Risky Biz News: Recent Okta source code theft part of a larger incident
In other news: Smart home wall pad hacker detained in South Korea; The Guardian newspaper hit by ransomware; E2EE coming to enterprise Gmail.
This newsletter is brought to you by Airlock Digital, Proofpoint, runZero, and Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed.
The Risky Business team is still on its December holiday break, but we thought to put out this weekly edition with some of the past week's biggest infosec stories.
Happy holidays!
Breaches and hacks
The Guardian ransomware attack: Some parts of The Guardian's IT infrastructure went down this week, with the paper tentatively calling the incident a ransomware attack. The UK news org has told staff to work from home until it sorts things out. The incident appears to have impacted their entire data center network, per researchers.
Raydium cyber-heist: Solana-based DeFi platform Raydium was hacked for $5.5 million. According to CertiK, "the attack appears to be the result of a trojan attack & private key compromise."
Nio extortion: Chinese EV maker Nio said it was being blackmailed by hackers. According to Bloomberg, hackers are asking $2.25 million in Bitcoin from the company to not leak sensitive information they stole from the company in August 2021. Nio said this data contains "information of users and vehicle sales in China before August 2021."
Thyssenkrupp hacked again: German industrial engineering and steel production giant Thyssenkrupp has confirmed that it was the victim of a new cybersecurity breach. The company was previously the victim of several ransomware attacks, and even APT intrusions.
GitHub/Heroku/TravisCI security incident: Okta told customers that a threat actor gained access to its GitHub repositories and stole some of its source code. RiskyBizNews understands this incident is actually part of a larger set of GitHub account intrusions that took place earlier in December. At the time, threat actors used Heroku and TravisCI integrations to access GitHub accounts in an incident similar to one that happened earlier in the year, in April. GitHub has not returned a request for comment.
General tech and privacy
Client-side encryption for Gmail: Google is adding E2EE support for Gmail's web client. The feature is currently available for Google Workspace users via a beta program. Users allowed in the beta trial will be able to send and receive encrypted emails within and outside their email domain. It's unclear when this will become available for regular Gmail personal accounts.
IE update: Microsoft says that an Edge browser update that will be released on February 14, 2023, will permanently disable Internet Explorer 11 on Windows 10. Talk about the perfect Valentine's Day gift! Lovely!
Epic Games settlement: The US FTC has settled with Epic Games, and the gaming company has agreed to pay a $520 million fine in two lawsuits that accused the company of (1) breaching COPPA and collecting data on small children, (2) and employing dark patterns to trick customers into making unintentional purchases.
Mozilla to launch Mastodon instance: The Mozilla Foundation announced plans to launch its own Mastodon server instance next year in early 2023.
Mastodon job: Joyent and Mozilla technologist Mark Mayo wants to hire a developer for the next three months to improve the authentication mechanism used by the Mastodon open-source project.
Twitter dumb stuff: Right-wing QAnon-friendly social network Twitter (yeah, I said it) has removed the feature that lets you see the source of a tweet. Famous hardware hacker George Hotz has also quit the company after realizing he won't be able to improve the company's search feature, something he bragged about last month. Journalists who have been suspended last week have had accounts reinstated, however, they said they have not been granted access to their Twitter profiles, with the company imposing the condition that they deleted tweets commenting or correcting Musk. In addition, Musk's fake journalists have also published part 7 of the Twitter Files "revelations," where they claim the FBI was paying Twitter to censor content. Alex Stamos, the former Facebook CISO, has corrected their absolutely unprofessional and skewed reporting on the topic in this Mastodon thread. Also, over the weekend, Twitter banned links to any other social network (except the right-wing ones) and then changed their mind when they realized they could face some serious antitrust investigations. [We’ve removed an entry about Musk’s stalker from this section since we misunderstood the reporting. Apologies for the error!]
Government, politics, and policy
Memory safety: The US Congress will require the National Cyber Director to study the use of memory safety languages in the federal government, according to a provision included in the Financial Services and General Government Appropriations Act 2023 [PDF, page 19]. (via Jack Cable)
Medical device security: Furthermore, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023 [PDF, page 3537] also codifies the PATCH Act and will require that medical devices be kept up to date with security updates and more. (also via Jack Cable)
Chris Inglis resigns: Chris Inglis will resign as National Cyber Director in the coming months, per CNN. Inglis has served as National Cyber Director in the White House since July 2021.
FBI recommends ad blockers: In a PSA this week, the FBI recommended that users install an ad-blocker in their browser to avoid seeing malicious ads in search engine results (and many other places too).
FBI warns about BEC attacks on food industry: The FBI also issued another security advisory [PDF] last week, warning about BEC attacks on the food industry where criminal groups have redirected shipments of food and ingredients rather than redirecting and stealing a company's bank funds.
NCSC security advice: The UK National Cyber Security Centre has a security advisory with a bunch of basic advice for beginners. Some of it includes recommending that users open PDF files in browsers rather than PDF readers, disabling the option to open/mount ISO files on a system, and the use of email server gateways in corporate environments.
Sponsor section
Risky Business podcast host Patrick Gray recorded this video with Okta, which shows users how to enable phishing-resistant authentication. It also goes into how enabling phishing-resistant auth for some users can benefit the whole org, even if it's not turned on everywhere.
Cybercrime and threat intel
JFK hack: The US DOJ has charged two US nationals for working together with two Russian hackers to hack the taxi dispatch at the JFK airport in New York. US authorities said the group hacked the taxi queuing software and allegedly allowed drivers to cut the waiting line for a fee.
Smart home wall pad hacker: South Korean authorities have arrested a local IT professional who hacked a server that manages smart home wall pads for 638 buildings, recorded photos and videos of people in their homes, and then attempted to sell the footage online.
Ring doorbell hackers: California officials have charged two men for hacking Ring doorbell cameras across the US and then recording victims while they were getting swatted by police, swat calls they placed themselves.
T-Mobile hacker sentenced: Argishti Khudaverdyan, the owner of a T-Mobile retail who hacked into T-Mobile's main network as part of a larger phone-unlocking scheme, was sentenced last week to 10 years in prison.
SpyTrac spyware: TechCrunch has linked the SpyTrac Android spyware apps to two companies, one called AztecLabs and the other named Support King. What makes this entire article extremely interesting is that the FTC banned Support King from running surveillance apps last year, in September 2021. Also, on a related note, this repo with spyware IOCs might also be useful for some.
Pop-under campaign: Malwarebytes has a report out on a malvertising campaign that uses pop-under ads on adult websites to redirect visitors to fake news sites as part of an ad fraud scheme.
XLL campaigns: Cisco Talos researchers have a review of recent malspam campaigns that abuse Excel add-in (XLL) files to trick users into installing malware on their systems. This includes the whole gamut of groups, from financially-motivated boy bands like FIN7 and Dridex to cyber-espionage outfits like APT10, Donot, and TA410.
RisePro Stealer: Flashpoint says they linked several listings on the Russian Market portal dedicated to the sale of stolen credentials to a new infostealer named RisePro Stealer. According to the company, RisePro appears to be a clone of the more well-known Vidar stealer strain.
Glupteba returns: The Glupteba ad fraud trojan has returned to operations after being disrupted by Google last year and after the conclusion of a recent lawsuit between the two parties.
OWASSRF: Crowdstrike said they identified OWASSRF, a new method of exploiting the ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities. The company said it saw the technique being used in the wild to deploy the Play ransomware.
Kiss-a-Dog expansion: Cado Security has an update on the Kiss-a-Dog crypto-mining gang. Researchers say the group, which was known to target Docker and Kubernetes servers, is now also going after Redis databases.
MitM phishing: PAN's Unit42 team has a breakdown of meddler-in-the-middle (MitM) phishing campaigns that have taken place throughout 2022. This includes campaigns targeting users of platforms like GitHub, Dropbox, Microsoft, CircleCI, and others.
Malware technical reports
Raspberry Robin: Trend Micro has its own analysis of the Raspberry Robin USB worm that has been recently used to deploy ransomware on some enterprise networks. The report focuses on the malware's obfuscation, anti-sandboxing, and anti-security tools evasion techniques—including, I kid you not, dropping fake malware to confuse researchers about what they're analyzing.
SiestaGraph: Elastic's security team has a report out on SiestaGraph, a PowerShell-based backdoor that leverages the Microsoft Graph API for command and control. The malware was found installed on an Exchange server belonging to the Foreign Affairs Office of an ASEAN country.
Godfather Android banking trojan: Group-IB researchers have an analysis of Godfather, an Android banking trojan built on top of the old Anubis trojan. Godfather currently contains modules to target the customers of 215 banks, 94 crypto wallets, and 110 crypto exchange platforms. The trojan has been active since June 2021.
Trojanized WhatsApp app: Chinese security firm Zero Hour Technology says it linked several instances of trojanized WhatsApp clients available in China to thefts of personal funds from infected devices. Reported losses have been estimated at nearly $1.5 million.
New PyPI malware: Since our last newsletter, Phylum researchers have documented two waves of malicious packages published on the PyPI portal, one deploying the W4SP Stealer and the second deploying the Satan Stealer malware strains. ReversingLabs and Fortinet also have reports on other unrelated attack too. The Python Foundation really needs to get on top of its package repository because things are getting tiresome now. We're at a new "malware on PyPI" report every and each week now.
Royal ransomware: Trend Micro has formally linked the Royal ransomware operation to one of the smaller groups that have splintered off the Conti ransomware. The ransomware was also previously known as the Zeon ransomware.
🎁Gift for the community: Post-#Conti #ransomware operation mindmap world. Enjoy!
— Vitali Kremez (@VK_Intel) 1:58 PM ∙ Aug 9, 2022
Coffee ransomware decrypter: Researchers from Chinese security firm Sangfor have released a free decryption utility to recover files encrypted by the Coffee ransomware. A technical analysis of the ransomware and its encryption flaw can be found here. The Coffee ransomware appeared in February this year and spread mainly via Chinese internet sites and social networks.
Ransomware strains go Rust: The Agenda (Qilin) and the Nokoyawa ransomware strains have been ported to Rust, following in the footsteps of BlackCat, Hive, and RansomExx.
Zerobot: After a Fortinet report last week, Microsoft has also put out a report on the new Zerobot IoT DDoS botnet. The original report found that Zerobot was written in Go, and its operator(s) used exploits for n-day vulnerabilities to deploy the malware to various devices. Microsoft also found that Zerobot also used a combination of eight common usernames and 130 passwords for IoT devices over SSH and telnet on ports 23 and 2323 to spread to devices. In addition, the Zerobot gang also appears to have added new n-day exploits to their botnet too.
Guloader: OALABS has released IOCs for the Guloader malware. Get them while they're hot.
Ekipa RAT: Trustwave has looked at recent distribution campaigns spreading the Ekipa remote access trojan.
IcedID's BackConnect protocol: TeamCymryu published a report on BackConnect, a custom command-and-control (C2) protocol used by the IcedID botnet. The company said it identified 11 BackConnect servers since July 2022, that some operators are based in Moldova and Ukraine, and that some servers have been managed via SpaceX Starlink terminals, the first known case of Starlink being abused for malware and cybercrime operations.
APTs and cyber-espionage
APT28: Cyberscoop reported last week that CISA researchers found the Russian APT28 cyber-espionage group lurking in the network of a US satellite network.
North Korean APTs: Sekoia has a year-in-review report on the North Korean cyber-espionage campaigns that have been documented this year.
FateGrab/StealDeal malware: CERT-UA has a report out on a recent spear-phishing campaign that used a compromised Ministry of Defense account to target users of Delta, a platform used by Ukraine's military forces for coordinating attacks.
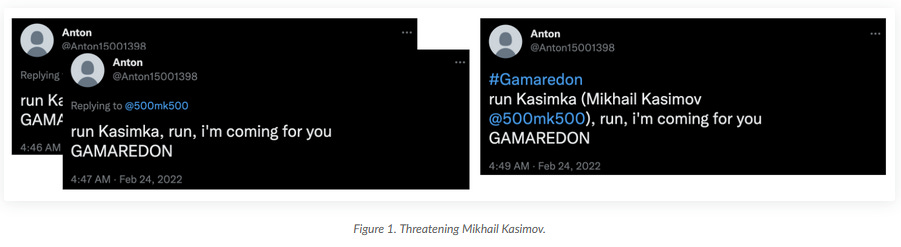
Gamaredon APT: PAN's Unit42 has a report out on recent operations of the Trident Ursa APT (aka Gamaredon, Armageddon). These operations have targeted Ukraine almost all year but have also included "an unsuccessful attempt to compromise a large petroleum refining company within a NATO member nation on August 30." However, the strangest part in the report is a series of threats made on Twitter by a Trident Ursa member against Mikhail Kasimov, a Ukrainian security researcher who has previously published Gamaredon IOCs and living in one of the Ukrainian war zones. Some of these tweets are still up.
Vulnerabilities and bug bounty
CVE-2021-38003: StarLabs has a breakdown of an old Chrome vulnerability tracked as CVE-2021-38003, patched last year after being exploited in the wild.
CVE-2022-41040 and CVE-2022-41082: Kaspersky has a report out on two Microsoft Exchange zero-days known as ProxyNotShell.
macOS Gatekeeper bypass: Microsoft has published a write-up on another macOS Gatekeeper bypass found by its MSTIC team. I don't know how I feel about Microsoft's security teams sifting through Apple's products when their Exchange servers keep getting ransomed left and right. Priorities, maybe.
MeshyJSON: NCC Group has a report on MeshyJSON, a stack overflow vulnerability in the tdpServer binary included with the firmware of TP-Link routers.
Infosec industry
Rust training: The Android Team has open-sourced its internal Rust training courses.
Trend Micro joins ADA: Trend Micro and McAfee will officially join the Google App Defense Alliance. Also known as ADA, this is a project through which Google gives security vendors access to the Play Store security systems so security firms can help it identify and remove Android malware faster. Previous members include the likes of ESET, Lookout, and Zimperium.




