Risky Biz News: US Treasury sanctions Russian cyber and influence firms
In other news: Security researcher detained in data extortion investigation; white-hat exploit helps recover 70% of stolen Wormhole funds; wave of 1,300+ malicious packages hits PyPI.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The US Treasury on Friday imposed new sanctions on Russian and foreign entities supporting the Kremlin's illegal invasion of Ukraine.
Authorities sanctioned 22 individuals and 83 entities in Russia and 30 individuals and companies in third countries that helped Russia evade previous sanctions.
Sanctions have been levied against Russia's financial sector, arms dealers, military supply chains, and metal and mining sectors.
For the first time since Russia's invasion, the US Treasury has also sanctioned cyber-adjacent entities.
The biggest name on this list is 0Day Technologies, a Moscow-based IT company and a known contractor for Russia's FSB intelligence agency. In March 2020, a hacktivist group named Digital Revolution hacked and leaked data from 0Day's network, including details about Fronton, a tool that could be used for DDoS attacks but also for orchestrating social media disinformation campaigns.
However, the US Treasury sanctioned the company for providing "databases of western nation citizens' personally identifiable information to Russian intelligence."
US officials have also sanctioned Forward Systems, R&DC, another Moscow-based IT company. Treasury officials say the company "developed specialized software and algorithms" for Russia's GRU military intelligence services as part of its "offensive cyber operations."
In addition, Treasury officials sanctioned Novilab Mobile, a Moscow-based software company, for developing a project to enable mobile device monitoring—a project they developed at the request of Advanced System Technology, a contractor for the Russian FSB agency, previously sanctioned in April 2021.
Other sanctions were also levied against AO Russian High Technologies and ZAO Akuta, two other IT companies that worked for Russian intelligence agencies and provided programming services, although it's unclear if these are offensive cyber-related or just mundane software development.
And last, Treasury officials also sanctioned OOO Lavina Puls and AO Inforus, two known entities that ran malign influence operations on behalf of the GRU military intelligence services.
Sanctions were also levied against Andrey Igorevich Masalovich, the head of both Lavina Puls and Inforus. Treasury officials say Masalovich sold internet monitoring and influence technology he initially designed for the GRU to other countries around the world. Reports from 2022 and 2023 found Masalovich hawking Lavina Puls' Avalanche election influence technology across South East Asia.
Breaches and hacks
NewsCorp breach update: US news agency NewsCorp provided an update on a security breach it disclosed in January 2022, when it revealed that a threat actor had gained access to a portion of its enterprise network, including the details of Wall Street Journal and New York Post reporters. In a data breach notification letter filed with authorities more than a year after the original disclosure, NewsCorp says the breach was far larger than it initially disclosed and that hackers had been in its network for almost two years, since February 2020. At the time, Mandiant said the breach was believed to have been carried out by a threat actor with a China nexus. [More in BleepingComputer]
The Good Guys breach: Aussie consumer electronics retail store chain The Good Guys says the data of some of its customers was improperly exposed after a threat actor gained access to a third-party contractor that was managing its customer rewards program. My Rewards Pty Ltd, the third-party contractor, says the breach most likely occurred in August 2021.
Dish Network cyberattack: US satellite TV broadcast provider Dish Network has fallen victim to a cyber-attack that is currently preventing employees from accessing corporate systems and tech support services. The incident has also affected the company's official apps and websites. While the company has not yet confirmed the incident, several employees have told BleepingComputer about having "blank icons" on their desktops, which is a common occurrence after a ransomware attack.
Some Wormhole stolen funds recovered: Cryptocurrency DeFi platform Oasis says it executed a proof-of-concept exploit that recovered $225 million worth of assets stolen by hackers from the Wormhole platform in February of last year. The recovered funds represent 70% of the $322 million stolen in the incident. Oasis says it learned of the counter-exploit to recover the funds from a "white-hat group" and obtained a court order from the High Court of England and Wales before retrieving the stolen funds.
Taiwan data breach: The Taiwanese Ministry of Justice says it linked the cryptocurrency wallet of a hacker who stole government data last year to the bank accounts of a Chinese national. The hacker, known as OKE, listed the data of 23 million Taiwanese citizens on sale on an underground hacking forum last October. The hacker claimed to have obtained the data from Taiwan's Household Registration Office and was selling it for a meager $5,000.
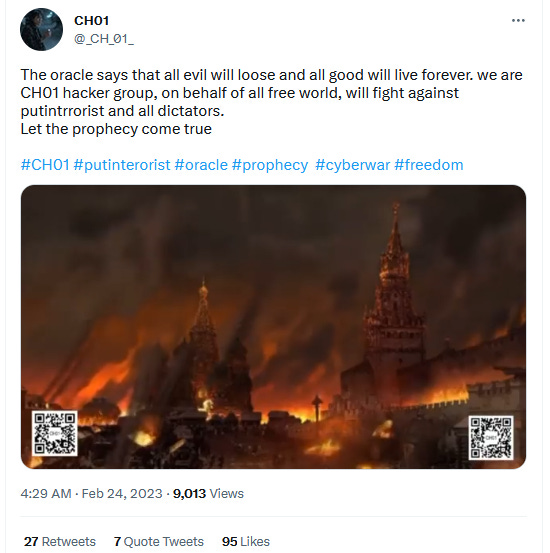
Russian site defacements: A hacktivist group named CH01 has defaced 32 Russian websites on the one-year anniversary of Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The websites were defaced with a video showing the Kremlin burning. Most of the defaced websites were small businesses. No official Russian government sites were affected.
General tech and privacy
Exchange scanning update: Microsoft has updated the guidelines for scanning Exchange servers for malware, and the company is now advising the scanning of additional directories. These folder locations were previously used by antivirus solutions, but Microsoft says it has seen malware campaigns abuse these directories to hide their malware.
Signal would leave the UK: Megan Whittaker, the president of the Signal secure messaging service, has told the BBC the company plans to leave the UK market if the country passes the controversial Online Safety Bill. The bill, which is currently receiving pushback from both the private sector and local politicians, would require tech companies to scan encrypted messaging apps for child sexual abuse material (CSAM).
More Twitter layoffs: Twitter fired last week its democracy and national security lead, Neema Singh Guliani, which kind of explains why that entire network's trending section is just state-run propaganda campaigns these days. Other layoffs followed at Twitter over the weekend too.
Chrome security overview: The Chrome security team has published its activity review for Q4 2022. Check it out for the latest security features that landed or are landing in Chrome/Chromium.
Government, politics, and policy
South Korea loses lawsuit: South Korea's Ministry of National Defense has lost an appeal to a lawsuit it filed against antivirus company Hauri. The ministry sued Hauri in 2017, alleging the company was hacked in 2015 and that hackers stole some of its private keys. Officials claim the keys were later used by North Korean hackers to access more than 3,200 army computers a year later, in 2016. The government formally blamed Hauri for the hack a year later, in 2017, and sued the company for 5 billion won ($3.8 million) for damages. The ministry lost the initial lawsuit in 2021 and now also lost the appeal. [Read more in ZDNet Korea]
Russian cyber-attacks: In a joint report authored by the Dutch General Intelligence and Security Service (AIVD) and the country's Military Intelligence and Security Service (MIVD), the two agencies say that many of Russia's cyberattacks and cyber operations carried out since its invasion of Ukraine have yet to become public knowledge. The report says that many of these attacks targeted sensitive targets, such as military and diplomatic agencies, which usually brings a good dose of secrecy around the intrusions. The same report also adds that Russia has "found it difficult to synchronize cyber operations with other military operations, such as airstrikes." [Additional coverage in The Record]
FTC scam stats: The US Federal Trade Commission says Americans lost more than $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022, more than 30% more than the previous year. The FTC says the Consumer Sentinel Network received more than 2.4 million fraud reports last year. The top 5 most common reports were for (1) imposter scams, (2) online shopping scams, (3) prizes, sweepstakes, and lotteries, (4) investment scams, and (5) business and job scams.

Sponsor section
Proofpoint is one of this newsletter's main sponsors. Below is a product demo Patrick Gray, the host of the main Risky Business podcast, recorded with them last year, where they show off Nexus People Risk Explorer, the company's product for mitigating insider threats:
Cybercrime and threat intel
Extortionists detained in the Netherlands: Dutch police have detained three members of a cybercrime group that hacked into corporate networks, stole sensitive data, and then tried to extort companies by threatening to publish the stolen files. Officials say the group typically asked between €100,000 and €700,000 from each victim. The group's suspected leader, a 21-year-old man from Zandvoort, is believed to have made more than €2.5 million alone. Officials say the group stole and eventually leaked the personal data of millions of users, much of which is still being sold and circulated online. According to Dutch news agency NOS, one of the three suspects is a security researcher who works for the Dutch Institute for Vulnerability Disclosure (DIVD), a Dutch cybersecurity collaboration group. In a message on its site, DIVD says it had no idea of the individual's actions and that they are now investigating if the individual misused any of its resources.
BEC money launderers sentenced: Two individuals were sentenced to 10 years and four years and three months in prison, respectively, for helping a BEC group launder more than $13 million of stolen funds.
PyPI malware wave: DevSecOps company Phylum has discovered a wave of more than 1,300+ malicious packages submitted to the official Python Package Index (PyPI). Phylum says the malicious packages would connect to a Dropbox account to download and install a Rust-based malware strain. Phylum says the attacker appears to be the same group spotted by Fortinet and ReversingLabs last week in a separate, smaller campaign.
Crypto phishing overview: Fairyproof has a summary of the most common phishing and social engineering tactics used to compromise blockchain and crypto users.
Zoho attacks: Bitdefender has a review of the various threat actors abusing a recently-patched Zoho ManageEngine vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-47966.
"We started detecting first attacks immediately the next day after the first public Proof of Concept (PoC) was released and documented by Horizon3.ai team. The identified victims are located across the globe and are from various industries, as is common with opportunistic attacks. Based on our analysis, 2,000 to 4,000 servers accessible from the internet are running one of the vulnerable versions. Not all servers are exploitable with the current PoC code, because SAML needs to be configured."
BHProxies dox: After earlier this month BitSight linked the BHProxies residential proxy service to the MyloBot malware botnet; infosec researcher Brian Krebs has identified the service's owner as Abdala Khafagy from Cairo.
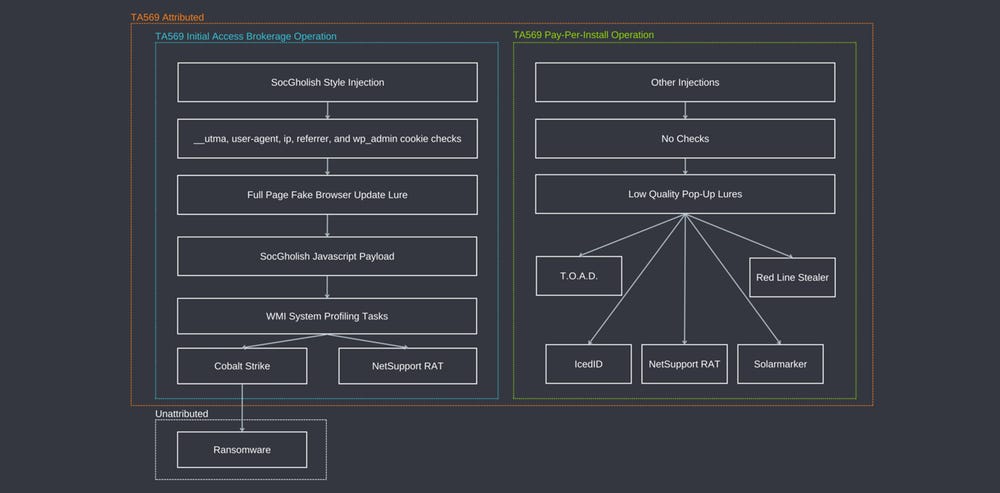
TA569: Proofpoint has a report on TA569, a prolific threat actor primarily known for operating SocGolish, a network of compromised websites through which they deploy various payloads, usually at the behest of other cybercrime groups. Proofpoint believes the group is now working both as an initial access broker (IAB) but also operating as a classic pay-per-install (PPI) service.
Malware technical reports
EXFILTRATOR-22: CyFirma researchers have a report on EXFILTRATOR-22 (EX22), a new post-exploitation framework that was launched earlier this year and is currently being advertised on Telegram and YouTube as a "ransomware spreading tool." There's also a Lockbit connection in there.
IcedID: Team Cymru has a report on the server infrastructure of the IcedID botnet, including an interesting finding about a Chilean IP address used when accessing "various elements of the IcedID infrastructure."
Web skimmer campaign: Malwarebytes has a report on a recent web skimmer campaign using some clever tricks to target shoppers in various geo-locations.
GuLoader+AgentTesla: Antiy researchers have a report out on a GuLoader campaign dropping AgentTesla.
RedLine campaign: K7 researchers have published a report on a phishing campaign using OneNote files to infect users with the RedLine stealer.
PureCrypter campaign: Menlo Security says it is seeing a campaign distributing the PureCrypter downloader through Discord and targeting government entities, out of all things. After infecting victims with PureCrypter, the attackers will often deploy other malware strains, such as Redline Stealer, AgentTesla, Eternity, Blackmoon, and the Philadelphia ransomware.
PlugX: Trend Micro says it discovered a version of the PlugX backdoor hidden inside a Windows open-source debugger tool. PlugX is remote access trojan that was developed and initially used by Chinese cyber-espionage groups but has since leaked and been adopted by many Chinese threat actors as well.
macOS crypto-miner: CrowdStrike has additional details on the macOS cryptominer spotted by Jamf last week.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Lazarus: ESET says it found a new backdoor that appears to have been created and deployed in the wild in recent attacks carried out by the Lazarus APT. They named this new malware WinorDLL64.
UAC-0056 (DEV-0586, UNC2589): Ukraine's CERT team says that a Russian hacking group known as UAC-0056 breached government servers as far back as December 23, 2021, two months before Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Ukrainian officials say they discovered the intrusion last week after spotting one of the gang's web shells on some of the compromised servers. The group's malware arsenal included CredPump, an SSH backdoor disguised as a server PAM module, and HoaxPen and HoaxApe, two backdoors disguised as Apache server modules.
SideCopy: We featured a report last week on the SideCopy APT from Rising researchers, but there was also another one on the same APT from NSFOCUS, also on the same campaign.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
QNAP bug bounty program: Taiwanese hardware vendor QNAP has launched a bug bounty program. Vulnerabilities relating to QNAP operating systems, applications, and cloud services are in scope, and rewards can go up to $20,000.
CVE-2022-25664 (Android): GitHub's Man Yue Mo has published details on CVE-2022-25664, a vulnerability in the Qualcomm Adreno GPU that was patched in the Android October 2022 patches.
Infosec industry
Anti-ransomware tech: WithSecure has launched a new tech named Activity Monitor that monitors the file system and reverts changes and actions made by a confirmed malicious process. The feature can be used for many threats, but it is particularly useful for ransomware attacks, the company said.
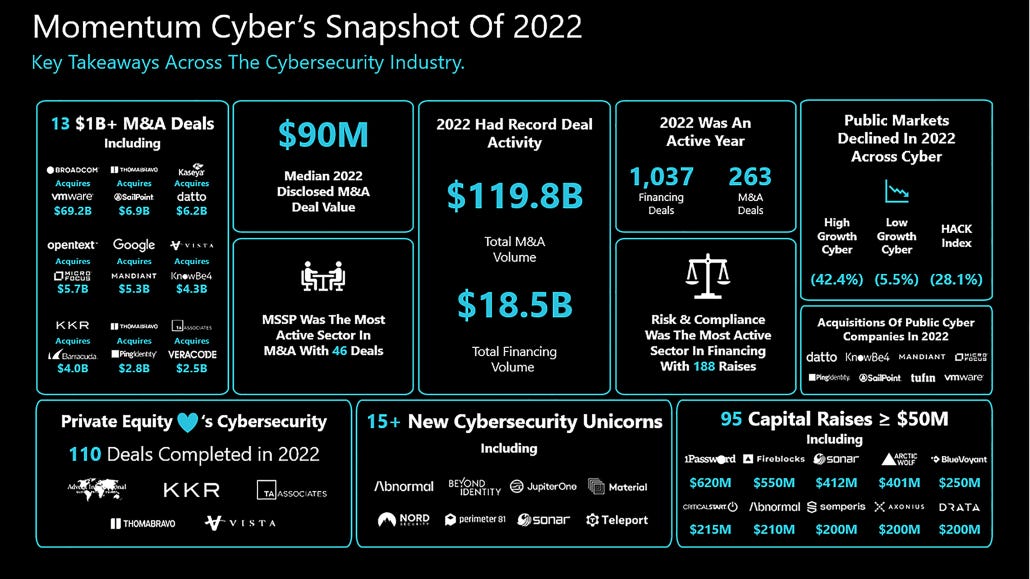
Infosec VC investments: Venture capital investments in cybersecurity startups amounted to only $18.5 billion last year, a major decline compared to the $30.4 billion invested in 2021. Players in the cybersecurity landscape focused on strategic acquisitions last year, consolidating their position in a waning tech market. Security firms arranged 263 M&A (merger & acquisition) transactions for a total value of $119.8 billion, 48% more than the previous year.
"Mega deals and acquisitions of public companies accounted for $103.2B of the total M&A in 2022, including the landmark $69.2B acquisition of VMware by Broadcom. 13 total deals in 2022 were valued greater than $1B, including Thoma Bravo's acquisition of SailPoint ($6.9B), Kaseya's acquisition of Datto ($6.2B), OpenText's acquisition of Micro Focus ($5.7B), Google's acquisition of Mandiant ($5.3B), and Vista Equity's acquisition of KnowBe4 ($4.3B)."

Risky Business podcast host Patrick Gray recorded this video with Okta, which shows users how to enable phishing-resistant authentication. It also goes into how enabling phishing-resistant auth for some users can benefit the whole org, even if it's not turned on everywhere.




