Risky Biz News: US sanctions Russian disinfo peddlers in LATAM
In other news: US to establish water sector cybersecurity task force; Russia suspected of wiping more Ukrainian telcos; Glassdoor doxes users.

This newsletter is brought to you by Kroll. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

The US government has sanctioned two Russian nationals and their respective companies for running years-long Russian disinformation campaigns across Latin America.
The US Treasury Department has levied sanctions against Ilya Andreevich Gambashidze, the founder of the Moscow-based company Social Design Agency (SDA), and Nikolai Aleksandrovich Tupikin, the CEO of Russian company Structura.
The sanctions come six months after a State Department report identified the two and their companies as the central pieces in Russia's disinformation effort across Latin America.
The two—together with a third company that was not yet sanctioned—managed a sprawling network of websites and operatives across Latin America.
This network would write articles in Russia, translate the stories into Spanish and Portuguese, and then send the content to its Latin America staff to be "localized."
The stories would then be published on a network of more than 60 websites that were designed to mimic and impersonate more legitimate news organizations.
Local staff would also attempt to covertly plant the stories with local journalists, news outlets, or social media influencers to boost their reach.
The articles were your usual "US bad, NATO bad, Russia good" content that we've seen from Russia's disinfo machine before.
"These themes align with Russia's broader false narrative that it is a champion against neocolonialization, when in reality it is engaged in neocolonialism and neo-imperialism in its war against Ukraine and its resource extraction in Africa."
The State Department described the companies as "influence-for-hire firms" and claimed they operated "at the direction of the Russian government."
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Pokemon account hacks: The Pokemon Company is resetting user passwords after it detected an attack on its systems. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Fujitsu data leak: Japanese IT giant Fujitsu left an AWS storage bucket with a trove of sensitive data exposed on the internet for almost a year. The server contained full mailbox backups, customer data, and a CSV file of passwords pulled from password manager LastPass. The server leak is different from another security breach the company disclosed last week when the company found malware on its internal network. [Additional coverage in The Stack]
"It takes a special kind of stupid to export a LastPass vault and dump it into a public bucket along with a bunch of AWS keys. How do these people win critical government contracts again, please?"
Trezor SIM swap incident: A threat actor gained access to the official Twitter account of the Trezor cryptocurrency wallet and posted links to a scam token sale. Trezor blamed the incident on a SIM swap. [Additional coverage in CCN]
Reg.ru incident: Pro-Ukrainian hacktivist group UHG claims to have breached Reg.ru, Russia's largest domain registrar. The group posted a portion of the stolen data on their Telegram channel. Reg.ru says it patched the vulnerability used to gain access to its system. [Additional coverage in TASS]
General tech and privacy
Ethereum Foundation deletes warrant canary: The Ethereum Foundation deleted its warrant canary after it received a request from a state government agency.
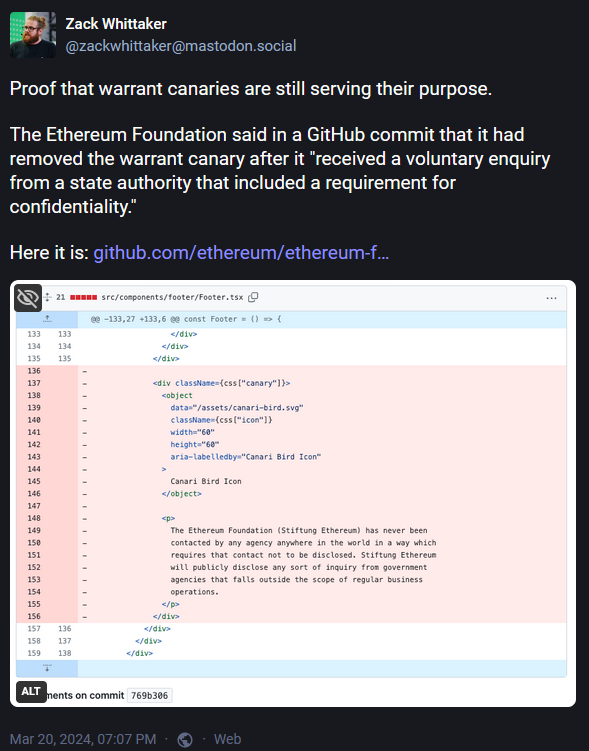
DOJ sues Apple over monopoly: The US Justice Department has sued Apple in an antitrust case over the iPhone monopoly on the US phone market.
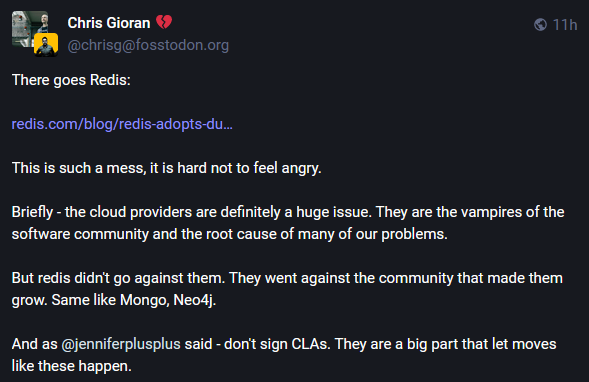
Redis license change: The Redis database has changed its license from BSD to a dual licensing model—Redis Source Available License (RSALv2) and Server Side Public License (SSPLv1).
Chrome 123: Google has released version 123 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes in this release include the ability to resume browsing sessions from any device on the user's main desktop browser. Chrome 123 also comes with a new feature named Private Network Access that can detect websites scanning a user's local network.
GitHub Code Scanning Autofix: GitHub has launched Code Scanning Autofix, a new feature that can suggest fixes for vulnerabilities the Copilot AI assistant finds in user code.
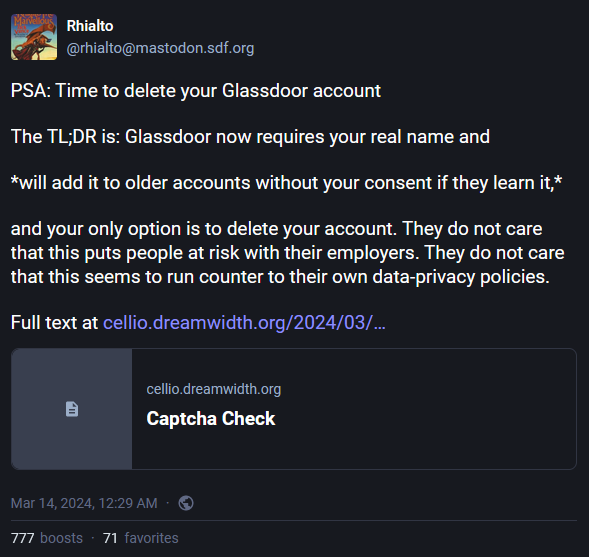
Glassdoor starts doxing users: Glassdoor users say the company is now adding their real names to public profiles without their consent. Users say they had to delete accounts after their real names appeared on anonymous employment reviews they made in the past. Many users don't know where the company obtained their real names. In some other cases, the company took real names from support requests and added them to profiles. Glassdoor has also changed its sign-up process and is now requiring users to disclose their full names, job titles, and employers. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
Government, politics, and policy
US water sector cybersecurity task force: The White House and the EPA will set up a cybersecurity task force for the US water sector. Officials announced their plan in a letter sent to US governors this week. The letter warned state authorities about a rise in cyberattacks against water utilities across the US. The White House and the EPA specifically mentioned Chinese group Volt Typhoon as a major threat to the US water sector. [Additional coverage in CyberScoop]
FBI returns to working with social media companies: The FBI's Foreign Influence Task Force has resumed some of its work with US social media companies over foreign propaganda campaigns. The new arrangement is a simple information-sharing effort, with the FBI sharing data with social media networks, which are then free to decide if they want to act on it. The FBI stopped working with social media companies last year after Republicans OAGs sued the US government. There's a lot of GOP derpy-derp in this one. [Additional coverage in NBC News]
ADPPA passes House: The US House of Representatives has unanimously passed a bill to block data brokers from selling the personal data of American citizens to companies linked to foreign adversaries. The bill is known as the American Data Privacy and Protection Act (ADPPA). It now moves to the Senate floor. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Canada's Flipper Zero ban: The Canadian government appears to be slowly walking back plans to ban Flipper Zero device imports. [Additional coverage in PCMag]
More US chip sanctions: The US is considering expanding sanctions on new Chinese chipmakers connected to Huawei's business. In the meantime, the EU is considering extending sanctions too. [Additional coverage in Reuters/Bloomberg]
China warns of hackers: China's state security agency has urged local companies to improve their cybersecurity defenses. The Ministry of State Security says foreign spy agencies have infiltrated hundreds of local businesses and government units. The agency published the message a day after the US similarly warned of Chinese hackers infiltrating critical infrastructure. [Additional coverage in SCMP]
Russia's GitHub clone delayed: Russia's planned GitHub clone has been postponed indefinitely due to lack of funding. The platform was announced at the end of 2022 and was scheduled to go live in April this year. The site was part of the Kremlin's effort to create national clones of popular US services. The government promised to invest 1.3 billion rubles ($14.1 million) in the project. According to a Vedomosti report, the two IT companies selected to build the platform never received any of the funds.
Microsoft services suspended in Russia: TASS has obtained the full list of Microsoft services that will be suspended in Russia by the end of the month. The list includes more than 50 services, from PowerBI to OneDrive and from Visual Studio to SharePoint. It's basically almost everything.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with George Glass, Senior Vice-President for Kroll's Cyber Risk business. George covers the company's latest report, a Kimsuky attack on ConnectWise ScreenConnect devices with a new malware strain named ToddlerShark.

Cybercrime and threat intel
UA hackers detained: Ukraine's Cyber Police has detained three suspects accused of hacking and selling access to email and Instagram accounts. The group used brute-forcing attacks to gain access to more than 100 million accounts. The suspects were detained in Ukraine's Kharkiv region. They face up to 15 years in prison. Officials are also investigating if the group's members cooperated with Russian agents after some of the hacked accounts were used in Russian cyber-attacks.
Tornado Cash developer charged: Dutch authorities have formally charged a Russian national with money laundering for his role in developing the Tornado Cash platform. Alexey Pertsev was arrested in August 2022, days after the US sanctioned the Tornado Cash platform. He is the third suspect to have been charged for their role in developing the platform. The two Tornado Cash co-founders were also charged in the US in August 2023. Officials claim Pertsev and his co-conspirators helped launder more than $1.2 billion worth of cryptocurrency. [Additional coverage in DL News]
Nemesis Market takedown: German authorities have seized servers hosting the Nemesis dark web marketplace. The market launched in 2021 and had more than 150,000 registered users and 1,100 seller accounts. It was primarily known for the sale of illegal drugs.

First cyberflashing conviction: An Essex 39-year-old man has become the first person to be convicted and sent to jail under the UK's new cyberflashing law. Authorities have sentenced Nicholas Hawkes to 15 years in prison for sending unsolicited d**k pics to two victims, a woman in her sixties and a 15-year-old girl. Hawkes also received a 10-year restraining order against both victims. [Additional coverage in The Independent]
Raven Logs: Security researcher g0njxa has published a report on Raven Logs, a Russian-speaking "traffer." The group has been active since at least October 2022 and likes to work with infostealer gangs.
Tax season campaigns: Tax season is here, and so are the phishing campaigns, per Malwarebytes and Microsoft.
RDP threat: Sophos has published an interesting multi-part series on RDP threats and how to investigate and secure devices.
Ivanti attacks: The Varonis security team reports an increase in activity targeting Ivanti Connect Secure devices. The attacks leveraged two vulnerabilities disclosed at the start of the year, initially targeted by APT groups but then widely abused by other threat actors as well.
TeamCity attacks lead to ransomware: A threat actor is exploiting two recently patched TeamCity vulnerabilities to deploy ransomware on unpatched servers. The attack is using an open-source ransomware variant named Jasmin. According to security firm Trend Micro, the same TeamCity vulnerabilities have also been exploited to deploy remote access trojans and cryptocurrency miners. JetBrains released fixes for the TeamCity bugs at the start of the month.
RaaS recruitment efforts: Three ransomware groups are using recent law enforcement takedowns to aggressively recruit new members. Groups like Cloak, Medusa, and RansomHub have posted ads on underground forums, according to GuidePoint Security. The ads are attempting to lure more experienced hackers from the defunct AlphV and LockBit gangs. Two ransomware platforms named BEAST and RAAS FLOCKER also launched this month and are attempting to fill the void left by AlphV and LockBit.
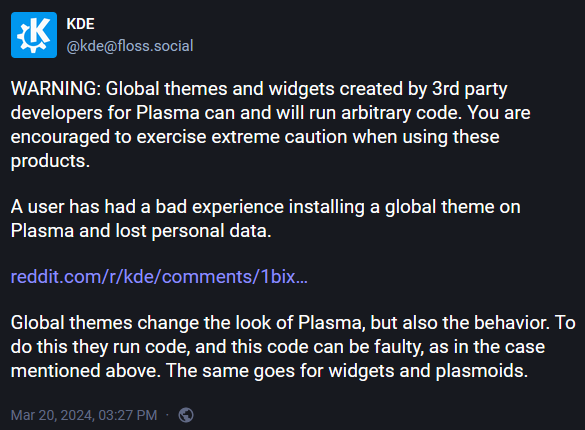
Malicious themes: KDE has confirmed that at least one malicious theme was uploaded to its official store. The theme wiped a user's files.
Threat/trend reports: DLBI, GuidePoint, Horizon3, Imperva, and Recorded Future, have recently published some interesting reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
Updated DDoS guidance: US authorities have updated their guidance on how to respond to DDoS attacks. The original guide was published back in 2022.
Malware technical reports
AceCryptor: ESET has published a report on AceCryptor, one of the most popular malware crypting services seen in the wild over the past few months.
New Android malware: Kaspersky looks at three new Android malware strains—Gigabud, Dwphon, and Tambir.
AndroxGh0st: Juniper's security team has published a report on AndroxGh0st, a botnet malware specialized in attacking web and cloud infrastructure. CISA published an advisory on the same malware earlier this year. The Juniper report focuses on the botnet's attacks on Laravel-based applications.
Sysrv: Imperva researchers have spotted a new version of Sysrv, one of the many crypto-mining botnets that refuse to die.
Sign1: GoDaddy's Sucuri has published a report on Sign1, a new piece of JavaScript malware that a threat actor has injected in at least 40,000 websites over the past months. The malware is being used to redirect a site's visitors to malicious URLs.
VCURMS: ANY.RUN has published a report on a campaign delivering the VCURMS and STRRAT remote access trojans. This looks to be the same campaign spotted by Fortinet here.
Sponsor Section
The Kroll CTI team observed a campaign using a new malware that appears to be very similar to BABYSHARK, previously reported to have been developed and used by the APT group Kimsuky (KTA082). Read more.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Kimsuky: Rapid7 has published a report on a recent Kimsuky operation. The group operates from North Korea and is also known as Black Banshee and Thallium.
TA450: In a recent report, Proofpoint describes a pay-related social engineering lure used by Iranian APT group TA450 to target Israeli employees at large multinational organizations. The group is also known as MuddyWater, Mango Sandstorm, and Static Kitten.
Curious Serpens's FalseFont: PAN's Unit42 has published a technical report on FalseFont, the latest tool in the arsenal of Iranian APT group Curious Serpens (aka Peach Sandstorm, APT33). The backdoor is written in ASP.NET and can capture a victim's screen, steal browser credentials, and interact with the victim's filesystem and processes.
Turla: Cisco Talos has published a report on new Turla operations that deployed the TinyTurla-NG backdoor. The report focuses on post-compromise activity.
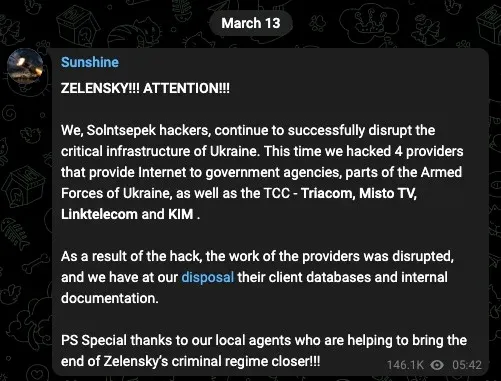
Sandworm's AcidPour: Security researchers believe Russian hackers have deployed a new version of the Viasat wiper against multiple Ukrainian telcos. Ukraine has not formally confirmed the incidents, but at least four telco providers have been offline since March 13. SentinelOne says it discovered a new version of the AcidRain wiper around the same time of the outages. The company named this new version AcidPour and said it can target Linux x86 systems. A hacking group named SolntsepekZ took credit for the attack, but SentinelOne linked the malware to Russia's Sandworm APT.
UNC5174: A Chinese hacking group is exploiting a vulnerability (CVE-2023-46747) in F5 BIG-IP devices to gain initial access to corporate and government networks. Google's Mandiant division has linked the attacks to UNC5174. Mandiant says UNC5174 is a former hacktivist known as Uteus, who now appears to work as a contractor for China's Ministry of State Security (MSS). Besides attacks on F5 devices, the same group has exploited a recent vulnerability in ConnectWise ScreenConnect.
i-SOON leak: BishopFox has published its own analysis of the i-SOON leak. Its analysis focuses on the cyber contractor's tools.
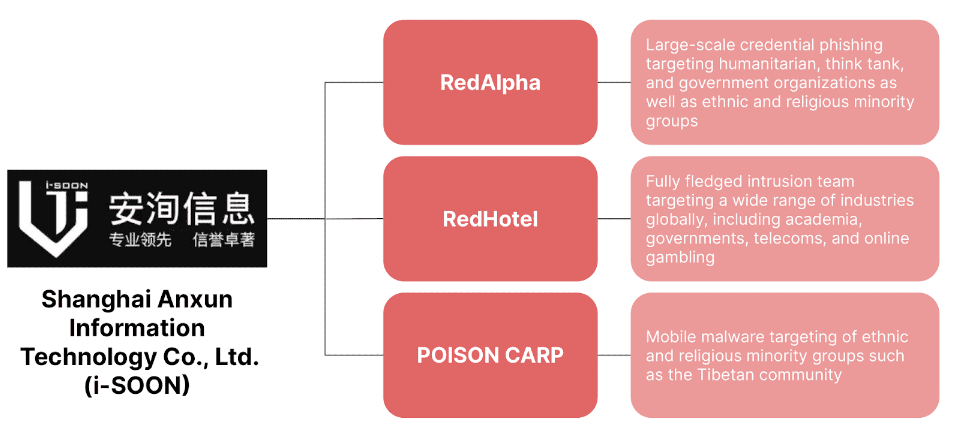
More i-SOON attribution: After Trend Micro did its best i-SOON attribution game earlier this week, it's now Recorded Future's turn. The company has linked the Chinese cyber contractor to three APT groups it tracks as RedAlpha, RedHotel, and POISON CARP. See chart below.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Atlassian security updates: Atlassian has published its monthly security updates for the month of March 2024.
Ivanti security updates: Ivanti has released two security updates for its Neurons for ITSM and Standalone Sentry products. Ivanti credited the Sentry bug to NATO's cybersecurity team. It is a major remote code execution bug with a severity rating of 9.6/10.
Jenkins security update: The Jenkins project has released a security update to patch its built-in Jetty engine.
OpenBSD RCE: Two security researchers plan to reveal an OpenBSD RCE at an upcoming infosec security conference in Finland this April.
FlowFixation vulnerability: Tenable researchers have published details on FlowFixation, a one-click RCE vulnerability in the AWS Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA) service.
Unpatched Artica Proxy vulnerability: Security firm KoreLogic has published details and proof-of-concept code for a major vulnerability in Artica Proxy appliances. KoreLogic described the vulnerability as a pre-auth PHP deserialization attack that allows threat actors to run malicious code on the appliance's admin web interface. The vendor has not replied to KoreLogic's bug report, and the vulnerability is still unpatched. Artica claims on its website that it sold more than 100,000 appliances, although it's unsure how many of these are its proxy.
Fortinet bug: CyFirma has published a report on CVE-2024-21762, one of the two Fortinet bugs disclosed at the start of February that came under active exploitation days after.
Fortinet SQLi PoC: Horizon3 has published a technical write-up and PoC for CVE-2023-48788, an SQL injection in Fortinet devices. A day after the PoC went live, Fortinet confirmed in-the-wild exploitation.
Deep links exploitation: Positive Technologies' Andrey Pesnyak describes how threat actors can abuse Android's deep links.
"Google considers this not a vulnerability but an error in the documentation. Therefore, all the company did to address this was add the following text."
Xbox security update: Microsoft has released an out-of-band security update for the Xbox platform. The update fixes a vulnerability in the Xbox service that can allow threat actors to gain SYSTEM privileges. The Microsoft Store will automatically install the update on all affected customers. Microsoft initially declined to patch the bug. The company changed its mind after a proof-of-concept was published online last week. [h/t Simon Tsui]
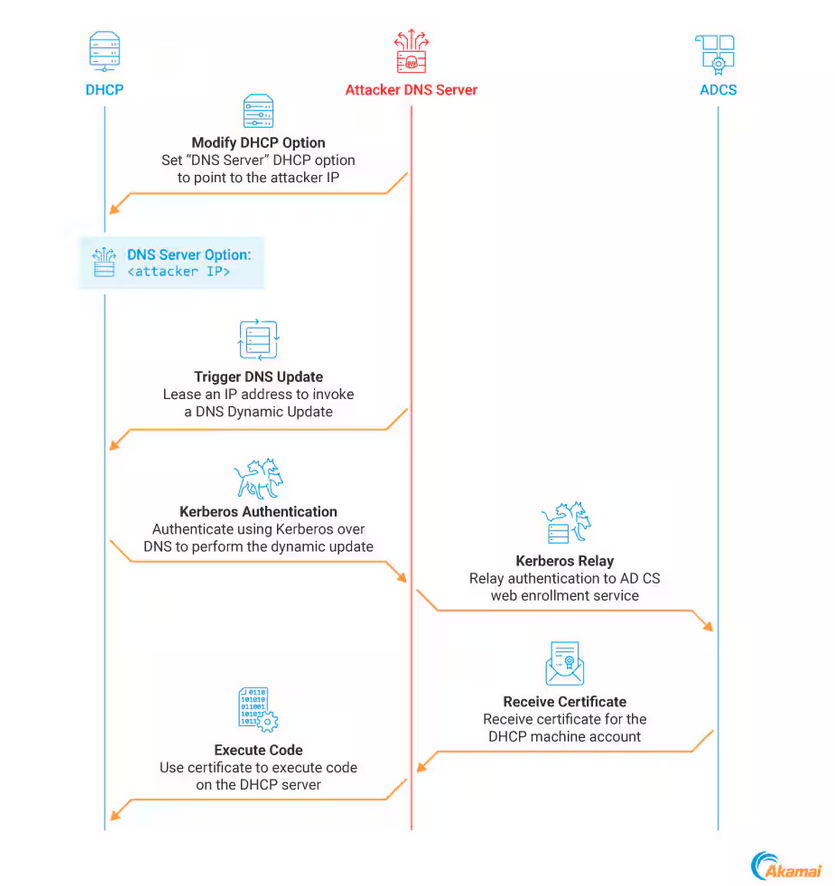
DHCP Coerce: Akamai researcher Ori David has published details on a new technique that abuses the DHCP administrators group to gain elevated privileges on a company's Active Directory environment. David says there's no CVE or fix for the attack because the technique is based on the abuse of legitimate features. David named the new technique DHCP Coerce.
Infosec industry
New tool—Attacknet: Security firm Trail of Bits has open-sourced a new tool named Attacknet. The tool is meant to test blockchain devnets with simulated network and side-channel attacks.
DefCamp 2023 videos: Talks from the DefCamp 2023 security conference, which took place in Bucharest in November of last year, are now available on YouTube.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at Russia's recent leak of an intercepted German military discussion. From an intelligence point of view, the content of the discussion is only moderately interesting, but Russia decided to leak it in an attempt to influence European attitudes towards providing military aid to Ukraine.




