Risky Biz News: SLP protocol can be abused for large-scale DDoS attacks with huge 2,200x amp factor
In other news: Israel to investigate police use of NSO spyware; VirusTotal gets an AI assistant to analyze and explain malware; Google Authenticator can now sync data to Google accounts.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
Security researchers from Bitsight and Curesec have discovered a vulnerability in the Service Location Protocol (SLP) that an attacker could abuse to launch large-scale DDoS attacks.
The SLP protocol was created in 1997 to allow devices like PCs, printers, routers, and file servers to easily discover each other inside corporate networks.
The protocol was designed for use inside LANs, but it is often exposed on the public internet mainly because it is included as a standard feature in most of today's enterprise software and hardware.
More than 70,000 servers are currently exposing their SLP ports (427 on both UDP and TCP) on the internet. This includes devices such as VMware ESXi hypervisors, Konica Minolta printers, Planex routers, Supermicro IPMI servers, and a ton of IBM gear.
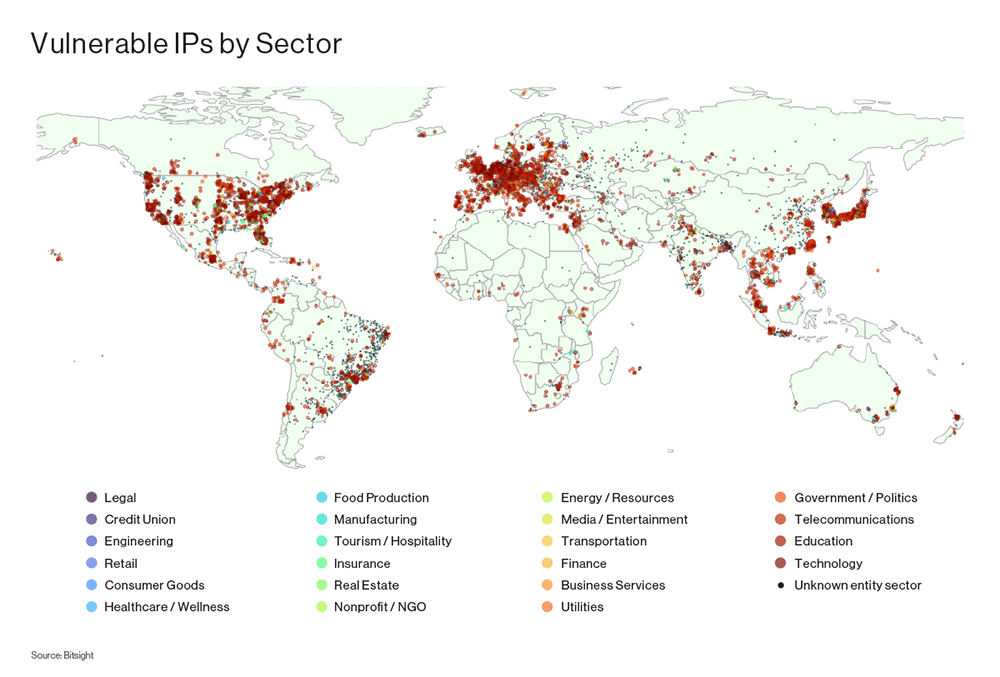
The vulnerability—tracked as CVE-2023-29552—allows an attacker to send a small request to an SLP server that is then bounced toward a victim's network at a much larger size.
This trick is used by threat actors to execute "reflected DDoS attacks," and in the case of SLP, researchers say the protocol's amplification factor is a whopping 2200x, which ranks SLP as the protocol with the third largest amplification factor ever observed.
Because of the protocol's huge output potential for DDoS attacks, both Cloudflare and Netscout expect " the prevalence of SLP-based DDoS attacks to rise significantly in the coming weeks" as threat actors learn to exploit it.
Bitsight says it recognized SLP's potential for abuse and has been working with CISA since February to alert software vendors and have them release mitigations and updates.
The same SLP protocol was also abused earlier this year to deploy the ESXiArgs ransomware on VMWare servers, which should technically mean that some organizations have already looked at securing their SLP ports already. We... presume!
Breaches and hacks
Iran hacks US election results website: US Cyber Command confirmed that an Iranian hacking group known as Pioneer Kitten breached a 2020 election website operated by a local US government. Speaking at the RSA security conference, CyberCommand says it discovered the intrusion during a "hunt forward" mission overseas and notified DHS, which secured the compromised website. Officials say they disrupted the hackers before they could abuse their access, such as posting fake election results. [Additional coverage in the Washington Post/non-paywall]
FilDA Finance crypto-heist: A threat actor exploited a vulnerability in one of FilDA Finance's smart contracts and stole $700,000 worth of cryptocurrency assets.
General tech and privacy
Google Authenticator update: Google has rolled out an update for its Authenticator app that adds the ability to safely back up one-time passcodes to a user's Google account. The update is live for both Android and iOS. Google says it developed and added this feature to help users who lose devices and need a way to gain access to their old Authenticator data and the online accounts secured by the Authenticator app.
Usual Twitter lame stuff: Congratulations to Elon Musk for allowing scammers to easily buy golden verified ticks to impersonate any company and continuing the trend of suspending the accounts of reporters who anger autocratic regimes and rich people. Also, congrats on having your alt-account exposed.
Amazon GuardDuty support for AWS Lambda: Amazon has upgraded its GuardDuty threat detection system to cover the AWS Lambda service. Amazon says GuardDuty will monitor network activity logs of Lambda functions to detect hidden cryptocurrency mining. The move comes after Cado Security discovered last year Denonia, the first known malware strain capable of infecting AWS Lambda and abusing it for cryptocurrency mining.
Government, politics, and policy
Israel to investigate police use of spyware: The Israeli government will establish a commission to probe the use of spyware by police forces to hack the smartphones of Israeli citizens. Reports in Israeli media claim police have used a "watered-down" version of NSO Group's Pegasus spyware—known as Saifan—to target activists, business figures, reporters, and politicians. An initial investigation by the Israeli Ministry of Justice cleared Israeli police forces of any wrongdoing. The report found that police acted in accordance with the law but exceeded the boundaries of the received warrants.
NATO CCDCOE Locked Shields 2023: NATO's annual cyber-defense exercise, known as Locked Shields, concluded last week in Tallinn, Estonia. More than 3,000 cybersecurity from 38 countries and grouped across 24 teams participated in this year's Locked Shields exercise, where they had to cooperate and defend their networks against large-scale cyber attacks. Officials say a joint team of cybersecurity experts from Iceland and Sweden was deemed the most effective participant in this year's edition. They were followed by a joint US-Estonia team and the Polish team.
US sanctions Iranian cyberspace head: The US Treasury has sanctioned Seyyed Mohammad Amin Aghamiri, the head of Iran's Supreme Council of Cyberspace (SCC). US officials say Aghamari played a crucial role in the Iranian regime's brutal crackdown against recent protests. Aghamari blocked access to social media platforms and news sites reporting on the protests and also used Iran's telecommunications systems to spy and harass journalists and regime dissidents.
Russia to force native OSes on new devices: The Russian government is working on a law to force retailers to pre-install Russian operating systems on all new PCs sold in the country. The first wave of feedback claims this will lead to an increase in laptop and PC prices across Russia. Despite efforts to get Russian companies and users to move to Russian operating systems, Windows' market share remained the same in Russia as last year. [Additional coverage in Kommersant]
Risky Business Demo
In this Risky Business demo, Tines CEO and co-founder Eoin Hinchy shows off the Tines no-code automation platform to host Patrick Gray.
Cybercrime and threat intel
eSentire disrupts GootLoader: Cybersecurity firm eSentire says it discovered a way to prevent the GootLoader malware from deploying its payload via hacked websites. The technique relies on visiting hacked sites known to serve GootLoader from a selected list of IP addresses. eSentire says this will trigger a lesser-known reaction of the GootLoader's infrastructure that will ban that IP and several address blocks around it—as a way to prevent security teams from inspecting hacked sites and its payload. Security researchers say that by carefully placing web requests to the more than 375,000 malicious URLs known to serve GootLoader, they can protect "a large swath of the Internet" from getting infected.
Bassterlord interview: The Record has interviewed Bassterlord, a Ukrainian cybercriminal who used to work as an affiliate for the LockBit ransomware gang but has since retired (allegedly). He's also known for selling a "ransomware manual."
TP-Link Mirai exploitation: The operators of a Mirai DDoS botnet have figured out how to exploit a TP-Link router vulnerability (CVE-2023-1389) that was privately exploited during the Pwn2Own hacking contest held in Toronto in December of last year. Pwn2Own organizer ZDI says it reported the issue to TP-Link, and the company released a security update in March. ZDI experts say that once the patch was out, a Mirai botnet shortly started exploiting the bug to hijack unpatched TP-Link routers.
PaperCut exploitation: Huntress Labs has more technical details about the active exploitation of PaperCut print management servers that was reported last week. A public PoC exploit is also available.
Bad bot traffic rises, human traffic decreases: Ad fraud security company Human has published its yearly report, and the company noted that bad bot traffic doubled last year while legitimate human-generated traffic decreased. The company says that most of the bad bot traffic it usually sees comes from behind faked devices and proxy servers.
"Web and mobile applications are treasure troves of value, and bots are an easy and cheap way to attack them at scale."
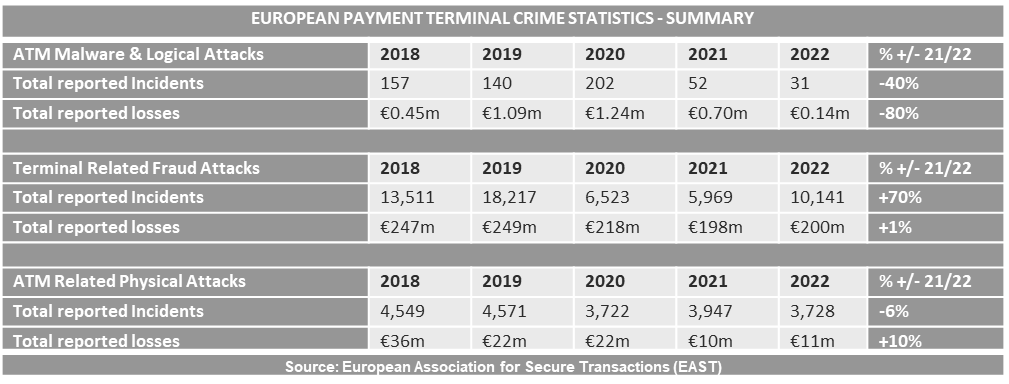
ATM attacks in 2022: The European Association of Secure Transactions (EAST), an industry group of banks and ATM vendors, says European banks lost €211 million to criminal groups last year. EAST says the vast majority of losses came from skimming devices installed on ATMs across Europe, which accounted for €167 million in 2022. Losses caused by malware installed on ATMs were only €140,000, the lowest figure since EAST started tracking these stats. EAST says it also received 502 reports of criminal gangs using a novel MitM relay attack to force ATMs to cash out, but most incidents took place in the first half of 2022 and seem to have stopped after that.
Meta support staff phishing: Group-IB uncovered more than 3,200 Facebook profiles impersonating Meta support staff as part of a campaign meant to phish users out of their Facebook credentials. Researchers say the campaign is conducted in more than 20 languages and appears to be aimed at the Facebook accounts of public figures, celebrities, businesses, sports teams, but also regular users. The campaign has been running since February and is still ongoing.
Don't: Just don't!

Malware technical reports
ViperSoftX: Trend Micro published a report on ViperSoftX, an infostealer that has been used since last year in attacks targeting the cryptocurrency space. Now, Trend Micro is reporting "a significant number of victims."
WhiteSnake: JFrog researchers have discovered 22 malicious PyPI packages that would secretly infect their users with a version of WhiteSnake, a C#-based infostealer.
Aurora Stealer builder: Security researcher Mohamed Adel has a report on the Aurora Stealer builder. He previously also published a report on the Aurora Stealer itself.
in2al5dp3in4er Loader: OALABS has published an analysis on in2al5dp3in4er Loader, a new malware strain spotted and covered by Morphisec last week.
Daam: CloudSek published a report on a new Android malware strain named Daam. The malware can work as an infostealer but also comes with file encryption capabilities.
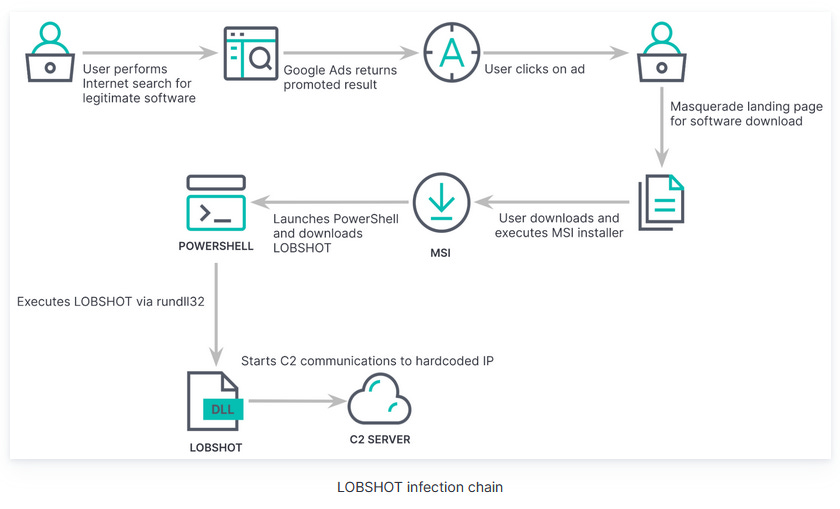
LOBSHOT: Elastic's security team has discovered a new malware strain named LOBSHOT that is currently being distributed via malicious Google ads. The malware's primary purpose is to open a hidden virtual network computing (hVNC) channel for threat actors to connect to compromised hosts. LOBSHOT also includes infostealer capabilities to collect and steal data from browsers and crypto-wallets. Elastic says the malware appears to be leveraged for financially motivated intrusions for the time being.
Sponsor Section
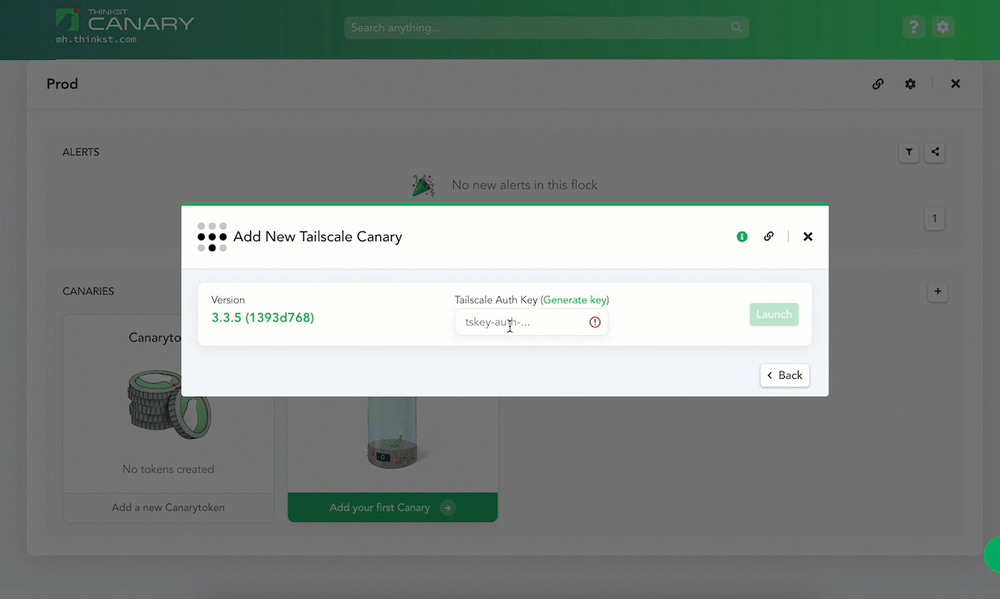
Thinkst is one of this newsletter's four main supporters and this week's featured sponsor. The company has launched a new type of canary token that can help companies detect intruders on their Tailscale VPN networks.
APTs and cyber-espionage
APT-LY-1007: Chinese security firm Anheng says it is tracking a new cyber-espionage group they have named APT-LY-1007. Anheng says the group has been active since August 2022 and has targeted Russian organizations like the Russian Army's Electronic Forces, the Russian Ministry of Defense, and the Russian Railways. Most of their operations have been phishing campaigns that try to trick victims into installing a remote access trojan known as Cyrillic RAT.
Tomiris: Kaspersky researchers have identified a new APT group named Tomiris that has been targeting CIS countries in Central Asia since 2021. Researchers say that even when they discovered victims in other regions, such as the Middle East and South-East Asia, those victims turned out to be foreign representations of CIS countries, illustrating the group's narrow focus on the CIS region. Kaspersky says that current evidence suggests Tomiris is a Russian-speaking group focused exclusively on espionage and the theft of internal documents.
Educated Manticore: Check Point published a report on the recent operations and upgraded tools used by Educated Manticore, a sub-group of the Iranian cyber-espionage group known as Phosphorus.
APT41: ThreatMon published a report on APT41's LolBin shenanigans.
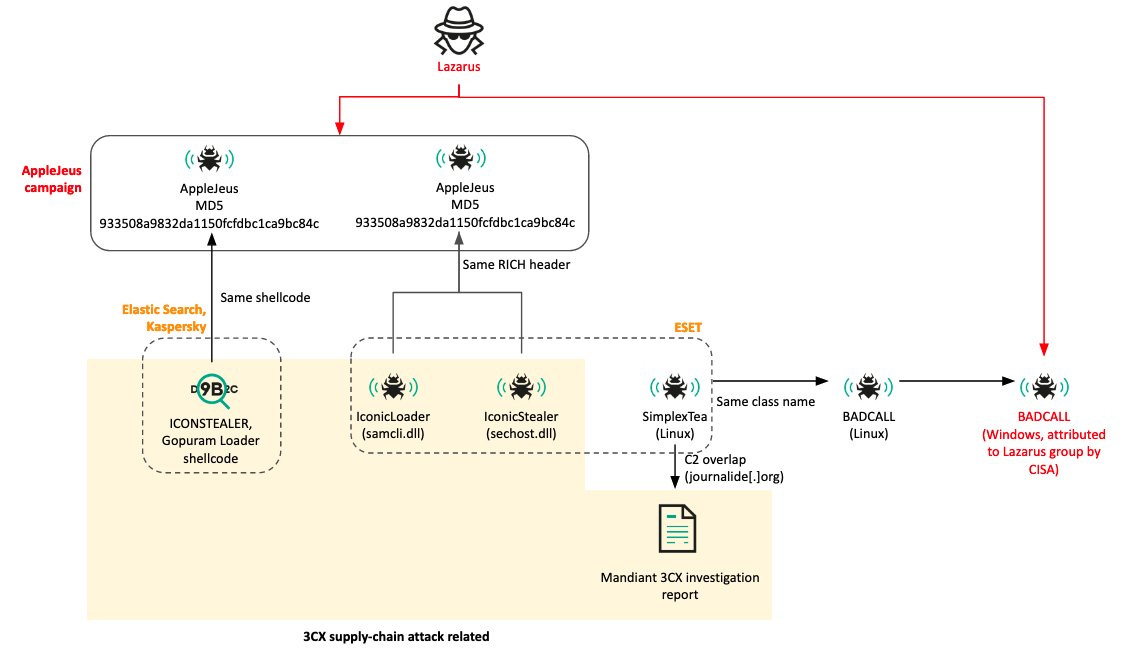
3CX attribution chart: Kaspersky's Seongsu Park has put together a chart with the complex attribution scheme from the 3CX supply chain attack. Also embedded below.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
Satellite hacking: Cybersecurity firm Thales says it intends to attempt a satellite hacking exercise at CYSAT, the yearly space industry cybersecurity conference taking place this week. Thales says its offensive team has identified vulnerabilities that could enable malicious actors to disrupt the operations of the European Space Agency ESA satellites and will test them in practice this week on a test bench hosted by ESA at CYSAT.
Intel TDX security audit: Google Project Zero has published a security audit of Intel's Trust Domain Extensions. Also known as TDX, this is a new CPU feature used for hardware isolation of virtual machine guests at runtime. Google says the security review was performed in cooperation with Intel engineers in anticipation of the TDX v1.0 source code release and before TDX ships with Intel Xeon Sapphire Rapids CPUs. Vulnerabilities found during the security audit could lead to arbitrary code execution, cryptographic weaknesses, and denial-of-service.
KeePassXC security audit: KeePassXC published a security audit of its password management utility performed earlier this year.
New Intel side-channel attack: Academics have discovered another side-channel attack on Intel CPUs. This one is unique because it uses the EFLAGS register to measure the execution time of context and does not rely on the CPU's internal cache like all previous work. They say the attack has a 100% success leak rate, and the attack is difficult to detect and mitigate.
Telegram bugs: Security researcher Davide Turi has published details about several bugs they found in the Telegram app that the company silently patched without acknowledging his research. Not the first time Telegram has done this, btw.
CVE-2023-27524 (Apache Superset): Horizon3 researchers have published a PoC for CVE-2023-27524, an RCE in Apache Superset data viz servers.
Git security updates: The Git team released security updates this week.
Infosec industry
Help for Ukrainian journalists: Granitt founder Runa Sandvik is offering pro-bono cybersecurity assistance to Ukrainian journalists.
Infosec Mastodon: Infosec.exchange, the go-to Mastodon instance for cybersecurity professionals, was down on Monday after its servers were bombarded with more than 100 million DNS requests.
New tool—ImpELF: Cybersecurity firm SignalBlur has open-sourced ImpELF, a Python-based ELF hashing utility that generates unique fingerprints for ELF binaries using their imported functions and libraries, aiding in malware analysis and similarity detection. The tool is a Linux analog of imphash, a similar utility released by Mandiant for Windows systems.
New tool—Mergen: Security researcher Samet Sazak released Mergen, an open-source app for auditing the security of macOS systems.
ETHOS launch: A group of cybersecurity companies specialized in ICS and OT security launched ETHOS (Emerging THreat Open Sharing), a platform for sharing early warnings against critical infrastructure. Shared information includes your typical threat intel indicators of compromise (IoCs), such as IP addresses, hashes, and domains. ETHOS currently has a beta API that provides data-sharing functionality, and a server is in development. Founding members include 1898 & Co., ABS Group, Claroty, Dragos, Forescout, NetRise, Network Perception, Nozomi Networks, Schneider Electric, Tenable, and Waterfall Security. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
AI comes to VT: At the RSA security conference, Google announced VirusTotal Code Insight, a new feature for the VirusTotal threat hunting service that uses AI/ML to generate simple natural language summaries from submitted malware and source code samples. Google says that, at present, the new functionality is deployed to analyze PowerShell files submitted to VirusTotal. The company says it plans to expand the service with additional file formats in the coming days.
RSA keynote: The RSA security conference is underway this week in San Francisco. The conference keynote is embedded below. We recommend going to the 1h:30min mark for the fireside chat between former CISA Director Chris Krebs and US Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco—with Monaco explaining how the US is pivoting to disrupting adversary infrastructure.




