Risky Biz News: UK GovAssure program to run annual security audits on government departments
In other news: CISA picks up abandoned NCSC security tool; China is developing cyber-weapons to hijack enemy satellites; Google Cloud patches GhostToken and Asset Key Thief vulnerabilities.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The UK government has announced a new program named GovAssure, through which government security teams will carry out annual security audits of government departments and key public services (known as arm's-length bodies).
The security audits will be conducted under a new and more stringent security scheme that UK officials say is needed to protect government IT networks "from growing hostile cyber threats."
At a technical level, the GovAssure security audits will review if government departments and crucial services follow the NCSC's Cyber Assessment Framework and its 14 core principles, but will also open the door for assessments by third parties to confirm and validate results.
At a bureaucratic level, the new GovAssure program will be managed by the Government Security Group (GSG), a department inside the Prime Minister's Office responsible for security across the UK government.
The National Cyber Security Centre, the country's main cybersecurity agency, will also provide input and support, officials said when they announced the program last week at CyberUK, the UK's premier security event organized each year by the NCSC.
The GovAssure program is part of the UK government's first-ever Government Cyber Security Strategy (GCSS), which officials announced in January 2022 and are currently slowly started implementing.
The GCSS represents a trend among Western governments, with the US, the UK, and the EU all working on centralizing and smoothing out their cybersecurity-related procedures in the wake of rising threats against their respective government bodies from the likes of state and financially motivated groups.
Breaches and hacks
Eurocontrol DDoS attacks: Europe's air-traffic control agency Eurocontrol says pro-Russian hackers attacked and caused interruptions to its public website last week. The agency says the attacks have not impacted EU air traffic. Pro-Kremlin group Killnet took credit for the DDoS attacks. [Additional coverage in CNN]
Capita ransomware incident: Security researcher Kevin Beaumont has a blog post summarizing Capita's good efforts at containing a recent ransomware attack but ridiculously bad PR work.
Trust Wallet crypto-thefts: The operators of the Trust Wallet cryptocurrency wallet say a threat actor exploited a vulnerability in its product to steal $170,000 from two wallets last November. The company says that only its browser extension wallet is affected. Trust Wallet says the vulnerability was found in one of the extension's third-party libraries. The company says it released a security patch last year and has asked customers to generate new wallet addresses to mitigate attacks. Trust Wallet says it will reimburse users who lost funds as a result of the hack. A detailed technical analysis of the vulnerability is also available.
General tech and privacy
BluesBlocker: There's now a Chrome browser extension that will automatically block Twitter Blue verified accounts as you browse through Twitter threads. The Twitter account promoting the extension was insta-banned on the site moments after #BlockTheBlue hashtag started trending worldwide. The extension was published after Twitter decided to remove all classic verified accounts and only left Twitter Blue verified accounts, most of which are just pushing crypto-spam, political propaganda, and conspiracy theories like there's no tomorrow. Yes, it's that bad!
LAPS comes to Intune: Microsoft has added support for the Windows Local Admin Password Solution (LAPS) tool to its Intune platform in order to allow companies to manage passwords for a host's default admin password from the cloud.
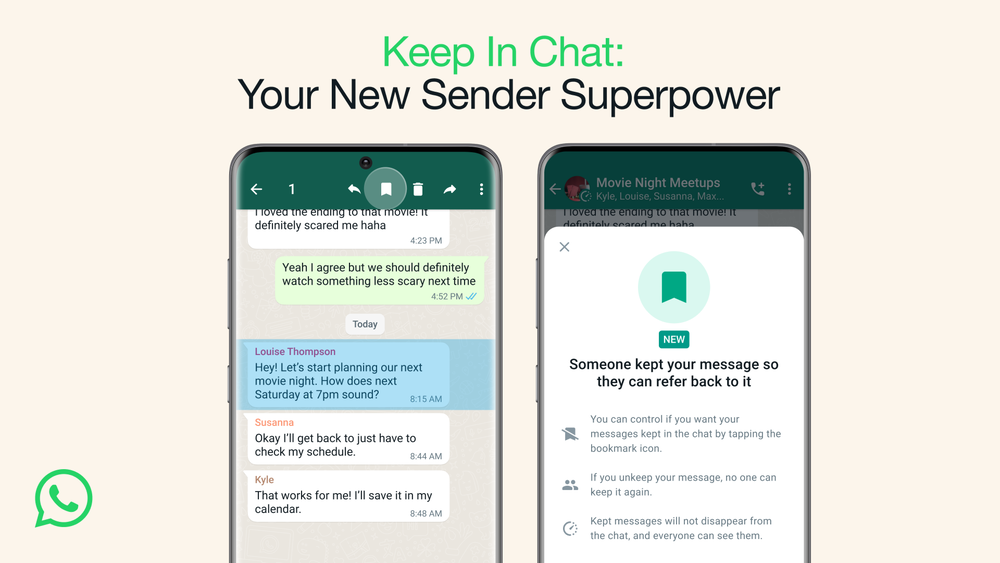
Not-so-disappearing WhatsApp messages: Meta has rolled out an update to the WhatsApp service that will allow users to keep disappearing messages from disappearing. Recipients can long-tap disappearing messages they want to keep, and if the sender agrees, the message will be stored on the device, just like regular WhatsApp messages.
Government, politics, and policy
CISA SBOM documents: CISA has released more documents relating to its SBOM push. Both are community-drafted documents. The first is a document named Types of SBOM, and it summarizes common types of SBOM files that tools may create in the industry today, along with the data typically presented for each type. The second is the Minimum Requirements for VEX documents, and it specifies the minimum elements needed to create Vulnerability Exploitability eXchange (VEX) documents, files typically used by SBOM solutions to track vulnerabilities.
VA found lacking in cybersecurity: A US GAO report found the Department of Veterans Affairs lagging behind in terms of implementing privacy and cybersecurity best practices.
"The report identified continuing significant deficiencies related to access controls, configuration management controls, change management controls, and service continuity practices designed to protect mission-critical systems from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction."
IRS to send agents abroad: The US Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plans to send four agents specialized in cybercrime investigations to Australia, Singapore, Colombia, and Germany. The new IRS agents will begin operations starting this summer. The IRS previously had one cyber investigator abroad, operating from The Hague, Netherlands, mostly working alongside Europol. TechCrunch reports the four new positions represent a significant increase in the IRS' global efforts to fight cybercrime and cryptocurrency-related fraud.
USAF to recruit cyber officers: The US Air Force has simplified its recruitment program to reduce the time needed to train and onboard cybersecurity professionals in officer roles. Officials hope the simplified recruitment program will attract cybersecurity professionals from the private sector who want to start military careers without having to complete a lengthy officer commissioning process. The Air Force says it will start accepting new applicants to its program on April 26. Those accepted could fill the ranks of Lieutenant to Colonel to meet "urgent and future mission needs."
Chinese satellite cyber-weapons: Leaked CIA documents claim the Chinese government is building cyber weapons that can hijack and disable enemy satellites during wartime. The CIA says China's project aims to mimic the signal enemy satellites receive from their operators, and "a cyber capability of this nature would far exceed anything Russia has deployed in Ukraine." The system is not yet operational. The documents are one of the many files leaked by a US Air National Guardsman earlier this year in an incident that has come to be known as the Pentagon Leaks. [Additional coverage in the Financial Times/non-paywall]
EU establishes ECAT: The European Union has established the European Centre for Algorithmic Transparency (ECAT), a new agency that will investigate how large tech companies use algorithms on their platforms. The new agency will analyze how algorithmic systems deployed on social networks and search engines impact or amplify systemic risks like disinformation, calls to violence, and illegal content. ECAT will operate under the new EU Digital Services Act and will be headquartered in Seville, Spain. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Risky Business Demo
In this Risky Business demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy shows off the Tines no-code automation platform to host Patrick Gray.
Cybercrime and threat intel
MediaWiki hacking campaign: A threat actor is hacking wiki websites across the internet to host Fortnite gift card scam sites that try to collect financial data from inattentive and distracted users. So far, the campaign has hit the wiki sites of several US universities, such as Stanford, MIT, Berkeley, UMass Amherst, Northeastern, Colorado State, Caltech, University of Arizona, and others. The attacks target wiki sites hosted on the MediaWiki CMS. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
RBAC Buster attacks: Aqua Security says a threat actor is hacking into Kubernetes servers and abusing the Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) feature to create persistent backdoors on the hacked clusters. The threat actor behind this campaign is deploying Monero cryptocurrency miners on compromised systems. Aqua says that at least 60 Kubernetes clusters have been hacked as part of this campaign, which they are calling RBAC Buster.
PostalFurious: Cybersecurity firm Group-IB says it discovered a new financially-motivated threat actor that has been running SMS phishing campaigns targeting users in Australia, Singapore, and other APAC nations. Group-IB named the group PostalFurious because its phishing sites often impersonated the brands of postal services and, to a lesser extent, toll operators. Researchers believe the group is primarily interested in obtaining customer personal and payment information and appears to be composed of Chinese-speaking members.
8220 Gang attacks: AhnLab says it is seeing the 8220 Gang threat actor exploit the Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228) vulnerability to gain access to unpatched VMware Horizon servers and install a cryptominer.
New npm malware: Twenty-one new malicious npm packages spotted. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for details.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with three new vulnerabilities that are currently being actively exploited. The first is CVE-2023-27350, a vulnerability exploited in PaperCut print management servers. The second is CVE-2023-2136, a zero-day that Google patched in Chrome late last week. And the third is CVE-2023-28432, a vulnerability in the MinIO Go library for AI applications that has been exploited in the wild since March, including against ChatGPT.
Windows secrets extraction: Synacktiv has published a summary of the various types of secrets that can be found on a Windows machine and public tools that can be used to retrieve them.
Project DDosia: Avast has a follow-up on Project DDosia, an initiative from pro-Kremlin hacktivist group NoName057(16) that pays users who install their DDoSia tool on their systems to carry out DDoS attacks on Western targets. Avast reports that besides the Python version they saw last year, the group has also released a Go version of their toolkit.
Malware technical reports
Decoy Dog: Infoblox researchers have discovered Decoy Dog, a malicious toolkit that helps threat actors set up command and control mechanisms for their malware operations via DNS.
BotenaGo botnet: Chinese security researchers have published an analysis of the BotenaGo IoT botnet. Spotted in 2021, the botnet can infect more than 30 routers and IoT devices to abuse for DDoS attacks.
EvilExtractor: Fortinet says that a new infostealer strain named EvilExtractor has been gaining in popularity on underground forums. EvilExtractor also has a ransomware function called Kodex, although it doesn't seem to be very sophisticated.
OCX#HARVESTER campaign: Securonix has published a report on a malware attack chain it is tracking as OCX#HARVESTER and which the company has seen in the wild between December 2022 through March of this year. Researchers seem to believe this is a "modernized" version of the More_eggs malware operation.
FakeCalls: McAfee researchers say they're tracking a campaign distributing the FakeCalls Android banking trojan where the malicious app is signed with the same signing key of a well-known South Korean app.
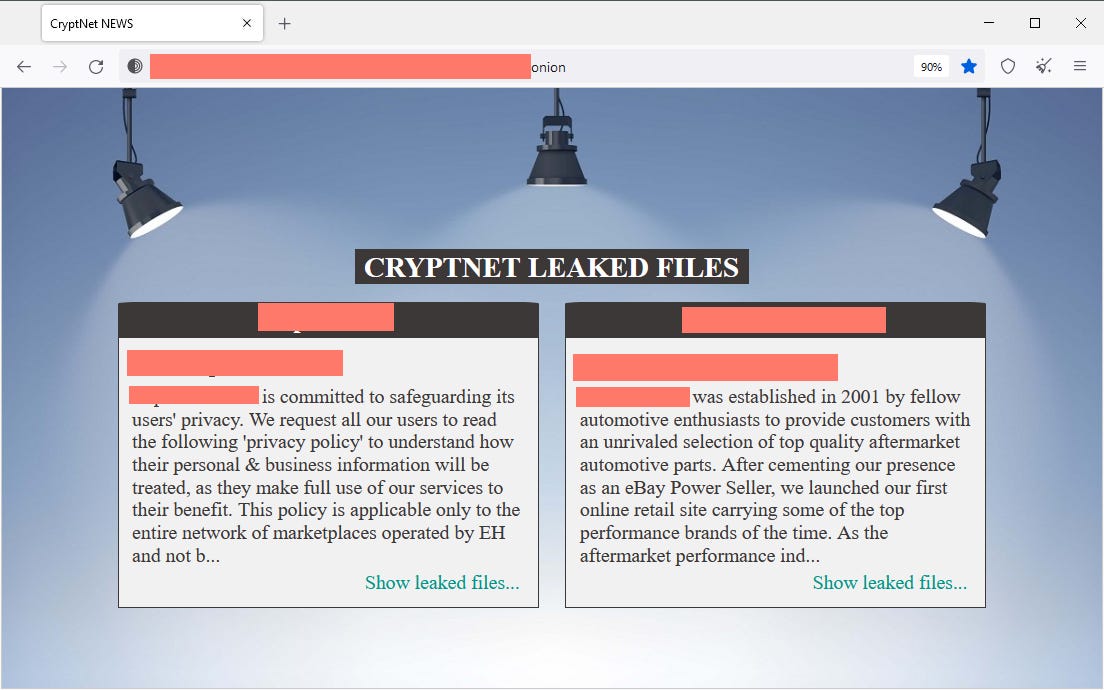
CryptNET ransomware: OALABS has shared details about CryptNET, a newly observed ransomware gang that engages in double-extortion schemes. The ransomware is written in .NET, and OALABS describes it as an unsophisticated "copy pasta wannabe."
Sponsor Section
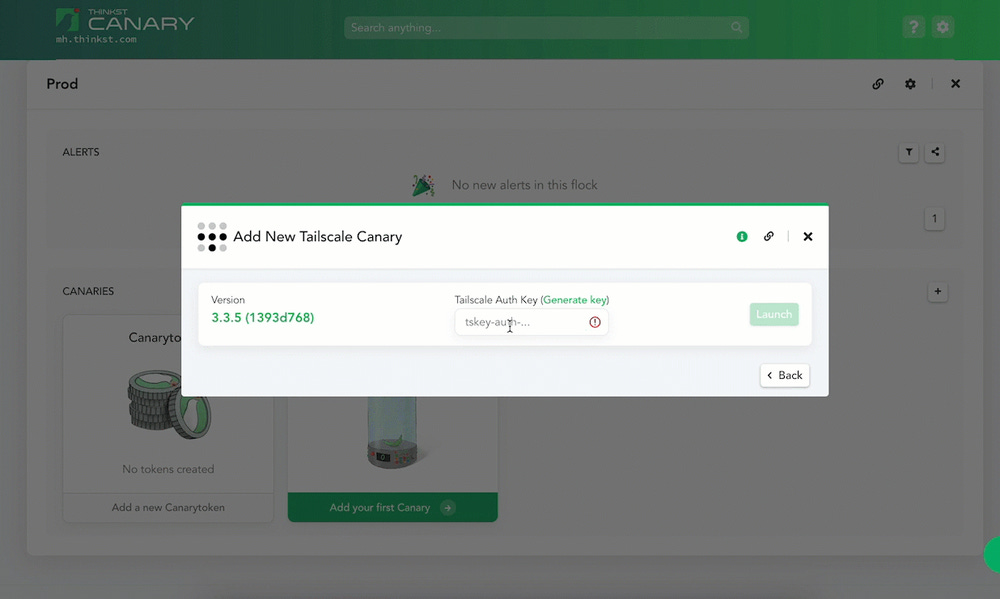
Thinkst is one of this newsletter's four main supporters and this week's featured sponsor. The company has launched a new type of canary token that can help companies detect intruders on their Tailscale VPN networks.
APTs and cyber-espionage
SideCopy APT: QiAnXin has published a report on new attacks carried out by the SideCopy APT. The attacks targeted Indian organizations with a new remote access trojan named AckRAT.
Patchwork APT: Sangor published a report on recent spear-phishing campaigns they linked to the Patchwork APT.
BlueNoroff APT: Jamf says it discovered a new macOS malware strain named RustBucket that they believe was created and is being used by the BlueNoroff North Korean APT group as a loader.
UCID902 (Kimsuky): South Korean security firm Interlab has discovered a series of watering hole credential harvesting campaigns that have targeted human rights groups and activists related to advocacy of human rights in North Korea. Interlab attributed the operation to a group it tracks as UCID902, which overlaps with classic Kimsuky activity.
UN North Korea report: The United Nations Security Council has published its yearly report on North Korea, and this year's report notes a significant increase in North Korean cyber activity, with DPRK groups stealing more cryptocurrency in 2022 "than in any previous year." The report also covers North Korea's 2022 cyber-espionage operations as well.
3CX/X_Trader supply chain attack: Broadcom's Symantec division says the X_Trader supply chain attack that was at the root of the 3CX incident also impacted critical sector entities. Symantec says that, to date, found that among the victims are two critical infrastructure organizations in the energy sector, one in the US and the other in Europe.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
GhostToken vulnerability: Astrix Security researchers have discovered a security flaw in the Google Cloud service that can be abused to hide third-party apps from Google users. Named GhostToken, the vulnerability was patched by Google this month. Astrix says threat actors that managed to trick companies and their employees into installing malicious apps on their accounts could abuse the GhostToken vulnerability to hide the apps from a user's Google Marketplace profile. Since this is the only page where third-party apps are listed, researchers say the GhostToken flaw could have been abused to "gain permanent and unremovable access to a victim's Google account." An attacker's access would have only been limited by the permissions the user gave the malicious app at runtime before the attacker made it "invisible."
Asset Key Thief vulnerability: Cloud security firm SADA has discovered a vulnerability in Google Cloud's Asset Inventory API that could have allowed threat actors to elevate the permissions of a low-level user and gain full access to a company's Google Cloud resources. SADA named the vulnerability Asset Key Thief because threat actors could have abused it to steal a Google Cloud account's private key and gain full control over a company's cloud infrastructure. The vulnerability was reported and fixed through Google's bug bounty program. SADA says it is not aware of in-the-wild exploitation. Asset Key Thief could not be used to take over existing accounts and is a post-compromise issue.
"Asset Key Thief is a privilege escalation vulnerability, meaning attackers would have already needed access to your environment with an IAM binding granting the cloudasset.assets.searchAllResources permission in order to have exploited this bug."
Pedersen hash function vulnerabilities: NCC Group researchers have found vulnerabilities in the Pedersen hash function.
"While the Pedersen hash function has many desirable advantages due to its simplicity, efficiency in arithmetic circuits, and the known security assumption it relies on, it is also susceptible to many pitfalls. Specifically, implementations adapting the Zcash approach but on different curves or with different encoding schemes may result in fragile constructions vulnerable to subtle issues, as illustrated in this blog post."
Drupal security updates: The Drupal team has released security updates for its CMS product. The updates fix a critical access bypass vulnerability that can be exploited via the CMS' file upload function.
SolarWinds security updates: The SolarWinds team released five security updates last week.
VMWare RCE: VMWare has released security updates to address RCE vulnerabilities in VMware Aria Operations for Logs, a centralized log management utility.
CVE-2023-1671 (Sophos): VulnCheck researchers have published an analysis of CVE-2023-1671, a pre-auth command injection vulnerability in Sophos firewalls. A PoC is included in the report.
Infosec industry
CyberWarCom 2023 videos: Talks from the CyberWarCom 2022 security conference, which took place in November of last year, are now available on YouTube.
CISA picks up NCSC's LME: CISA says it plans to pick up and continue developing Logging Made Easy (LME), an open-source Windows application that cybersecurity experts have been using for years to analyze application logs. The toolkit was originally developed by the UK NCSC, but the agency formally retired the app in January this year. CISA says it plans to re-release an "enhanced LME" this summer.
SLSA v1.0: The Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) has announced the release of version 1.0 of SLSA. Pronounced "salsa" and standing for Supply-chain Levels for Software Artifacts, this is a framework for securing software builds and their supply chains.
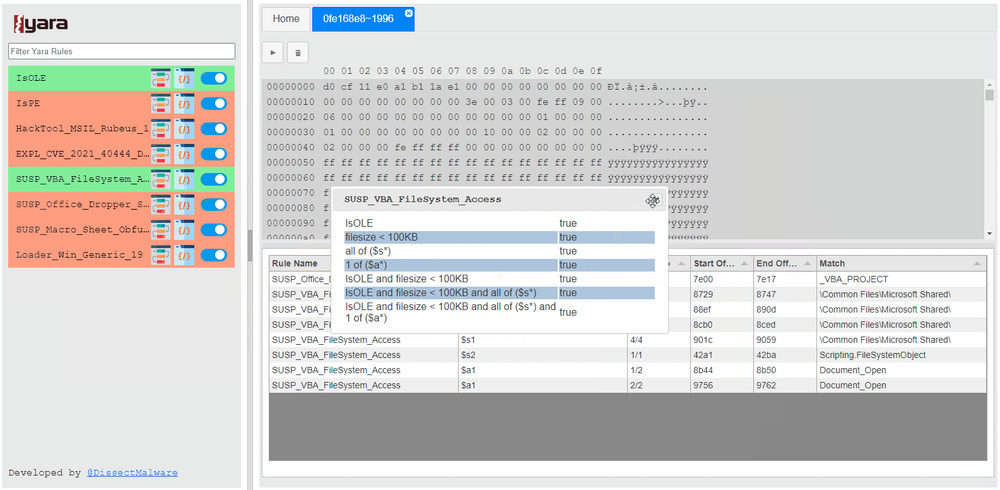
New tool—YaraDBG: Microsoft security researcher DissectMalware has launched YaraDBG, a web-based Yara debugger to help security analysts to write hunting or detection rules.