Risky Biz News: Vo1d infects 1.3 million Android TV boxes
In other news: Microsoft to move security products out of the kernel; Mastercard buys Recorded Future; Slovakia denies buying Pegasus.

This newsletter is brought to you by Sublime Security, an email security platform that's not a black box. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

A mysterious threat actor has built a giant botnet by infecting over 1.3 million Android TV set-top boxes across the globe.
The devices were infected with a new backdoor named Vo1d.
The malware's main function is to gain reboot persistence on the device through three different methods and then watch a folder and install any Android APK file placed there.
This suggests the botnet may be part of a pay-par-install scheme for Android apps, or Vo1d may still be under development, and further capabilities will be added later.
According to data collected by Russian security firm Dr.Web, most of the Vo1d devices are located in Brazil, which accounts for nearly a third of all current infections.
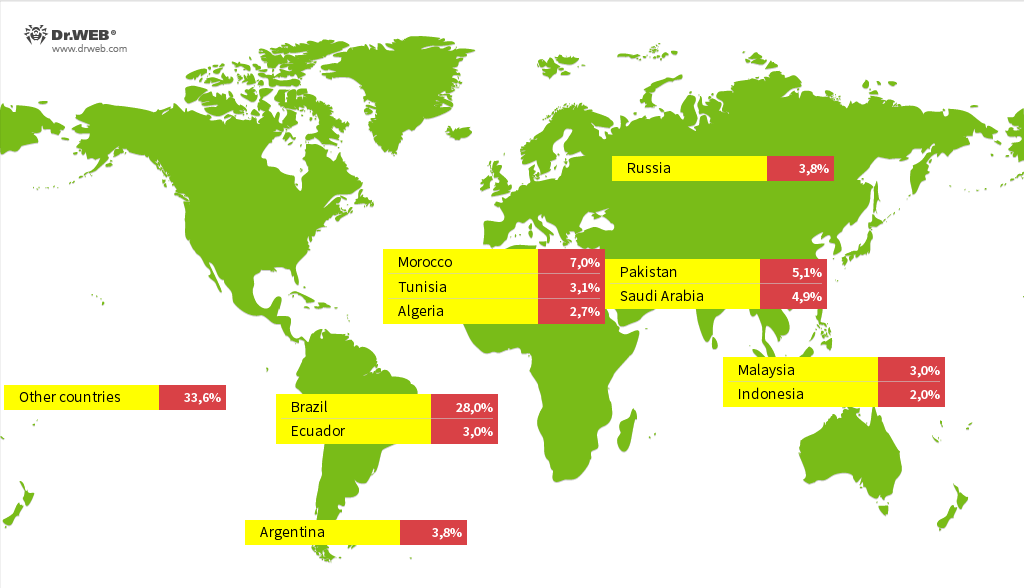
Dr.Web says it wasn't able to determine how the devices were infected but found several cases where compromised set-top boxes reported incorrect Android OS versions.
"For example, the users who contacted us have models that are based on Android 7.1, despite the fact that for some of them the configuration indicates much newer versions, such as Android 10 and Android 12. Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for budget device manufacturers to utilize older OS versions and pass them off as more up-to-date ones to make them more attractive."
In theory, this could explain how the devices were infected—with the Vo1d gang exploiting older Android vulnerabilities since the set-top boxes didn't actually have the older patches installed.
Vo1d is the latest in a long list of botnets that specifically target TV set-top boxes. Past examples include the likes of Bigpanzi, Pandora, Ares, the Lemon Group, and BADBOX. Some of these botnets were used to launch DDoS attacks, but the vast majority is typically used for advertising click fraud, which may also be where V01d may end up operating later on.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
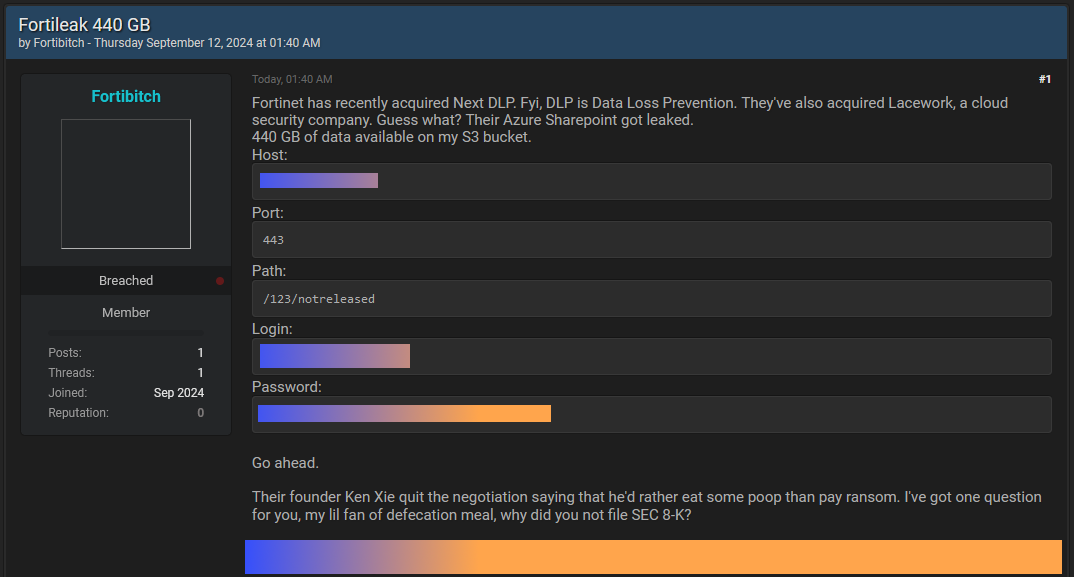
Fortinet data breach: Cybersecurity firm Fortinet has disclosed a data breach of its APAC division. The company says that the attacker accessed customer records stored on a third-party cloud provider. Fortinet says the incident impacted only a limited number of customers and has not seen any follow-up malicious activity. The company's admission comes after a threat actor named Fortibitch claimed credit for the breach on a hacker forum. [Additional coverage in CyberDaily]
Taiwan DDoS attacks: "Hacktivist" group NoName057 has launched DDoS attacks against Taiwanese government sites after the country's president warned that China may seek to regain lost land from Russia. Oh, global power drama! We love it! [Additional coverage in Taipei Times]
Indodax crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen more than $22 million worth of crypto-assets from Indonesian cryptocurrency exchange Indodax. The company has confirmed the incident and suspended all operations while it investigates the breach. Blockchain security firm SlowMist believes the hackers appear to have gained access to a system that controls the exchange's hot wallet withdrawal operations. [Additional coverage in CoinDesk]
Banking spree: The Hunters International ransomware group has taken credit for attacks on two major banks—Malaysia's Bank Rakyat and the UK branch of the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC). The ICBC is the same Chinese bank that dealt with a ransomware attack from the LockBit gang last year.
Pregnancy clinic cyber wars: A women's gynecological clinic from Attleboro, Massachusetts, is suing a neighboring pregnancy center for allegedly hacking its online reservations portal. Four Women Health Services claims that staff from the Attleboro Women's Health Center next door has been contacting its patients every time they reach out via their online contact widget. The lawsuit alleges the next-door clinic is operating as an anti-abortion center and is misleading patients seeking abortion care. Four Women says it does not know yet how the neighboring clinic has hacked its IT system but is now seeking an injunction to stop the Attleboro Women's Health Center from accessing its systems and contacting its patients. [Additional coverage in Boston.com] [h/t DataBreaches.net]
Hacks of Icelandic politicians: An Icelandic businessman who was providing financial support for Assange and the WikiLeaks project has allegedly asked LulzSec to hack the emails of two Icelandic politicians. [Additional coverage from Emma Best]
Record settlement: US healthcare provider Lehigh Valley Health Network (LVHN) has agreed to a $65 million settlement in a class-action lawsuit filed by former patients and employees who had their data stolen in a ransomware attack in 2023. The leak included nude photos of some of the clinic's cancer patients. One of the settlement terms is that any patient who had nude photos leaked would be entitled to as much as $80,000. [Additional coverage in DataBreaches.net]
General tech and privacy
Microsoft's kernel meeting: Microsoft will develop a new technical capability to allow security software to work outside of the Windows kernel. The new capability is designed to avoid causing global IT outages like the one caused by CrowdStrike in July. Details about how this new technical feature are still being discussed. Microsoft announced the news after holding a summit with security software makers this week. Government officials from Europe and the US also attended.
Play Integrity API: Google has added a new Android API that allows app makers to verify if their apps have been installed from the official Play Store. The new Play Integrity API can prevent users from side-loading Android apps and using pirated or modified versions. Google says the API has already been adopted by mobile games and financial apps. [Additional coverage in Android Authority]
Mandatory 2FA comes to WordPress repo: The WordPress team will require that all WordPress.org accounts enable 2FA by October 1 this year. Accounts that do not enable 2FA by next month will not be able to make any changes to themes and plugins made available through the official repository. The move to mandatory 2FA is meant to put more barriers against brute-force attacks and other supply chain attack scenarios.
Government, politics, and policy
UK NCA ICO MOU: The UK's privacy watchdog and main police agency have signed a memorandum of understanding on cybersecurity. The document clarifies that the NCA won't pass data to the ICO as long as victims of cyberattacks report intrusions to law enforcement. British companies have often not reported breaches to authorities because they feared data from an incident response could be used against them by the UK's privacy watchdog. The ICO signed a similar agreement with the country's cybersecurity agency last year—urging companies to report cyberattacks to the NCSC on the promise of smaller fines.
UK reclassifies data centers as critical infrastructure: The British government has reclassified data centers as critical national infrastructure. The reclassification will allow the government to invest new resources and provide better cybersecurity services to the data center operators. Data centers are the UK's fourteenth critical infrastructure sector. It is the first new addition to the list since 2015 when the government added space and defense to the list.
Chinese crane drama: Chinese cargo crane manufacturer ZPMC has pressured multiple American ports for remote access to its machines. A congressional report found that several ports initially denied the request but eventually caved to the vendor's pressure. US officials say ZPMC focused on gaining access to its machines in American West Coast ports. ZPMC currently accounts for 80% of ship-to-shore cranes in operation at US ports. The US Congress began investigating the issue after suspicions that China might use the cranes for espionage and sabotage. [Additional coverage in The Record/Full report PDF]
Slovakia denies buying Pegasus: Slovakia's prime minister has denied allegations that the country's intelligence service has acquired access to the NSO Group's Pegasus spyware. Local media reported last week that the Slovakian government switched from a test to a full version of Pegasus this month. Reporters cited four different sources in the country's security sector. The spyware has often been abused by elected governments to spy on the opposition, journalists, and activists. A staunch Putin fan, Slovakian Prime Minister Robert Fico accused without evidence the opposition, the Soros-controlled media, and foreign NGOs of the assassination attempt on his life earlier this year.
Australia introduces anti-doxxing law: Australia's Attorney General has introduced a bill that will ban the publishing of personal information online, also known as doxxing. The proposed law amends Australia's 1988 Privacy Act and imposes a prison sentence of up to seven years for offenders. Officials introduced the bill after pro-Palestinian activists published the personal details of almost 600 Jewish academics and artists in February this year. [Additional coverage in ABC]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Josh Kamdjou, founder and CEO of Sublime Security, about the spectrum of attacks that are taking advantage of generative AI. These range from taking basic attacks with a pinch of AI pixie dust to more complex attacks where AI is used to construct message threads with multiple personas. Josh also talks about how different AI models can be used to identify these attacks, even when they are novel.

Cybercrime and threat intel
TfL hacker arrested: UK officials have arrested a 17-year-old male for hacking London's public transportation agency Transport for London (TfL). The teenager was detained last week on September 5, three days after the hack. The NCA says it questioned and released the suspect on bail. Some TfL services are still down 10 days after the attack. The teen is believed to have stolen the personal data of some TfL customers.
IronChat creators sentenced: Dutch authorities have sentenced three men to years in prison for their role in selling a crypto-phone named IronPhone and managing the IronChat encrypted IM service. The group's leader was sentenced to 4.5 years in prison, while his two accomplices will go to jail for 22 months and 18 months, respectively. The trio was detained in 2018 after Dutch authorities shut down the platform. Officials decrypted over 258,000 chat messages and disrupted several criminal organizations as a result. [h/t Betje C.]
Singapore cybercrime arrests: Singapore police have arrested six men for their involvement in a cybercrime operation. Five Chinese nationals and one Singapore resident were detained this week following raids across the city. Officials have seized laptops that stored stolen data and hacking tools and software. One of the seized laptops was allegedly being used to control a copy of the PlugX malware.
US sanctions cyber scam tycoon: The US Treasury Department has imposed sanctions on Cambodian businessman Ly Yong Phat and two of his companies. US officials say workers who applied for jobs at Ly's companies had their passports seized and forced to work in local cyber scam compounds. Local authorities rescued foreign workers on two occasions from one of Ly's resorts. Ly is one of Cambodia's richest persons, a senator, and an advisor to Cambodian Prime Minister Hun Manet.
Romance scammer money launderer pleads guilty: A 30-year-old woman from Florida has pleaded guilty to laundering over $2.7 million on behalf of a romance scam group overseas.
Fourth time's a charm: Dutch police arrested a teenager from the city of Amersfoort for the fourth time on phishing-related charges. He was previously convicted for all three of his previous charges.
Tor node raids: German authorities have raided the home and offices of a Tor exit node operator. No reasons were given and Tor's German team is holding a meeting on how to deal with the incident.
Hikki-Chan exposé: CodeAIntel has published a report on Hikki-Chan, a threat actor who has recently claimed credit for several hacks and leaks. The company's investigation has found that Hikki-Chan is repurposing old leaks or misrepresenting the value of unrelated data.
"The evidence strongly suggests that Hikki-Chan is not a legitimate threat actor but rather a fraudulent entity engaged in misinformation and reputation-building through deception. Their claims consistently fail to withstand scrutiny, relying on misattributed attacks, recycled data, and misrepresented information."
AppleCare+ scam campaign: Malwarebytes researchers have uncovered a malvertising campaign that uses Google Ads to lure users to GitHub pages listing fake AppleCare+ support services and phone numbers.
Olympics typosquatting: Sekoia looks at all the Olympics-related typosquatted domains the company saw over the summer.
New SecondEye members: Security firm HudsonRock claims to have identified two new members of the SecondEye cybercrime group. The company found the members while searching infostealer logs sold on the underground market. The credentials belonged to two Pakistani men and were for old SecondEye infrastructure. The US charged two Pakistani men in 2021 for running SecondEye, a web service that sold counterfeit IDs and government documents.
Kiosk mode abuse: Malware authors have developed a new technique that can force users into sharing credentials for a desired website. The technique works by forcing a victim's Chrome browser into the fullscreen Kiosk Mode, from where users cannot escape until they log into a specific website. Once the user logs in, the password is stored inside Chrome's local database from where an infostealer can easily extract it. According to OALABS, the technique is currently used by infostealer strains such as Amadey and StealC.
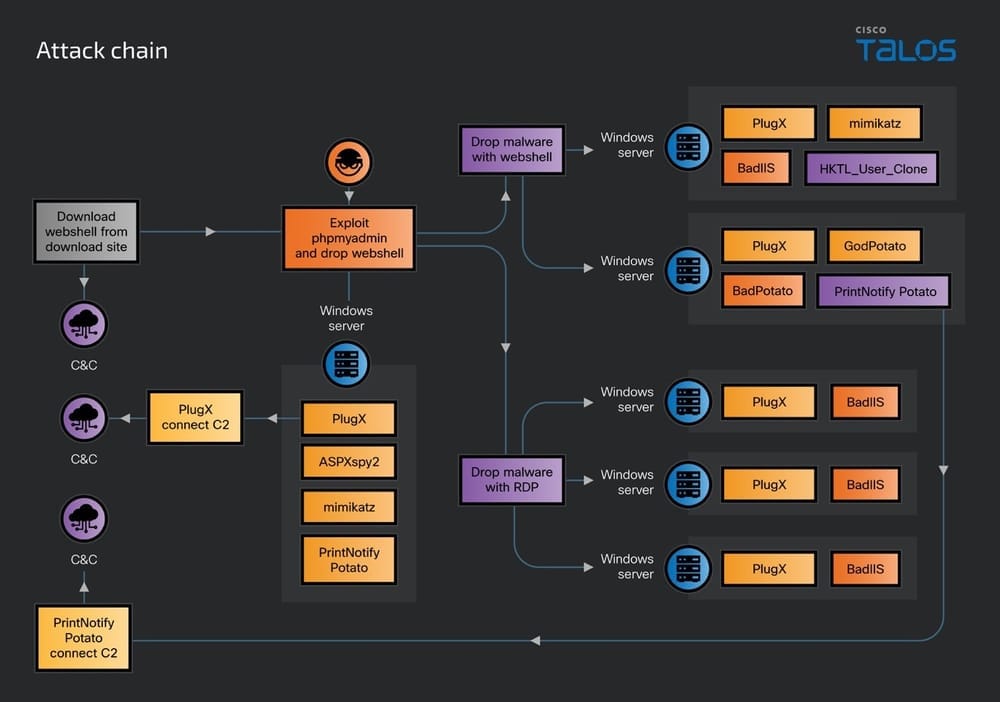
DragonRank group: A Chinese cybercrime group named DragonRank is hacking IIS servers to modify web pages as part of a large SEO poisoning operation. The modified pages redirect users to various types of online scams. Cisco Talos says the group appears to be made up of Chinese-speaking users based out of mainland China.
Malware technical reports
Lynx ransomware: Rapid7 has published a report on Lynx, a ransomware group that started operations in July this year and already has 24 victims listed on its leak site.
macOs infostealer: SentinelOne looks at several of the recent infostealers targeting macOS users over the past few months—Amos, Banshee, Cthulu, Poseidon, and RodrigoStealer.
TrickMo: Mobile security firm Cleafy has found a new variant of the TrickMo Android banking trojan with a new anti-analysis mechanism.
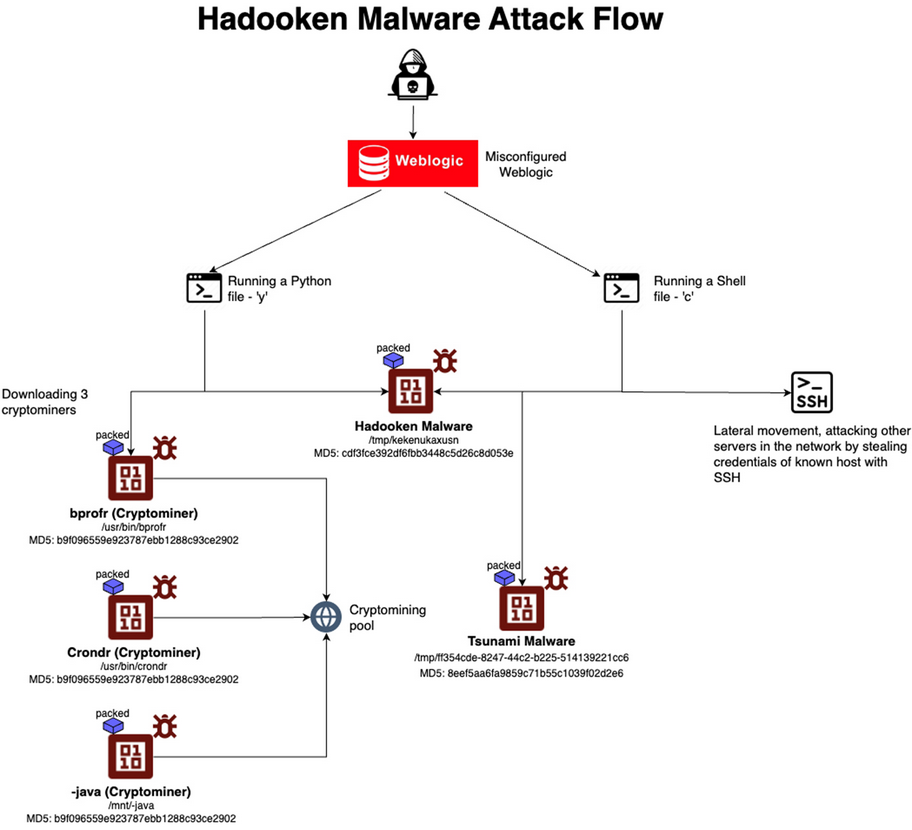
Hadooken: AquaSec has discovered Hadooken, a new Linux malware found infecting Linux-based Oracle WebLogic servers. The malware seems to function as a downloader and is currently being used to drop secondary payloads such as cryptominers and the Tsunami DDoS bot.
Sponsor Section
Sublime Security shares a recent payroll fraud campaign, likely produced using generative AI.

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Operation WordDrone: The Acronis security team has published a report on a new cyber-espionage campaign targeting Taiwan's drone industry. The report comes days after Trend Micro published a report on TIDRONE, a suspected Chinese APT targeting the same sector.
Kimsuky: AhnLab researchers have uncovered a Kimsuky operation using a lure a paper on the Russia-North Korea partnership. Also, CyFirma has published a profile on the same threat actor here.
Lazarus fake recruiter attacks: ReversingLabs has discovered a repository containing malware-laced coding tests that North Korean hacking group Lazarus uses for its "fake recruiter" social engineering campaigns. The company says the tests appear to be part of a campaign they discovered last year named VMConnect.
APT34 targets Iraq: APT34, an Iranian MOIS-affiliated threat actor, is behind a recent espionage operation targeting Iraqi government infrastructure.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
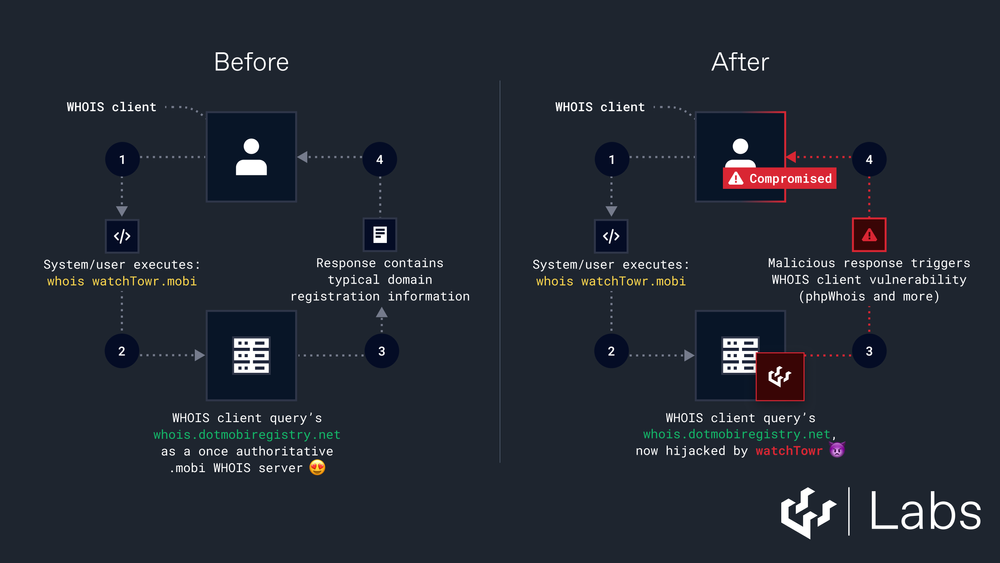
MOBI TLD hijack: watchTowr security researchers could have hijacked thousands of MOBI websites after they registered a sensitive domain that used to be part of the MOBI TLD core infrastructure. The domain dotmobiregistry.net was used in the past to process WHOIS queries for MOBI websites but was replaced with a new WHOIS server at whois.nic.mobi. watchTowr says it registered the domain after it was allowed to expire last December. Over the course of a week the old domain still received WHOIS queries from more than 135,000 systems from across the globe. watchTowr says the domain could have been used as a springboard for attacks on these systems by using vulnerabilities in WHOIS clients.
Adobe zero-day patch: Adobe has patched an Adobe Reader zero-day (CVE-2024-41869) that can be used for remote code execution attacks. Security researcher Haifei Li discovered [archived] the zero-day earlier this year while scanning public PDF files for potential exploit code. Adobe was initially scheduled to fix the bug in August but delayed the update to create a more complete patch. Li says the exploit appeared unfinished and did not deliver a payload.
Windows zero-day write-up: SEC Consult has published a write-up of CVE-2024-38014, a Windows zero-day patched this month that was abused in the wild. The zero-day abuses the repair function of MSI installers and can allow threat actors to elevate privileges to SYSTEM. The company also published a tool to scan for MSI installers vulnerable to this bug on GitHub.
Veeam RCE write-up: Orange Cyberdefense has published a technical write-up on CVE-2023-27532, a bug that can be used for RCE attacks against Veeam backup solutions.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released eight security advisories for multiple products.
GitLab security updates: Source code management system GitLab has released patches to fix 17 security updates.
Feeld security flaws: Security firm Fortbridge has discovered eight vulnerabilities in the Feeld dating app that could allow threat actors to access and perform sensitive operations. This includes reading other users' private chats, viewing their private photos, forcibly updating their profiles, or accessing their match history. Fortbridge says it notified Feeld, but the app maker has failed to fix any of the issues over the past six months.
PIXHELL attack: A team of academics from Israel has devised a new method to transfer data from air-gapped computers using noise generated by LCD screens. Named PIXHELL, the attack uses malicious modulated pixel patterns to make LCD screens generate sounds in the 0-22 kHz range. These sounds can be picked up by a nearby attacker and then demodulated to recover the transmitted data.
GAZEploit attack: A team of academics has found a way to analyze eye movements and extract passwords entered inside Apple's VisionPro VR headset. Named GAZEploit, the attack works by tracking and mapping a user's eye movements to the device's virtual keyboard. Researchers say GAZEploit has an accuracy rate from 85% to 97%. [Additional coverage in WIRED]
Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Abnormal Security, AU10TIX, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), and Recorded Future have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
New tool—Bomctl: The Open Source Security Foundation has released Bomctl, a tool for working with SBOM files. The tool is intended to help users retrieve, manipulate, and push multiple SBOM documents that represent a system.
New tool—ChromeKatz: Finnish security researcher Aleksi Vepsäläinen has released ChromeKatz, a red-team tool for dumping sensitive information from the memory of Chromium-based browsers.
Mastercard buys Recorded Future: Mastercard has agreed to buy threat intelligence company Recorded Future from private equity firm Insight Partners for $2.65 billion. Insight Partners acquired a controlling interest in the threat intel firm in 2019 for $780 million. Mastercard had previously collaborated with Recorded Future to detect and identify compromised payment cards. Recorded Future co-founder and CEO Christopher Ahlberg says the company will operate as an independent subsidiary inside Mastercard.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq dissect an FBI advisory about North Korean groups targeting cryptocurrency firms with social engineering.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about the structure of the spyware ecosystem. It's concentrated, with lots of vendors in India, Israel, and Italy. And its a small pool of talent, with many companies being founded by just a few individuals.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!





