Risky Bulletin: EU has a problem attracting and retaining cyber talent
In other news: Coupang CEO resigns following breach; NoName057 and CARR member charged in the US; Chrome and Gogs zero-days.

This newsletter is brought to you by Mastercard. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
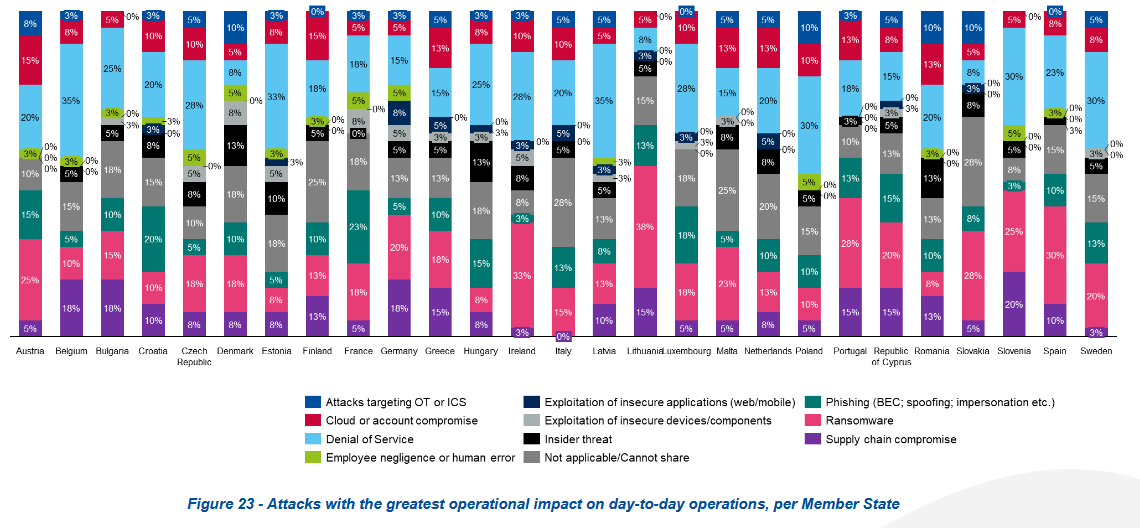
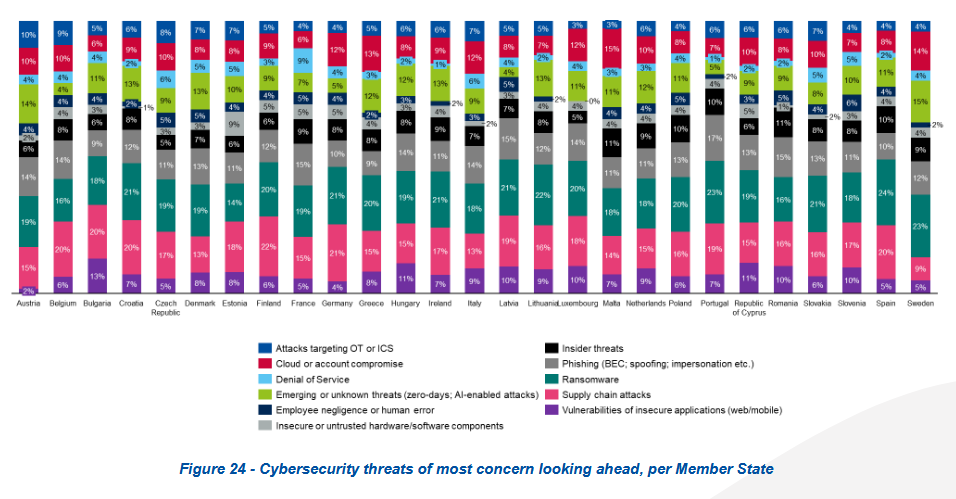
Public and private critical sector organizations across the EU are having issues attracting and retaining cybersecurity talent.
According to a survey by the EU's cybersecurity agency, candidates don't have the necessary skills or the employers don't have the proper training programs.
Cyber experts who leave companies cite excessive workloads, burnout, and the lack of competitive salaries and bonuses.
This resulted in high turnover rates at most surveyed companies, raising their exposure risk and preventing more investments in cybersecurity.
"Difficulties in attracting (76%) and retaining (71%) cybersecurity professionals persist, intensified by a shortage of skilled professionals and fierce competition for limited talent," ENISA said on Monday.
The survey included answers from 1,080 EU public and private orgs active in the NIS2 high-criticality sector, which includes healthcare providers, energy, transportation, public administration, banks, and others.
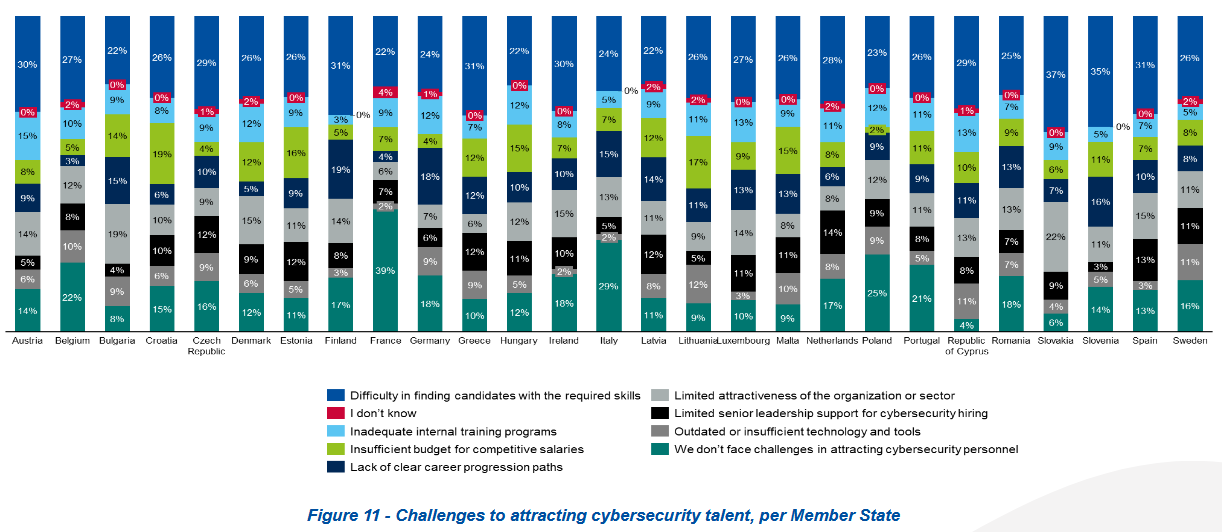
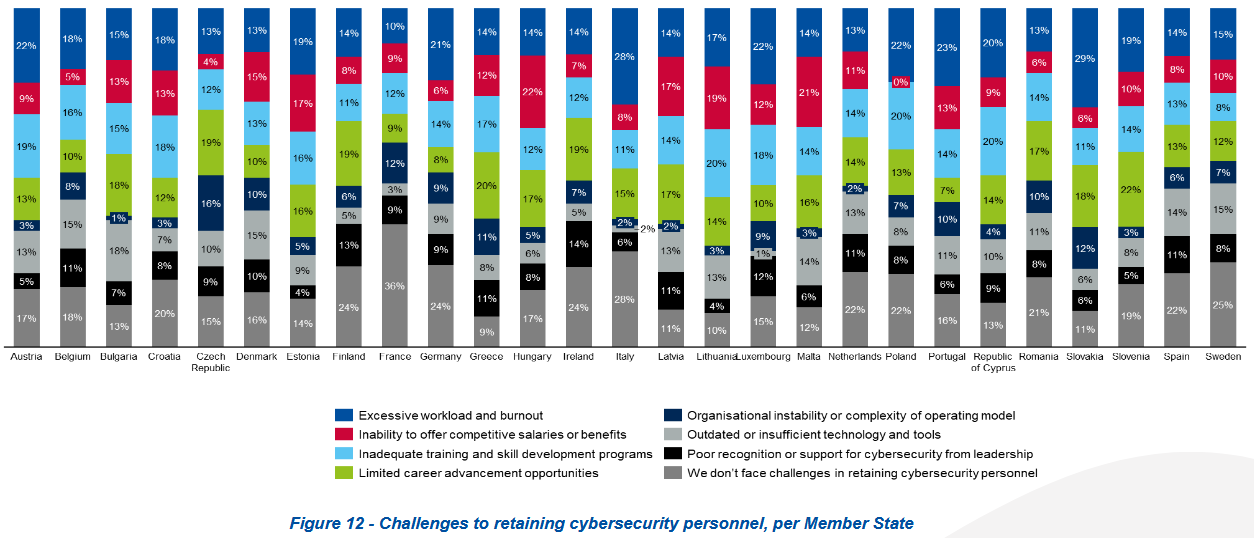
The study also looked at other facets of the EU cybersecurity landscape, such as budgets, with orgs spending €1.5 millions on average on cybersecurity budgets this year, roughly 9% of their total IT allocations.
Compliance was cited as the main driver behind 70% of all cybersecurity investments.
Despite all the work done on cybersecurity and NIS2 compliance, the patching of critical vulnerabilities and mission-critical systems can still take months.
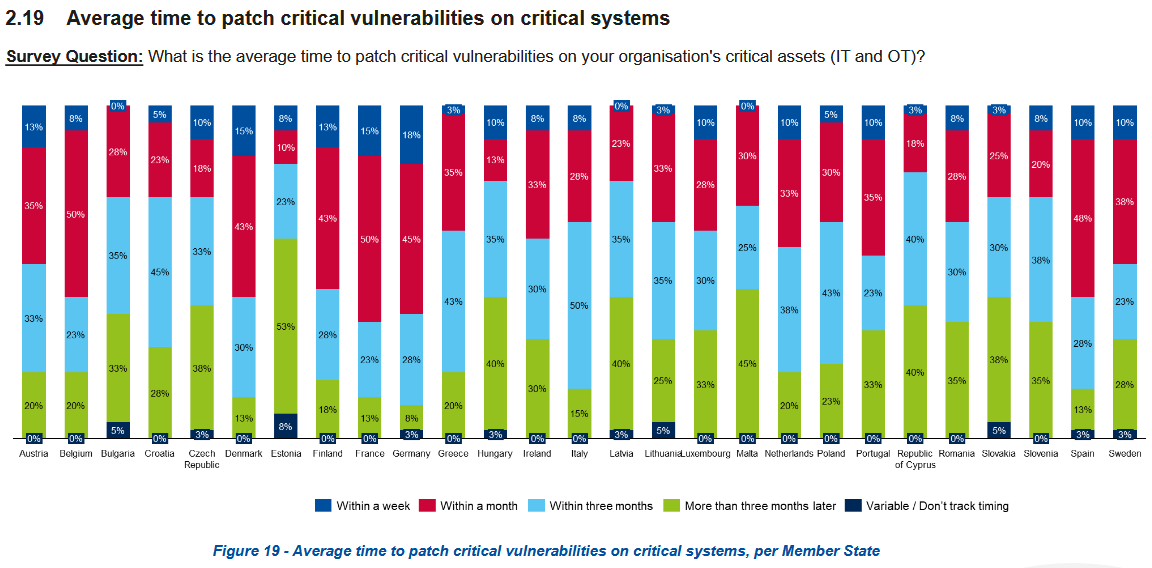
As for cyberattacks, while EU orgs reported a surge in DDoS attacks, they said they're more concerned about ransomware, supply-chain attacks, and phishing.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Coupang CEO resigns over data breach: The CEO of South Korean e-commerce giant Coupang has resigned after a massive security breach. Park Dae-jun filed his resignation on Wednesday after authorities raided the company's headquarters. The police search sought evidence related to a recent hack that exposed the personal data of two-thirds of the country's population. Coupang is the third major South Korean company that was breached this year. The CEOs of SK Telecom and Korea Telecom also resigned following their breaches. [The Korea Times]
Coupang hacker was a cybersecurity employee: South Korean authorities have identified the hacker as a 43-year-old Chinese national who worked inside the company's security program. He worked for the company between 2022 and 2024 and has already left the country. The suspect was employed in a department that handled authentication operations. [Korea JoongAng Daily//Chosun Biz]
Eltrans hack: Ukraine has hacked and wiped the servers of Russian logistics company Eltrans+. The cyberattack was conducted by Ukraine's military intelligence agency GUR and hacktivist group the BO Team. The two claim they wiped more than 165 TB of data from 700 servers and user systems. [UNN]
Petco takes down leaky Vetco site: Pet wellness company Petco has taken down the websites for its Vetco clinics. The portals were found to be exposing customer data without authentication. This included highly sensitive details such as customer names, home addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, signatures, medical tests, and more. [TechCrunch]
UK fines LastPass over breach: The UK's privacy watchdog has fined password manager LastPass £1.2 million over the company's 2022 security breach. The incident exposed the personal data of 1.6 million UK customers. The ICO says LastPass failed to implement robust technical and security measures. The hack took place in August 2022, when a hacker gained access to a LastPass employee's personal laptop and then jumped to the company's network.
Ransomware at HSE Ireland, again: The Irish healthcare system has fallen victim to a ransomware attack earlier this year in February. News of the incident came out just as the HSE started paying €750 to a group of 620 people who sued the agency for a similar 2021 that exposed their personal data. [BreakingNews.ie] [h/t DataBreaches.net]
Russia denies military registry hack: The Russian government has denied that hackers breached its military registry. The hack allegedly targeted the system's developer, a company named Micord. A group named Idite Lesom took credit for the breach. In the meantime, Micord's website has been offline for days. [iStories//The Record]
General tech and privacy
Startup goes after Twitter trademark: A new US startup named Operation Bluebird has asked the US Patent and Trademark Office to vacate old Twitter trademarks, claiming that Elon Musk has abandoned them. The effort is backed by a former Twitter trademark lawyer. [Reuters]
New PowerShell security feature: Microsoft is adding a new PowerShell security feature to warn users when they're about to execute web content. The new feature is rolling out with PowerShell version 5.1. The warning will alert users when executing the Invoke-WebRequest command without additional security parameters. It will advise users to add the -UseBasicParsing parameter to prevent possible malicious scripts from that page running on the system.
Meta restricts abortion accounts: Meta has restricted or banned the accounts of more than 50 organizations providing abortion advice. Some LGBTQ groups were also impacted. The bans seem to have been triggered by Meta's AI-based moderation tools triggering on non-explicit nudity posted by the groups and accounts. [The Guardian]
Twitter's right-wing bend: There's yet another piece of research on how Twitter is favoring right-wing accounts and how Musk is responsible for the push.
New research on Twitter (right before rebranding to X) shows right leaning accounts got outsized visibility from the algorithm & suggests this bias stemmed from different content production techniques (more sensational, outrage-bait) and from direct interaction w/ the new king of the platform: Musk.
— Kate Starbird (@katestarbird.bsky.social) 2025-12-10T20:40:20.481Z
OpenAI sees cyber trouble on the horizon: OpenAI says it's investing in AI model protections to prevent their abuse for cyber operations. This comes as lawmakers are cracking down on their abuse for offensive cyber and as the company expects the models to get even better at automating cyber abuse.
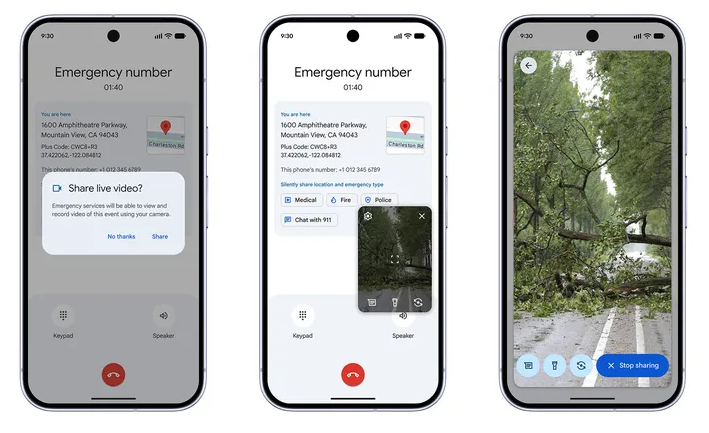
Android Emergency Live Video: Google is rolling out a new feature for Android users that will let them share live video with emergency services. The new feature is being rolled out in the US and some regions in Mexico and Germany. It will be available for all devices running Android 8 or higher. Android 8 was released in 2017.
CA/B Forum to sunset 11 domain validation methods: The CA/B Forum will sunset 11 domain validation methods used to issue TLS certificates. This includes methods that rely on email and phone verification, and IP and reverse address lookups. The verification methods will be phased out by March 2028.
Let's Encrypt to reach 1 billion certs: The Let's Encrypt project expects to reach one billion active certificates over the course of 2026.
Government, politics, and policy
Belarus blocks six crypto exchanges: The Belarusian government has blocked access to six cryptocurrency exchanges: OKX, BitGet, BingX, ByBix, Weex, and Gate.com. Officials said the companies ran "improper advertising" on their sites.
Russia preparing full Google ban: Russian lawmakers are preparing to block all Google services as they view the company's monopolistic position on the IT market as a threat to their entire economy. They're not wrong. [Gazeta.ru]
UK sanctions Chinese hacking firms: The UK government has imposed sanctions on two Chinese security firms for "reckless and irresponsible activity in cyberspace." Sanctions were levied against i-Soon and Integrity Tech. Both are contractors and have provided hacking services to Chinese intelligence services. Integrity Tech has been linked to a Chinese cyber-espionage group known as Flax Typhoon. Both companies have also been sanctioned by the US. The UK also sanctioned seven Russian individuals and networks for information warfare against the UK and Ukraine.
US readies "thought police" for foreign travelers: The US government will soon require all foreign travelers to provide five years worth of social media history. Foreign travelers will be required to provide social media accounts, email addresses, and phone numbers used over the past five years. The new requirement will be applied to foreigners from all countries, including those on the visa waiver program. This will include allied countries such as Japan, the EU bloc, Australia, and others. According to reports, US officials will be looking to deny entry to individuals who expressed anti-US, anti-Trump, and anti-Israel views. [BBC]
This is nothing more nor less than a method for the government to pick and choose which foreigners it deems suitable to allow into the country. This is a fascist infringement on free speech, and will be a huge problem for the World Cup and Olympics and tourist dependent communities.
— Ross Macfarlane (@rossmacfarlane.bsky.social) 2025-12-10T16:25:14.029Z
DAY THREE CBP is accepting 60 days of public comment on this proposal. According to the text of the proposal, comments must be in English and must include the OMB Control Number 1651-0111 and the agency name in the subject line. The email address to send them to: CBP_PRA@cbp.dhs.gov
— Shrub Dryad (@shrubdryad.bsky.social) 2025-12-11T17:44:57.919Z
Europe is destroying free speech, also when Europeans come to the U.S. we screen five years of their posts for thoughtcrime. https://t.co/FRjkoh9Z8R
— Matthew Gertz (@MattGertz) December 10, 2025
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Mike Lashlee, CSO of Mastercard talks to Tom Uren about why the company got into threat intelligence. Mike talks about bringing together payments insights with threat intel to get strong signals about fraud or crime, the benefits of international collaboration and when it makes sense for your CSO to also be the CISO.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Ukrainian bot farm operator arrested: Ukrainian authorities have arrested a 22-year-old man for hacking and selling social media accounts. He also managed a bot farm with more than 5,000 accounts. The suspect went online as FroZZZ and was also a dispute arbiter on the LOLZ hacking forum. He faces up to 15 years in prison.
US charges NoName057 and CARR member: The US has indicted a Ukrainian woman for participating in cyberattacks against critical infrastructure. Victoria Eduardovna Dubranova was allegedly part of two pro-Kremlin hacktivist groups named NoName057 and CyberArmyofRussia_Reborn (CARR). The US Justice Department says the groups tampered with US public water systems and caused an ammonia leak at a US meat processing factory. Dubranova pleaded not guilty in a US court this week. The US is also offering rewards for additional information on other members of the two groups [CARR//NoName057]. CISA, the NSA, and other international cybersecurity agencies also released joint security advisories on the activity of pro-Kremlin hacktivists, while Twitter also took down NoName057's account.


Crypto money launderer pleads guilty: A 22-year-old California man pleaded guilty to laundering cryptocurrency for a group of hackers. Evan Tangeman laundered $3.5 million worth of crypto-assets stolen by the hackers. He also helped them rent and buy homes across California and disguise the ownership.
Dutch man attacked emergency 112 service: Dutch prosecutors are seeking an eight-month prison sentence for a man who launched DDoS attacks against the country's 112 emergency line. The suspect was identified as a 47-year-old man from the city of Delft. He allegedly executed the attack using the SIM boxes of a company that rents telephone numbers. The man tried to frame the owners of the business, with which he had a business conflict.
US charges Accenture manager: The US Department of Justice has indicted an Accenture product manager with fraud for lying about compliance in government contracts. Danielle Hillmer allegedly claimed the company's cloud platform was FedRAMP compliant. She also allegedly obstructed federal auditors during 2020 and 2021, trying to hide the platform's deficiencies. She faces more than 30 years in prison if found guilty. [NextGov]
Cybercrime trainer gets jail sentence: A Malaysian man was sentenced by a Singaporean court to five years and six months in prison for training cybercriminals on how to use malware. Cheoh Hai Beng was charged with recording 20 videos that taught members of a cybercrime group how to deploy and use the Spymax Android remote access trojan. Cheoh was recruited by the group while incarcerated in a South Korean prison. [The Strait Times]
Crypto-exchange pleads guilty to laundering hacked funds: The Paxful cryptocurrency exchange has pleaded guilty to laundering crypto-assets and helping sanctions evasion. The platform has agreed to pay a $4 million fine to the US to settle the charges. Paxful failed to maintain a know-your-customer system and other anti-money-laundering measures. According to the US Justice Department, the platform was used to launder funds from online fraud, romance scams, extortion schemes, and prostitution.
More VS Code malicious extensions: ReversingLabs has identified 19 malicious VSCode extensions. Most used a technique to hide their payload (a Rust-based trojan) as a PNG image in their dependency folder.
SHADOW-VOID-042: Trend Micro looks at SHADOW-VOID-042, a phishing campaign abusing the company's brand. Trend believes the campaign may be linked to Void Rabisu, a Russian dual e-crime and cyber-espionage group.
Malware technical reports
PeerBlight Linux backdoor: Huntress has spotted a new Linux backdoor named PeerBlight that is being installed on systems hacked using the React2Shell vulnerability.
NANOREMOTE: Elastic's security team has discovered NANOREMOTE, a new Windows backdoor that appears to have evolved from the FINALDRAFT backdoor used by the REF7707 threat actor cluster.
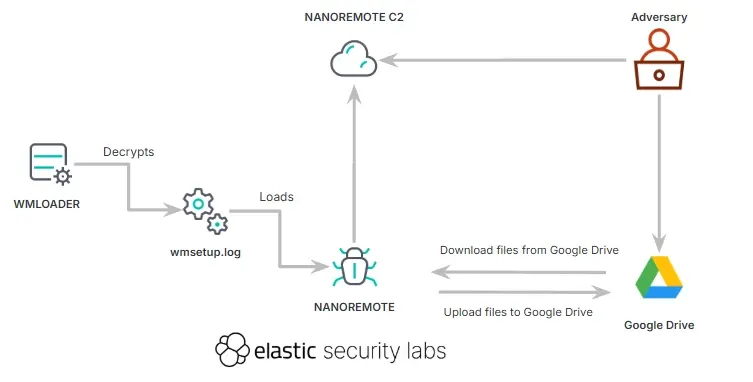
Mythic: Kaspersky looks at how defenders could detect the Mythic red team framework, which has been recently adopted by several threat actors for their offensive operations.
InboxPrime AI: Researchers at Abnormal AI have spotted a new phishing kit called InboxPrime AI. It obviously uses AI for automation, hence the name.
PyStoreRAT: Morphisec has identified PyStoreRAT, a previously undocumented JavaScript-based RAT delivered through Python and JavaScript files embedded inside GitHub-hosted Python repositories. The repos were themed as development utilities or OSINT tools.
ValleyRAT: Check Point has published a technical analysis of ValleyRAT, a remote access trojan developed and used by China-based threat group SilverFox.
BTMOB: Italian security firm D3Lab looks at BTMOB, a new Android remote access trojan.
VolkLocker RaaS: The CyberVolk pro-Kremlin hacktivist group has returned with a new ransomware strain named VolkLocker. The ransomware does some "new stuff," but it's not that good, since you can decrypt it. Pretty glaring flaw if you wanna run a RaaS.
"Our analysis reveals an operation struggling with the challenges of expansion: taking one step forward with sophisticated Telegram automation, and one step backward with payloads that retain test artifacts enabling victim self-recovery."
Warlock ransomware: Sophos has published a report on how the Gold Salem group deploys its Warlock ransomware on compromised networks. The report covers 11 incidents across six months.
01flip ransomware: A new Rust-based ransomware named 01flip has been spotted in attacks targeting orgs across the APAC region. The ransomware can run on Windows and Linux and data from past incidents is being sold on dark web forums.
DroidLock ransomware: Mobile security firm Zimperium has discovered a new Android ransomware strain named DroidLock. It's not actually ransomware, since it doesn't encrypt files but only locks the screen.

Sponsor section
In this sponsored Soap Box edition of the Risky Business podcast, host Patrick Gray chats with Mastercard's Executive Vice President and Head of Security Solutions, Johan Gerber, about how the card brand thinks about cybersecurity and why it's aggressively investing in the space.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Charming Kitten payroll leak: The salaries of 35 cyber operatives linked to Iran's Charming Kitten (APT35) espionage group have been leaked online.
Ashen Lepus (WIRTE): Palo Alto Networks has detected new activity and malware (AshTag) from Ashen Lepus (WIRTE), a threat actor linked to Hamas. The AshTag attacks were used for hands-on activity on compromised hosts.
New Russian disinfo op backs Musk's EU attacks: Russian disinformation group Matryoshka is running a campaign claiming that fact-checking groups are responsible for fake news spreading on Twitter. The campaign launched shortly after the EU fined Twitter for failing to act on disinformation.
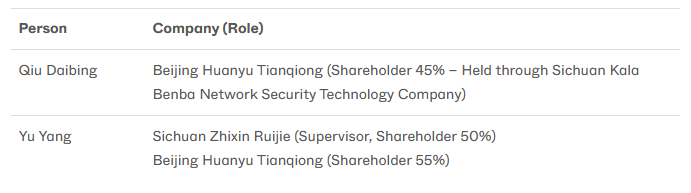
Salt Typhoon operators trained with Cisco: At least two individuals linked to China's Salt Typhoon hacking group have participated in Cisco cybersecurity training programs. According to SentinelOne, Yu Yang and Qiu Daibing participated in the Cisco Network Academy while they were students in the early 2010s. The two own cybersecurity companies that the US has tied to Salt Typhoon intrusions. Beijing Huanyu Tianqiong and Sichuan Zhixin Ruijie have allegedly hacked more than 80 telcos for Chinese intelligence.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Traefik misconfiguration disables TLS verification: A popular reverse proxy and ingress controller shipped misconfigured versions for the past five months. The Traefik setting that enabled TLS verification was actually disabling it across the board. The issue (CVE-2025-66491) was found by Aisle Security and corrected this month.
Chrome zero-day: Google has released a security update to patch an actively exploited Chrome zero-day. The company has not provided any details about the bug or its CVE. This suggests the zero-day was discovered in recent attacks and a patch shipped before all formalities were completed. It is the eight Chrome zero-day patched this year.
Gogs zero-day: Threat actors are exploiting a zero-day in the Gogs open-source self-hosted Git server. The zero-day (CVE-2025-8110) is a bypass of a previous remote code execution attack. According to Google's Wiz security division, more than 700 Gogs servers have already been compromised. The Gogs project has yet to release a patch.
SOAPwn vulnerabilities: .NET applications are vulnerable to a new set of vulnerabilities known as SOAPwn. The issues were discovered by WatchTowr Labs and can lead to remote code execution attacks. Vulnerable applications include the Umbraco CMS, Barracuda's Service Center, the Ivanti Endpoint Manager, and more. Microsoft classified the issues as DONOTFIX and are still unpatched.
Notepad++ fixes update hijack flaw: The Notepad++ code editor has rolled out a patch to fix its update system. The project released the patch after users reported that their code editor downloaded and installed malicious updates containing malware. The patch enforces file signature and certificate validation to prevent users from being redirected to malicious update servers.
Aye. Notepad++ didn’t verify the network traffic during the update process nor the download it received and executed. Activity goes back to August, I tweeted a payload and the threat actor nuked their infrastructure. Gonna put out IOCs later but the hunting guides in the write up will catch.
— Kevin Beaumont (@doublepulsar.com) 2025-12-11T20:00:02.695Z
Microsoft bug bounty expands: Microsoft has expanded its public bug bounty program to cover any vulnerability impacting its online services. The new rules will apply to both Microsoft-owned domain and third-party code. The company will pay bounties for vulnerabilities in other projects, as long as the vulnerability has a direct impact on Microsoft services.
ConsentFix attack: Push Security researchers have discovered a new variation of the ClickFix attack. The new ConsentFix technique relies on tricking users into copy-pasting text that contains their OAuth material into an attacker-controlled web page. Push Security has spotted the technique in attacks targeting Microsoft business accounts. The technique is a variation of an attack used by Russian state-sponsored hackers earlier this year. Those attacks relied on tricking victims into sending their OAuth material in an email reply to the hackers.
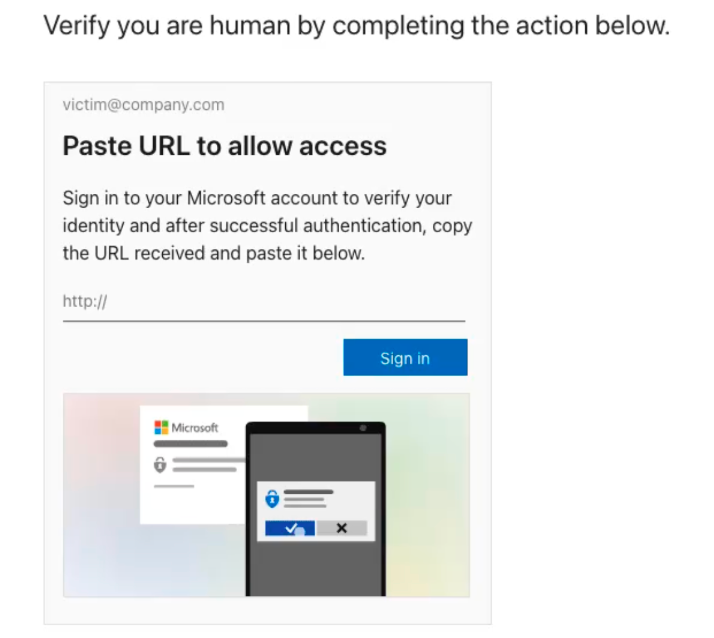
MCP server exposure: Security firm Bitsight has found more than 1,000 MCP servers exposed on the internet with no authorization in place and exposing sensitive data.
SPA exposure: Security firm Intruder scanned almost 5 million single-page applications and found more than 42,000 tokens exposed in their code.
Docker Hub secrets leak: Security firm Flare has scanned the Docker Hub portal and found secrets and tokens, including for production systems, in more than 10,000 images.
Gonna flog this dead horse since this mirrors my experience with GCR and other registries: BUILD CONTEXT LEAKS ARE EVERYWHERE (and OCI images are the absolute worst offenders). You're probably doing it _right now_.
— amenbreakpoint (@amenbreakpoint.com) 2025-12-11T11:55:40.631Z
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Check Point, DryRun Security, ENISA, ITRC, and Netwrix have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
Deepfake insurance: With the proliferation of AI technology, cyber insurance provider Coalition has added deepfake response to its cyber insurance services.
New tools—SCOMHound and SCOMHunter: SpecterOps has released SCOMHound and SCOMHunter, tools for enumeration and attacking System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) infrastructure.
New tool—Vulnhalla: CyberArk has released Vulnhalla, a new open-source tool that uses AI and other methods to comb through CodeQL datasets.
New tool—SessionHop: Security researcher Andrew Oliveau has released SessionHop, a tool to hijack specified user sessions.
New tool—KustoHawk: Security engineer Bert-Jan Pals has released KustoHawk, an incident triage and response tool for Microsoft Defender XDR and Sentinel environments.
AWS re:Invent videos: Talks from the AWS re:Invent 2024 security conference, which took place earlier this month, are available on YouTube.
OpenSSL Conference videos: Talks from the OpenSSL Conference, which took place in October, are available on YouTube.
Swiss Cyber Storm videos: Talks from the Swiss Cyber Storm 2025 security conference, which took place in late October, are available on YouTube.
OWASP Agentic Top 10: The OWASP Foundation has released a Top 10 list of risks to Agentic AI Applications.
2025 CWE Top 25: MITRE has published the list of Top 25 most common software vulnerabilities of 2025, also known as the CWE Top 25.

Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray discuss a new report proposing a framework for deciding when cyber operations raise red flags. It suggests seven red flags and could help clarify thinking about how to respond to different operations.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq wonder whether it is possible to deter states from cyber espionage with doxxing and other disruption measures.




