targeting a 2024 X-Wiki vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-3721.
IngressNightmare POC: A public POC for the IngressNightmare cloud vulnerability is now publicly available.
NSO BLASTPASS iMessage exploit: Google's Project Zero has published a root-cause analysis of two vulnerabilities used by NSO's BLASTPASS iMessage exploit. These are old vulnerabilities patched back in September 2023.
Android VRP update: Google says it will start giving bug hunters a $1,000 bonus for valid vulnerability reports that include an AutoRepro test.
OpenAI increases bounties: OpenAI has increased the maximum bug bounty payout for critical vulnerabilities to $100,000 from the previous $20,000.
Infosec industry
DOD contractor fined for security lapses: A DOD government contractor has agreed to pay a $4.6 million fine for failing to comply with cybersecurity requirements related to US Army and Air Force contracts. Massachusetts-based MorseCorp admitted to using a third-party email provider that did not meet DOD cyber requirements. It also admitted to lying about other cybersecurity standards in order to win government contracts.
Threat/trend reports: Dr.Web, ENISA, Horizon3, Netskope, Palo Alto Networks, RMIT, SecurityScorecard, and Trustwave have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
New tool—The Firewall Project: The Firewall Project is now open-source. Read the announcement here. The code is on GitHub.
New tool—Kereva: Software engineer Iman Malik has open-sourced Kereva, a scanner to check for issues in prompts and LLM calls. The code is also available on GitHub.
New tool—SpyAI: Dark Space Security has released SpyAI, a proof-of-concept malware that "takes screenshots for entire monitors and exfiltrate them through Trusted Channel Slack to the C2 server that's using GPT-4 Vision to analyze them and construct daily activity — frame by frame."
New tool—smugglo: A security researcher named b3rito has released smugglo, a script for wrapping files into self-dropping HTML payloads to bypass content filters. The tool is also available online.
New tool—Ultimate-RAT-Collection: Swedish security researcher Cryakl has put together a GitHub repo with samples from over 450 different remote access trojan families. She previously released a similar database for ransomware strains.
REcon 2024 videos: Talks from the REcon 2024 security conference, which took place last June, are available on YouTube.
RE//verse 2025 videos: Talks from the RE//verse 2025 security conference, which took place at the end of last month, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business Podcasts
Tom Uren and Patrick Gray discuss how the Signalgate messages betray an alarming lack of security nous at the highest levels of the US natsec leadership. It's head-scratchingly bad.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about why people studying cyber operations are fascinated by zero-days. These are vulnerabilities or exploits that have been found in a system before the vendor or manufacturer is made aware of them, and so, therefore, no fix exists.




