Risky Biz News: Researchers propose new privacy.txt format
In other news: FTC fines US telcos $196 million for selling location data; Change Healthcare hacked via unprotected Citrix account; Vastaamo hacker sentenced to prison.

This newsletter is brought to you by Socket, a developer-first security platform that prevents vulnerable and malicious open-source dependencies from infiltrating software supply chains. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Academics, security, and privacy researchers have proposed a new standard for the management of privacy policies and consumer rights.
The new standard is named privacy.txt and was inspired by similar solutions like robots.txt, security.txt, and ads.txt.
Just like the aforementioned, it is designed to be hosted in a website's root (/) or "/.well-known" directory and provide instructions to both users and automated systems about a company's privacy policies and user data controls.
The standard's authors say they designed privacy.txt as more countries are adopting stricter consumer privacy regulations and as the IT sector is developing tools for allowing users to manage their personal data online.
For example, a tool designed to remove a user's data from internet sites will be able to scan a website for the privacy.txt file, and use information provided there to tell an online service to delete that user's data.
According to a draft of the proposed standard, a privacy.txt file will provide information such as:
- Corporate information about the website owner;
- URLs where a site's privacy policy is available, either in a simple UTF8 text or other formats;
- A contact email address;
- Emails or URLs where users can request that their personal data be deleted;
- Emails or URLs where users can request that their profile be deleted;
- Emails or URLs where users can opt out of having their data shared with third parties;
- Emails or URLs where users can request that their personal data be deleted;
- Emails or URLs where users can opt out of receiving marketing materials;
- Controls to configure cookie disclosure policies.
Researchers hope the new file format will make it easier for consumers to take privacy actions, similar to one-click unsubscribe features present in modern-day newsletters and email services.
Privacy.txt will be submitted to the IETF and follow the normal internet standard approval process in the hopes of receiving a formal RFC and gaining broader adoption.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
London Drugs hack: Pharmacy chain London Drugs has closed its stores across Western Canada in the aftermath of a cyberattack. The incident took place over the weekend and is suspected to be a ransomware attack. The company operates more than 80 stores, with the vast majority being on the West Coast. [Additional coverage in the CBC]
MovieBoxPro data breach: A threat actor has hacked and leaked the data of 6 million users of illegal streaming platform MovieBoxPro.
AlabugaLeaks: InfoNapalm has more details from a recent breach at Russian drone maker Albatross. The new article covers how some of the company's drones are running Kaspersky AI software.
defi SOLUTIONS plays down hack: Financial SaaS company defi SOLUTIONS has played down the impact of a recent ransomware attack. defi says hackers only accessed its legacy server infrastructure and did not steal any customer or employee data. The BianLian ransomware gang listed defi as one of its victims last week.
Change Healthcare hack: UnitedHealth CEO Andrew Witty says hackers breached the network of its Change Healthcare subsidiary using stolen credentials for the company's Citrix web portal. In a written testimony [PDF] to be delivered later this week at a Senate hearing, Witty says Change Healthcare failed to enable MFA on the hacked Citrix account. The UnitedHealth CEO didn't mention the exploitation of any Citrix vulnerabilities. He also took credit for deciding to pay the hacker's ransom demand. The decision backfired after the leaders of the AlphV ransomware group stole the $22 million for themselves. This led the AlphV affiliate who carried out the attack to continue the extortion against Change Healthcare, seeking a new payment. The hearing will take place on May 1 and will be live-streamed on YouTube via the URL embedded below.
General tech and privacy
FCC fines US telcos: The US Federal Communications Commission has fined the US' four largest wireless carriers for selling customer location data without consent. The FCC has fined T-Mobile $80 million and AT&T with $57 million. It also fined Verizon $47 million and Sprint with $12 million. The fines are related to a 2018 New York Times article on Securus Technologies, a company that sold location data to US law enforcement.
QTS anti-ransomware protection: QNAP has released the first version of its NAS operating system that features an anti-ransomware feature. The feature is included in the OS Security Center. It works by constantly monitoring file operations for unusual activity. Once a possible attack is detected, it will act to block and back up the user's data. QNAP devices have been the target of several ransomware strains over the years, such as AgeLocker, Qlocker, DeadBolt, eCh0raix, Muhstik, and QSnatch.
Microsoft Trusted Signing: Microsoft has rolled out its new Trusted Signing service into public preview. Trusted Signing is a code-signing and timestamping service designed for software developers.
MS-DOS source code: Microsoft has published the source code for MS-DOS v4.0. The source code for v1.25 and v2.0 has been available since 2018.
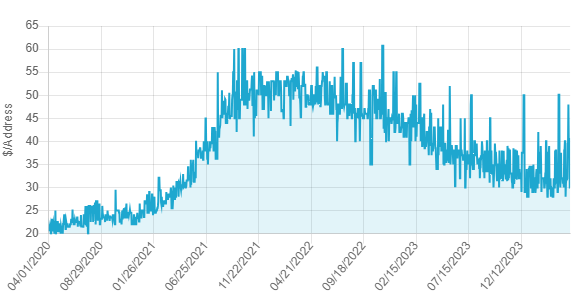
IPv4 prices go down: Prices for IPv4 addresses started to decline for the first time last year. Dutch internet registry SIDN says cloud providers appear to have played a major role in the IPv4 market slowdown. The organization says cloud companies secured IPv4 inventories in previous years and have exited the IPv4 market, causing demand and prices to go down. Other reasons also included the increase in IPv6 adoption (now at 45%) and the proliferation of better dual-stack technologies.
Government, politics, and policy
FTC expands breach notification rules to health apps: The US FTC has expanded its data breach reporting rules to cover the makers of healthcare apps. The updated rules will apply to fitness trackers, fertility apps, and similar technologies. App makers will have to notify regulators, consumers, and the public when they suffer a security breach or face similar fines to healthcare orgs. The new rules also apply to third-party service providers, which will have to notify healthcare orgs when their data is compromised. The new rules will go into effect 60 days after publication in the Federal Register.
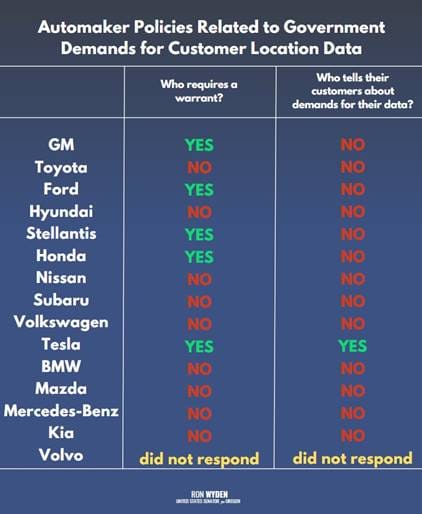
Senators ask for FTC investigation of auto industry: Two US senators have urged the FTC to investigate automakers for their failure to safeguard user consumer location data. Sen. Ron Wyden and Edward Markey claim that automakers lied to their customers on how they respond to law enforcement requests for their car's location data. The two claim that most automakers provide data to law enforcement without a warrant, and they don't notify customers of the request. Earlier this year, the same two senators also asked the FTC to investigate automakers for deceptive privacy policies and illegal sale of user data to third parties. [Read the full letter here/PDF]
Cybercom gear: US Cyber Command has begun the process of standardizing the gear used for its defensive cyber operations and hunt-forward missions. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
NIST on AI: NIST has published four draft standards on the responsible use of AI technology.
DHS AI guide: The DHS has published a guideline on the safe use of AI technologies by critical infrastructure operators.
Sextortion alert across the UK: The UK NCA has sent out a security alert [PDF] to schools and educational professionals about the rise in sextortion cases across the UK.
UK's rip-and-replace of Chinese security cameras: The UK government says it's on track to remove all Chinese-made security cameras from sensitive government sites by April next year. Officials say the vast majority of secure sites never deployed such equipment anyway. Half of the sites that did have already replaced the devices. The UK government's rip-and-replace plan is expected to reach 70% by October this year before full 100% coverage next year. [h/t Ravi Nayyar]
EU iPadOS investigation: The EU has started an investigation into Apple and the dominant position iPadOS holds in the mobile tablet market.
EU Meta investigation: The European Commission has opened an investigation into Meta over deceptive advertising and its handling of political content. EU officials are looking at Meta for failing to detect a pro-Russian propaganda network that ran ads on Facebook and Instagram for months. Non-profit research organization AI Forensics linked the campaign to Russian disinfo group Doppelganger. AI Forensics says the campaign reached a whopping 38 million users and that Meta flagged only 20% of the ads as political in nature.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to CEO and founder of Socket, Feross Aboukhadijeh about the open source software and supply chain security. Feross says the software ecosystem has evolved in ways that make it more vulnerable to trust-based attacks (such as seen in XZ Utils) and discusses what can be done to defend against this type of supply chain subversion.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Vastaamo hacker sentenced: A judge has sentenced Finnish hacker Aleksanteri Kivimäki to 6 years and 3 months in prison. Kivimäki was found guilty of hacking the Vastaamo Psychotherapy Center, stealing medical records, and extorting the center and its patients. He leaked medical records on the dark web and sent ransom demands to 33,000 of the clinic's clients, asking for €200 from each. Kivimäki was detained in France last year while attempting to use a fake passport. His lawyer says they will appeal the sentence. The Vastaamo hack is considered one of the worst in the country's history due to the highly sensitive nature of the leaked information and the massive extortion campaign that followed. [Additional coverage in YLE]
UA pro-Kremlin arrests: Ukraine's SBU has detained two Ukrainians who created accounts on social media to spread pro-Kremlin propaganda. Some of the accounts impersonated Ukrainian government and military officials.
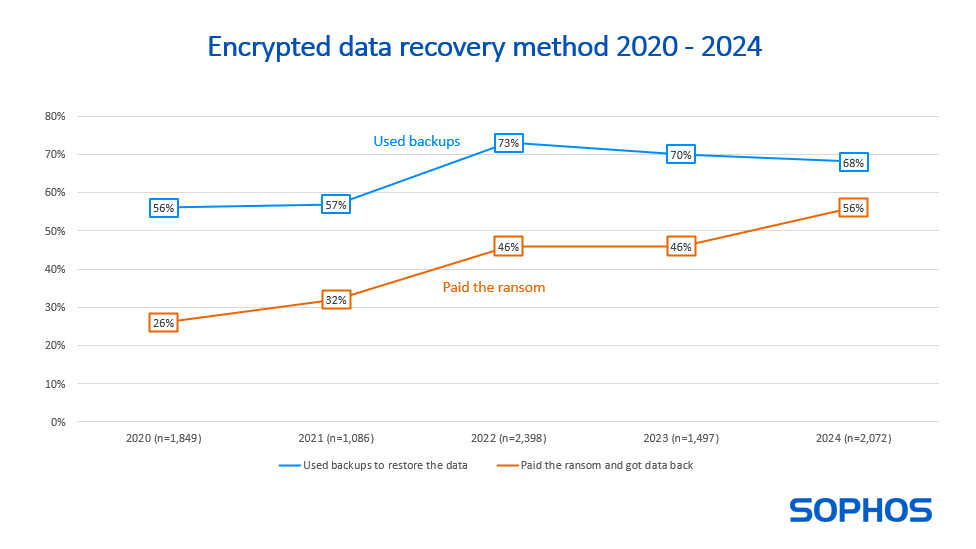
Threat/trend reports: Cloudflare, French privacy watchdog CNIL, Corvus Insurance, Kaspersky, and Sophos have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
DLL attacks: Security firm Logpoint has published a 22-page report [PDF] on how threat actors have been using DLL files for attacks. It also covers a DLL side-loading vector in KeyScrambler, an app for real-time keystroke encryption.
Google Play Store threats: Google says it blocked 2.28 million malicious apps from being uploaded to the official Play Store last year. The company also banned 333,000 Play Store developer accounts for malware and other policy violations. Google says it also detected more than 5 million malicious Android apps that were hosted outside the Play Store. The apps were detected through a new feature of the Google Play service added last year that scans user devices and warns them off malicious non-Play apps.
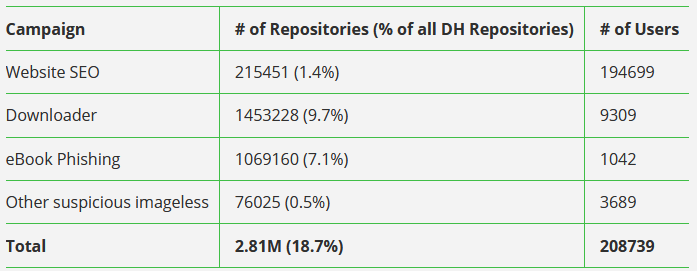
Docker Hub abuse: Nearly 20% of all Docker Hub repositories hosted malware or malicious content, according to DevSecOps company JFrog. The percentage accounts for nearly 3 million Docker images out of the total 15 million hosted on the platform. JFrog says that most of the malicious repositories did not even contain functional Docker images. They hosted metadata or resources for malware operations taking place outside the Docker Hub ecosystem, such as spam or black-hat SEO campaigns.
Malware technical reports
Dagon Locker ransomware: The DFIR Report team has published a report on an IcedID infection that led to a ransomware attack with the old Dagon Locker strain. This whole thing took 29 days, so there were lots of missed detection opportunities.
Cuckoo: Kandji researchers have found a new macOS malware. Named Cuckoo, the malware contains typical spyware and infostealer features.
DarkGate: McAfee has published a technical write-up of the DarkGate MaaS.
Zloader: Zscaler has published a report on Zloader's latest anti-analysis features.
"The latest version, 2.4.1.0, introduces a feature to prevent execution on machines that differ from the original infection. A similar anti-analysis feature was present in the leaked ZeuS 2.X source code, but implemented differently."
XZ backdoor: Chinese security firm Knownsec 404 has published an analysis of the XZ incident and backdoor.
COSMU: OALABS has published an analysis of COSMU, a USB worm that has been spreading around the internet for over a decade.
Wpeeper: QiAnXin has discovered a new backdoor named Wpeeper targeting Android devices. Researchers say activity from the malware C&C stopped four days after they discovered it.
"The encryption, signature verification, C2 Redirectors, and other mechanisms employed by Wpeeper all reflect the creators' professional proficiency. Even its current mysterious "silence" could likely be part of their attack strategy, aiming to enter the AI learning sample set of antivirus software as a trusted entity. Once Wpeeper’s characteristics are learned by AI as normal behavior, such threats could remain hidden for longer."
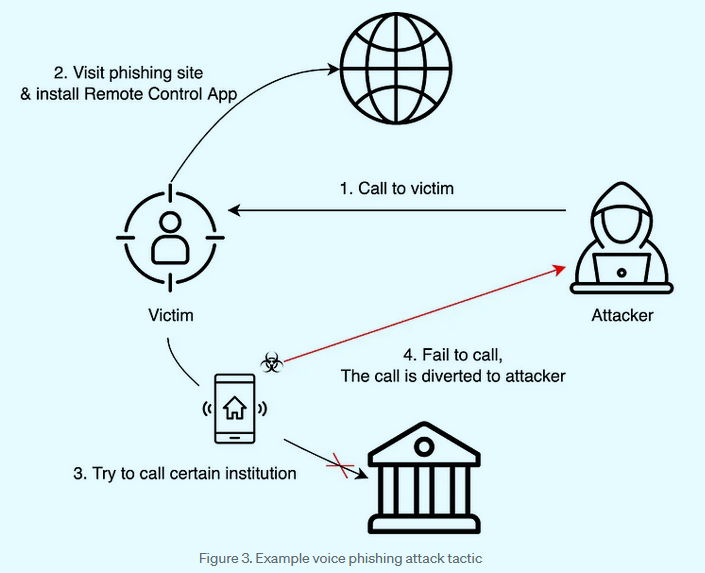
SecretCalls: A threat actor known as SecretCrow is conducting vishing operations targeting South Korean users. The group is luring users to installing malicious Android apps on their devices that are infected with a new malware strain named SecretCalls. According to South Korean security firm S2W Talon, the malware is designed to intercept calls to financial institutions and divert payments to the attacker's accounts. The group has been active since last year and some of its apps were available through the official Play Store. [See part 1 and part 2 of the research for more]
Sponsor Section
This podcast episode is brought to you by Socket Security. Socket makes a security platform for developers that protects their software from vulnerable and malicious open-source dependencies. Find them at Socket.dev.
The `xz` package backdoor is just the tip of the iceberg.
— Feross (@feross) March 30, 2024
There's a CONSTANT low-level stream of malware and spyware being uploaded to npm, PyPI, and Go registries.
I want to share a few examples from the 20,000+ malicious packages we detected so far: pic.twitter.com/f0FqCeUPqC
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Muddling Meerkat: A suspected Chinese state-sponsored threat actor named Muddling Meerkat is using China's Great Firewall technology to hide a years-long operation. Security firm Infoblox says the group has been active since at least October 2019. The company says the group manipulates DNS queries in a novel way to perform passive reconnaissance of foreign networks for future attacks.
Lazarus money laundering: Blockchain investigator ZachXBT has published an analysis on how North Korean hackers laundered more than $200 million worth of crypto-assets from 25+ hacks between 2020 and 2023.
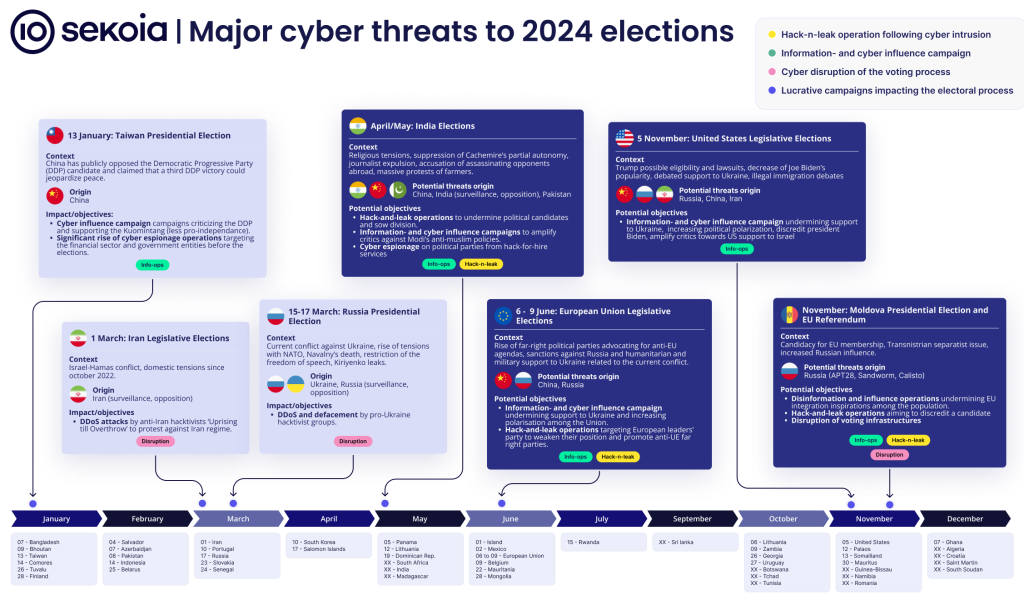
Election info-ops: French security firm Sekoia has published a 30-page report on the info-op and disinformation groups and threats for this year's huge election cycle.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Google Mobile VRP: Google says it awarded $100,000 to security researchers for 40 bug reports in the company's mobile apps last year. This year, the company increased some bounty payouts, some by 10 times.
Vanguard bug bounty: Riot Games, the company behind Valorant and League of Legends, is offering up to $100,000 for bug reports in its Vanguard anti-cheat system. [Additional coverage in Kotaku]
Judge0 vulnerabilities: Tanto researchers have found sandbox escape and code execution vulnerabilities in the Judge0 open-source online code execution system. The vulnerabilities allow attackers to take over servers running the Judge0 app.
Horacius vulnerability: Brazilian security firm Pride Security has discovered an unauth privilege escalation (CVE-2024-29417) in e-Trust's Horacius IAM platform.
R vulnerabilities: Researchers at HiddenLayer have discovered a vulnerability in the R programming languages used for statistical analysis and data visualization. The vulnerability (CVE-2024-27322) is a classic code execution attack through the deserialization of untrusted data. Many other programming languages are also vulnerable to the exact same attack, such as Java, Ruby, PHP, and .NET.
Infosec industry
New tool—AHHHZURE: Security firm JUMPSEC has open-sourced AHHHZURE, an automated deployment script that creates a vulnerable Azure cloud lab for offensive security practitioners.
New tool—ScrapeGraphAI: Software engineer Marco Vinciguerra has released ScrapeGraphAI, a Python library for scraping the web with the help of an LLM.
New tool—CloudInject: SpecterOps' Adam Chester has released CloudInject, a tool to inject a DLL into third-party AD connectors to harvest credentials. It currently supports AzureAD Connect, Octa AD Connector, and OneLogin AD Connector.
F1 sponsorship news: Security firms have been obsessed over the past years with sponsoring F1 teams. There's been some updates on this front lately. Keeper Security will sponsor Williams while Ferrari has signed with HP. Bitdefender, which has been sponsoring Ferrari since 2022, has remained a sponsor.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at the life cycle of zero-days, dissect the conventional wisdom, and talk about how zero-days are never truly "burnt."




