Risky Bulletin: African freelancers behind anti-US and anti-French disinfo campaigns
In other news: US prepares to let contractors run cyber operations; Germany blames Russia for air traffic control agency hack; Apple patches two WebKit zero-days.

This newsletter is brought to you by Push Security. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Meta's security team has shut down a disinformation network spreading Russian propaganda across Africa.
The network has been active for more than six months and was run by Russia-based entities, the company said in its quarterly security report [PDF].
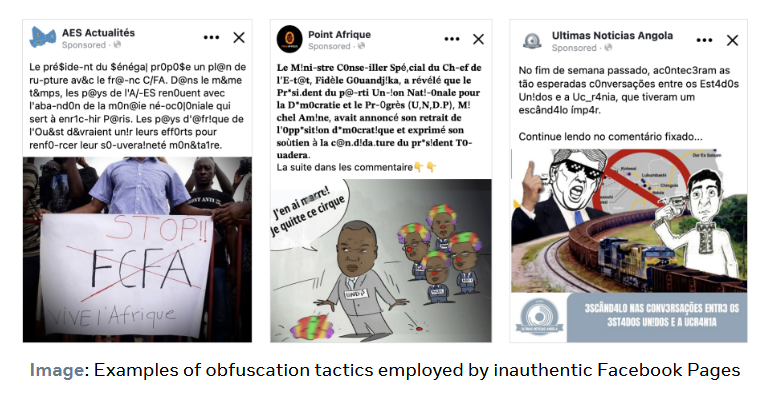
The network ran over 65 accounts and 70 pages that mimicked legitimate news outlets and published content critical of France and the US and promoted Russian geopolitical narratives.
Meta says the network consisted of freelancers hired via job-seeking platforms like Upwork. The individuals advertised their services as social media managers or search engine optimization specialists.
Most of the freelancers were based in sub-Saharan countries.
"The individuals behind these Pages repeatedly returned to our platform after we removed them, often using fake accounts to recreate similar brands. This network of individuals operated independently, though they likely received centralized tasking through channels outside of Meta’s platform. This assessment is supported by our observations of these individuals running the same or slightly adjusted ad content - often within a two day window - and utilizing the same text obfuscation methods, such as 4ng0la, uk_ra_ine, and fr@nce."
Meta's security team credited a report from VIGINUM, France's anti-disinformation agency, for exposing Russia's info-ops operation in the region.
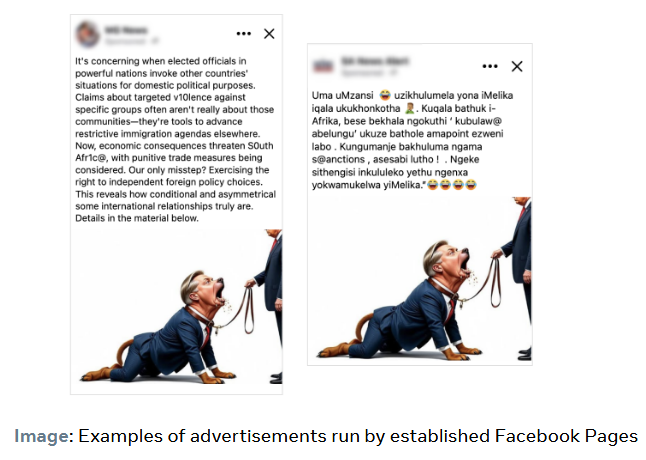
Meta also discovered a second smaller disinfo network also operating in the region. This one was run by a Cameroonian freelancer and likely working for Russia's state-controlled news agency RT.
"For the majority of time this campaign ran, a Cameroon-based individual operated the Facebook and Instagram accounts associated with these brands. This individual was associated with a Page advertising the individual’s own digital communications agency. We assess it is possible the operator had knowledge of the ultimate sponsor of this operation."
Risky Business Podcasts
The main Risky Business podcast is now on YouTube with video versions of our recent episodes. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Hama Film exposes everyone's photos: A photo booth maker has exposed all its customers' photos and videos online. Hama Film has not secured its servers after being notified of the leak in October. The company operates photo boots in Australia, the UAE, and the US. [TechCrunch]
700Credit Suffers Data Breach: American credit check company 700Credit has disclosed a security breach. The incident took place in October and impacted 5.6 million customers. Personal information such as names, homes addresses, and Social Security numbers were exposed.
Home Depot had a leak for a year: Home Depot leaked a private access token to its internal network for more than a year. The token was exposed sometime early last year. The company was notified by a security researcher but revoked the token only after being contacted by a TechCrunch reporter.
Game USBs spread malware: Physical USB hardcopies of a popular manga game were infected with malware. Gaming studio MangaGamer has withdrawn from sale the USB version of the "Higurashi: When They Cry Hou" remaster while it investigates the incident. Digital versions of the game were unaffected. The company says only 67 copies of the game were sold in a USB hardcopy. The USBs were infected with the Floxif Windows virus. [h/t Clearspark]
Breach at the French Interior Ministry: French authorities are investigating a breach at the country's Interior Ministry. Hackers have allegedly breached the agency's email server and accessed files. Officials have not attributed the attack. [Reuters]
General tech and privacy
M365 Baseline Security Mode: Microsoft is rolling out a new security feature for Microsoft 365 apps. The new Baseline Security Mode can automatically configure apps with minimum security requirements. The feature began rolling out in phases last month and will complete by March next year. It will be available for Office, SharePoint, Exchange, Teams, and Entra.
GNOME bans AI-generated code: The GNOME project has banned developers from including low-quality AI-generated code in shell extensions.
MSC Cruises bans smart glasses: MSC Cruises has banned passengers from wearing smart glasses in public spaces. Staff have been instructed to confiscate smart glasses. The company cited privacy concerns with passengers being able to quietly record photos and videos. The Mediterranean Shipping Company is the third-largest cruise operator in the world. [Cruise Hive]
Government, politics, and policy
South Korea to introduce breach fines: The South Korean government will introduce fines on businesses that suffer repeated data breaches. The new legislative effort comes after major breaches at SK Telecom, KT, and e-commerce giant Coupang. Companies with repeated security breaches will face fines of up to 3%of their annual sales. Companies will also face new fines for delaying the reporting of a breach to authorities. [The Korea Times]
White House tries to prevent state AI laws: The Trump administration has signed an executive order threatening to withhold broadband funding if they pass state AI laws. The order has also instructed the DOJ to create a special task force to sue states that don't comply. At the same time, the White House also wants AI models not to return any "woke" content. fReE sPeEcH! [NPR]
US to issue cyber letters of marque: The Trump administration is preparing an executive order to allow private companies to carry out offensive cyber operations on behalf of the government. According to Bloomberg sources, a strategy document is also being prepared by the Office of the National Cyber Director. The document will also call for streamlining cyber regulations, adopting post-quantum cryptography, and securing critical infrastructure. Congress has already allocated $1 billion for offensive cyber operations through the annual spending bill.
Satellite Cybersecurity Act: Two US lawmakers have reintroduced a bill to help secure the country's fleet of commercial satellites. The Satellite Cybersecurity Act was initially proposed in 2023. It directs the Commerce Department to work with other agencies to develop satellite cybersecurity recommendations. The guidelines will be voluntary.
SAFE LiDAR Act: US lawmakers have introduced a bill to phase out the use of LiDAR technology from foreign adversaries. The Stopping Adversaries From Exploiting LiDAR (SAFE LiDAR) Act wants to ban the use of LiDAR sensors made in China. Officials cite risks to national security, such as data exfiltration, sabotage, and the compromise of critical infrastructure. LiDAR technology uses lasers to measure distance and is used across a large number of domains, including military equipment.
CISA updates guide for critical operators: CISA has updated the Cross-Sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals, a set of guides and benchmarks for critical sector operators.
Canada to probe face-scanning billboards: Canada's privacy commissioner launched a probe of billboards using facial-recognition software. The billboards are installed near the Toronto train station. The company behind the billboards said the technology estimates a passer-by's age and sex and that all facial scans are deleted. [The Record]
Pope gets involved in Italy's spyware scandal: Pope Leo has asked Italy's intelligence service to respect people's privacy and not leak data and smear people with hacked data. The Pope made the request at the centenary ceremony for Italy's spy service. The country's intelligence service is under fire for using spyware to hack and surveil activists, including several priests. [Reuters]
Germany blames Russia for DFS hack: Germany has blamed Russia for hacking its air traffic control agency, the DFS, last year. The hack has been blamed on APT28, a hacking unit inside Russia's military intelligence agency, the GRU. German officials have also accused Russia of meddling in its elections last year through disinformation campaigns. According to the Gnida Project, those campaigns are still ongoing. The government summoned the Russian ambassador last week to make formal complaints. [BBC]
New: The German government summoned the Russian ambassador and accused Moscow of playing a "central role" in an influence operation that targeted the German elections earlier this year, which we uncovered. correctiv.org/hybride-krie...
— Max Bernhard (@mxbernhard.bsky.social) 2025-12-12T15:08:33.623Z
The latest Storm-1516 disinformation campaign is targeting Germany, the campaign promotes a false narrative that CDU/CSU bloc has agreed on a pension reform, which includes the increase of the retirement age and raised contribution rates pic.twitter.com/dEydqiBQih
— gnida project (@gnidaproject) December 13, 2025
Sponsor section
In this sponsored interview Casey Ellis is joined by Push Security’s Field CTO, Mark Orlando. They chat about the ways that browser-based attacks are evolving and how Push Security is finding and cataloging them.
Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Destruction of evidence charges for wiping a phone: US authorities have charged an activist with destruction of evidence after he reset his phone to factory settings. Atlanta activist and musician Samuel Tunick allegedly wiped his phone when returning from an international trip in January. He was detained by CBP agents at the Atlanta airport and asked to unlock his device. Tunick was a protestor with the Stop Cop City movement that is trying to prevent the construction of a police mega facility in the city. [Rough Draft Atlanta]
MKVCinemas takedown: The Alliance for Creativity and Entertainment (ACE) has taken down the MKVCinemas movie piracy service after it identified its operator, a man living in the city of Bihar, India.
Package repo malware: Veracode has recorded an 86% increase in malicious packages uploaded to open-source package repositories this year. That's 206,632 packages, with most being uploaded to npm.
Chaya_005: A new threat actor named Chaya_005 is targeting industrial routers. The group has been active for at least two years and has primarily compromised outdated Sierra Wireless devices. The group has since expanded to target other network edge devices.
Operation MoneyMount-ISO: Seqrite looks at what looks to be a phishing campaign targeting Russia's private business sector that seems to originate from the country.
Cheap disposable phone numbers: SMS verification on social media platforms can be bypassed for pennies. A team of academics has found online platforms that sell access to disposable one-time phone numbers for as low as $0.08. Japanese numbers are among the most expensive while UK numbers are the cheapest. [Reuters]
Dark Shinigamis: A threat actor named Dark Shinigamis launched a dark web leak portal last week. The site doesn't list any victims yet. [h/t @PaduckLee]
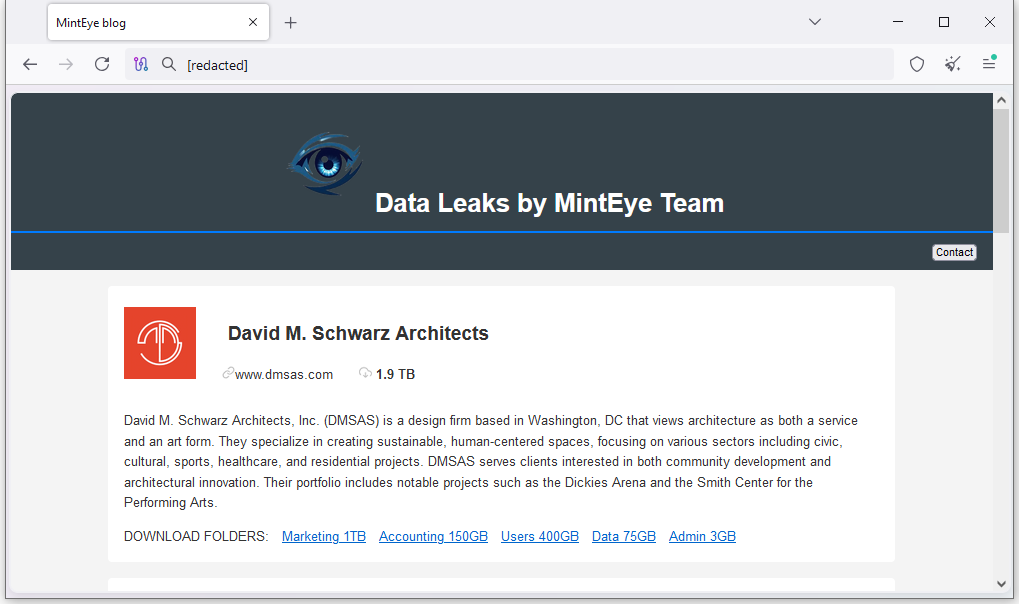
New MintEye group: A new extortion group named MintEye launched last week. It's unclear if it also deploys ransomware.
Malware technical reports
Weyhro C2: Ann Pham, aka RussianPanda, looks at Weyhro C2, a new offensive toolkit advertised on underground forums. The toolkit appears to be the work of the individual behind the (now-failed) Weyhro ransomware from March this year.
JSCEAL: Cato Networks has spotted new versions and infrastructure related to JSCEAL, a malware strain used to target cryptocurrency users.
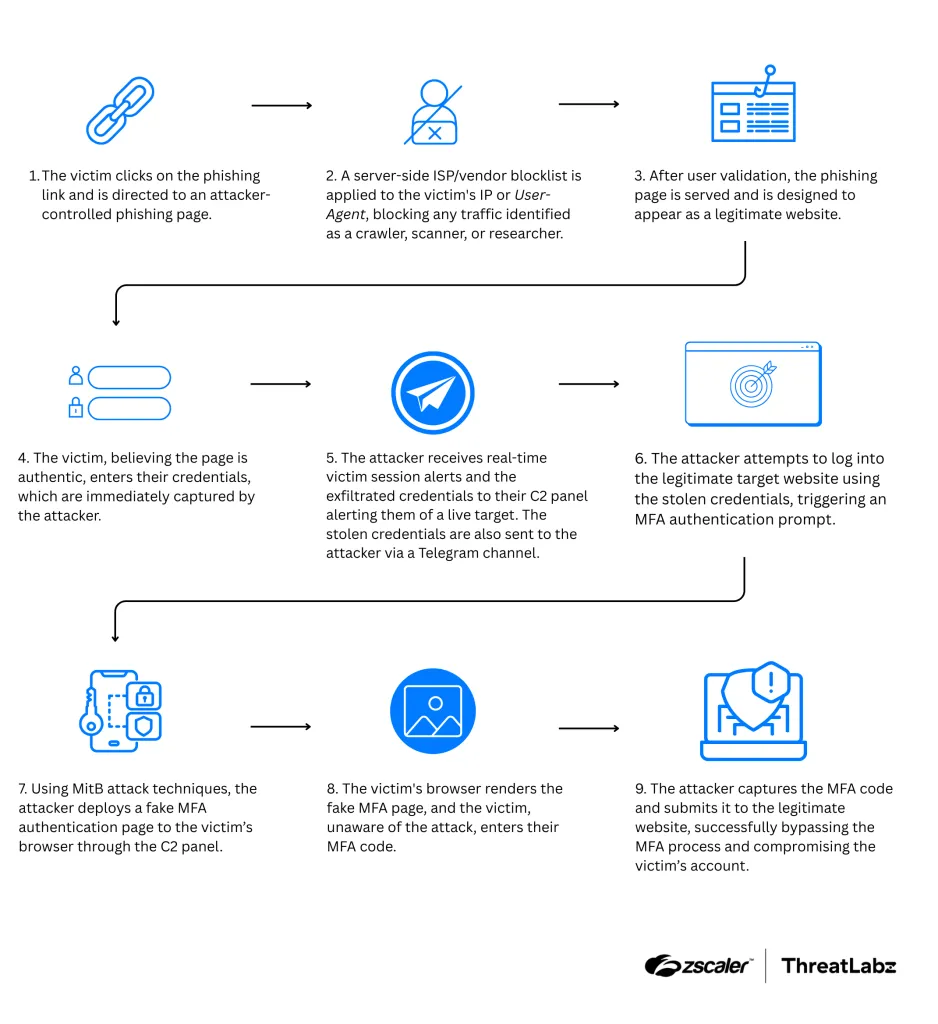
BlackForce PhaaS: Zscaler researchers have spotted a new Phishing-as-a-Service named BlackForce. The service launched in August and can perform MitM attacks to intercept MFA challenges. It is sold on Telegram for €200–€300 and can impersonate up to 11 brands.
Sponsor section
In this wholly sponsored Soap Box edition of the show, Patrick Gray chats with Adam Bateman and Luke Jennings from Push Security.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
PRC conducting research on US grid vulnerabilities: Chinese researchers have published more than 2,700 research papers on the US power grid and its vulnerabilities. According to security firm Strider, some of the research was conducted by entities tied to China's military and security services. At least 225 papers explored potential attacks on the US grid.
China's React2Shell exploitation: Google is now tracking at least five Chinese cyber-espionage groups that are exploiting the React2Shell vulnerability for initial access. The groups are UNC6600, UNC6586, UNC6588, UNC6595, and UNC6603. This is up from two at the beginning. There is also loads of exploitation from e-crime groups.
APT-C-26: Qihoo 360 looks at an APT-C-26 (Lazarus) campaign abusing a recent WinRAR vulnerability to deploy the Blank Grabber infostealer.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with three vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. This includes a recent Google Chrome zero-day, a 2018 Sierra Wireless AirLink bug, and a GeoServer XXE from last month.
Apple zero-day: Apple has released a security update to patch two actively exploited WebKit zero-days. Apple says the zero-days were used in an "extremely sophisticated attack." The targeted users ran iOS versions before iOS 26, the current release. The attacks were spotted by Google's security team. The WebKit patches were released on the same day Google also patched a Chrome zero-day.
LANDFALL exploit write-up: Google Project Zero has published its own analysis of the LANDFALL exploit (CVE-2025-21042) that was used to hack Samsung devices in the Middle East and deploy spyware.
"This case illustrates how certain image formats provide strong primitives out of the box for turning a single memory corruption bug into interactionless ASLR bypasses and remote code execution. [...] These types of exploits do not need to be part of long and complex exploit chains to achieve something useful for attackers. By finding ways to reach the right attack surface and using a single vulnerability, attackers are able to access all the images and videos of an Android’s media store, which is a very interesting capability for spyware vendors."
Freedom Chat exposes phone numbers: Secure messaging app Freedom Chat has fixed two vulnerabilities that exposed its users' phone numbers and their security PINs. The issues were discovered by security researcher Eric Daigle. Freedom Chat has reset all user PINs to prevent abuse. The messaging app has been promoted to the MAGA community as an alternative to more mainstream apps. [TechCrunch]
FreePBX auth bypass: The FreePBX open-source telephony software has released security updates to patch several security flaws. The project fixed an authentication bypass, several SQL injections, and a file upload bug that can lead to remote code execution. All the bugs were found and reported by security firm Horizon3. Almost 12,000 FreePBX servers are connected to the internet and potentially vulnerable to attacks.
New React vulnerabilities: Meta has released new security updates for the React JavaScript framework. The new patches fix two denial of service bugs and a vulnerability that can expose an app's source code. The new bugs were found by security researchers investigating a more dangerous React bug that is currently being exploited in the wild.
New Windows EoP: 0Patch has found a variation of a Windows Remote Access Connection Manager (RasMan) elevation of privilege vulnerability (CVE-2025-59230). The company has released its own micro-patches until Microsoft releases its official one.
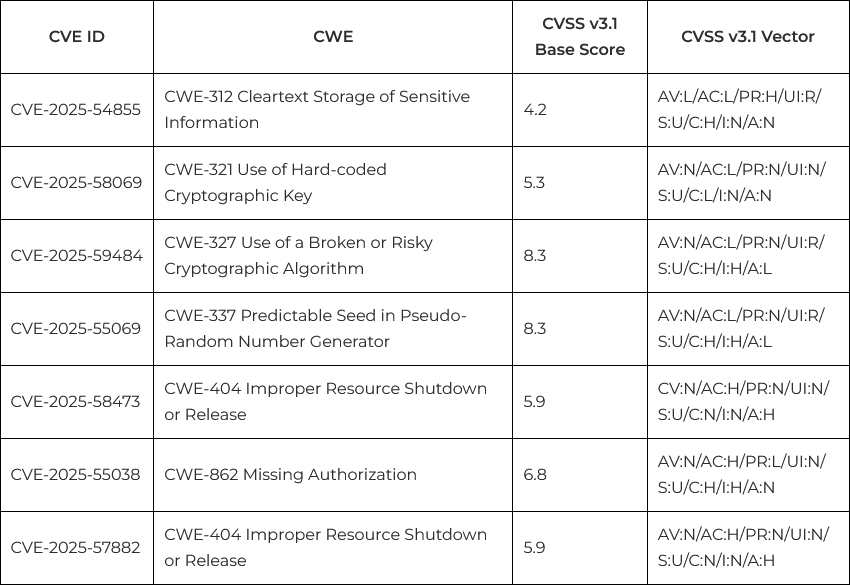
Vulnerabilities in AutomationDirect CLICK Plus PLCs: AutomationDirect has released security updates for its CLICK Plus programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Seven vulnerabilities were discovered and reported by Nozomi Networks. They include the use of hardcoded cryptographic keys and cleartext passwords, the use of weak cryptographic algorithms, and a predictable RNG. The affected PLCs are typically used for factory-floor machinery and recreational systems such as amusement-park rides.
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Forescout, Frontegg, HP Wolf Security, Trellix, Veracode, and Virus Bulletin have recently published reports and summaries covering various threats and infosec industry trends.
Acquisition news: Cloud software service provider ServiceNow is in talks to acquire IoT security firm Armis. [Globes]
New tool—Stillepost: Security researcher dis0rder has released Stillepost, a tool to proxy traffic through the Chrome DevTools protocol.
New tool—Phantom Keylogger: Software researcher Mattia Alessi has released Phantom Keylogger, a keylogger with a minimal footprint on target systems.
Ghidra 12: The NSA has released version 12 of its Ghidra reverse-engineering toolkit.
LPC streams: Live streams from the Linux Plumbers Conference 2025, which took place over the weekend, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business podcasts
In this edition of Seriously Risky Business, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray discuss a new report proposing a framework for deciding when cyber operations raise red flags. It suggests seven red flags and could help clarify thinking about how to respond to different operations.
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq wonder whether it is possible to deter states from cyber espionage with doxxing and other disruption measures.




