Risky Bulletin: Browser extensions hijacked for web scraping botnet
In other news: Hafnium APT member arrested in Italy; Russian drone volunteer group gets hacked; Satanlock shuts down and leaks all victim data.

This newsletter is brought to you by Knocknoc. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
More than one million users have installed browser extensions that turn their browsers into proxies for a web scraping botnet.
The extensions contain a library named Mellowtel that waits for users to go inactive, disables page security protections, and then loads a remote website inside a hidden iframe. The parsed/scraped website is then sent to a remote URL for analysis.
SecureAnnex found the Mellowtel library in 245 extensions for Chrome, Edge, and Firefox.
Some developers have started removing it from their code after the browser makers started cracking down on its use. Currently, 12 of the 45 Chrome extensions have removed it, 8 of the 129 Edge extensions, and 2 of the 69 Firefox ones.
Mellowtel gained traction by advertising itself to developers as a way to monetize their extensions by selling their users' "unused bandwidth."
SecureAnnex has found connections between Mellowtel and Olostep, an online service that advertises a "cost-effective web scraping API" that can avoid bot detection and parallelize up to 100,000 requests.
John Tuckner, the SecureAnnex founder, believes the library serves as a backend to Olostep, allowing the company to funnel some of the web scraping through Mellowtel extensions.
This may not be illegal if users are informed properly, but Tuckner points out several problematic issues why surrendering your browser to random people is a horrible idea.
The first is that Mellowtel removes security headers from websites where it loads the hidden iframe, in order to allow the web scraping behavior. Those security headers were added to web pages over the course of the past three decades for legitimate reasons, and you want them active at all times.
Second, Mellowtel can easily run malicious code inside intranet portals and other enterprise apps, opening companies that don't control their users' browsers to unforeseen attacks.
Third, it is unclear to whom Olostep or the Mellowtel team might sell their services in the future or how the library may be used. It may be scraping pages today and running phishing portals next week. You never know.
This research is the type of threat that's been recently keeping security teams up at night as more of today's enterprise work is being done through browsers, and mostly through poorly managed ones.
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
"Russian Hackers for the Front" get hacked: An unidentified threat actor has hacked a Russian volunteer group that provides customized drone firmware to the Russian army. The hackers wiped the group's servers and defaced laptop terminals used by soldiers to reflash DJI drones. The "Russian Hackers for the Front" volunteer group confirmed the hack and told members to shut down terminals. The group said they found no evidence that attackers tampered with the drone firmware. [Additional coverage in Packets from Cyberia]
ETHcode extension compromise: A threat actor has compromised a VS Code extension used by nearly 6,000 cryptocurrency developers. The ETHcode extension was compromised last month via a malicious GitHub commit. ReversingLab says the attacker added a new dependency that would allow them to run malicious code on systems where the extension is installed. The ETHcode extension is typically used for Ethereum smart contract development.
M&S doesn't wanna say: Marks & Spencer chairman Archie Norman has refused to say if his company paid a ransom demand to recover from a recent cyberattack. Speaking to UK officials, Norman said two other large UK companies failed to disclose similar cyberattacks in recent months. Marks & Spencer has slowly recovered from a May ransomware attack that took out most of its online websites. The company said it expects to lose £300m in profits this year. [Additional coverage in Yahoo Finance]
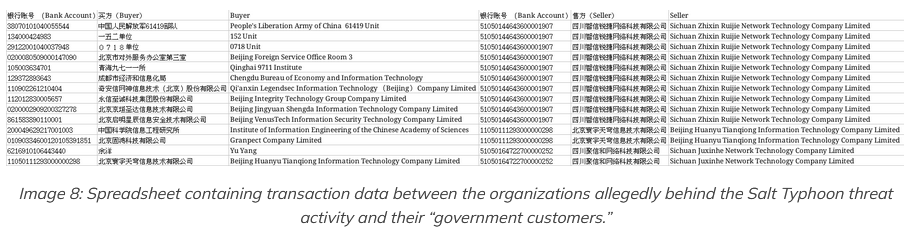
VenusTech and Salt Typhoon leaks: Private documents from China's hacker-for-hire industry were posted on hacking forums in May. The documents were offered for sale in two separate posts on the DarkForums platform. According to a SpyCloud analysis, the first batch allegedly contains documents from the network of Chinese network security firm VenusTech. The second batch allegedly contains details about several companies behind the Salt Typhoon APT and their government customers.
General tech and privacy
Chinese AI drama: Huawei has denied claims that one of its AI dev teams copied an Alibaba LLM. The company is responding to a paper published on GitHub showing multiple similarities between Huawei's Pangu Pro LLM and the Alibaba Qwen 2.5 14B model. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Thunderbird Exchange support: Mozilla has released Thunderbird 140, which comes with experimental support for Microsoft Exchange accounts.
Advanced Protection in Chrome: Google recently launched Advanced Protection, a lockdown kind of mode for Android. In a blog post this week, Google described all the security features that are enabled in Chrome for Android when this is turned on.
BlueSky new features: BlueSky has added a bunch of new features this week, with the two most important being the ability to get notifications for specific accounts and the ability to fine-tune notification settings.
Government, politics, and policy
EU SIS II audit: The EU's border crossing software system, the Schengen Information System 2 (SIS II), is rife with security vulnerabilities and overprivileged access, according to an audit conducted by EU officials. [Additional coverage in Heise]
German Cyber Dome: The German government will build a national cyberdefense system in cooperation with Israel's national intelligence agency. The new Cyber Dome project is designed to protect the country against foreign cyberattacks. The new Cyber Dome project will include a joint cybersecurity center, stronger drone protection, and improved civil warning systems. [Additional coverage in NextGenDefense]
Dutch government won't remove disinformation: A Dutch government official says the Dutch government has no legal authority to remove disinformation from social media platforms.
Cyber funds in US spending bill: Cyberscoop takes a look at all the cyber-related funding included in the One Big Beautiful Bill that passed over the weekend.
Rubio deepfake campaign: An unknown individual is contacting American and foreign officials, posing as Secretary of State Marco Rubio. The impostor contacted officials via text messages and via Signal chats. In at least two cases, the impostor left audio messages using Rubio's deepfake voice. According to the Washington Post, known targets include three foreign ministers, a US governor, and a member of Congress.
Cambodia accuses Thailand of hacking: Cambodian officials claim that a Thai hacking group has attacked multiple government agencies. The BlackEye-Thai has allegedly attacked "nearly all" Cambodian government systems over the past two weeks. The attacks are viewed as payback after a Cambodian hacktivist group named AnonSecKh attacked tens of Thai websites last month. Tensions between the two countries are high after the death of a Cambodian soldier near the Thai border. [Additional coverage in the Asia News Network]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Bulletin sponsor interview, Patrick Gray chats with the CEO of Knocknoc, Adam Pointon. They talk about the woeful state of internal enterprise networks and how many control system networks aren't appropriately segmented. Adam also explains why Knocknoc released a very simple identity-aware proxy: For too long, the Zero Trust "industry" has focused on securing access to critical applications, while everything else is left behind to get owned. This is Zero Trust for crappy apps! Zero Trust, for the rest of us!
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Phishing gang detained: Dutch authorities arrested five members of a phishing gang that operated out of the city of Lelystad. Four of the group's members are teenagers aged 14 to 17. They used QR codes sent via email to collect login credentials for local banks.
New Terrorgram member charged: The US Justice Department has charged Noah Lamb, another member of the Terrorgram group, with putting together a list of federal officials to be assassinated across the US.
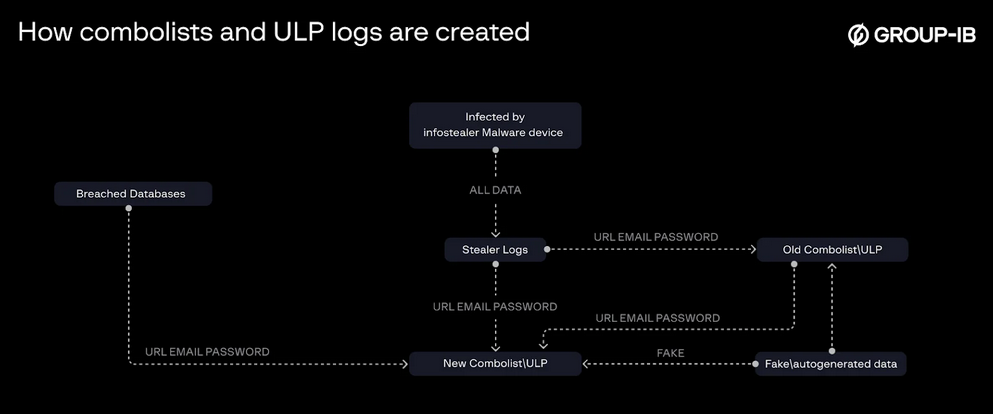
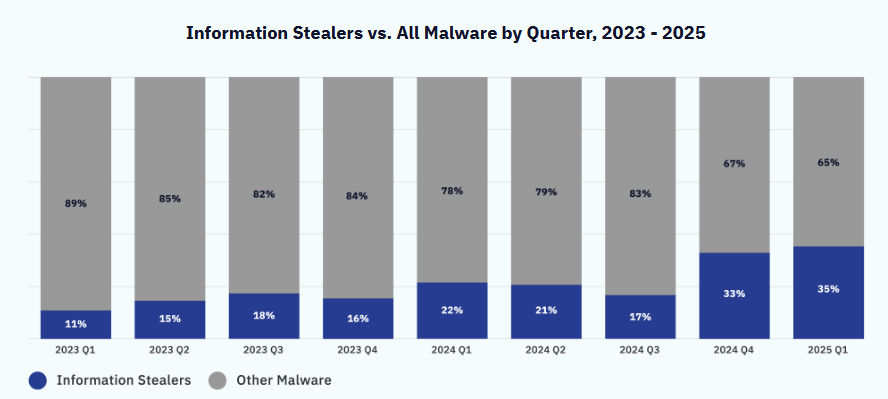
Combolists and ULPs: Group-IB has a good explainer on the differences between infostealer logs, combolists, and URL-Login-Password (ULP) files that are often advertised as "new leaks" on hacking forums and the dark web, and why most of the time they are likely to be very old data.
Scattered Spider: Research from CyberCube has found that 2% (287) of the top 15,000 companies across multiple industry verticals use technologies that were previously targeted by the Scattered Spider group and may be vulnerable to future intrusions.
Malicious RedDirection extensions: More than 2.3 million Chrome and Edge users have installed malicious extensions that track their activity and can hijack their browsers. The extensions pose as entertainment and productivity tools and are still available through both official browser stores. Some were featured on the stores and even received verification badges.
Anatsa targets NA via the Play Store: ThreatFabric says the Anatsa Android banking trojan is now being used to target American and Canadian banks. The kicker—infected apps are available via the official Play Store.
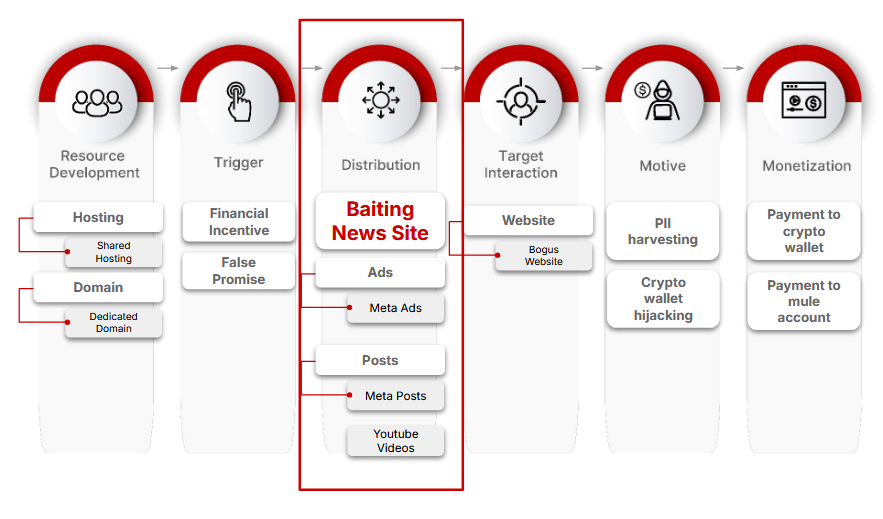
BaitTrap network: A network of more than 17,000 websites is mimicking trusted brands to redirect visitors to online scams. The BaitTrap network uses Google and Meta ads, social media posts, and YouTube videos to lure victims. The bogus sites typically collect personal information and attempt to hijack online crypto accounts. They target audiences in more than 50 countries all over the globe.
Gold Melody profile: PAN's Unit42 has published a profile on Gold Melody (UNC961, Prophet Spider), an initial access broker who uses leaked machine keys to take over ASP.NET sites and then compromise and sell access to the underlying IIS servers.
Pay2Key returns: Iranian hacking group Pay2Key has returned online with a new Ransomware-as-a-Service platform. The group has allegedly collected over $4 million in ransoms since relaunching in February this year. Pay2Key was previously active in 2020 when it launched data-wiping attacks against Israeli organizations. Security firm Morphisec says the group is now trying to recruit members of the Russian and Chinese ransomware ecosystem to launch attacks against Western organizations.
Satanlock shuts down: The Satanlock ransomware group has shut down operations and leaked the stolen data of all past victims. The group did not provide a reason for the shutdown. The Satanlock operation launched in early April and listed over 70 victims on its dark web leak site. [h/t cR0w]
Malware technical reports
Ducex packer: ANY.RUN has published a technical analysis of Ducex, a packer used for the Triada Android malware.
Batavia spyware: More than 100 users at Russian industrial organizations have been infected with a new Windows spyware strain. The new Batavia spyware has been used in campaigns across Russia since July last year. Kaspersky says the malware is used to identify and then steal sensitive documents from infected orgs.
NetSupport RAT: Cybereason has published a report on a campaign using hacked WordPress sites and the ClickFix technique to distribute the NetSupport RAT.
AiLock ransomware: S2W has published a report on AiLock, a new RaaS platform that launched in March and has infected five victims so far.
Bert ransomware: Trend Micro has published a technical analysis of the new Bert ransomware. Threat intel analyst Rakesh Krishnan also published a similar report last month.
"The group's tactics include PowerShell-based loaders, privilege escalation, and concurrent file encryption, allowing them streamlined attack execution and evasion despite their reliance on a simple codebase. On Linux systems, BERT's ransomware variant supports up to 50 threads for fast encryption and can forcibly shut down ESXi virtual machines to maximize impact and disrupt recovery efforts."
VELETRIX Loader: Malware researcher 0x0d4y analyzes VELETRIX Loader, a malware strain linked to Earth Alux APT. The group has a China nexus, and the malware was used in attacks against Chinese telcos.
Atomic update: The Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS) has received a considerable update and now includes a built-in backdoor component for easier interactive access to infected hosts.
Sponsor section
In this product demo, Knocknoc CEO Adam Pointon walks Patrick Gray through the Knocknoc secure access platform. Knocknoc is a platform that restricts network and service availability to authenticated users via existing network security equipment. Users don't need to install an agent. It also has an identity-aware proxy component that supports web applications and RDP.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Hafnium APT member detained in Italy: Italian authorities have arrested a 33-year-old man believed to be part of a Chinese APT group. Xu Zewei was arrested at the Milano airport on Monday. He was detained on a US arrest warrant for allegedly hacking and stealing information on a COVID vaccine being developed at the University of Texas in 2020. The US Justice Department says Xu worked for a Chinese company named Shanghai Powerock Network while conducting the hacks. He is a suspected member of the Hafnium APT. Hafnium is another name for Silk Typhoon, but it's unclear if Xu was involved in the group's recent hacks of US critical infrastructure.
Treasury sanctions Andariel member: The US Treasury Department has sanctioned a member of the Andariel for his role in North Korean remote IT worker schemes. Sanctions were levied against Song Kum Hyok for managing groups of IT workers and providing them with stolen US identities. Sanctions were also levied against two North Korean companies that hired the workers. The Treasury also sanctioned a Russian national and two Russian companies that contracted and hosted the workers in Russia.
Kimsuky (APT-C-55): Qihoo 360 researchers have published a report on HappyDoor, a new backdoor used by the Kimsuky APT in attacks targeting South Korea. Also, see this AhnLab report.
DNS data exposes Russian harassment network: DomainTools worked with Frontstory.pl and VSquare reporters to link a network that was doxing Ukrainian soldiers and harassing their families to Russian organizations based on domain names and DNS data.
Biolab disinfo hits Armenia: Russian disinfo groups have taken their "US biolabs" shtick to Armenia, accusing the local government of harboring American labs that manufacture and test bioweapons. I'm honestly surprised people still fall for this s**t in 2025.
Coordinated death threats hit French judiciary: Open Measures published a report looking at online death threats made against French judges after they sentenced members of the French far-right. The biggest spike was seen on TikTok and VK—go figure! Researchers say this follows a global trend of calls to violence and death threats spiking every time a far-right leader faces legal problems.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Supabase MCP leaks databases: General Analysis has found an issue in Supabase MCP servers that can be used to leak SQL database tables.
"This attack stems from the combination of two design flaws: overprivileged database access (service_role) and blind Trust in user-submitted content. While MCP unlocks powerful automation capabilities, it requires careful handling to avoid security regressions."
CitrixBleed 2 write-up: After a similar write-up from watchTowr Labs last week, Horizon3 has also published its own look at the CitrixBleed 2 (CVE-2025-5777) vulnerability.
SailPoint RCE: Default installations of the SailPoint IQService use a hardcoded encryption key that can allow remote attackers to run malicious code against SailPoint IAM services. According to security firm NetSPI, the encryption key is stored in one of the SailPoint DLL files. SailPoint has released security updates to harden its service against possible exploitation in its May security updates. A PoC is also available.
NOTLogon vulnerability: Silverfort has discovered a new DoS vulnerability in Microsoft's Netlogon protocol. Tracked as CVE-2025-47978 and named NOTLogon, the vulnerability allows any domain-joined machine with minimal privileges to send a specially crafted authentication request that will crash a domain controller and cause a full reboot.
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the July 2025 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Microsoft, Ivanti, SAP, Dell, IBM, Fortinet, Juniper Networks, D-Link, Supermicro, Gigabyte, Schneider Electric, Siemens, ServiceNow, and Splunk. Cisco, AMD, Kubernetes, Qualcomm, Drupal, Thunderbird, and Zoom released security updates last week as well.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday: This month, Microsoft patched 139 vulnerabilities. No zero-days this month.
No Android security updates this month: There are no Android security updates this month, for the first time in six years since Google introduced the monthly security bulletin.
TapTrap attack: A team of academics has developed a new attack that can hijack user interactions on Android smartphones. The TapTrap attack overlays animations on a user's screen but silently opens user interface elements underneath. This allows malicious apps to use fancy animations or games to trick users into performing unwanted actions, such as installing malware or granting intrusive permissions.
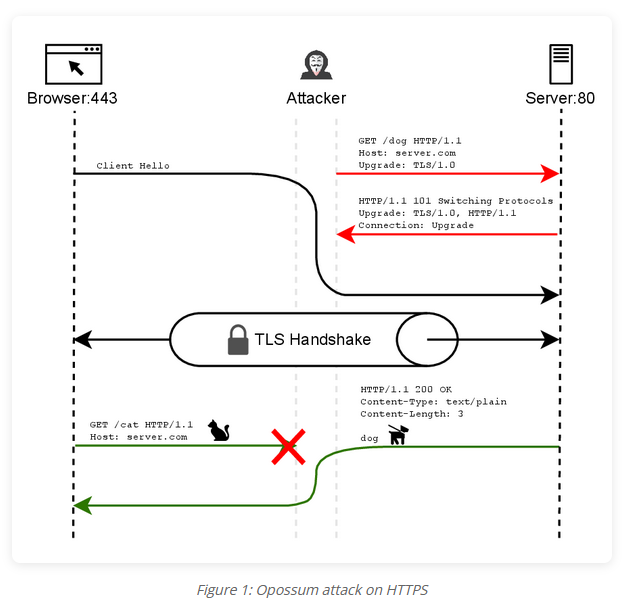
Opossum attack: A team of academics has published details on a new attack on TLS connections. Named Opossum, the attack can be used from MitM positions to cause session fixations, resource confusion, improve XSS attacks, or leak cookies. Researchers say the attack is very reliable, but the prerequisites are very rarely met.
Infosec industry
New tool—Kanvas: Security firm WithSecure has open-sourced Kanvas, an incident response case management tool.
New tool—RingReaper: A Russian security researcher has released RingReaper, a Linux post-exploitation agent that uses io_uring to stealthily bypass EDR detection by avoiding traditional syscalls.
New tool—Bitchat: Jack Dorsey has open-sourced Bitchat, a decentralized, encrypted, peer-to-peer messaging app that works over Bluetooth mesh networks. Aaaaaaaaand, it's already hacked!
Threat/trend reports: eSentire, Sonatype, and ZDI have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how there is an opportunity for the US to expand its zero-day and talent acquisition pool to Asia. They revisit a paper comparing the Chinese and American zero-day acquisition strategies and have some quibbles.
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray discuss warnings about Iranian cyberattacks on US critical infrastructure. Despite many warnings, there have been no actual attacks, and they discuss the reasons why Iran would want to avoid escalatory cyber attacks.




