Risky Biz News: Slack discloses security breach, access to code repositories
In other news: ENLBufferPwn vulnerability impacts Nintendo consoles; 3Commas eats its words after disclosing security breach; PyTorch discloses supply chain attack.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The Risky Business team is still on its holiday break, but we thought to put out this weekly edition with some of the past week's biggest infosec stories.
The biggest story, by far, even if it didn't get any media coverage, was Slack's secret data breach disclosure published just ahead of New Year's Eve.
The company said a threat actor stole "Slack employee tokens" and gained access to its GitHub source code repositories.
This happened on December 27, according to Slack, and the company disclosed the breach four days later, on December 31, so a pretty quick turnaround from detection to disclosure.
The incident is eerily similar to what Okta disclosed ahead of Christmas when the company also found that someone used a TravisCI token to gain access to its GitHub repos. Just like Okta, Slack said the intruder didn't gain access to its main infrastructure or to any customer data.
It's unclear if the two incidents are related, as both disclosures lack fine-grained details about what's what. You can blame lawyer-speak for that.
Post-publication edit: Two hours after we sent out this newsletter, CircleCI also disclosed a major security breach, admitting that a threat actor gained access to its infrastructure and advised all users to rotate their CircleCI tokens and review their environments for unauthorized access via CircleCI integrations that may have taken place between December 21, 2022 and January 4, 2023.
In a previous newsletter, we reported that in early December, GitHub’s security team had sent out alerts to several companies about suspicious activity tied to their Heroku and TravisCI integrations. It previously did the same in April as well. With the recent CircleCI disclosure, it sure looks that at least one very determined threat actor is very enamoured with using CI/CD service providers as a way to gain access to private corporate code-hosting infrastructure.
Risky Business News, both the podcast and newsletter, will be resuming their regular three-times-per-week output (Monday, Wednesday, Friday) next week, starting January 9.
Breaches and hacks
Twitter data leak: On Christmas, a threat actor put up for sale the public and private details of more than 400 million Twitter users that they claimed to have scraped off the site using a vulnerability in the platform's API. This week, the details of more than 235 million Twitter users were leaked online and are accessible to anyone.
Potsdam cyberattack: The German city of Potsdam took its IT network offline on December 29 following a warning from the security team of the state of Brandenburg that the city's network was being targeted with a brute-force attack. Officials said they plan to reconnect their network to the internet next week following a series of security audits.
Port of Lisbon ransomware attack: The administration of the port of Lisbon (Portugal) suffered a ransomware attack over Christmas. The port's activity wasn't disrupted. However, the subsequent disruptions were caused by a planned workers' strike.
SickKids ransomware attack: The LockBit ransomware gang has apologized for its attack on the Sick Kids Hospital chain and released a free decrypter to help the victim recover files without paying.
Wabtec ransomware attack: US rail and locomotive company Wabtec has confirmed a ransomware attack at the hands of the LockBit ransomware gang. The incident took place in June 2022 and impacted its US, Canada, UK, and Brazil operations.
3Commas cyber-heist: The CEO of the 3Commas cryptocurrency platform has confirmed that a hacker has stolen the API keys of its users after multiple victims have claimed over the past two months that they had unauthorized access to their cryptocurrency accounts via the 3Commas platform and lost assets worth millions of USD. After news of some of these hacks started to become public, the hacker leaked 10,000 API keys on Pastebin as a way to advertise a larger batch of 100,000 keys. 3Commas came under heavy criticism for denying the hack for two months, claiming that users were phished rather than admitting a breach on its side.
PyTorch supply chain incident: The team behind the PyTorch machine learning library said it discovered a supply chain attack that impacted its nightly builds on Linux. Between December 25, 2022, and December 30, 2022, a previously safe dependency named "torchtriton" turned malicious and installed a binary that could collect system information and read sensitive files, the team said.
T-Mobile breach settlement: Users who've been affected by T-Mobile's 2021 data breach are eligible to receive up to $100 from a $350 million settlement. The catch—they have weeks to make a claim.
LastPass gets sued: LastPass has been sued over its disastrous handling of the August 2022 security breach, which resulted in a second breach in December 2022, and then in the theft of encrypted password vaults.
Deezer data breach: Back in 2019, a third-party contractor was hacked and allowed a threat actor to collect the data of almost 230 million Deezer users. The company confirmed the hack in November, weeks after a threat actor began selling the old data. The data has now leaked and was indexed on Have I Been Pwned.
Five Guys breach: US fast food restaurant chain Five Guys has disclosed a data breach that took place in September 2022. The company, which runs more than 1,700 locations across the US, said the incident "involved unauthorized access to files on a file server." A class-action lawsuit is being prepared—because, of course it is.
General tech and privacy
Meta fined in the EU: EU officials have fined Meta a total of €390 million (€210 million for Facebook and €180 million for Instagram) after the company was found to have bypassed GDPR through clauses in its terms of service and used its EU users' personal data for targeted advertising without their explicit consent. EU officials have also given Meta three months to become GDPR compliant.
Google spam call warning: Google has announced that its Google Voice service will be adding a "suspected spam caller" warning to calls the company's service believes are automated spam.
Twitter advertising: Twitter has lifted its ban on political advertising—because the site wasn't a trash heap of propaganda, and we all needed more misleading tweets about that garbage in our life.
Firefox browser detection: Mozilla will change the Firefox user-agent string to avoid situations where the browser is accidentally detected as Internet Explorer 11 and blocked from loading certain websites.
Russia's Android clone: Major Russian companies like VK, Yandex, Sberbank, and Rostelecom are reportedly planning to create their own mobile operating system to be used inside the country. According to Kommersant, the new OS will be based on the Android open-source project, will be used for devices in the Russian consumer market, and will be different from Rostelecom's Aurora OS, which will target Russia's enterprise and government sectors.
Government, politics, and policy
Ukraine dismantles another bot farm: Ukraine's Cyber Police said it dismantled another Russian bot farm operating inside its borders. The group operated out of 13 locations using more than 100,000 SIM cards and 1.5 million online accounts to spew Russian propaganda inside Ukraine and abroad. The crackdown marked the seventh time in 2022 that Ukrainian officials have gone after Russian bot farms operating inside Ukraine, after similar operations in February (18,000 bots), March (100,000 bots across five bot farms), August (1,000,000 bots), September (7,000 bots), and October (50,000 bots), twice (10,000).
Poland warning: The Polish government has warned of impending cyber-attacks carried out by Russian hackers because of the country's active support of Ukraine.
Propaganda pact: Files hacked and leaked from the VGTRK Russian state broadcaster show that Russian and Chinese government officials and media executives have signed bilateral agreements to pick up each others' fake news coverage and narratives in order to boost their anti-western propaganda. [See coverage in The Intercept]
US court ruling on ransomware and insurance: The Ohio Supreme Court has ruled that classic insurance policies do not cover cyber-security incidents such as ransomware attacks for which dedicated cyber-insurance policies should be used. The court ruled that only "direct physical loss" or "direct physical damage" are covered by classic insurance policies.
Sponsor section
Risky Business podcast host Patrick Gray recorded this video with Okta, which shows users how to enable phishing-resistant authentication. It also goes into how enabling phishing-resistant auth for some users can benefit the whole org, even if it's not turned on everywhere.
Cybercrime and threat intel
RedZei: William Thomas has discovered a new threat actor. He named the group RedZei, which he said engages in scam calls from Chinese-speaking fraudsters targeting Chinese international students at universities in the UK.
Data leak site on I2P: The BianLian group has become the first ransomware gang to establish a data leak portal on the I2P network.
BitRAT campaign: Qualys has an analysis of a malspam campaign distributing the BitRAT malware.
Pupy RAT campaign: K7 researchers have broken down a malware distribution campaign that deployed the Pupy RAT via Windows Error Reporting, a legitimate tool found on all Windows installations.
MBR locker campaign: An MBR locker campaign is hitting Chinese users. The malware is currently being distributed via local free software download sites.
New npm malware: Twenty new malicious npm packages were recently discovered on the official npm portal. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for details.
CISA KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with two new vulnerabilities that are being exploited in the wild. Both are vulnerabilities in the JasperReports library that were disclosed and patched in 2018 (CVE-2018-5430 and CVE-2018-18809) but have recently come under attack.
Ransomware stats: Emsisoft has published its 2022 yearly stats for ransomware incidents.
- 105 local governments
- 44 universities and colleges
- 45 school districts operating 1,981 schools
- 25 healthcare providers operating 290 hospitals
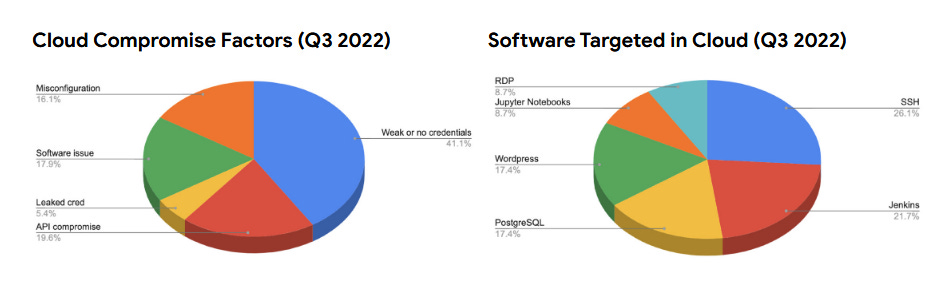
Google Cloud threat analysis: In its quarterly threat report [PDF], Google Cloud said that threat actors had diversified their methods of breaching customer accounts, with API compromise accounting for a large subset of intrusions in Q3 2022 (20%), with the method being rarely used before this quarter. The use of weak or no credentials to protect accounts remained the top way of entry in most intrusions (41% in Q3, down from 57% in Q2).
Malware technical reports
New WordPress backdoor: Dr.Web researchers have found a new exploit tool designed to attack WordPress sites, infect them with a backdoor, and then inject malicious scripts in their codebase. The malware targets vulnerabilities in more than 30 WordPress themes and plugins and exclusively targets Linux-based servers.
OrBit dropper: Stormshield researchers have a technical analysis of the OrBit Linux malware, first spotted last year by Intezer.
Hornet ransomware: Rixed Labs researchers have published a technical analysis of the Hornet ransomware.
CatB ransomware: On the same note, Minerva Labs has a similar report on the new CatB ransomware, which they found to be using a two-year-old DLL hijacking technique to evade detection and a ransom note cobbled up with parts from other ransomware families.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Confucious APT: NSFocus researchers have analyzed recent operations of the Indian-based Confucious APT that have targeted the armed forces in the Multan area of Pakistan.
Transparent Tribe: Qihoo 360 researchers have a report on the recent operations of the Pakistani APT Transparent Tribe and its recent use of a new remote access trojan (RAT).
"A simple RAT was used in this attack, including screen monitoring, keyboard monitoring, and network transmission functions. We suspect that it is an undiscovered component in the operation."
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
Android security updates: ...for January 2023 are out!
Breaking 2048-bit RSA: In a recently published study, a team of Chinese academics claims that quantum computers currently available on the market are theoretically capable of breaking the 2048-bit RSA encryption algorithm. As Bruce Schneier points out, the paper has not been proven in practice just yet.
Mastodon DDoS protection: Apparently, it's quite trivial to determine the real IP address of a Mastodon server, even if it's behind Cloudflare's proxy network. Cool, let the DDoS attacks begin, then.
API vulnerabilities in carmakers' infrastructure: A team of security researchers has found a bevy of vulnerabilities in the API infrastructure of several carmakers, including big names such as Mercedes-Benz, Ford, Porsche, Honda, Nissan, Kia, Hyundai, BMW, Land Rover, Rolls Royce, Jaguar, Ferrari, Toyota, and others. Some of the vulnerabilities could lead to full account and vehicle takeover and remote code execution.
Google Home smart speaker vulnerability: Bug hunter Matt Kunze has published details on a vulnerability that could be used to access the microphone of Google Home smart speakers over the internet and turn them into remote listening devices (among other things). Google awarded the researcher $107,500 as a bug bounty for his report.
ENLBufferPwn: Spanish software developer has discovered a vulnerability in the firmware of Nintendo consoles such as 3DS, Wii U, and Switch. Named ENLBufferPwn (CVE-2022-47949), the vulnerability "allows remote code execution in a victim console by just having an online game session with an attacker." Apparently, Nintendo has refused to acknowledge the issue (no surprise here) and did not release security patches.
Infosec industry
Twitter whistleblower update: Former Twitter security chief Peiter Zatko has joined cybersecurity firm Rapid7 as a consultant.
New tool—dnstwist: Belgian security researcher Niels Hofmans has open-sourced dnstwist, an online tool that can scan for lookalike and IDN domains that could be abused for phishing attacks.




