Risky Biz News: Russia arrests Cryptex founder a week after US sanctions
In other news: DPRK IT workers found at more than a dozen crypto companies; US disrupts Star Blizzard APT; Russian internet trolls try to blame Ukraine for their own disinfo op.

This newsletter is brought to you by Zero Networks. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Russian authorities have arrested 96 individuals linked to the Cryptex cryptocurrency exchange, the UAPS anonymous money transfer system, and 33 other illegal payment systems.
The arrests took place following house searches at 148 locations across 14 Russian regions in what Russian media has called one of the country's largest crackdowns against cybercrime and cryptocurrency gangs.
According to Russian news agency Interfax, one of the detained suspects was identified as Sergey Ivanov, the administrator of Cryptex and UAPS.
Ivanov's arrest comes a week after US authorities charged and sanctioned him for running the same platforms and facilitating a large-scale money laundering business for cybercrime operations.
US officials claimed Ivanov's services were involved in laundering $1.15 billion in criminal proceeds, including for carding groups and ransomware operations.
Russian authorities said they seized more than 15 billion rubles (~$15 million) following the house searches. They also seized a small-sized Robinson helicopter, boats, snowmobiles, and a bunch of expensive Porsche, Bentley, and Rolls Royce cars.
Authorities did not say if they received any information from their US counterparts. Based on the ice-cold relations between the two countries, we doubt they will ever admit to acting on a tip from US officials.
According to Ivanov's indictment last week, he'd operated undisturbed for more than 11 years without being bothered by Russian authorities.
The detained suspects were charged in Russia with participating in a criminal organization, unauthorized access to computer systems, and running an unlicensed banking operation. They face up to 20 years behind bars.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
UK Post drops Moneygram after cyberattack: The UK Post Office has dropped MoneyGram as a money transfer option after the company suffered a major security breach last week. The two companies were in talks for a contract extension when the cyberattack interrupted the negotiations. The Post Office has now removed MoneyGram from more than 11,500 of its branches. [Additional coverage in Payment Expert]
State actor suspected behind Dutch police hack: Dutch intelligence services believe that a state-sponsored group was behind the recent hack of the Dutch national police. Officials disclosed last week that hackers stole the work details of more than 65,000 Dutch police officers. This included names, roles, and work telephone numbers but no personal data.
Red Barrels breach: A cyberattack has crippled the activity of French gaming studio Red Barrels. The company says it has now contained the attack. Red Barrels says the incident will have a "significant" impact on its production timeline and may lead to delays in future games. Red Barrels is primarily known for its horror game series Outlast.

General tech and privacy
BSI endorses passkeys: Germany's cybersecurity agency recommended that users adopt passkeys as an upgrade for account passwords.
I-XRAY glasses: A Harvard academic has modified a pair of Meta Ray Ban 2 smart glasses to include automatic face recognition features for people coming into a wearer's view. [Additional coverage in New Atlas]
PayPal TOS update: PayPal is updating its ToS to grant itself the right to share user data with merchants starting in November. How American privacy tech of them! [See how you can opt out via TechRadar]
Google pilot fraud protection program: Google is launching a limited fraud protection pilot program in India.
Firefox 131: Mozilla has released Firefox 131. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest features in this release include the ability to set temporary permissions and support for tab previews (here's how to disable that garbage because it can be annoying af).
uBOL drama: Raymond Hill has removed the uBlock Origin Lite add-on blocker from the Mozilla Add-on Store after the platform incorrectly detected malicious code in the plugin and refused to ship an update to users. Hill said he removed the plugin because he did not have time for this "nonsense."
Thunderbird donations: Mozilla says over 300,000 users donated $8.6 million to the Thunderbird email client last year.
Government, politics, and policy
Welfare fraud bill: Privacy rights groups have urged the current Labour UK government not to resurrect an old Conservative plan to use algorithms to scan the bank accounts of people on welfare programs. [Additional coverage in The Guardian]
CRI guidance: The Counter Ransomware Initiative has released official guidance this week to help victims deal with ransomware attacks. The guide urges victims to report incidents to authorities instead of rushing to pay ransoms and keeping breaches hidden. It also recommends that companies consult with law enforcement or insurance experts before paying a ransom, as there might be other avenues for recovering encrypted or stolen data.
Schools cybersecurity guide: The Federal Communications Commission and the Department of Education, with input from the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, released a guide to help schools and libraries evaluate their cybersecurity risks and identify the most impactful cybersecurity solutions.
ICE signs contract with known spyware maker: The US Immigration and Customs Enforcement has signed a one-year contract with Paragon, a known Israeli spyware maker. [Additional coverage in WIRED]
EU petitions YouTube, Snapchat, and TikTok: The European Union has requested that YouTube, Snapchat, and TikTok share information on how their recommendation algorithms work.
"YouTube and Snapchat are requested to provide detailed information on the parameters used by their algorithms to recommend content to users, as well as their role in amplifying certain systemic risks, including those related to the electoral process and civic discourse, users' mental well-being (e.g. addictive behaviour and content 'rabbit holes'), and the protection of minors. [...] TikTok has been requested to provide more information on the measures it adopted to avoid the manipulation of the service by malicious actors and to mitigate risks related to elections, pluralism of media, and civic discourse, which may be amplified by certain recommender systems."
South Korea criminalizes deepfake porn: South Korea has passed a bill that criminalizes the possession and watching of sexually explicit deepfake images and videos. The new law criminalizes new actions after the country previously banned the creation and distribution of deepfake porn. Now, Individuals who buy, store, or watch such content can be fined up to $22,000 and even face up to three years in prison. The bill passed last week and was sent for approval to the country's president. [Additional coverage in CBS]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Benny Lakunishok, CEO and co-founder of ZeroNetworks, about network microsegmentation, why it is important, how to do it, and what the NSA gets wrong about it.

Cybercrime and threat intel
DoorDash wage theft: The US government has charged two Texas men for stealing more than $1 million from DoorDash drivers. Officials claim Oluwatobi Otukelu and Evan Edwards called DoorDash support, impersonated the drivers and hijacked wages to their own accounts. At least 138 DoorDash drivers across six US states reported losses to the scheme over the past two years. DoorDash told 404 Media it reimbursed some of the affected workers. [Additional coverage in CourtWatch]
QR code phishing gang detained: Authorities in Nigeria and the Ivory Coast have arrested eight suspects on cybercrime and online fraud charges. The group allegedly posed as sellers on online advertising platforms where they used QR codes to send users to phishing sites mimicking legitimate payment portals. The group collected personal data and payment card details and often followed through with phone calls to scam the victims. Interpol says the group mainly targeted Swiss citizens and is believed to have stolen more than $1.4 million from their victims.

BEC scammer sentenced: A US judge has sentenced a dual Nigerian and UK national to seven years in prison for a series of BEC attacks across the US. Oludayo Kolawole John Adeagbo stole almost $2 million from a North Carolina university. His group also attempted to steal $3 million from government agencies, a college, and a construction firm in Texas. He was arrested in 2022 in the UK and sent to the US for trial.
Crypto-thief pleads guilty: An Indiana man has pleaded guilty to stealing more than $37 million worth of crypto assets. Evan Frederick Light admitted to hacking an investment holdings company in February 2022 and stealing the personal data of hundreds of customers. Officials say Light and an accomplice used the stolen data to steal crypto funds from over 600 of the company's customers.
SugarLocker case sent to court: Russian authorities are going through the prosecution of Aleksandr Ermakov for his involvement in the SugarLocker ransomware operation. Ermakov is scheduled for hearings in a Moscow court on October 8, next week. Ermakov was detained by Russian authorities earlier this year. He is also wanted by Australia for his role in the REvil ransomware gang and the attack on Australian medical insurance company MediBank.
Operation Kraken: Australia's Federal Police claims it deciphered the seed phrase of a cryptocurrency wallet owned by the administrator of Ghost, an encrypted phone platform used by criminal organizations. Officials say they've now seized $9.3 million worth of crypto assets previously owned by Ghost admin Jay Je Yoon Jung. The AFP has also announced the arrest of a suspected believed to have worked as a Ghost distributor.
North Korean IT workers, everywhere: More than a dozen blockchain companies have inadvertently hired undercover North Korean IT workers. According to a CoinDesk investigation, this includes well-established blockchain projects such as Injective, ZeroLend, Fantom, SushiSwap, Yearn Finance, and Cosmos Hub. The workers passed checks using fake IDs and fake job histories. Hiring North Korean workers is against the law in the US and other countries that sanction North Korea. It's also a bad idea and a major insider risk since North Korean hackers have constantly targeted crypto companies to steal funds.
DPRK IT worker alert: And since we're on the topic, following similar alerts in the US, it's now Germany's time to warn local companies about the dangers of inadvertently hiring remote North Korea IT workers.
Edge device mitigation guide: Australia's cybersecurity agency has published guidance on how to secure internet-facing 'edge' devices, such as firewalls, routers, virtual private network (VPN) gateways, internet of things (IoT) devices, and internet-facing servers.
MSSQL attacks: AhnLab researchers look at recent attacks against MSSQL database servers that dropped the CLR SqlShell web shell.
Election crypto-scammers: Netcraft researchers are reporting a surge in crypto-scams using the current US presidential election as a lure.
FIN7 nude generators: A famous cybercrime group known as FIN7 is using at least seven websites advertising AI nude generators as a lure to trick victims into infecting themselves with malware. According to security firm Silent Push, the gang is offering a free trial of the AI nude generator software that contains a version of the NetSupport RAT.
Telegram cybercrime assessment: Intel471 says that based on current evidence, cybercrime operations are likely to continue operating on Telegram going forward, most likely due to the platform's huge reach.
October 7 DDoS wave: DDoS mitigation company Radware warns that Israeli and other Western organizations might see a surge of DDoS attacks on October 7 on the one-year anniversary of the Hamas attack on Israel.
Record DDoS attacks: Cloudflare says it mitigated two huge DDoS attacks, one of 3.8 terabits per second (Tbps) and a second one of 2.14 billion packets per second (Bpps). The company says the two attacks were separate byt targeted the same customer.
CyberVolk: Rapid7 has published a profile on CyberVolk, a pro-Kremlin hacktivist group that shifted in June from DDoS attacks to launching ransomware attacks.
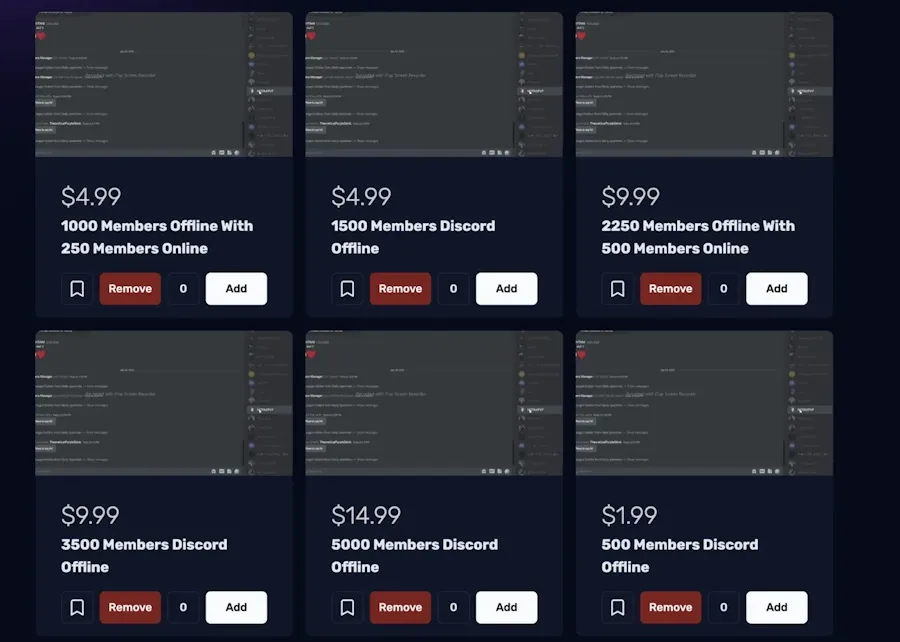
Members Hub: Socket Security has identified an underground community named Members Hub that provides Discord server boosting services to artificially inflate server metrics to paying customers.
Malware technical reports
AsyncRAT: Forcepoint researchers have published a report on a recent AsyncRAT distribution campaign abusing Cloudflare tunneling services.
Amnesia Stealer: ThreatMon has published a technical report about the new Amnesia Stealer MaaS.
StealC: LEXFO has published a three-part analysis of the StealC infostealer malware family.
UniShadowTrade: Group-IB has discovered a cluster of malicious Android and iOS apps available through the official app stores that were part of a large-scale fraud campaign. The malicious apps posed as known crypto and trading platforms, collected heaps of personal and financial data, and stole money users deposited in the apps' accounts. Group-IB named the new malware UniShadowTrade because all the apps were built using the UniApp framework.
Prince ransomware: Proofpoint has spotted a malspam campaign posing as British postal carrier Royal Mail to deliver a version of the Prince open-source ransomware.
Akira ransomware: Qualys has published common IOCs associated with the Akira ransomware gang.
BabyLockerKZ ransomware: Cisco Talos has published a profile on a threat actor using a version of the MedusaLocker ransomware known as BabyLockerKZ in attacks since at least late 2022.
Perfctl rootkit: AquaSec published an analysis of Perfctl, a Linux rootkit that has been used in attacks against the customer infrastructure of Chinese web hosting providers over the past year. AquaSec confirmed initial reports that the malware might be tied to a crypto-mining operation.
SkidMap: Dr.Web researchers have found a new version of the SkidMap backdoor that is currently being deployed on Redis database servers.
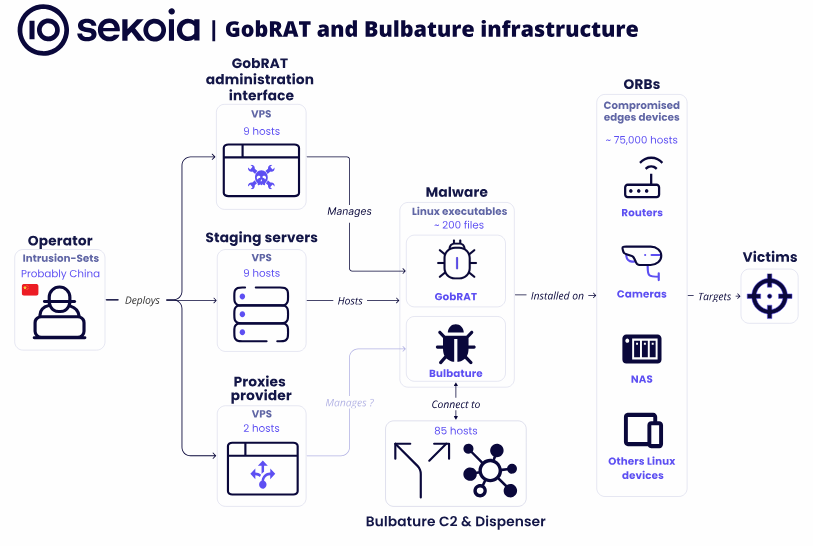
Bulbature+GobRAT: Sekoia has published a report on a new IoT botnet that is being used as a proxy system to relay and hide malicious cyber activity. The company says the botnet is currently involved in the distribution of malware such as Bulbature and GobRAT. Based on current evidence, the botnet appears to be managed by a Chinese operator.
Sponsor Section
Founded in 2019, Zero Networks is a unified zero-trust platform for network segmentation, identity segmentation, and secure remote access. Zero Networks' microsegmentation module is automated, agentless, and segments all network assets to stop lateral movement and block ransomware with a firewall and just-in-time MFA.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Stormkiller: Russian internet trolls are trying to blame Ukraine for a broad disinformation campaign that the US government has linked to Russia and a troll factory known as the Social Design Agency. Experts from the Alethea Group have discovered over 400 Twitter accounts (of course) that used manufactured comments from prominent counter-disinformation experts to blame Ukraine for SDA's work. Alethea says the comments were posted from "fresh" Twitter accounts that were previously involved in boosting cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
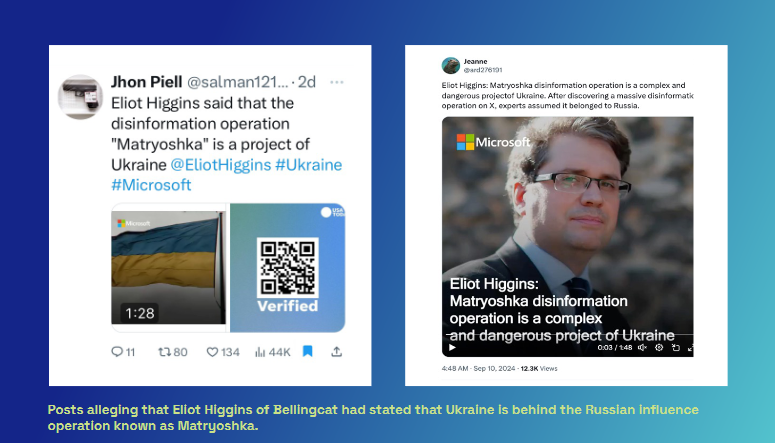
If you're wondering why I put "of course" in the paragraph above, here's a story looking at leaks from Russian troll factory SDA that explains why Russian disinfo ops love Twitter and idolize Musk.
"And the documents do reveal that efforts by social media companies to identify and remove disinformation work. Meta's vigilant internal intelligence teams and relentless takedowns blunted the project's overall reach: after Meta kept shutting down Doppelganger-associated accounts on Facebook and Instagram, the SDA appears to have dialed down its efforts to sow disinformation on Meta's platforms, although some abuse continues. An SDA project proposal disclosed by the FBI argued that X, formerly known as Twitter, had become 'the only mass platform that could currently be utilized' in the United States."
The same leaked SDA documents that are the base of the story above were also used for an article in The Conversation that looks at how Russia has adapted its classic propaganda techniques for the current modern-day social media environment.
US seizes Star Blizzard domains: The US government and Microsoft have seized more than 100 domains used by Russian cyber-espionage group Star Blizzard (ColdRiver) for its spear-phishing operations. The domains were used in phishing campaigns aimed at US government agencies, journalists, and over 30 civil society organizations. The US previously charged and sanctioned members of the group in December of last year. Officials linked the group to Russian intelligence agency FSB.
CeranaKeeper: ESET researchers discovered a new China-aligned threat actor named CeranaKeeper that has targeted governmental institutions in Thailand. The group appears to share tools with a larger Chinese APT group named Mustang Panda.
CharmingKitten: DomainTools has published a collection of IOCs linked to the CharmingKitten Iranian APT.
Stonefly: Symantec says it uncovered new Stonefly (Andariel, APT45, Silent Chollima, Onyx Sleet) attacks after some of the group's members were charged in the US in July for participating in ransomware attacks.
"Symantec, part of Broadcom, found evidence of intrusions against three different organizations in the U.S. in August of this year, a month after the indictment was published. While the attackers didn't succeed in deploying ransomware on the networks of any of the organizations affected, it is likely that the attacks were financially motivated. All the victims were private companies and involved in businesses with no obvious intelligence value."
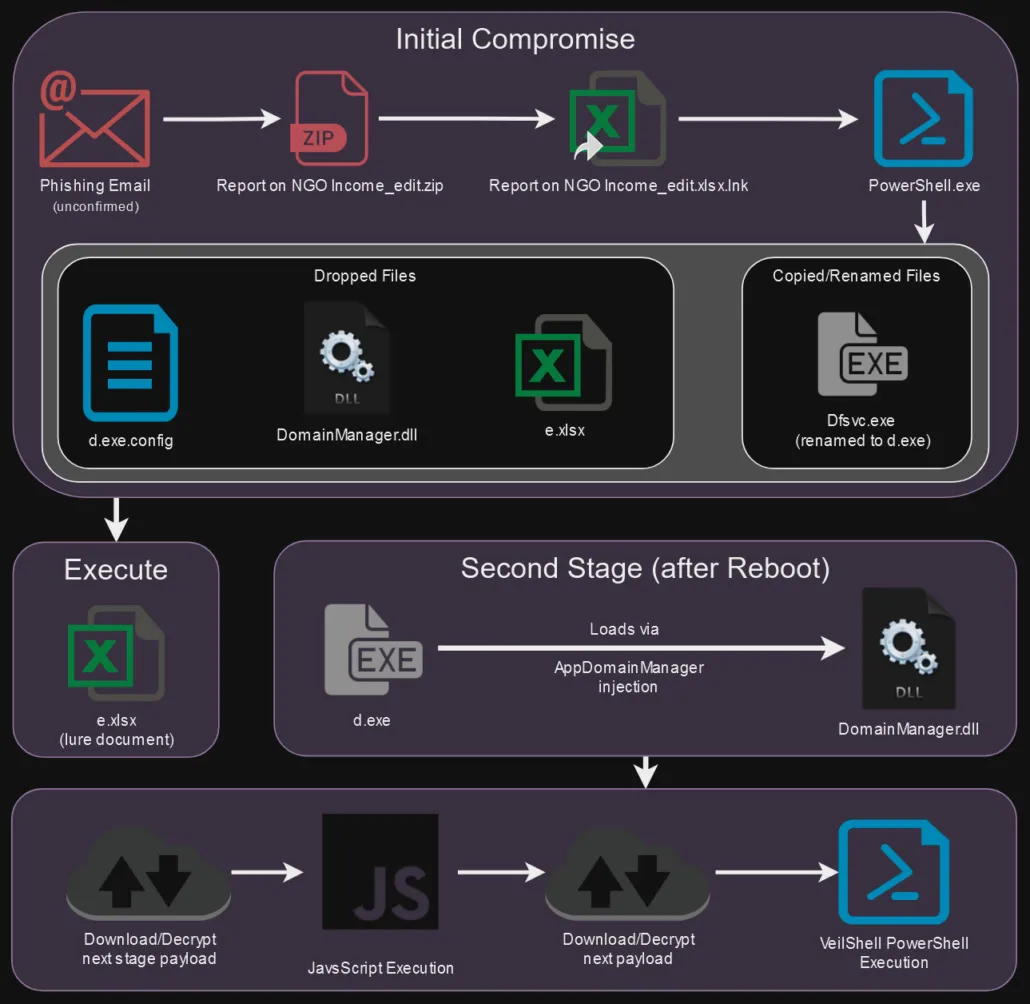
SHROUDED#SLEEP: Securonix researchers look at VeilShell, a new PowerShell backdoor used in attacks by a group the company tracks as SHROUDED#SLEEP (APT37, Reaper, Group123).
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Ivanti exploitation: Ivanti says threat actors are now exploiting a vulnerability in its Endpoint Manager (EPM) product. Tracked as CVE-2024-29824, the vulnerability is an SQL injection that allows attackers to take over EPM servers. The bug was initially patched back in May before attacks were first spotted this week. Proof of concept code has been available online since July.
Zimbra exploitation: Threat actors are exploiting a recently patched vulnerability to take over Zimbra email servers. The attacks started this week, four days after researchers published a write-up and proof of concept for the bug. Harfang Labs and Proofpoint detected the active exploitation, but they did not attribute the attacks to any known threat actor. The attacks use malicious code embedded in an email's CC field. The Zimbra team patched the bug (CVE-2024-45519) in a security update at the start of September.
New OData Injection Attack: Nokod Security CTO Amichai Shulman has published details on a new attack technique named OData Injection.
CUPS for DDoS attacks: Akamai researchers have discovered that the Common UNIX Printing System can be abused to launch large-scale DDoS attacks. An attacker can send a single packet to a CUPS server that will amplify and relay it to a desired target—in what researchers call an amplification and reflection DDoS attack. Akamai says that 58,000 of the almost 200,000 CUPS servers currently exposed on the internet can be exploited to relay DDoS attacks. Researchers say they discovered the new DDoS attack vector while analyzing the new CUPS vulnerabilities disclosed at the end of last week.
DrayTek vulnerabilities: Forescout researchers have found 14 vulnerabilities impacting a wide range of DrayTek routers. The most severe of these is a remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2024-41592) in the routers' web management panel that received a severity score of 10. The vulnerabilities impact 24 different DrayTek router models, and some are likely to see exploitation. More than 700,000 DrayTek routers are currently connected to the internet and are often the target of IoT botnets. DrayTek patched all reported issues at the end of August.
Jenkins security update: The Jenkins project has released a patch with fixes for the core platform and two of its plugins.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released 14 updates to fix several security issues. The most dangerous one is a 9.9 bug (CVE-2024-20432) in the REST API and web UI of Cisco Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller (NDFC).
Pixel security: Google has published a description of how it secured the cellular modem component of its Pixel smartphone.
Arc Browser VDP: The Arc web browser has launched a bug bounty program.
Infosec industry
New tool—Better Auth: Bereket Engida has released Better Auth, a comprehensive authentication library for TypeScript.
New tool—Segugio: Italian security researcher reecDeep has published Segugio, a tool to track the execution of malware payloads.
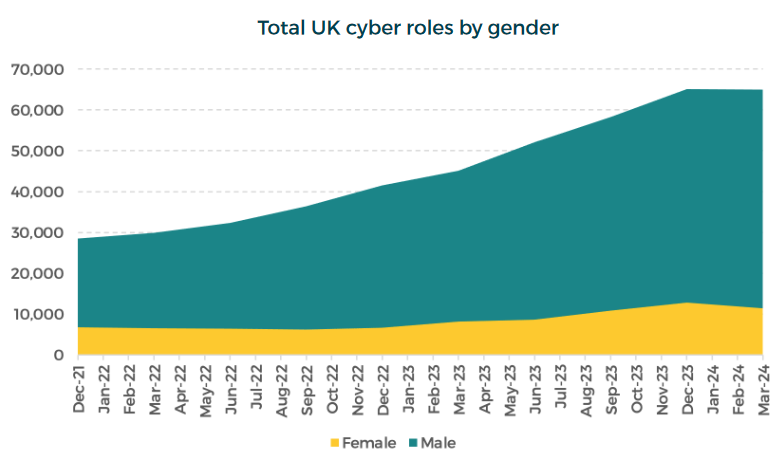
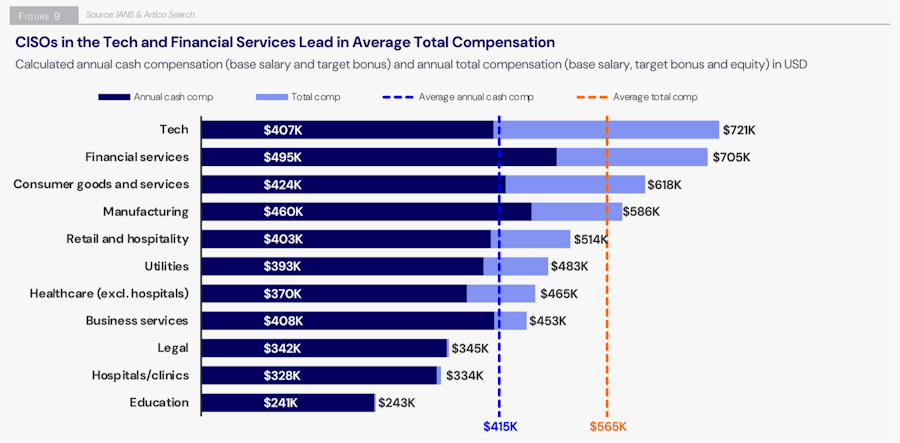
Threat/trend reports: Artico+IANS, Deloitte+NASCIO, Elastic, IBM X-Force, Red Canary, and Socura have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about various Southeast Asian countries investing in cyber forces, the drivers behind these decisions, and what kind of actions make sense.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Adam Boileau talk about how the US government's response to Iranian election interference is proceeding at light speed. This allows other actors, such as Meta, to make decisions relating to interference with certainty.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!






