Risky Bulletin: EU launches private DNS service
In other news: Trump scraps and revises Biden and Obama cyber EOs; supply chain attack hits popular npm packages; mysterious iOS attacks in the US and EU.

This newsletter is brought to you by Push Security. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The EU launched last week its own DNS service, with versions for government agencies, telcos, and home users.
The DNS4EU service is designed to provide a secure and privacy-focused DNS resolver for the EU bloc as an alternative to US and other foreign services.
The project was announced in October 2022 and was built under the supervision of the EU cybersecurity agency ENISA.
It is currently managed by a consortium led by Czech security firm Whalebone, and members include cybersecurity companies, CERTs, and academic institutions from 10 EU countries.
DNS4EU is more than a regular DNS resolver. It comes with built-in DNS filters for malicious and malware-linked domains that prevent users from connecting to known bad sites.
These lists are managed from a central location by EU threat intel analysts at no cost to users, companies, or the governments that decide to adopt the service.
The benefits of the DNS4EU versions for governments and telcos are that the service can help alleviate the costs of running your own separate DNS infrastructure, and the service can also take some work off SOC teams, who can basically outsource some of their DNS security work to the DNS4EU team.
The version for home users comes in different variants with different DNS filters, such as filters to block malicious domains, adult content, ads, all three, or none.

The service is available under both IPv4 and IPv6 and with versions for DNS-over-HTTPS and DNS-over-TLS for users who want to use a more secure version of the DNS protocol.
Although some skeptics have raised issues that the service could be used to censor Europeans, the EU said adoption is not mandatory, and the project's purpose is to ensure digital sovereignty.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
GUR takes down Russian Railways sites: Ukraine's military intelligence agency claims it took down the DNS service of the Russian Railways using a 6 Gbps and 2.5 million packets per second DDoS attack. [Additional coverage in RBC Ukraine]
General tech and privacy
The FAIR package manager launches: The Linux Foundation has launched the FAIR package manager. The new system is a decentralized alternative to the WordPress.org plugin and theme ecosystem. It was developed with help from veteran WordPress developers who were pushed out from the main WordPress project last year during a power grab by Automattic and Matt Mullenweg.
this is a pretty fun project! it is basically a decentralized WordPress plugin package manager, using DID PLC as an identifier and store for package signing keys; and atproto for discovery/indexing of plugins in the ecosystem. github.com/fairpm/fair-...
— bryan newbold (@bnewbold.net) 2025-06-06T22:27:58.330Z
Spanish ISPs do a boo-boo: Spanish ISPs accidentally blocked Google domains trying to crack down on illegal soccer live streams.
Brazil's dWallet project: The Brazilian government is testing a pilot program named dWallet that lets citizens earn money by selling their personal data to advertisers. [Additional coverage in Rest of World]
OpenAI ordered to preserve user ChatGPT logs: A US court has ordered OpenAI to preserve user AI ChatGPT logs, including deleted and sensitive prompts, following a lawsuit filed by news organizations. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
Twitter sues content farmers: Twitter, now X, has sued eight Vietnamese nationals who are part of its Creator Revenue Sharing Program for posting fake content to boost their Twitter revenue. [Court documents PDF]
Government, politics, and policy
Trump scraps Biden and Obama cyber EOs: The Trump administration has scrapped or revised cybersecurity executive orders issued during the previous Biden and Obama administrations. The new Trump EO pulls back efforts to enforce BGP and PQC protections for federal networks. It also pulls back efforts to test phishing-resistant authentication and roll out email encryption. The order also removes software security requirements for federal contractors and limits the use of cybersecurity-related sanctions only against foreigners. [Additional coverage in CybersecurityDive/Eric Geller's Bluesky thread]
3. Eliminates a provision that would have required agencies to start testing phishing-resistant authentication technologies.
— Eric Geller (@ericjgeller.com) 2025-06-06T23:03:46.788Z
DOGE gets SSN access: The US Supreme Court has granted DOGE the right to access the Social Security data of all Americans. [Additional coverage in NPR/ Supreme Court ruling PDF]
Italy admits to using spyware against NGOs: The Italian government has admitted (again) to using spyware against NGOs. This time around, the government denied using the spyware against an Italian journalist and government critic.
Indonesia's novel internet censorship system: CitizenLab researcher Irene Poetranto looks at how the Indonesian government is using a novel DNS redirection technique to censor the internet. The technique requires local ISPs to sync their DNS resolvers with a National DNS system, allowing the state control to filter traffic at the DNS level from a central hub. [Additional coverage in the Carnegie Endowment]
FSB can allegedly intercept some Telegram messages: Russian human rights NGO First Department claims the FSB can now intercept Telegram messages after the agency has kept arresting people who communicated or donated to pro-Ukrainian Telegram communities. [Additional coverage in Novaya Gazeta]
Russia has a WeChat surveillance program: Hackers claim to have obtained and are selling a large collection of sensitive documents from Russian intelligence agencies. Samples shared with the New York Times have exposed a secretive FSB project designed to organize and analyze content from China's WeChat platform. The hacker group, named Ares Leaks, has been active since 2021. They're selling the larger cache of Russian intelligence documents for $120,000. They also claim to have similar sensitive data from North Korea, China, India and other countries.
Prison sentence for DDoS attacks in Russia: Russian lawmakers are preparing to amend the country's criminal code to introduce prison sentences for DDoS attacks. Offenders can face up to eight years in prison and fines of up to 2 million rubles (~$25,000). The law also carves out an exemption for users who launch attacks against what the Russian government classifies as "prohibited sites." This, ladies and gentlemen, from the country behind the UN's latest cybercrime treaty. [Additional coverage in Kommersant]
Sponsor section
In this sponsored interview, Casey Ellis interviews Push Security co-founder and Chief Product Officer Jacques Louw about how good phishing crews have gotten at evading detection.
Attackers are hiding their payloads behind legitimate bot-detection tools to stop things like email security gateways from seeing them, as well as locking up phishing pages behind OAuth challenges.
Push sees all this because it’s installed as a browser plugin and sees what users see.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Nigerian hacker sentenced: The US has sentenced a Nigerian man to 63 months in prison for hacking tax preparation firms and using the data to file fraudulent tax returns.
Nigeria sentences 72 for cybercrime: Nigerian authorities have sentenced 72 suspects to prison for their roles in cybercrime and internet fraud operations. The suspects included 55 (21+34) Nigerians, nine Chinese, and eight Filipinos. Some of the suspects were detained in December during Operation Eagle Flush when Nigerian police arrested 792 suspects running online scams from a Lagos seven-story office building. The Chinese nationals were allegedly the scam compound's leaders.
Operation Chakra V: Indian authorities have arrested six suspects and raided 19 locations across the Delhi, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh states. The suspects ran tech support scams and two call centers targeting Japanese users. The group was arrested following a joint investigation between Microsoft, Indian, and Japanese officials.
Feds go after pig-butchering couple: A Chinese couple stole $9.5 million worth of crypto-assets from at least 120 victims. The couple operated for four years out of a five-bedroom house in Frisco, Texas, and targeted Americans with Chinese heritage. The FBI is now trying to seize crypto wallets holding $6 million of the stolen funds. The couple fled to China before they were charged in June of last year. [Additional coverage in USA Today]
DR32 to be extradited: After being sentenced to time served, US authorities will deport Australian hacker David Kee Crees (aka DR32, aka Abdilo) back home. [Additional coverage in DataBreaches.net]
HMI exposure: Almost 400 HMI administrative panels for US water facilities are exposed on the internet, according to new research from security firm Censys. Forty of these systems do not require authentication and allow full control over water management systems. Censys worked with the US EPA, and 94% of systems have been secured. What remains online is in a read-only state that attackers can't abuse.
Mysterious iOS attacks in the US and EU: Security firm iVerify has found traces of a mysterious exploit on the iPhones of individuals in the US and the EU. Possible victims include government officials and individuals linked to political campaigns, media organizations, and AI companies. iVerify says the targets were previously targeted by Chinese state-linked groups. The underlying vulnerability was patched in January, and the latest exploit attempts were detected in March. iVerify says the exploit targeted a feature that let iPhone users set a nickname and avatar for their contacts. Apple denied the vulnerability was exploited in the wild.
ClickFix now targets macOS users: The AMOS macOS infostealer is now distributed via ClickFix campaigns—now with macOS-specific terminal instructions.
New Grey Nickel group: Security firm iProov has spotted a new financially motivated group named Grey Nickel that is targeting banking, crypto exchanges, e-wallets, and digital payment platforms.
"This group employs advanced face-swap technology, metadata manipulation, and injection techniques specifically designed to defeat single-frame liveness-based verification systems used by banks and payment platforms."
APT-Q-27 (Golden Eye Dog) targets the gambling sector: Chinese security firm QiAnXin has published a report on APT-Q-27 (Golden Eye Dog), a financially motivated group targeting the gambling sector with SERP poisoning, social engineering, and DDoS attacks.
Dark Gaboon linked to ransomware attacks in Russia: Russian security firm Positive Technologies has linked a financially motivated group named Dark Gaboon to attacks with the LockBit ransomware inside Russia. The group is not a customer of known RaaS platforms but instead uses a leaked version of the LockBit code. Dark Gaboon started operations in May 2023, and past attacks previously involved the only deployment of RATs.
Black Basta adopts PhaaS services: KELA looks at how the Black Basta ransomware group adopted PhaaS services for initial access over the past two years.
Ransomware mindmap: DomainTools and Analyst1 have mapped out connections in the ransomware underground ecosystem. More on this when their Sleuthcon talk goes live on YouTube.
New npm malware: Eighty-four malicious npm packages were discovered and taken down last week. Check out the GitHub security advisory portal for more details. This also includes two packages spotted by Socket that would wipe production systems.
npm supply-chain attack: A threat actor has compromised 16 npm libraries from the Gluestack UI framework. The attacker compromised a Gluestack admin's account, added a remote access trojan to the libraries, and pushed updates on Friday. The affected packages are extremely popular and have almost one million weekly downloads. Aikido Security says the attacker is the same threat actor behind another supply chain attack on the rand-user-agent package last month.
Stark Industries rebrands after sanctions: Stark Industries, a well-known bulletproof hosting provider, has rebranded under a new company named THE.Hosting. Stark Industries and its two founders were sanctioned by the EU last month for hosting cybercrime and Russian disinformation networks. In a blog post, the new company claims there is no connection between it and the old Stark Industries. Depending on your level of gullibility, you might actually believe that. But don't. [h/t Brian Krebs]
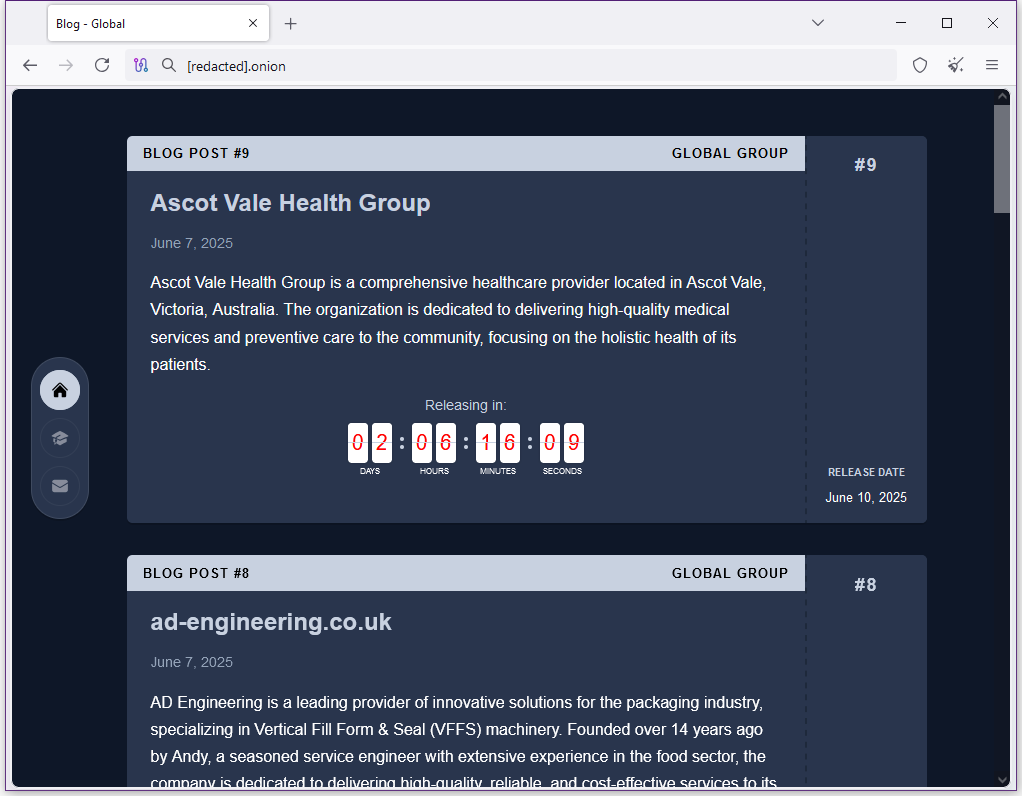
Weyhro returns: The Weyhro ransomware has returned from its slumber and published new leaks on its dark web portal.
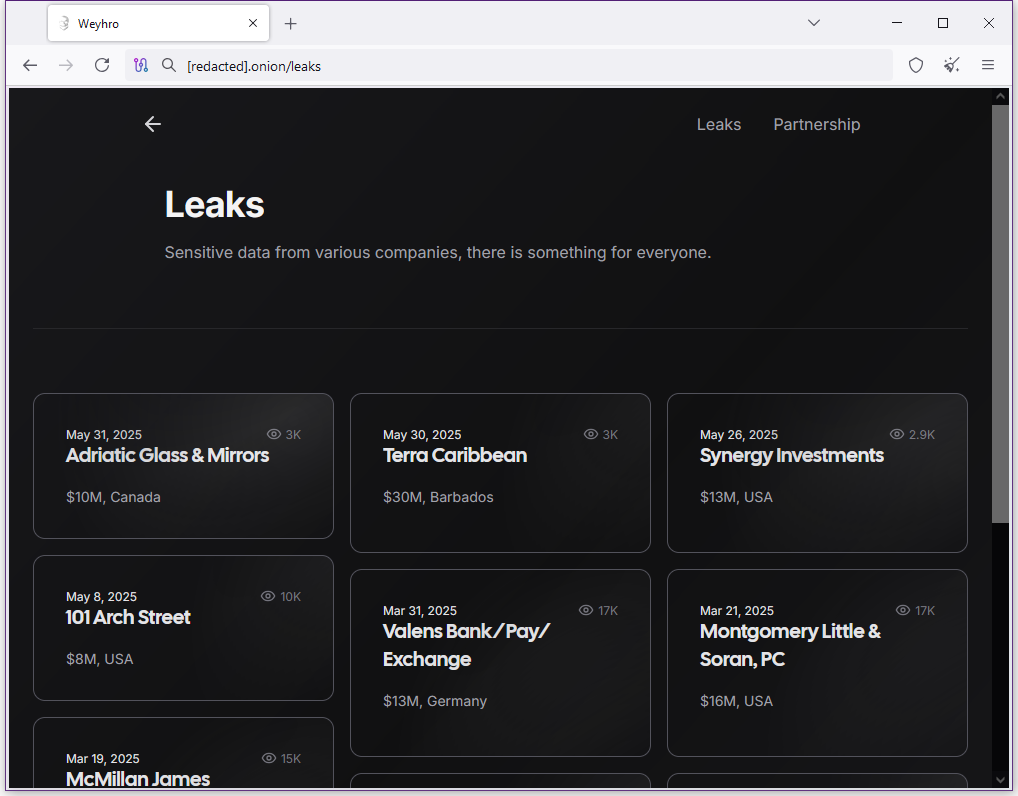
New Global ransomware gang: A new ransomware operation named Global launched this month. Its dark web leak site currently lists nine victims.
Malware technical reports
Mirai version: Kaspersky looks at a Mirai botnet using a 2024 vulnerability to take over TBK DVR devices.
New Blitz version: PAN's Unit42 has uncovered a new version of the Blitz trojan, currently distributed through backdoored game cheats.
DuplexSpy RAT: CyFirma looks at DuplexSpy RAT, a multifunctional remote access trojan (RAT) with extensive capabilities for surveillance, persistence, and system control.
slince_golden WP backdoor: Trunc has published a report on slince_golden, a backdoor found on hacked WordPress sites.
"It has been going on for a while, and it is not a new backdoor, but just recently we decided to look more into it since we could not find any articles or public information about it."
Sponsor section
In this wholly sponsored Soap Box edition of the show, Patrick Gray chats with Adam Bateman and Luke Jennings from Push Security.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Cyber Partisans: Kaspersky has published a collection of IOCs and TTPS linked to the Cyber Partisans hacktivist group.
Transparent Tribe (APT36): Indian security firm CloudSEK has published a report analyzing recent infrastructure linked to Pakistani APT Transparent Tribe.
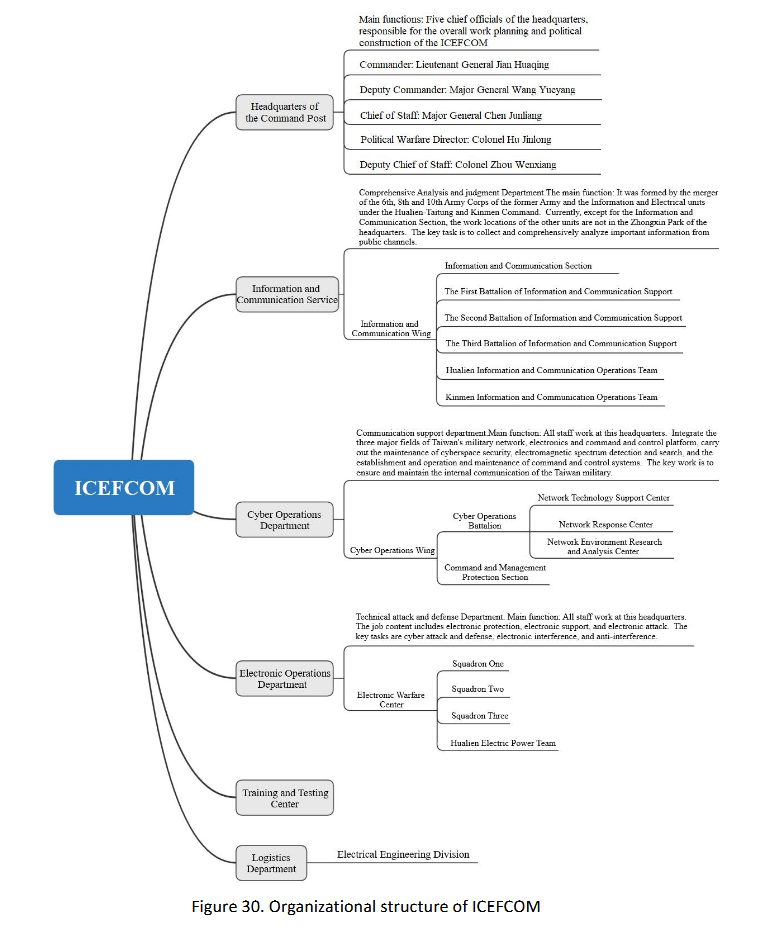
Taiwanese/ICEFCOM APTs: China's National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center has published a report on the APT groups associated with Taiwan's ICEFCOM cyber warfare unit. The groups are APT-C-01 (Poison Vine), APT-C-62 (Viola Tricolor), APT-C-64 (Anonymous 64), APT-C-65 (Neon Pothos), and APT-C-67 (Ursa). [English report PDF]
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Jenkins security updates: The Jenkins project has published a security update for its Gatling plugins.
QNAP security updates: Taiwanese NAS vendor QNAP has released security updates for nine of its products.
Splunk security updates: Cisco has patched four vulnerabilities in the Splunk SIEM platform.
Apache InLong security update: The Apache InLong data ingestion platform has patched an untrusted data serialization vulnerability.
SolarWinds security update: SolarWinds has published a security update for the DameWare Mini Remote Control remote desktop tool.
vBulletin 4.x vulnerability: Security researcher Egidio Romano looks at how a patch for a 2014 PHP object injection vulnerability in the vBulletin forum software secretly introduced an insecure deserialization attack vector.
"This vulnerability in vBulletin 4.x — ironically introduced by a misguided patch meant to improve security — is a textbook case of how insecure deserialization can creep into legacy applications through overconfident assumptions and hasty fixes. By replacing serialize() with json_encode() in an attempt to fix alleged PHP Object Injection vulnerabilities, the developers inadvertently made it possible for attackers to sign and submit base64-encoded payloads. These payloads can then be used to trigger a call to the unserialize() PHP function, enabling the deserialization of malicious objects."
SonicDoor write-ups: Orange's security team has published a technical analysis of five vulnerabilities they found in SonicWall's SMA 500 devices, which were patched in December 2024.
"Vulnerabilities in commercial-grade SSL VPN devices have been all too common in the past few years. An internal research project aimed at comparing the security level of these devices identified that SonicWall devices tend to have fewer reported vulnerabilities while displaying relatively poor security practices. This pushed us to perform additional research into SonicWall devices and determine the reason behind this counter-intuitive conclusion."
BLASTPASS write-up: DFSEC has published an analysis of the old BLASTPASS iOS exploit.
AWS Amplify RCE PoC: SecureLayer7 has published a write-up and PoC for an RCE in the AWS Amplify Codegen UI, tracked as CVE-2025-4318.
Loads of Tenda POCs published online: As spotted by security researcher cR0w, there's been a major dump of PoCs for Tenda routers last week. [Here, here, here, here, here, and here]
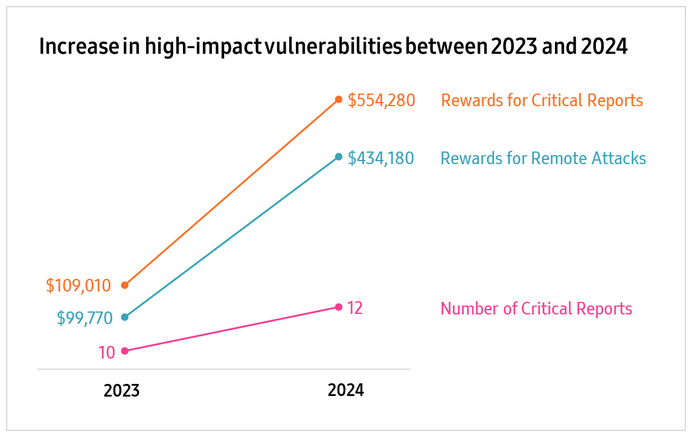
Samsung bug bounty payouts: South Korean phone maker Samsung has paid over $6 million to security researchers through its official bug bounty program since it began in 2017. The company handed out over $1 million in rewards last year alone. Over half of that sum was paid out for critically-rated and remote attack vectors. The rise in critical reports came after Samsung increased payout ranges a year before.
Infosec industry
Infosec drama: Cybersecurity firm Scamnetic has sued rival BlackCloak for breaking an NDA and copying its product. [Court document PDF/via CourtWatchNews]
Acquisition news: F5 has acquired cybersecurity AI company Fletch.
New tool—ProxyBlob: Security firm Quarkslab has released ProxyBlob, a tool designed to create SOCKS5 proxy tunnels through the Azure Blob Storage service.
New tool—Newtowner: Security firm Assetnote has released Newtowner, a tool designed to test firewalls and network boundaries by masquerading traffic to appear as if it's originating from different data centers around the world. The tool is meant to discover holes in security policies that may allow a threat actor to exfil data to a server on the same cloud provider and use it as a proxy point for data theft without triggering alerts.
New tool—DroidGround: UK security firm SECFORCE has developed DroidGround, a platform for Android CTF challenges.
New tool—Code Auditor CTF: Bushido Security has released Code Auditor CTF, a web-based Capture The Flag (CTF) platform to practice finding real-world C/C++ vulnerabilities. The platform code is also on GitHub.
Just launched Code Auditor CTF — https://t.co/S87nvpjfht
— 2OURC3 (@2ourc3) May 16, 2025
A web platform to practice finding real-world C/C++ vulnerabilities
• 8000+ challenges
• Progress tracking + leaderboard
• Beginner-friendly
• Fully open source (beta): https://t.co/0yqyGmviCM
Threat/trend reports: BlackCloak, Google, Honeywell [PDF], Kaspersky, and Red Hat have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Security Fest 2025 streams: Live streams from the Security Fest 2025 security conference, which took place over the week, are available on YouTube.
CyCon 2025 videos: Talks from the NATO CCDCOE's CyCon 2025 security conference, which took place at the end of May, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about how Operation Endgame, the multinational law enforcement effort to tackle ransomware, is approaching the problem holistically. It's tackling the enablers of ransomware, and although it won't eliminate the crime, it'll make it harder for criminals.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at the NSA's take on information warfare, all the way back from 1997.




