Risky Biz News: Ukrainian hackers wipe equipment of major Russian telco
In other news: Turkiye's e-government portal got hacked; Russia to limit foreign vulnerability scanners from checking RuNet; CVSSv4 coming in Q4 2023.
This newsletter is brought to you by Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
A Ukrainian hacking group named the Cyber Anarchy Squad has breached the network of Russian telco Infotel JSC and wiped some of its routers and networking devices.
The incident took place last Thursday—June 8—and brought the telco's network to a full stop for 32 hours.
The company confirmed the attack via a short message on its website.
Reports in both Russian and Ukrainian media say the attack had a huge impact on Russia's financial system, which was unable to process any electronic transactions for more than a day.
According to reports, Infotel operates the Automated Electronic Interaction System (ASEV) for the Central Bank of Russia, a system through which all major Russian banks and financial institutions report and register transactions with the CBR.
Once Infotel's routers went down, banks, online stores, e-banking systems, credit organizations, and other financial institutions couldn't complete transactions.
The hackers also dumped diagrams for Infotel's network and a list of all the company's customers on their Telegram channel.
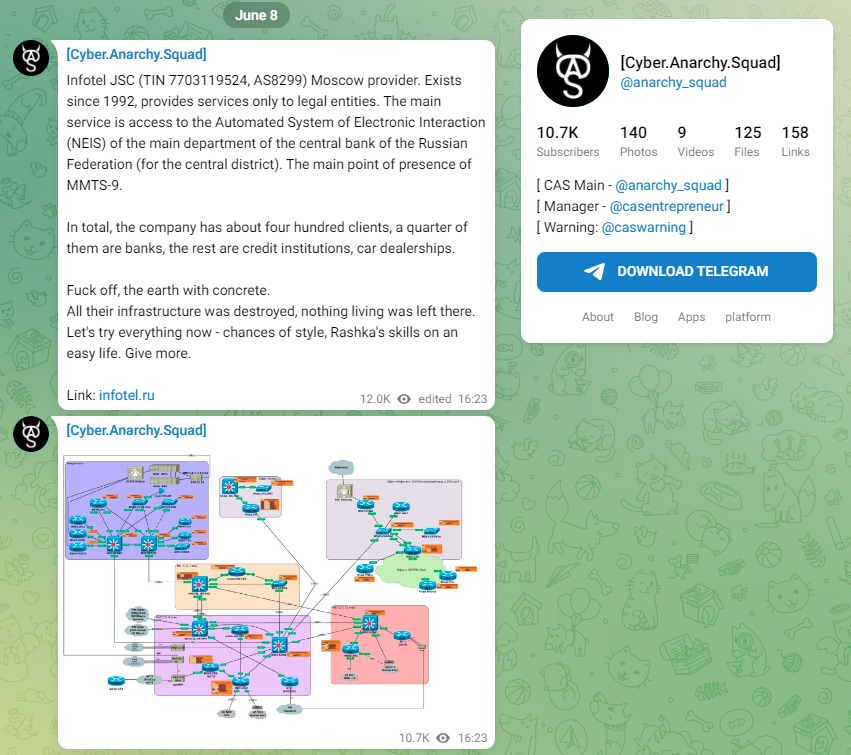
Besides wiping Infotel's network, the Cyber Anarchy Squad says it also defaced 14 Russian websites with messages of support for Ukraine's military counter-offensive.
Breaches and hacks
e-Devlet hack: A threat actor is claiming to have hacked the e-Devlet (e-Government) portal and stolen the personal information of 85 million Turkish citizens. The data is being offered for sale on a dedicated website. It allegedly includes sensitive details like full names, home addresses, ID numbers, phone numbers, real estate deeds, and information about family members. The Turkish government has yet to confirm the hack. Local security experts believe the data was stolen after the threat actor breached the company managing the e-Devlet portal. If confirmed, this would be the largest hack in the country's history, larger even than the 2016 hack of the country's voter registration database. [English coverage in BalkanInsight]
Shell data leak: Oil giant Shell has left a database exposed online containing the personal details of customers who used its Shell Recharge electric vehicle charging stations. The database contained millions of logs with details such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and even vehicle identification numbers. The researcher who found the exposed AWS server could not determine for how long the database was left online without a password. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
More MOVEit disclosures: The University of Manchester in the UK and the Illinois Department of Innovation & Technology and the Minnesota Department of Education in the US have disclosed breaches connected to the global ransom campaign carried out by the Clop gang against companies using the MOVEit file-transfer utility.
CoD account banning: After earlier this year, cheat-makers found a way to get players banned in GTA Online, there's now a similar exploit for two Activision games—Call of Duty Black Ops: Cold War and Call of Duty Modern Warfare 2022. The same tool that can get players banned can also be used to crash lobbies and players' gaming clients. Also, here's some CoD trivia regarding the game's infamous "Hacked" emblem.
General tech and privacy
NIST TLS 1.3 visibility project: The National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology is working on a project meant to standardize the way TLS 1.3 interception is done in enterprise equipment. TLS interception, or TLS visibility, has been a core component of the cybersecurity landscape for more than a decade and has allowed security teams to inspect encrypted traffic for possible threats. NIST standard SP 800-52 currently contains technical guidance on how to perform TLS 1.2 interception without breaking or weakening encryption, but since its release in 2018, no such standard has been available for the more powerful and complex TLS 1.3.
GCP Cryptomining Protection Program: Google Cloud has introduced a new feature named the Cryptomining Protection Program that will cover up to $1 million worth of cloud expenses caused by undetected cryptomining attacks. The new feature is available for all Google Cloud customers with a Security Command Center Premium subscription.
Just Musk things: Twitter is allegedly refusing to pay its Google Cloud bill. This comes after AWS had a hard time extracting payment from the company last month. Grabs popcorn!
Xandr revelations: Reporters with The Markup have a deep dive into how the advertising industry is secretly trading everyone's personal information, including very sensitive data. The article came to be after reporters discovered a 2021-dated spreadsheet containing more than 650,000 "audience segments" based on which data is organized. The spreadsheet was available on the website of Microsoft's Xandr ad platform. Each segment also includes the names of companies involved in collecting the data. The Markup has an interface in its article to let you explore the spreadsheet.
Government, politics, and policy
Russia to limit foreign vulnerability scanners: Russian internet watchdog Roskomnadzor plans to limit foreign-based vulnerability scanning services from operating on its portion of the internet, also known as RuNet. According to officials, more than ten such services are constantly scanning the RuNet for vulnerable systems that are then exploited in cyberattacks. The Roskomnadzor also plans to create a domestic vulnerability scanning service.
Пиратская бухта: Several Russian Duma members want the government to create a national torrent portal to "legally" distribute content from "unfriendly nations" without a license. [Additional coverage in TASS]
GAO report: A new GAO report found that the Department of Interior needs to do some work to address threats to federal systems and critical infrastructure.
First hunt-forward mission in Latin America: US Cyber Command has conducted its first-ever hunt-forward mission in Latin America. Officials didn't say which country invited CNMF's hunt-forward mission. So far, Cyber Command has deployed 70 of these operations in 22 different nations. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
Sponsor section
This edition is brought to you by Thinkst Canary. Most companies find out way too late that they've been breached. Thinkst Canary changes this. Deployed and Loved on all seven continents. Deploys in minutes; almost zero admin overhead. It just works!
Cybercrime and threat intel
Alcasec co-conspirator detained: Spanish authorities have detained a second suspect in connection to the hack of the country's tax and judiciary services. The suspect was identified as a 29-year-old man from Cartagena. Authorities say he is an expert in anonymization, operational security measures, communications encryption, and multi-identity. He also participated in select and closed cybercrime forums, where he had a high reputation. Police investigators say the suspect aided a 19-year-old hacker going by the name of Alcasec in breaching the tax and judiciary services last year. Data stolen from the two agencies was sold online through a service named "The Eye of Horus." Alasec was detained earlier this year at the end of March.
Mt. Gox charges: The US Department of Justice has charged two Russian nationals for the 2011 hack of the Mt. Gox cryptocurrency exchange. Officials say Alexey Bilyuchenko and Aleksandr Verner took control of a Mt. Gox server located in Japan in 2011 and proceeded to slowly siphon funds until the exchange collapsed in early 2014. More than 647,000 bitcoin, worth $1.67 billion today, were stolen from the exchange during the multi-year hack. The DOJ says Bilyuchenko used his funds to help create the BTC-e cryptocurrency exchange together with Alexander Vinnik. The FBI shut down BTC-e in 2017 after the platform was linked to multiple money laundering operations, including funds from ransomware attacks, drug cartels, and corrupt public officials.
Pink Drainer: A hacking group named Pink Drainer has stolen more than $3 million worth of crypto assets. According to Web3 security platform ScamSniffer, the group impersonates journalists from the crypto blogosphere to phish the administrators of popular Discord servers and high-profile Twitter accounts. They then use the hacked accounts to push phishing links to their communities. Communities compromised by this gang include LiFi, Flare, Evomos, the Pika Protocol, and Orbiter Finance. The group has also gained access to the Twitter accounts of Steve Aoki and OpenAI CTO Mira Murati. The ScamSniffer report details the same campaign documented by Brian Krebs at the end of May.
BEC scams hit $50B worldwide: The FBI says that losses to business email compromise (BEC) incidents have passed the $50 billion mark worldwide. The agency says it received more than 277,000 complaints from the US and 177 countries since October 2013, when it started tracking the BEC statistics.
Cyber extortion peaks in Q1 2023: Cyber extortion activity reached the highest volume ever recorded in Q1 2023, according to Orange Cyberdefense. The rise in cyber extortion attacks comes as ransom activity saw an 8% decline in 2022. Orange says it also saw a shift in the geography of attacks, with threat actors moving from the United States (-21%) and Canada (-28%) to target more victims in the Southeast Asia region (+42%), the Nordics (+40%), and Latin America (+32%).
DDoS attacks increase fivefold: Nokia's threat intelligence team says DDoS attacks carried out using IoT botnets have increased fivefold over the past year. The number of IoT devices turned into DDoS bots has risen from around 200,000 a year ago to approximately one million devices today. These devices are generating more than 40% of all DDoS traffic.
New npm malware: Sixty-nine new malicious npm packages were discovered last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for more details.
Malware technical reports
KrisR: Chinese security researchers have a breakdown of KrisR, a variation of the open-source Gh0st remote access trojan.
BatCloak: Trend Micro looks at BatCloak, a malware obfuscation engine at the heart of ScrubCrypt.
Risky Business Demo
In this Risky Business demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy shows off the Tines no-code automation platform to host Patrick Gray.
APTs and cyber-espionage
APT32's SpectralViper: Elastic's security team has discovered a new backdoor malware operated by Vietnamese cyber-espionage group APT32 (OceanLotus). Named SpectralViper, the malware has been used against Vietnamese victims, including a local agri-business.
Operation Triangulation: Qihoo 360 linked Operation Triangulation to APT group Sand Eagle (APT-C-63), then deleted the research.
Redteam Pretender: Chinese security firm Venustech ADLab has published details on Redteam Pretender, a new threat actor that is targeting the financial departments of Chinese companies. ADLab says the threat actor is actively trying to hide its operations as a cybersecurity read team. Based on the time the group primarily operates, ADLab believes the group may be based in Southeast Asia.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
H1CA shuts downs after bug report: Chinese certificate reseller H1CA has taken its website offline after a security researcher uncovered a hidden mechanism in its certificate management client. Discovered by Caddy Server creator Matt Holt, this mechanism allowed the company to execute code on the servers of its customers. The commands were executed through a modified version of ACME.sh, an open-source project that lets companies automatically install and renew TLS certificates. The ACME.sh team has released a security update to patch the loophole exploited by H1CA. More drama on this topic and the shady CA world can be found here.
Libssh PoC: GitHub security researcher Kevin Backhouse has published a PoC for CVE-2023-2283, an authentication bypass in the Libssh library that can allow a remote attacker to gain unauthorized access to a user's account via SSH.
Windows Win32k PoC: Chinese security firm Numen Cyber Labs has published a write-up and a PoC for CVE-2023-29336, an EoP in the Windows Win32k component. The vulnerability was patched in May and actively exploited in the wild.
More MOVEit vulnerabilities: Progress Software has released new security updates for its MOVEit file-transfer appliance. The company says the updates patch a new vulnerability discovered by HuntressLabs, a security firm it is working with to audit its software following the recent zero-day attacks against its products. The vulnerability is also an SQL injection, just like the CVE-2023-34362 zero-day. No CVE has been assigned to this as of yet.
Sony BRAVIA RCE: White Oak Security has disclosed an RCE in Sony BRAVIA, a signage management platform. An update is out, but I expect at least one rick-rolling event to come from this.
Eyes on Fortinet: Fortinet is privately notifying customers about a new vulnerability. It's unclear if this is exploited in the wild. The last time we got a tip about Fortinet doing the exact same thing, it was (looking at you, CVE-2022-41328). The company is expected to release security updates this week as part of its regular Patch Tuesday updates.
CVSS 4.0: The next iteration of the CVSS vulnerability scoring system (CVSSv4) is expected to go live in Q4 2023. A preview of the upcoming standard was presented at the FirstCon23 security conference last week [PDF]. Upcoming features include simplified threat metrics, an improved scoring impact system, new attributes for vulnerability response, and new features to make the scoring system more compatible with OT, ICS, and IoT vulnerabilities. A new CVSS 4.0 calculator is also on the way.

Infosec industry
Lawyers are bad for IR, mkay: Academic research set to be presented at the upcoming USENIX security conference has found that cyber insurance companies and legal teams have had a negative impact on incident response procedures. The research found that cyber insurance firms tend to outsource investigations to a small number of IR firms, have driven down the fees for IR work, and often appoint lawyers to direct investigations instead of technically-skilled personnel. Putting lawyers in charge has also had its own negative effects. Legal teams introduced contractual and communication steps that slow down incident response operations, and they also typically advise IR teams not to write down any remediation steps or IR reports as a way to prevent leaving documents around that may show the victim's legal culpability.
CISOs on boards: A study conducted by IANS Research has looked at how cybersecurity is represented on modern boards. The study was conducted in light of an upcoming SEC rule change that will require public companies to disclose the cybersecurity expertise of board members. Some of the study's main findings are below.
- Less than half of Russell 1000 CISOs stand out as eligible board candidates.
- A mere 2% of Top 1000 CISOs are board-certified.
- 90% of public companies lack even one qualified cyber expert, showing a significant cyber board supply-demand gap.
- Only 15% of CISOs have broader traits required for board level positions, with another 33% having a subset of those necessary traits.
- Half of qualified CISO candidates are female or from an underrepresented group, showing companies can add diversity and cyber expertise in a single candidate.
Industry news: Tavis Ormandy, one of the founders of Project Zero, has moved to a new Google team named Google ISE (Independent Security Evaluators). Bad news for a CPU vendor is on the way.
New tool—CRY.ME: ANSSI has open-sourced CRY.ME, a secure messaging application based on the Matrix protocol that contains cryptographic vulnerabilities deliberately introduced for educational purposes.
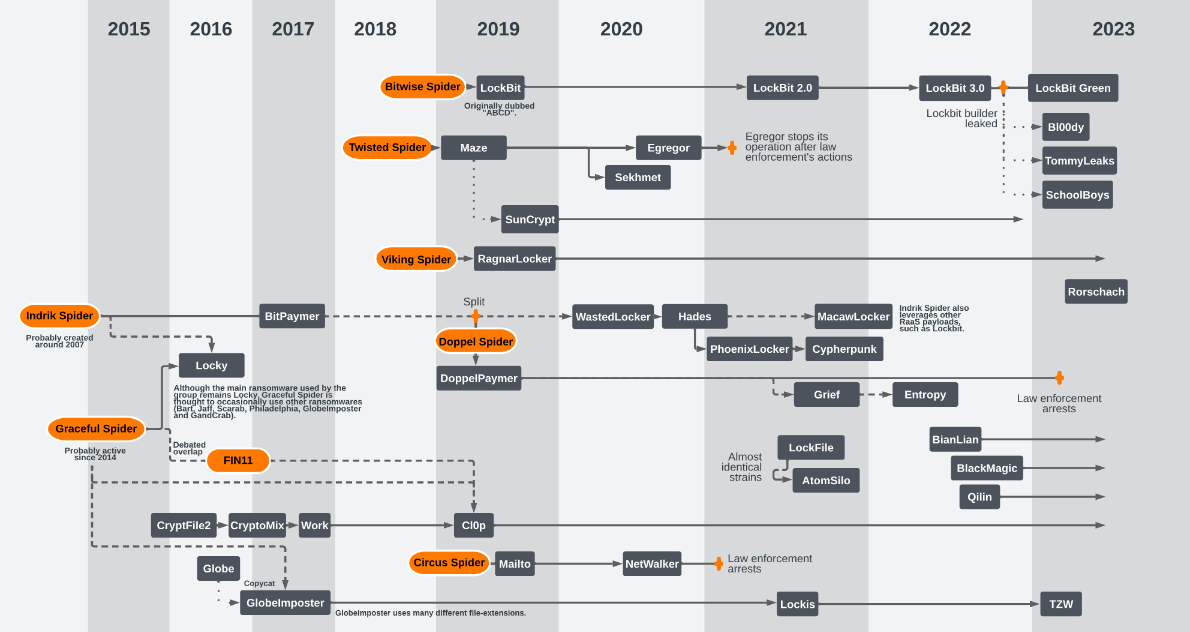
New tool—Ransomware Map: Orange's cybersecurity team has this very cool map of all the ransomware crews and strains and how they evolved over the years. The full map is here. It was put together by Marine Pichon.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of "Between Two Nerds," Tom Uren and The Grugq look at how different cyber powers leverage companies through coercive power, regulation, and the attraction of values.




