Risky Bulletin: Chrome 140 comes with new hardened cookies
In other news: Cyberattack disrupts Bridgestone tyre factories in NA; a new infostealer takes your photo when you watch porn; CA misissued certificates for Cloudflare infrastructure for more than a year.

This newsletter is brought to you by Push Security. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Google has released version 140 of its Chrome browser this week, with support for a new security feature designed to protect server-set cookies from client-side tampering.
The new feature is a cookie prefix, a piece of text added before the names of a browser's cookie files.
Cookie prefixes are different from cookie headers and, in the words of security firm ERNW, are a lesser-known browser security feature that is rarely used by web developers.
They were first introduced in 2016, when two cookie prefixes, __Secure- and __Host-, launched with Chrome and Firefox. The first required cookies to be sent via HTTPS only, while the second pinned cookies to a desired domain in order to block session fixation attacks.
Standards-making is a convoluted and annoying process with loads of layers of unending conversations, but it appears that earlier this year, the Web gods agreed that we will get two new prefixes in __Http and __HostHttp.
The new prefixes were purely designed to help server operators determine when someone messed with their cookies.
The __Http prefix will be used for cookies set by the server, while the __HostHttp is a former server-set cookie that was modified on the client-side, in the browser.
As Google explains, this can happen quite often, and can be something innocous such as a confused developer modifying a wrong file, or a malicious modification made via an XSS exploit or by a malicious browser extension.
These two prefixes can be layered with other cookie security features like the Secure flag and the HttpOnly attribute via the Set-Cookie header, which can't be modified via JavaScript, ensuring that these cookies were set by the server only.
The new cookie prefixes are live in Chrome 140, released this week. According to this Bugzilla entry, they also shipped with Firefox 142 last month, although this is not listed in the official release notes.
In addition to the new cookie prefixes, Chrome 140 also released with security patches and other webdev-related changes.
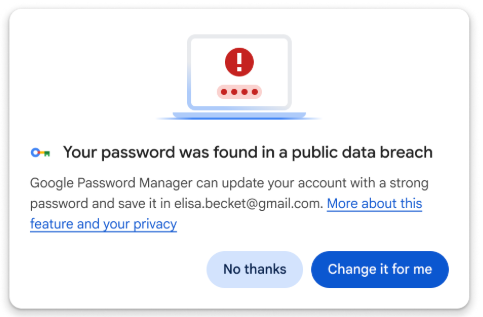
Other features that shipped with this release include a system that lets Chrome change compromised passwords on the owner's behalf, the Gemini AI assistant is now included in Chrome for US users, and the ability to launch Chrome into new profiles via the command line (software testers will love this one).
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Brazil mega-hack: Hackers have breached an IT provider for Brazilian banks and attempted to steal more than $77 million from multiple customers. The hack targeted Sinqia, a provider of software that integrates with the country's Pix payment system. The attempted theft targeted funds owned by British bank HSBC. Sinqia says it blocked most of the attacker's transfers. [Additional coverage in O Globo/English coverage in Bloomberg]
Bridgestone factories disrupted: A cyberattack is disrupting the activity at some Bridgestone tyre factories across North America. Factories in South Carolina and Quebec, Canada, have been affected. It's unclear if this was ransomware, and no group has yet taken credit for the intrusion. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
Google extorted to fire two employees: Hackers are threatening to release Google data unless the company fires two members of its security team. A group calling itself Scattered LapSus Hunters demanded the firing of the two employees and that the company stop any investigations into its activity. The group is believed to be the one that hacked Google's Salesforce account last month. [Additional coverage in SC Media]
Proofpoint breach: Email security firm Proofpoint has joined the long list of infosec vendors that have been impacted by the Salesloft Drift incident.
Workiva breach: SaaS provider Workiva says hackers have accessed and stolen data from their Salesforce account. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
Chess.com breach: Online chess portal Chess.com said hackers stole the data of 4,500 users in a June breach. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Texas sues PowerSchool over hack: The Texas OAG has sued edu software platform PowerSchool over its 2024 security breach. [h/t Dissent Doe]
Venus Protocol recovers hacked funds: The Venus Protocol cryptocurrency project has recovered $13.5 million in stolen assets. The funds were stolen on Tuesday after a phishing attack on a whale account. The project used its governance powers to reverse the theft and restore the funds to the owner. [Additional coverage in CoinCentral]
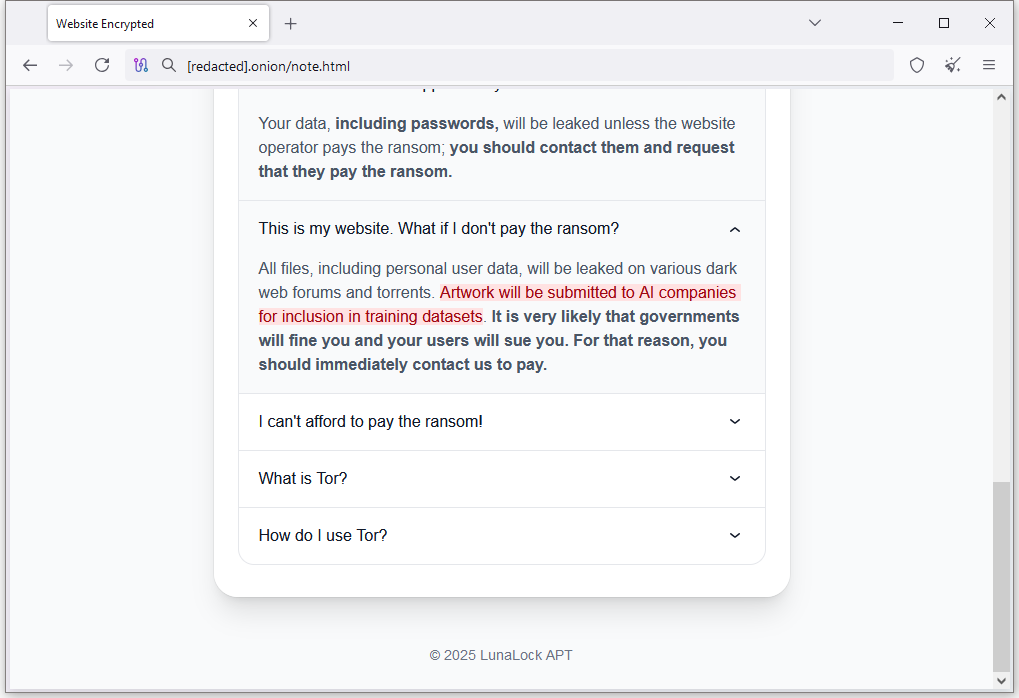
New ransomware extorts artists: A ransomware group has hacked an art-commissioning portal and is extorting its owners and artists. The new LunaLock group has threatened to submit the stolen artwork to AI data training sets unless the Artists&Clients website pays their ransom. The group is asking for a $50,000 ransom. Artists&Clients is LunaLock's first victim. [Additional coverage in Cybernews]
General tech and privacy
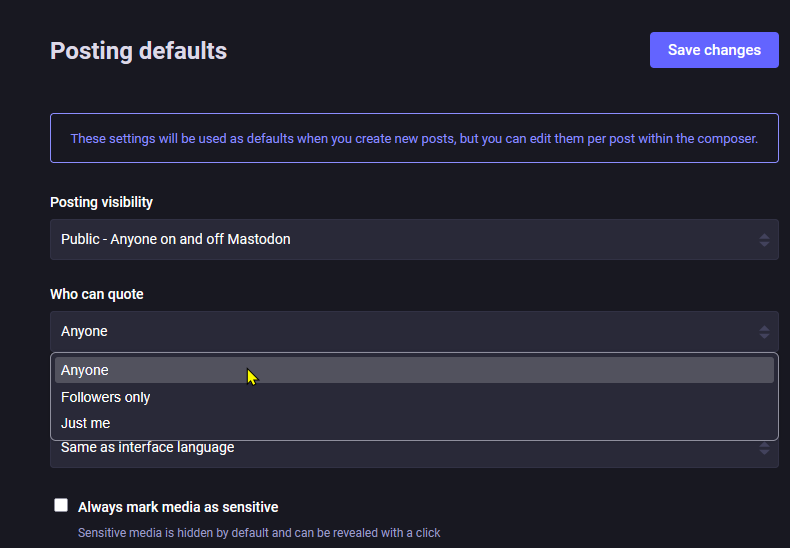
Mastodon adds support for post quotes: About half a decade later after the feature was first requested, Mastodon has added support for post-quoting. This will go live in the platform's next update, but users can configure it in advance.
Mozilla extends Firefox EOL again: Mozilla has extended the Firefox on Windows 7 and 8 for a third time. The company will support Firefox until March next year. It was initially supposed to discontinue Firefox support in September last year, before delaying the deadline to this month.
Microsoft BASIC source code: Microsoft has released the source code of its Microsoft 6502 BASIC programming language. [Additional coverage in Thurrott]
Google antitrust lawsuit ruling: A US judge ruled that Google will not be required to break up its search business, nor divest Android or Chrome. Google will be barred from using exclusive contracts with smartphone makers and browsers that lock out rivals. The company will also have to share some of its search index data with rivals and establish a five-person antitrust committee to monitor its business practices. The ruling ends the DOJ's antitrust case against Google's search monopoly, barring any appeals. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch/Court ruling PDF]
France fines Google over Gmail tracking: France's privacy watchdog has fined Google €325 million for tracking Gmail users with advertising cookies. CNIL says Google broke cookie consent laws and failed to obtain user consent before inserting ads and tracking cookies in their Gmail inboxes. The agency also fined Chinese e-commerce giant Shein €150 million for a similar infraction.
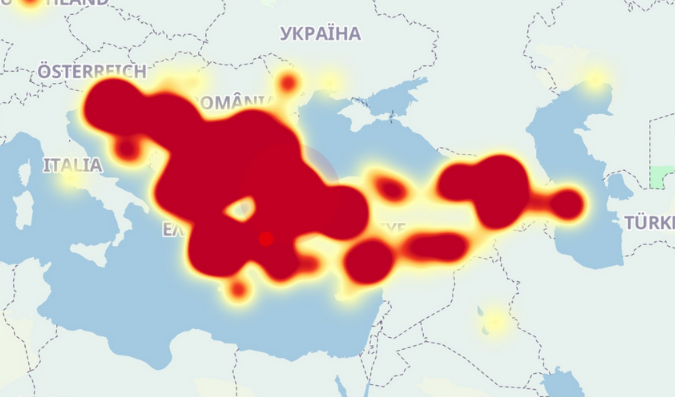
Major Google outage hits Southeast Europe: A major outage took down Google services across Southeast Europe on Thursday. The cause is still unknown. [Additional coverage in Novinite]
HCF beats classic fiber for the first time: A team of academics and Microsoft researchers have developed a new version of hollow-core fiber (HCF), a technology Microsoft uses inside its data centers instead of classic quartz-based fiber. This new version can transmit data over longer distances than classic fiber without amplifiers, making it ideal for use in the real world, and not just inside smaller-scale networks.
Disney settles kids-tracking lawsuit: Disney has settled an FTC investigation for collecting the personal data of children watching its YouTube videos. The company will pay $10 million for failing to obtain parental consent. The fine is basically for Disney's failure to mark its videos as "Made for Kids," a setting that tells YouTube to not collect certain data.
Apitor settles kids-tracking lawsuit: Toy robot maker Apitor also reached a similar settlement, but for just $500,000. The company was investigated for allowing Chinese third parties to collect the data of US children.
Misissued Cloudflare DNS cert: A Croatian certificate authority has issued 12 certificates without authorization for Cloudflare's private DNS known as 1.1.1.1. Fina RDC 2020 issued the certificates for over a year, between February 2024 and August this year, without being detected. Cloudflare confirmed the incident and apologized for not spotting the certificates earlier. Microsoft was the only major browser provider that appeared to have included the CA into its root store. Chrome and Firefox never trusted the CA and their users were never in danger.
There is some chatter about a CA misissuing a certificate for 1.1.1.1. This CA (crt.sh?caid=201916, only ~300 certs) is only trusted by the Microsoft root program and the eIDAS QWAC trusted list. MS has not been actively managing their roots for years, and the EU wanted to push theirs on browsers.
— Filippo Valsorda (@filippo.abyssdomain.expert) 2025-09-03T20:03:31.698Z
Government, politics, and policy
Singapore tells Meta to deploy anti-scam measures: Singapore police have ordered Meta to implement anti-scam measures on Facebook or face a major fine. Meta will have to detect ads, accounts, and business pages impersonating government officials. A third of all reported scams in Singapore last year took place on Facebook. Authorities will be able to fine Meta S$1 million ($775,698) if it fails to comply. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
EU court sides with tech firms: The EU General Court has dismissed a lawsuit that tried to annul the EU and US Data Privacy Framework. The court ruled [PDF] that the new treaty and the US adequately safeguard the personal data of EU citizens. Plaintiffs tried to argue that the US Data Protection Review Court was not independent enough inside the US Department of Justice. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Czechia warns against using Chinese apps/devices: The Czech intelligence agency has warned citizens and organizations against using apps or devices that send data to Chinese servers.
Joint SBOM guidance: Twenty-one cybersecurity agencies from across the world have released a joint guide on implementing the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) standard.
Two DOD cyber officials leave: Two top US cyber officials have left the Department of Defense. Ashley Manning, principal deputy assistant secretary of Defense for cyber policy, and Jonathan Owen, the acting deputy assistant secretary of Defense for homeland defense integration and defense support to civil authorities, have left their positions. [Additional coverage in The Hill]
Texas creates foreign adversaries unit: Texas has established a new unit designed to hunt and stop Chinese influence operations in the state. The new "hostile foreign adversaries unit" will operate under the Texas Department of Public Safety. The law adds criminal penalties for state employees who fail to report foreign influence activity. [Additional coverage in StateScoop]
Cybersecurity and Information Sharing Act update: The House Homeland Security Committee has passed a measure to renew the Cybersecurity and Information Sharing Act. The law provides liability protections for the private sector to share threat intel with the government. It was adopted for ten years in 2015 and will expire at the end of September, unless reauthorized by Congress. Both the House and Senate need to pass the measure to reauthorize the Act. [Additional coverage in NextGov]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business sponsor interview, Casey Ellis chats with Push Security co-founder Jacques Louw. Push's browser plugin gives a unique level of visibility into how users interact with the web and the attacks they face. Jacques talks through what they're seeing and their recently published taxonomy of phishing attacks. It's on GitHub, for everyone to contribute to!
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Streameast taken down: Egyptian authorities have taken down Streameast, the world's largest live sports streaming service. More than 80 domains were seized, and two administrators were arrested last week. The site was taken down following a complaint from a coalition of 50 media and entertainment companies, known as the Alliance for Creativity and Entertainment (ACE). Streameast was established in the mid-2010s and had recently become one of the largest sites on the internet. All seized domains will now redirect to ACE's Watch Legally page—like that's gonna work!
IPTV piracy network linked to Afghan national: Cybersecurity firm Silent Push has published a report on an underground IPTV streaming service running on top of 1,000 domains and over 10,000 IP addresses. [A previous version of this report included a name of an Afghan national who was believed to have run the service. This was removed after Silent Push also removed his name from the original report.]
DamageLib profile: KELA looks at DamageLib, a new forum that has emerged as the primary replacement for the seized XSS (formerly known as DamageLab). Another major contestant to take XSS's place is XSS PRO, but neither is really even close to replacing the original.
"Per KELA's observation, neither XSS PRO nor DamageLib currently hosts substantial discussions or offerings. While XSS PRO is flooded with unverified commercial posts (an issue that at one point led to the introduction of a paid subscription model, which was later abandoned), DamageLib shows limited posting activity overall."
Colombia malware campaign: VirusTotal has uncovered a malware campaign targeting Colombian organizations with malicious SVG and SWF files. Yes, SFW as in Adobe Flash files. You read that right!
Cheating in video games is bad: CyberArk researchers have spotted a malware campaign using video game cheats to deploy a cryptominer and the StealC infostealer.
TAG-150 activity: Recorded Future has identified a new threat actor. Tracked as TAG-150, the group is behind new malware strains such as CastleLoader, CastleBot, and CastleRAT. The group has been active since at least March this year, and most of its victims appear to be based in the US.
We definitely believe it is a financially motivated group given their TTPs and targeting but have not linked it to any other actor.
— Julian-Ferdinand Vögele (@julianferdinand.bsky.social) 2025-09-04T15:22:17.205Z
GhostRedirector manipulates Google results: A Chinese hacking group is manipulating Google search results using hacked IIS servers. The GhostRedirector gang operates out of China and runs an SEO-fraud-as-a-service. According to ESET, the group has hacked dozens of dozens of servers and deployed backdoors named Rungan and Gamshen. The two can intercept Googlebot search crawls and modify responses to boost certain terms.
Tycoon PhaaS evasion tricks: Barracuda's security team looks at new evasion techniques employed by the Tycoon PhaaS.
- Adding obscure characters, such as a 'Unicode' symbol into the link that looks just like a dot but isn't one.
- Inserting a hidden email address or special codes at the end of the link.
- Using web links with strange symbols, such as backslashes' \' or dollar signs' $', which aren't normally used in URLs.
Crypto workers under siege: Reuters has published a look at how employees of cryptocurrency-related projects have been under siege of North Korean hackers and remote IT workers for the past few years.
From infosec blogs to the wild, via AI vibe coders: Trend Micro believes threat actors are taking infosec technical blogs and using AI vibe coding tools to weaponize security research.
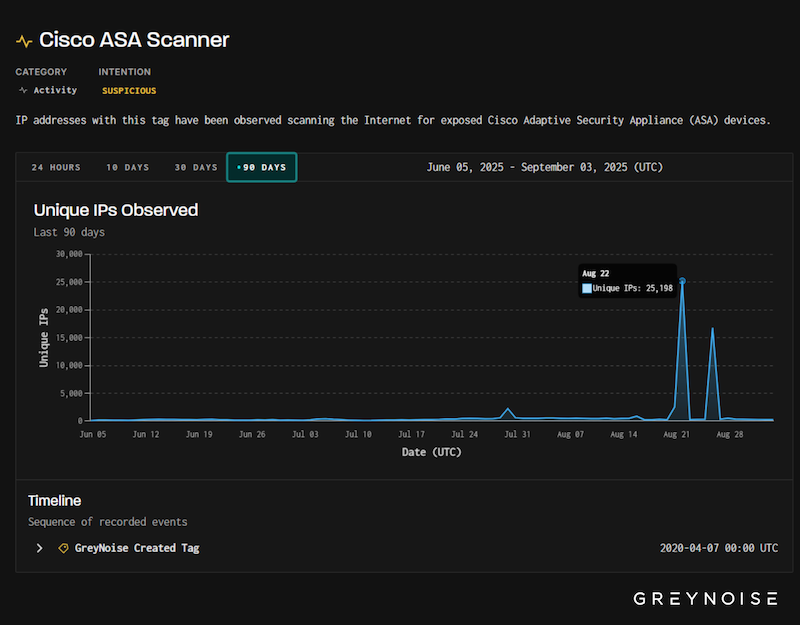
Cisco ASA reconnaissance campaign: GreyNoise observed two scan waves against Cisco ASA devices in late August. The attackers used as many as 25,000 unique IPs to find internet-exposed devices. The attacks appear to be the same campaign spotted by NadeSec last week. GreyNoise believes this may be a reconnaissance campaign that might predate a future exploit.
Malware technical reports
Abyssal DDoS V3: Radware looks at Abyssal DDoS V3, a DDoS attack tool currently used by the Mr Hamza hacktivist group in pro-Palestine DDoS campaigns.
NBMiner cryptominer: DarkTrace researchers have spotted a new cryptominer family in the wild, named NBMiner.
TinyLoader: Hunt Intelligence researchers analyze TinyLoader, a malware strain acting as a loader for various infostealers, also capable of spreading via USB. The particular campaign the company looked at focused on cryptocurrency theft.
Obscura ransomware: Huntress looks at Obscura, a new ransomware family that started leaking victim data this month.
DireWolf ransomware: AhnLab has published a report on the DireWolf ransomware group, which began operations back in May.
AMOS Stealer: Trend Micro looks at a campaign using "cracked apps" and ClickFix lures to target macOS users with the AMOS infostealer.
Stealerium: An infostealer named Stealerium takes desktop screenshots and webcam photos whenever users are watching adult content in their browser. According to Proofpoint, the collected data will likely be used in future sextortion campaigns. The infostealer is currently distributed in the wild by at least two threat actors. It is based on an open-source project available on GitHub.

Sponsor section
In this wholly sponsored Soap Box edition of the show, Patrick Gray chats with Adam Bateman and Luke Jennings from Push Security. Push has built an identity security platform that collects identity information and events from your users' browsers. It can detect phish kits and shut down phishing attempts, protect SSO credentials, and find shadow/personal accounts that a user has spun up.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
North Korean hackers abuse cyber intel platforms: North Korean hackers are registering accounts on cyber intel platforms to monitor when their servers get detected. SentinelOne spotted accounts on platforms like Validin, VirusTotal, and Maltrail. The hackers are associated with a group known as Contagious Interview. As its name suggests, the group uses job interviews to lure victims into infecting themselves with malware. SentinelOne says the group has compromised 230 individuals in the first three months of the year.
Kimsuky: South Korean security firm looks at a Kimsuky operation that targeted victims via three channels—Facebook, email, and Telegram.
APTs attacking Russia: Kaspersky has published a threat landscape report with all the APTs and hacktivist groups attacking Russia and Belarus.
BeserkBear reward: The US State Department is offering a $10 million reward for information on three FSB agents who are part of the BerserkBear APT. The three were charged by the DOJ in March 2022 for a hacking campaign that targeted critical infrastructure all over the world. In a security advisory last month, the FBI said the group continued its hacks despite the indictments and primarily targeted old and unpatched Cisco routers.

NoisyBear's Operation BarrelFire: Russian cyber-espionage group NoisyBear has launched a campaign targeting the Kazakhstan oil and gas industry.
APT28's NotDoor: Russian cyber-espionage group APT28 has compromised multiple companies across NATO countries. Victims were infected with a novel backdoor named NotDoor. The malware is a VBA macro for Microsoft Outlook that monitors incoming emails for trigger words. Based on the triggers, NotDoor can steal emails and files, and even execute commands on the victim's system.
Interesting write-up coming out of Lab52 where #APT28 (aka Fancy Bear) appear to be using a backdoor communicating through MAPI and Outlook, ie. using email as a C2-channel with base64 encoded instructions etc. https://lab52.io/blog/analyzing-notdoor-inside-apt28s-expanding-arsenal/ […]
— Christoffer S. (@cstromblad.com) 2025-09-03T08:31:21.000Z
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Google fixes two Android zero-days: Google has patched two actively exploited zero-days in the Android mobile operating system. Patches were released on Monday with the September security update. The two bugs are tracked as CVE-2025-38352 and CVE-2025-48543. They are both elevation of privilege bugs, one in the Linux kernel and the second in the Android runtime.
Sitecore CMS zero-day: The Sitecore CMS has released a patch to fix an actively exploited zero-day (CVE-2025-53690). The active exploitation was spotted by Google's Mandiant team. The issue impacts Sitecore customers who copied and pasted example machine keys from the official documentation instead of generating new ones. Attackers are using the default machine keys to perform deserialization and RCE attacks on vulnerable sites.
Model Namespace Reuse attack: Palo Alto Networks has introduced Model Namespace Reuse, a new type of supply chain attack against AI tools.
"Model Namespace Reuse occurs when cloud provider model catalogs or code retrieve a deleted or transferred model by name. By re-registering an abandoned namespace and recreating its original path, malicious actors can target pipelines that deploy models based solely on their name. This potentially allows attackers to deploy malicious models and gain code execution capabilities, among other impacts."
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database (twice) (thrice) with seven vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. This includes three TP-Link router bugs, a recently patched WhatsApp zero-day, and the SiteCode and Android zero-day lister above in this newsletter. TP-Link says two of the bugs marked as "exploited" have been used by the Quad7777 botnet to brute-force M365 accounts.
Chromium backdooring: Trail of Bits discovered a bug in Chromium-based apps that can be used to backdoor Signal, 1Password, Slack, Chrome, and Electron apps by tampering with executable content outside of their code integrity checks. This is CVE-2025-55305.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released eight security advisories for its firewall products.
Jenkins security updates: The Jenkins project has released security updates to fix vulnerabilities in four of its plugins.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Cobalt, Gurucul, OPSWAT, Radware [PDF], and Singapore CSA have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
Acquisition news: Israeli cybersecurity company Cato Networks has acquired AI security firm Aim Security.
Deciper returns: Former infosec news site Decipher has returned online.
New tool—WSL Payload Builder: Security researcher M1ddl3W4r3 has open-sourced WSL Payload Builder, a tool to automate the building of Alpine Linux-based WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) distributions that can execute custom payloads upon launch.
New tool—VMDragonSlayer: Italian security researcher Agostino Panico has released VMDragonSlayer, a framework for analyzing binaries protected by Virtual Machine (VM) based protectors such as VMProtect 2.x/3.x, Themida, and custom malware VMs.
HITCON 2025: Talks from the HITCON 2025 security conference, which took place in August, are now available on YouTube. Talks are available in Chinese and English.
SteelCon 2025: Talks from the SteelCon 2025 security conference, which took place in July, are now available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Amberleigh Jack talk about Google starting a cyber disruption unit. It's a sign of the times, but could also point the way forward for policymakers looking to involve the private sector in government-endorsed efforts to strike back in cyberspace.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how cyber threat actors are using AI tools to fill in resource and skills gaps that they have.




