Risky Biz News: Ransomware passed $1 billion mark in 2023
In other news: Volt Typhoon breached US government networks for five years; security researcher charged for hacking Apple; and Chinese PR firm behind large pro-Beijing disinfo network.

This newsletter is brought to you by Thinkst, the makers of the much-loved Thinkst Canary. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Ransomware gangs made out like bandits last year, collecting an estimated $1.1 billion worth of cryptocurrency via ransomware payments, according to blockchain tracking company Chainalysis.
The number is at an all-time high for ransomware operations and is almost double 2022's figure when experts saw only $567 million going to ransom payments.
The 2022 dip can be attributed to Russia's invasion of Ukraine, which disrupted relations in the cybercriminal underground as gangs shuffled members or some operations were "redirected/hijacked" towards hacktivism or cyber espionage.
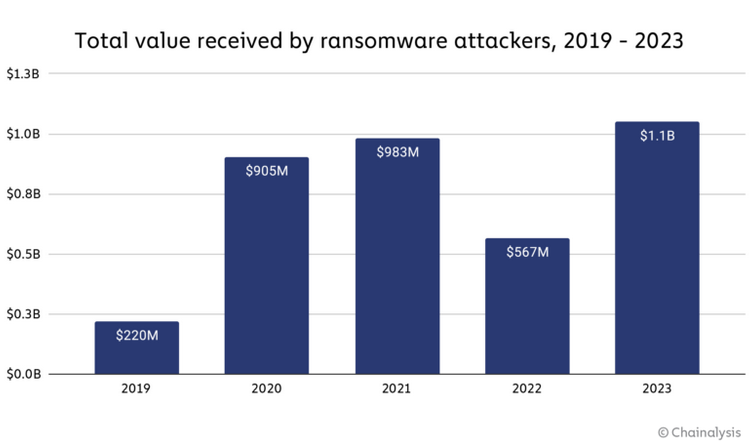
Chainalysis points out that payments from ransomware attacks also reached their all-time high despite several takedowns of gangs like AlphV, Hive, RagnarLocker, and Trigona.
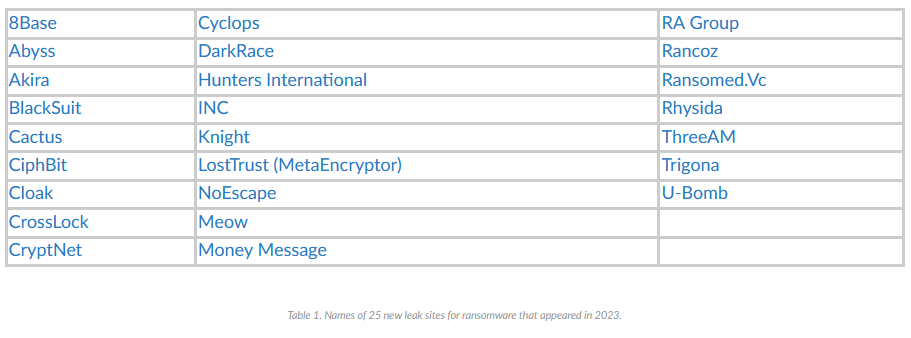
That's because even if four ransomware groups bit the dust last year, more than 25 groups also launched operations, as documented by Palo Alto Networks in this report.
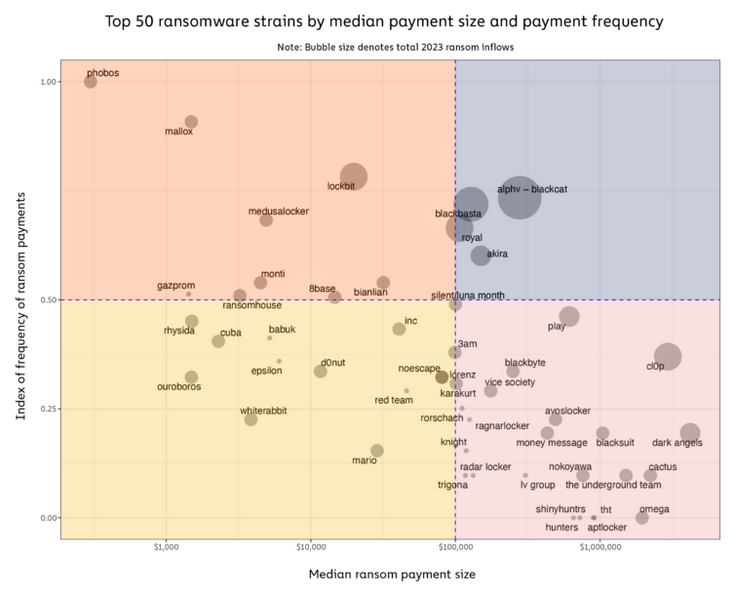
Another thing to take out from the Chainalysis report is that last year, large payments of over $1 million accounted for most of recorded ransom payments.
These large payments are usually made following targeted attacks against large organizations, in a tactic known as "big game hunting" or "human operated ransomware"—a name that comes from the fact that a human operator takes control of the malware behind a keyboard to make sure intrusions are not detected, and files are stolen and then encrypted correctly, for maximum damage (and profits).
Chainalysis notes that "big game hunting has become the dominant strategy" for ransomware operations over the past year, which is also what Microsoft saw as well in its Digital Defense Report last October.
As for who made the most money last year, Chainalysis says the AlphV, Black Basta, Royal, LockBit, and Clop were the most successful in extracting ransoms from their victims. These names are no surprise since most monthly ransomware activity reports put out by most cybersecurity firms always had these groups at the top of their charts in terms of hit victims.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Viamedis: Threat actors have breached Viamedis, a French company that provides payment solutions to 84 local hospitals. French privacy regulator CNIL says the attackers stole details on 33 million of the company's customers. Viamedis says it shut down its payment platform as soon as it learned of the intrusion and that no financial data was exposed.
Spoutible API leak: Microblogging platform Spoutible has fixed a leak in its API that was exploited to collect data on its users. The threat actors collected data such as email addresses, phone numbers, hashed passwords, and password reset tokens. The attacker is believed to have collected at least 207,000 user records, according to Troy Hunt, creator of the Have I Been Pwned database.
New Relic hack: New Relic has published an IR report from its November 2023 data breach.
AnyDesk hack: AnyDesk has posted a FAQ on its recent security breach.
GoAnywhere lawsuits: All the class-action lawsuits filed against software maker Fortra have been consolidated in a single federal court in Florida. The lawsuits are related to the ransomware attacks that targeted the company's GoAnywhere file transfer server. [Additional coverage in Bloomberg Law]
General tech and privacy
Patternz gets sued: Israeli ADINT seller Patternz has been sued in Israel by business development firm Improvate The Future. [Additional coverage in Intelligence Online]
Meta to label AI content: Social media company Meta says it will start labeling images and videos that have been generated using AI technologies. The new detection system will roll out to Meta sites such as Facebook, Instagram, and Threads in the coming months. Meta says it's working with AI companies like Google, Midjourney, and OpenAI to add invisible watermarks and metadata to AI-generated content.
OpenAI to label DALL-E images: Following Meta's announcement, OpenAI says it plans to add hidden metadata to images generated by its DALL-E 3 model in an effort to prevent abuse. The new metadata follows standards from the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA). The new metadata system is scheduled to roll out on February 12.
Denmark bans Google Workspace in schools: The Danish data protection agency has ordered schools to stop sending student data to Google. The agency has instructed schools to reconfigure Chromebooks and Google Workspace to adjust configurations and prevent data from being sent abroad. In July 2022, the same agency also banned local governments from using Chromebooks and Google Workspace for the same reasons.
Microsoft facial recognition: Microsoft announced that its Entra service now supports facial scanning. The feature is currently in preview.
Bluesky update: Micro-blogging platform BlueSky has exited its invite-only beta and is now free to sign up. The platform boasts more than 4 million users.
Disney+ cracks down on password sharing: Disney+ has updated its Terms of Service to ban password sharing with individuals outside a household. The new changes are set to enter into effect on March 14, first for North American users. Both Hulu and Netflix rolled out similar measures already. [Additional coverage in The Verge]
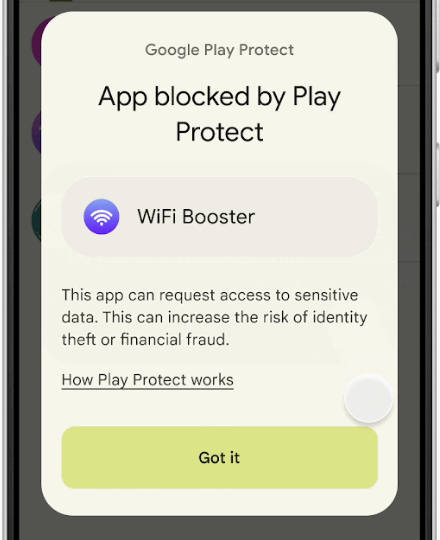
Google Play Protect pilot: Google is running a pilot test for its Play Protect security service that will scan sideloaded apps for permissions frequently abused for financial fraud. Play Protect will look for sideloaded apps that try to gain access to Accessibility features, notifications, and SMS capabilities. Google says that 95% of financial fraud apps are sideloaded, usually after being downloaded off the internet. The pilot program will run in Singapore for the coming weeks before a broader launch.
Government, politics, and policy
EU and Russia: EU officials fear a wave of cyberattacks after they freeze Russian assets as part of a plan to help Ukraine rebuild from Russia's invasion. [Additional coverage in Politico Europe]
CISA Protect 2024: CISA has launched this week Protect 2024, a new portal to help state and local officials protect election infrastructure.
DETECT Act: Two US senators have introduced new legislation directing NIST to develop cybersecurity guidelines for how the government's use of civilian drones. The DETECT Act will require drone contractors to disclose vulnerabilities in their products to the US government. The DETECT Act will also forbid agencies from using drones that do not meet the cybersecurity guidelines.
US water sector cybersecurity: The US Senate, CISA, and the EPA held events with the private sector on ways to improve the cybersecurity of the water and wastewater sector.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to Haroon Meer of Thinkst Canary. They discuss how network attackers win, how their tactics have changed over time, and what this means for network defenders.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Apple hacker charged: US authorities have arrested a security researcher for allegedly hacking and defrauding Apple. Noah Roskin-Frazee allegedly gained access to Apple backend systems and obtained access to $2.5 million worth of gift cards, which he later resold to third parties. The hack allegedly took place between December 2018 and March 2019. Authorities arrested Roskin-Frazee in January this year. Two weeks later, Apple thanked the researcher for two macOS bug reports. [Additional coverage in CourtWatch]
Crypto bot developer convicted: A jury has convicted a Philadelphia man for defrauding investors of the Hydro cryptocurrency. Officials say Shane Hampton worked with a South African company to develop a bot that placed more than $300 million in spoof trades. The fake transactions inflated Hydro's exchange prices and allowed Hampton and his co-conspirators to earn more than $1.5 million over seven months. Hampton is scheduled to be sentenced in April and faces up to 20 years in jail.
Djamix dox: Infosec researcher Brian Krebs has linked the identity of a very active Mazafaka hacking forum user named Djamix to a Russian national from Sochi named Aleksei Safronov, a member of the Spetsnaz GRU forces.
Hive reward: The US State Department is offering a $10 million reward for information on administrators of the Hive ransomware operation. Officials are also offering a $5 million reward for tips that may lead to the identification or arrest of Hive affiliates. The Hive gang ceased operations in January of 2023 when the FBI seized its servers and released a free decrypter for past victims.
LockBitSupp ban: LockBitSupp, the main individual behind the LockBit ransomware operation, has been banned on Exploit and XSS, two of the most prominent hacking forums for Russian-speaking cybercriminals.
DDoS attacks in Poland: Netscout says that DDoS attacks targeting Poland's infrastructure have increased after the country elected a pro-EU prime minister. Most attacks came from the we're-definitely-not-intelligence-agencies Russian hacktivist groups.
QR code fraud: The UK NCSC has published a short advisory on the rising threat of QR codes, advising British citizens to avoid installing third-party QR code scanners and use the built-in QR code scanner that ships with their devices.
Phishception: Netcraft has published a report that looks at a phishing campaign that abuses SendGrid's own services to target SendGrid customers.
Ransomware exploitation trends: Recorded Future has published a report looking at the exploitation trends and techniques commonly used by ransomware gangs between 2017 and 2023.
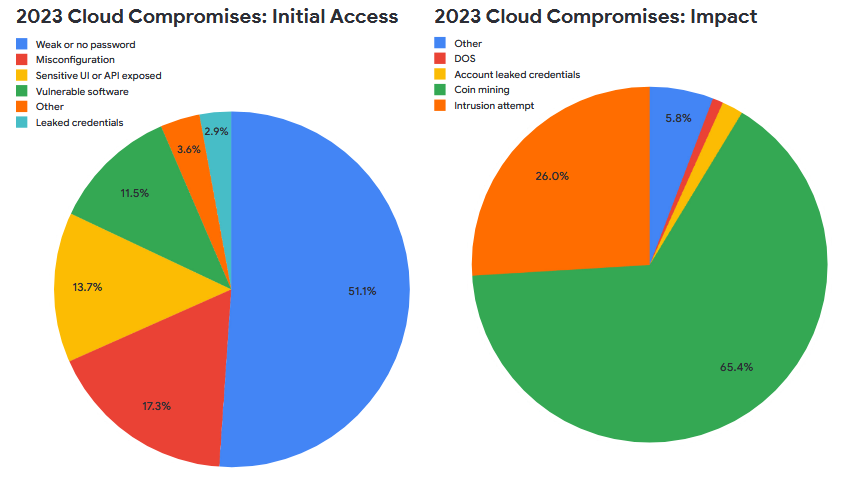
Google Cloud Threat Horizons Report #9: In the ninth edition of its threat and trends report [PDF], the Google Cloud security team reveals that weak or no passwords are still the main root cause for most intrusions into cloud environments. Coinmining remained the primary malicious activity observed across Google Cloud infrastructure.
Malware technical reports
Mythic Arachne: SpecterOps has published a technical report on Arachne, a new Mythic framework agent for creating and working with web shells.
RedLine Stealer: Security researcher Ayush Anand has published the second part of his analysis of the RedLine Stealer.
Zloader: New Zloader samples now come with improved support for 64-bit systems.
HijackLoader: CrowdStrike has published a report on HijackLoader (aka IDAT Loader), a malware loader first spotted in the wild last year by Zscaler and Alpine Security.
Coyote: Kaspersky researchers have discovered a new banking trojan named Coyote. The malware currently supports mounting attacks against 60 banking institutions, with most located in Brazil. Coyote is unique on the Brazilian banking trojan scene because it's built mainly with newer technologies such as Node.js and Nim, rather than the older Delphi programming language.
Raspberry Robin: The operators of the Raspberry Robin malware have incorporated several one-day exploits in recent attacks. Some exploits were added to the Raspberry Robin code before public proof-of-concept was published online. Security firm Check Point believes the gang is either buying exploits from an underground market or has a talented exploit developer in their ranks.

Sponsor Section
Most companies discover they've been breached way too late. Thinkst Canary fixes this: just 3 minutes of setup, no ongoing overhead, nearly 0 false positives, and you can detect attackers long before they dig in. Check out why our Hardware, VM, and Cloud-based Canaries are deployed and loved on all 7 continents.

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
PAPERWALL: CitizenLab has discovered a network of 123 websites spreading pro-Beijing disinformation. The websites are operated from within China but pose as local news outlets in 30 countries across Europe, Asia, and Latin America. Dubbed PAPERWALL, the network disseminates pro-Beijing disinformation and ad hominem attacks hidden in a stream of commercial press releases. CitizenLab says the sites are managed by a Chinese PR firm named Shenzhen Haimaiyunxiang Media. In November of last year, South Korean spy agency NIS also linked the same PR firm to a network of 38 sites posing as Korean news agencies.
"While the campaign's websites enjoyed negligible exposure to date, there is a heightened risk of inadvertent amplification by the local media and target audiences, as a result of the quick multiplication of these websites and their adaptiveness to local languages and content."
Volt Typhoon past activity: Chinese cyber-espionage group Volt Typhoon has breached and maintained access to US government networks for at least five years. CISA, the FBI [PDF], and the NSA say the group's actions and choice of targets suggest this is not traditional cyber espionage. Officials believe the group is prepositioning to execute destructive cyberattacks against critical infrastructure in the case of a potential military conflict with the US. Officials didn't name any of the supposedly compromised US government networks.
Volt Typhoon LotL advisories: On the heels of the aforementioned warnings, officials from the Five Eyes intelligence alliance have published a joint advisory [PDF] on Volt Typhoon's usage of Living of the Land (LotL, LOLBin) techniques to avoid detection.
Volt Typhoon reward: The US State Department Rewards for Justice program is offering a $10 million reward for information on members of the Volt Typhoon APT group.
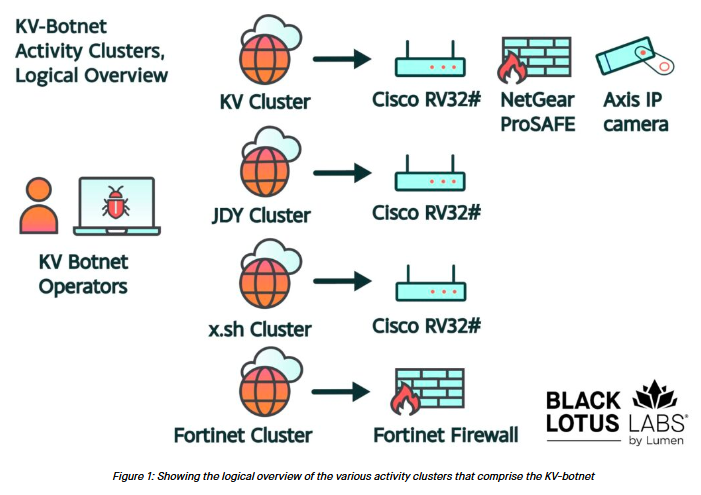
Volt Typhoon's KV botnet: Chinese APT group Volt Typhoon has been struggling to rebuild a botnet named KV that US authorities took down last month, according to Lumen's Black Lotus Labs.
"We assess that KV-botnet has encountered significant resistance over the past several weeks. We believe that the main arm of the botnet, the KV cluster, has been rendered inert due to the action of U.S. law enforcement. We assess that the Fortinet activity had dissipated sometime in August of 2023. The JDY cluster has lost over half of its bots in the past month, but still remains operational. Finally, the signal associated with the x.sh cluster has been lost, likely due to public exposure."
Zardoor: Cisco Talos has discovered a new backdoor named Zardoor. The company says the malware was used in a cyber espionage campaign that appears to have started in March 2021. Talos says the malware was used in a cyber-espionage operation targeting an Islamic charitable non-profit organization in Saudi Arabia. The campaign appears to have been active since March 2021. Talos researchers didn't attribute the backdoor to any group or state.
Roaming Mantis: McAfee has published a report on MoqHao (or XLoader), an Android malware strain used by the Roaming Mantis APT, typically deployed via SMS phishing.
Kimsuky's Troll Stealer: South Korean security firm S2W Talon has found and analyzed a sample of Troll Stealer, an infostealer used by the Kimsuky APT in recent operations.
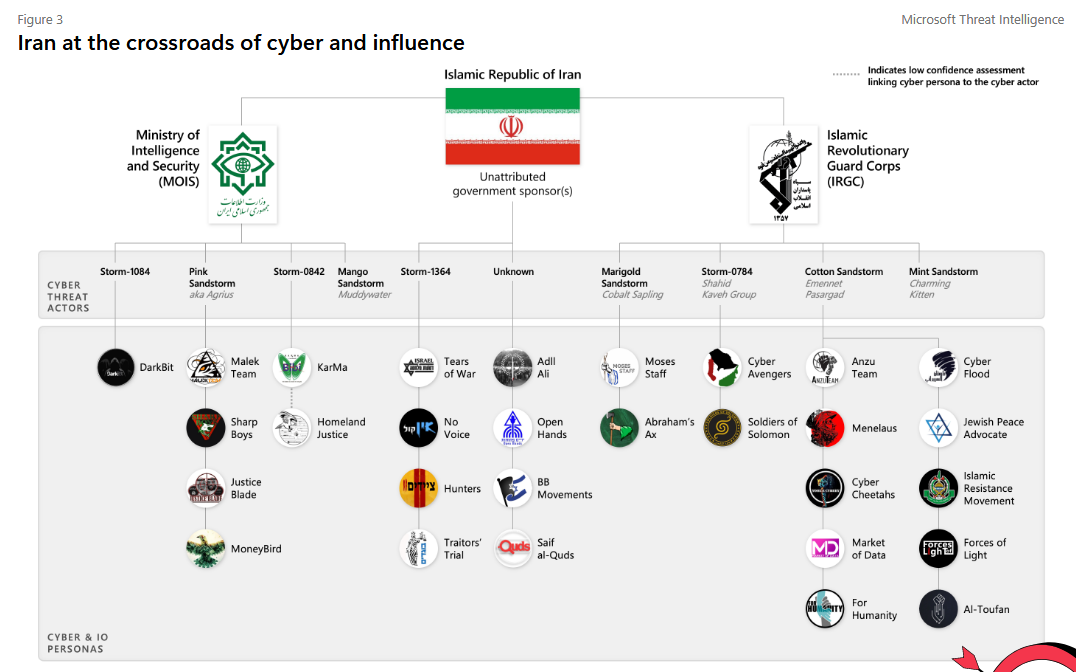
Iran APT activity: Iranian cyber activity increased by 42% in the first week after the Hamas attack in Israel in October of last year. The number of active Iranian cyber groups went from nine to 14, according to one of Microsoft's security teams. Observed activity included hack-and-leaks, destructive attacks, and cyber-enabled influence operations. Microsoft saw little or no coordination between Iranian hackers and Hamas.
"Influence operations grew increasingly sophisticated and inauthentic, deploying networks of social media 'sockpuppets' as the war progressed. Throughout the war these influence operations have sought to intimidate Israelis while criticizing the Israeli government's handling of hostages and military operations to polarize and ultimately destabilize Israel. Eventually, Iran turned its cyberattacks and influence operations against Israel’s political allies and economic partners to undermine support to Israel's military operations."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released two security advisories for its products.
VMWare security updates: VMWare has released a security update to fix five vulnerabilities in its Aria products.
JetBrains security update: JetBrains has pushed a security update for its on-premises TeamCity servers to fix CVE-2024-23917, an auth bypass bug discovered last month. No exploitation spotted in the wild yet.
Shim vulnerability: Red Hat has published a security update for Shim, a library used by major Linux distros as a first-stage UEFI bootloader. The update fixes a remote code execution bug (CVE-2023-40547) that can allow threat actors to hijack OS boots using malicious HTTP requests. The vulnerability impacts all Linux distributions that support Secure Boot, such as Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, SUSE, and others. The bug was discovered by Bill Demirkapi of the Microsoft Security Response Center. [Additional coverage from Eclypsium]
KiTTY unpatched bugs: Security researcher Austin A. DeFrancesco has disclosed details and proof-of-concept code about three unpatched vulnerabilities (2+1) in KiTTY, a fork of PuTTY.
TOTOLINK unpatched bugs: SSD has published details on an unpatched auth bypass impacting TOTOLINK routers. SSD said multiple emails to the vendor went unanswered.
Atlassian Confluence vulnerability: Trend Micro has published a technical report on CVE-2023-22527, an unauth RCE in Atlassian Confluence servers that was patched earlier this month and is currently exploited in the wild.
Jenkins vulnerability: Zscaler has published a technical report on CVE-2024-23897, a major bug in the Jenkins CLI component that allows attackers to hijack Jenkins installs.
Livall smart helmet: Sportswear maker Livall has fixed a bug in its smart ski and bike helmet that could have allowed threat actors to track owners' precise locations.
Infosec industry
ShmooCon 2024 videos: Talks from the ShmooCon 2024 security conference, which took place in late January, are now available on the Internet Archive.
Acquisition news #1: Entrust is acquiring AI-based ID verification service Onfido for roughly $400 million. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Acquisition news #2: US data security firm Cohesity is acquiring Veritas' data protection business in a $7 billion deal. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
New tool—Microsoft Graveyard: Software engineer Victor Frye has published Microsoft Graveyard, a portal that keeps track of Microsoft projects that have been killed or are about to be killed by Microsoft.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about what up-and-coming countries should expect from a Cyber Command and whether they should invest in it.





