Risky Bulletin: DRAM price hikes set to impact firewalls too
In other news: China bans Israeli and US cybersecurity products; Trump re-nominates Sean Plankey for CISA Director; Microsoft takes down RedVDS RDP marketplace.

This newsletter is brought to you by cloud security firm Prowler. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
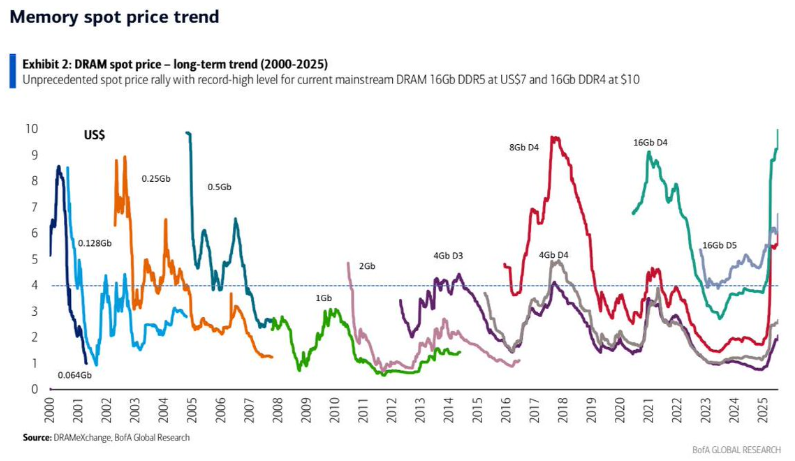
The current price hikes and supply shortage of DRAM memory chips are expected to also impact firewall makers and the cybersecurity market.
Powerful DRAM is a crucial component for the manufacturing of modern next-gen firewalls, a staple in the cybersecurity defense of any major enterprise.
Investment advisory firm Wedbush says firewall companies will see thinner margins this year due to the rising DRAM costs. This will impact their bills of materials, with the extra costs being passed down to customers as product price increases. This will likely lead to lower sales, smaller profit margins, and weaker investor yields.
Companies like Fortinet, Palo Alto Networks, and Check Point are expected to see the biggest headwinds on the stock market this year as a result of DRAM hikes.
Firewall makers join laptop, PC, and smartphone vendors, all of which are expected to see big headwinds this year due to collapsing sales.
DRAM prices have been up between 60% and 70% since last year and are expected to grow another 50% in the first quarter of the year alone.
Most of this year's supply has already been bought by AI companies for their future data centers.
DRAM maker Micron has exited the consumer market and focused strictly on supplying AI and data center makers. South Korean company SK Hynix is also pondering a similar decision from both the DRAM and NAND/SSD markets.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this special documentary episode, Patrick Gray and Amberleigh Jack take a historical dive into hacking in the 1980s. Through the words of those that were there, they discuss life on the ARPANET, the 414s hacking group, the Morris Worm, the vibe inside the NSA and a parallel hunt for German hackers happening at a similar time to Cliff Stoll’s famous Cuckoo’s Egg story.
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Whistleblower leaks names of ICE agents: The names and personal details of more than 4,500 ICE agents were released by a DHS whistleblower. The list includes names, work emails, telephone numbers, and roles. The whistleblower released the data after an ICE agent shot Renee Good in Minneapolis last week. The leak site was immediately targeted with DDoS attacks. [The Daily Beast]
Major hack at Victorian schools: A hacker has accessed the information of Victorian government schools in Australia. All current and former students are affected. Stolen data includes names, email addresses, and encrypted passwords. The data hasn't yet been leaked online. [ABC]
CIRO hack: Hackers have stolen data on more than 750,000 investors on the Canadian stock market. The incident took place last August and was the result of a phishing attack. The Canadian Investment Regulatory Organization is currently notifying affected parties.
Free Mobile fined for breach: France's privacy watchdog has fined Free Mobile €42 million for a 2024 data breach. The incident exposed the details of more than five million customers, from names to addresses and even IBAN numbers. CNIL said the company failed to implement basic security measures. Free Mobile also misled customers in the notification email about what happened and what data was stolen.
Pax8 exposes customer data: Cloud app marketplace Pax8 says it mailed the data of 1,800 partners to 40 UK orgs. LOL!
Keylogger at US bank: Sansec identified a keylogger on an internal store of a major US bank. The store is used by the bank's 200,000 employee-strong workforce for work-related purchases.
"This breach is worrying because bank employees often reuse corporate credentials. Stolen passwords could provide attackers with footholds into internal banking systems. Employee stores frequently fall outside the scope of standard security audits, making them juicy targets."
General tech and privacy
Anthropic donates to PSF: AI company Anthropic has donated $1.5 million to the Python Software Foundation. The funds will be used to improve the security of the Python ecosystem, for projects like CPython and PyPI.
Twitter nerfs pedo-Grok: After almost any privacy watchdog worth its salt started investigations, Twitter is finally disabling Grok's ability to generate sexualized and nude images. Took them a damn while.
FTC bans GM from selling data: The US Federal Trade Commission has banned General Motors from selling car owner data to consumer reporting agencies. The data was collected via the OnStar platform installed on the company's cars. It was later resold to insurance companies, which then increased insurance coverage fees based on driving patterns.
Google settles COPPA lawsuit: Google has agreed to pay $8.25 million to settle a class-action lawsuit for COPPA violations in the US, aka tracking children under the age of 13. [The Record]
Teens embrace cellphone bans: The number of teens that support banning cellphones in class has risen this year to 41%, according to Pew Research, although a full school-day ban is still widely considered a bit of a stretch.
Closed Australian accounts: Australia says online platforms have closed about 4.7 million accounts to comply with the country's new kids under 16 social media ban.
Mullvad drops OpenVPN: The Mullvad VPN service has dropped support for OpenVPN tunnels in its client. The company says WireGuard provides the same anti-censorship features as OpenVPN, but better security.
Chrome 144: Google has released version 144 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest change in this release is support for the new <geolocation> HTML element, preference tampering protection on Windows, and a simplified new tab page. The Google Gemini AI assistant is now also fully integrated into Chrome on macOS and Windows. <sarcasm> Yey! </sarcasm>
Government, politics, and policy
China bans US and Israeli security products: The Chinese government has told local companies to stop using cybersecurity products from almost a dozen of American and Israeli companies. VMware, Fortinet, Palo Alto Networks, and Check Point are on a list of companies Beijing has sent to domestic firms. According to Reuters, officials cited national security concerns for the ban.
Russia increases fines for illegal SIMs: Russia is doubling the fines for individuals who sell unregistered SIM cards. The fines will grow to 1 million rubles ($13,000), according to a new bill. Russia started requiring telcos to register SIM cards to their buyers last year to counter fraud and their use in Ukrainian drones. [Vedomosti]
US tech giants ally with EU far-right parties: Lobby groups of US tech giants have aligned themselves with far-right groups in the EU Parliament to roll back tech regulations across the bloc. [The Brussels Times]
New ANCHOR team will replace CIPAC: The US Department of Homeland Security is preparing to launch a new body to help secure US critical infrastructure. The new ANCHOR team is set to replace the old Critical Infrastructure Partnership Advisory Council, or CIPAC. The DHS shut down CIPAC last year after Trump took office. The new body will serve as a communications hub between the public and private sector and will help operators defend against threats, including cyber attacks. [CyberScoop]
Confirming this story about DHS readying a CIPAC replacement called ANCHOR. It's been sitting on DHS Secretary Noem's desk for weeks, my sources said, even as some details remain in flux. DHS hasn't told infrastructure sector representatives much, either. www.cybersecuritydive.com/news/dhs-cri...
— Eric Geller (@ericjgeller.com) 2026-01-15T16:36:55.630Z
White House re-nominates Plankey for CISA: The Trump administration has re-nominated Sean Plankey for the role of CISA Director. Plankey was also nominated for the role last year, but never passed through the Senate. Senators on both sides of the aisle put a hold on his nomination. [CSO Online]
US asks UN to crack down on DPRK remote IT workers: The US has asked the United Nations to crack down on North Korea's use of remote IT workers to collect funds for its nuclear missile program. More than 40 countries have been impacted by the scheme last year. [The Record]
Senate passes DEFIANCE Act: The US Senate has passed a bill to allow victims of nonconsensual deepfake pornography to sue those who produced and distributed the images or videos. The DEFIANCE Act passed with unanimous consent. The bill was also introduced in the US House, with multiple sponsors from both parties.
Offensive US cyber ops get momentum: During a hearing at the US Subcommittee on Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Protection at the House Homeland Committee, experts have called for a deeper integration of cyber capabilities in military doctrine to enable mass-scale industrialized US offensive cyber capabilities. [NextGov]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Prowler founder and CEO Toni de la Fuente explains how implementing AI systems brings new security challenges that differ for traditional cloud workloads. Toni also talks about ‘attack paths’ in the context of cloud infrastructure and using them to minimise risk.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Nefedov poster: A Russian man named Oleg Nefedov has been finally confirmed to be the leader of the BlackBasta ransomware group. A wanted poster was issued by German authorities last week. Nevedov was arrested in Armenia in June of 2024. He was released and fled to Russia three days later after a judge failed to extend the arrest warrant. In BlackBasta internal chats, Nefedov bragged of calling Russian officials and requesting a "green corridor" back home. [Der Standard]

US Supreme Court hacker to plead guilty: A Tennessee man is expected to plead guilty to hacking the US Supreme Court. Nicholas Moore accessed the court's systems at least 25 times between August and October 2023. Court documents don't reveal what data Moore accessed. [TechCrunch]
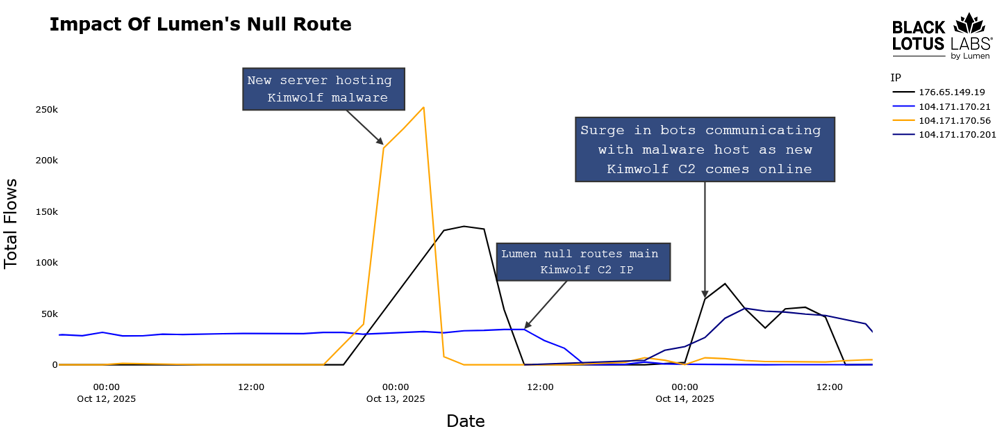
Lumen sinkholes Kimwolf servers: Internet infrastructure company Lumen has sinkholed more than 550 command and control servers for the Kimwolf DDoS botnet. Malware on almost 250,000 devices was cut off from communicating with the attackers. Kimwolf recovered a day after the takedown, but only managed to pull together a fraction of its original size. The botnet is known for its use in hyperscale size DDoS attacks and the use of residential proxy infrastructure to relay scans and exploitation activity inside local networks.
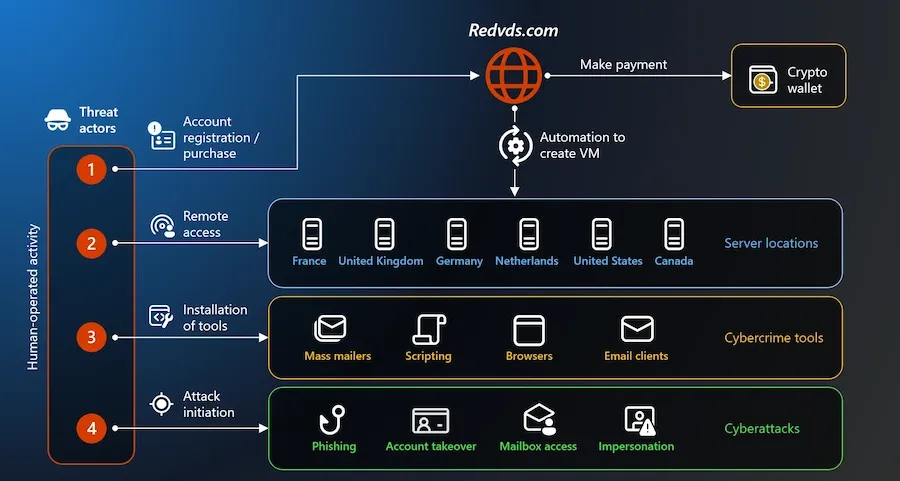
Microsoft takes down RedVDS: Microsoft and law enforcement agencies have shut down the RedVDS server marketplace. The site sold access to compromised RDP servers to other cybercrime gangs. The servers were later reused as infrastructure to host or carry out mass-phishing, BEC scams, account takeover, and other crimes. Raids took place across Germany, but no suspects have been arrested so far.
CyberArk hacks StealC infrastructure: The operator of the StealC infostealer is a Russian-speaking individual based in the former Soviet space. Security firm CyberArk tracked down the operator after finding and exploiting vulnerabilities in the malware's infrastructure. The company's researchers found the bugs after analyzing the malware's source code, which was leaked online early last year.
Money mule sentenced in Russia: A Russian has sentenced a man to six years in prison for working as a money mule for telephone scammers.
Australia warns about AI leaks: The Australian cybersecurity agency has warned local businesses against uploading customer data and files to AI chatbots or genAI platforms.
GhostPoster size doubles: Back in December, Koi Security discovered GhostPoster, a network of 17 malicious Firefox extensions. LayerX says it found an additional cluster of 17 more extensions, these ones also impacting Chrome and Edge. These new ones have an install base of over 840,000 users and some of them date back to 2020.
SmarterMail exposure: Around 8,000 of 18,000 internet-exposed SmarterMail servers lack a crucial patch for a recent vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-52691.
Microsoft, most abused brand in phishing mails: According to Check Point, Microsoft is today's most abused brand in phishing emails, with its logo plastered over one of every five phishing lures, way over the 13% seen by Google in second place.
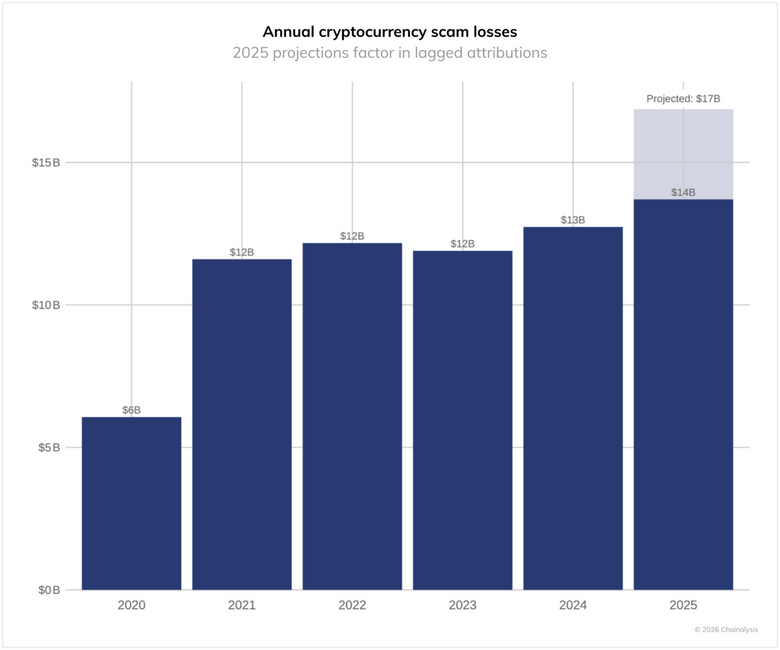
Scammers stole $14b last year: Scammer groups received $14 billion worth of cryptocurrency in 2025, just above the $13 billion they made the year prior. The average scam payment extracted from victims also increased this year from $782 to $2,764. High-yield investment and pig butchering remained dominant categories by volume, according to Chainalysis.
Malware technical reports
Magecart campaign: Silent Push researchers have uncovered a new Magecart campaign dating back to at least 2022. The company discovered the campaign while studying the infrastructure of bulletproof hosting provider Stark Industries.
GootLoader: Expel looks at recent campaigns leveraging malformed ZIP files to deliver the GootLoader malware.
Sicarii's one-off activity: Check Point looks at the strange case of Sicarii, a ransomware operation that appeared last year and only listed one single victim.
DeadLock ransomware abuses smart contracts: Group-IB researchers have spotted the first-ever ransomware strain (named DeadLock) to abuse blockchain smart contracts for its operations. The technique has been used before by other cybercrime ops and APT crews.
DragonForce ransomware: S2W looks at DragonForce, the ransomware group behind the RansomBay leak portal.
Predator spyware: Jamf researchers have analyzed the Predator spyware and have specifically focused on the malware's anti-analysis techniques. The report also uncovered a new feature that allows Predator operators to know why an implant failed and fine tune future targeting attempts.
Sponsor section
In this sponsored product demo, Prowler founder and CEO Toni de la Fuente walks Risky Business host Patrick Gray through the company's open-source cloud security platform. Toni demonstrates how Prowler can identify and remediate security issues across AWS, Azure, GCP, and Kubernetes. There's a pointy-clicky GUI interface and a CLI, and both come in handy in different ways. The Prowler platform is completely free and open source, but there is a hosted version you can pay for if you don't want to run it yourself.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Turla's Kazuar: Security researcher Dominik Reichel looks at v3 of Turla's Kazuar loader, "a sophisticated, multi-stage infection chain designed to bypass modern security layers."
UAT-8837: A Chinese APT group has focused last year on compromising critical infrastructure across North America. Cisco has linked multiple intrusions to a group it tracks as UAT-8837. The intrusions seek to establish an initial foothold and backdoor networks for future access.
Mustang Panda's LOTUSLITE: An Acronis report looks at LOTUSLITE, a new C++ backdoor used in Mustang Panda's espionage operations.
"Infrastructure analysis and execution patterns show moderate-confidence overlap with Mustang Panda tradecraft, including delivery style, loader–DLL separation and infrastructure usage. Attribution is assessed at a behavioral level and does not rely on code reuse alone."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
ProtonVPN security update: ProtonVPN has urged customers using manual OpenVPN config files for their client to check their dates. Customers using files older than September 2023 were urged to re-download their configs, citing security reasons.
Node.js fixes DoS bug: The Node.js team has patched a pretty bad denial of service bug in its engine that can easily exhaust server memory. The bug can allow attackers to crash servers using large nested data structures. It was discovered by the Vercel team and impacts almost all Node.js applications. This includes Next.js, Node.js frameworks, and most performance monitoring tools.
Redis write-up: jFrog researchers have published a write-up on a Redis RCE from last November, tracked as CVE-2025-62507, and fixed in Redis 8.3.2.
Revive says the obvious: The Revive ad server project has reassured its customers that the recent spike in security updates is a good thing for them, since that means security flaws are getting patched. I honestly have no idea who could have complained about this.
"The Revive Adserver software has a long and rich history, and many parts of the code are more than 2 decades old. A good portion of the software was developed in a time when security was much less top of mind than it is today. The overall understanding of, and attention for, security in software and systems is much more sophisticated nowadays."
BLUVOYIX patches bugs: Bluspark Global has patched several vulnerabilities in the BLUVOYIX logistics service. The bugs could have allowed threat actors to access customer accounts and track freight and component shipments. The vulnerabilities allowed full access to the platform's API without the need to authenticate, which could then be used to create admin accounts for deeper access on the platform.
Delta DVP vulnerabilities: OPSWAT has discovered multiple vulnerabilities in Delta DVP PLCs. The bugs can be used to bypass authentication, leak sensitive data, and write on the device.
Google releases Net-NTLMv1 rainbow tables: Google's Mandiant division has released the largest-ever collection of Net-NTLMv1 rainbow tables. The tables will help security researchers recover NTLM keys in under 12 hours using cheap consumer hardware. Mandiant is releasing the tables to help highlight the insecure protocol and convince decision makers to move away to more modern authentication standards.
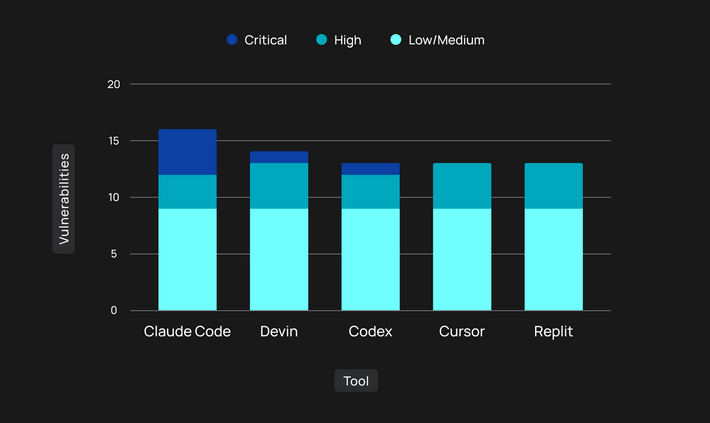
Coding agents good at one thing, bad at others: AI coding agents are outputting vulnerable code. A test of five top coding agents found 69 vulnerabilities in their code. According to Tenzai, agents didn't generate any code injection bugs like SQLi and XSS, but couldn't handle other vulnerability classes like business logic and SSRF.

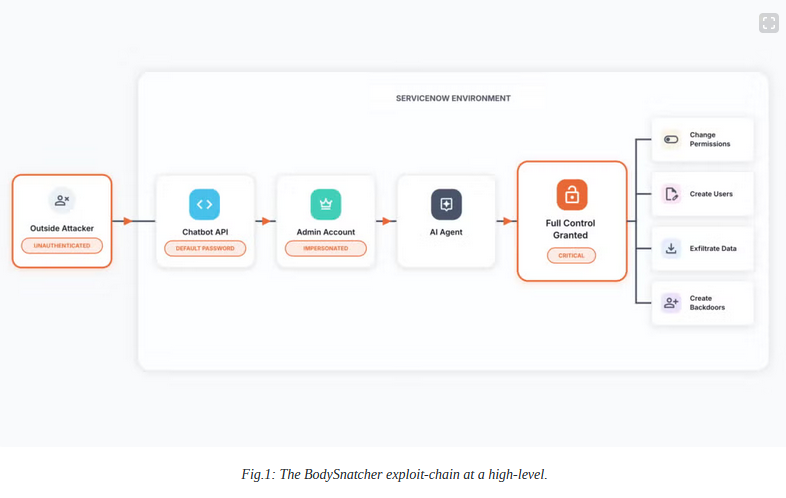
BodySnatcher attack: AppOmni researchers have found a vulnerability in the ServiceNow Virtual Agent that could have allowed attackers to bypass authentication and run prompts on any customer accounts.
Reprompt attack: Varonis has discovered a "reprompt" attack against Microsoft's Copilot AI agent that bypasses its security protections and could allow data exfiltration. Varonis call it a reprompt attack because the malicious commands are retrieved from a remote server after an initial prompt.

WhisperPair attack: More than a dozen headphone and speaker models are vulnerable to a new vulnerability in the Google Fast Pair protocol. The WhisperPair attack allows threat actors to hijack a user's accessories without user interaction. In certain scenarios, the attackers can also register as the owners of those accessories and track the movement of the real owners via the Google Find Hub. Google awarded the researchers $15,000 for their finding and notified accessory makers about the issue and the need for patches.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Akamai, Check Point, Dr.Web, GuidePoint Security, Reflectiz, ReliaQuest, and Sophos have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
China's top cybersecurity companies: The Natto Thoughts team looks at China's top 20 biggest cybersecurity companies and what they do.
New tool—ConfigManBearPig: SpecterOps has released ConfigManBearPig, a PowerShell script that collects SCCM data and maps out misconfigurations.
New tool—TokenFlare: Jumpsec Labs has released TokenFlare, a serverless AitM simulation framework for Entra ID and M365 accounts.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about the Chinese government's reactive approach to tackling scam compounds. It's driven by bad news on domestic media and therefore focuses on the compounds that are targeting Chinese citizens. Rather than eliminating the industry, that may instead be shaping the industry to focus on other countries and particularly Americans.
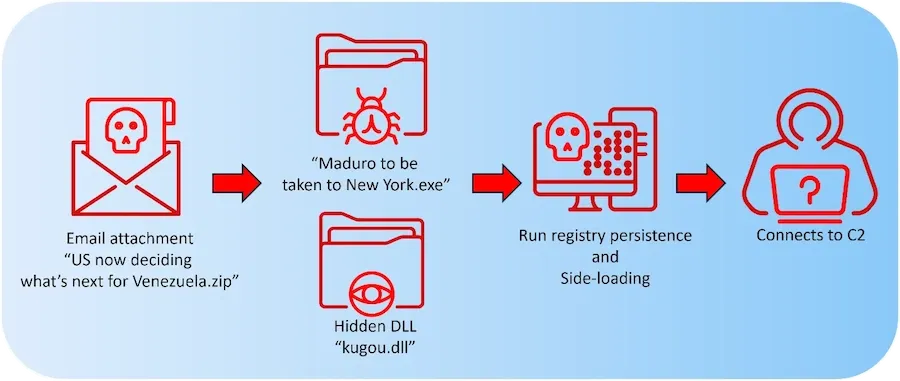
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq about the role of cyber operations in the US capture of Venezuela’s president Nicolas Maduro.




