Risky Biz News: New DoS loop attack impacts 300,000 systems
In other news: Russia sanctions WaPo cyber reporters; Trend Micro links another APT to i-SOON leak; Fujitsu discloses data breach.

This newsletter is brought to you by Kroll. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
Academics have discovered a new variation of the network loop attack that can crash servers by putting them in an infinite loop of data exchange.
The new attack is named Loop DoS and was discovered by Yepeng Pan and Professor Dr. Christian Rossow from the CISPA German research institute.
It is a variation of classic network loops but one that takes place at the application layer instead of the network routing level.
Unlike routing loops, which are countered by the TTL (Time to live) mechanism, Loop DoS attacks have no existing countermeasures.
The attack works by identifying two servers that run vulnerable software and then using a spoofed malicious packet to initiate an infinite data exchange between the two, which may lead to traffic jams or server crashes.
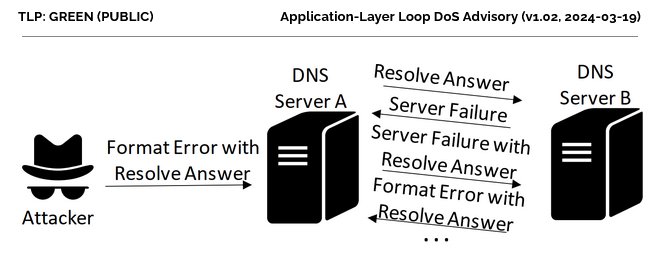
CISPA says it identified nine UDP-based protocols that are vulnerable to Loop DoS attacks. They include popular protocols such as DNS, NTP, and TFTP, as well as six legacy protocols such as Daytime, Time, Active Users, Echo, Chargen, and QOTD.
Attacks using same- or cross-protocol loops are possible.
Researchers estimate the number of vulnerable internet-connected hosts to be around 300,000, with most running NTP software.
"We are aware of servers with vulnerable implementations at least for TFTP (~23k hosts), DNS (~63k), NTP (~89k), Echo/RFC862 (~56k), Chargen/RFC864 (~22k) and QOTD/RFC865 (~21k). We have not tested other protocols and focused on those that were either widely deployed (TFTP, DNS, NTP) or easy to abuse (legacy)."
The research team says it disclosed the new DoS attack to network operators and major software vendors in December of last year.
Microsoft, MikroTik, Broadcom, Brother, Honeywell, and Zyxel have confirmed that some of their products are affected. Efforts to identify affected software are still underway.
CISPA says it has not detected any attacks in the wild exploiting the new Loop DoS vector. Rossow said it would be "easy for attackers to exploit this vulnerability."
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Mintlify API incident: Documentation building service Mintlify says that a threat actor used an undocumented API vulnerability to gain access to internal systems. The company says the intruder used stole GitHub tokens for 91 customers. At least one token was used to access a customer's GitHub repositories. Mintlify says it received a bug report on the API vulnerability after discovering the intrusion but did not formally accused the researcher of the breach and the subsequent chaos. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Fujitsu breach: Japanese IT giant Fujitsu has disclosed a security breach after discovering malware on its internal network. The company says the breached systems contained customer personal information. Fujitsu has disconnected the impacted systems while it investigates if any data was taken from its systems. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
MediaWorks hack: A threat actor has stolen and is now selling the personal data of 2.5 million New Zealanders from local media company MediaWorks. The company believes hackers gained access to a database that collected entries from website competitions. [Additional coverage in RNZ]
France DDoS attacks: French news outlet Le Point debunks the French government's statements about a recent cyberattack of "unprecedented intensity" that experts say was just a simple DDoS attack. It's your typical exaggeration by government talking heads. [h/t Gabriel Thierry]
Apex hacking incidents: Two professional Apex Legends players were hacked in the middle of a major tournament over the weekend. Hackers appear to have exploited a bug in the Apex Legends game to remotely install and activate cheats on the two players' PCs. Early rumors claimed the hackers exploited a bug in the game's anti-cheat. The anti-cheat maker says it investigated the reports and found no evidence of any remote code execution bug in its software. EA Games has postponed the Apex Legends North American Finals to investigate the incident. [Additional coverage in IGN]
General tech and privacy
Firefox 124: Mozilla has released Firefox 124. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest change is the ability to edit PDF files inside the browser.
VLOGGER: Google Research has unveiled VLOGGER, an advanced LLM that can create lifelike videos from still photos.
Quantum computer threats: Google estimates that quantum computers will become a threat to cryptographic protocols within the next 10 to 15 years. The company expects to see significant improvements in the quantum computing field by 2030. Google urges the adoption of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) to safeguard against store-now-decrypt-later scenarios.
Apple AirTag class-action: Apple lost a bid to dismiss a lawsuit and will now have to face a class-action case over faulty and negligent design of its AirTag product, which plaintiffs claim has enabled stalkers to track unsuspecting victims. [Additional coverage in AppleInsider]
FTC investigates Reddit: The Federal Trade Commission has launched an investigation into Reddit's plans to license user-generated content to AI companies. The company came under heavy criticism last year for selling its content without its users' approval. Reddit disclosed the FTC investigation in an SEC filing last week. The company is scheduled to go public and sell shares later this week on March 21.
TikTok fined in Italy: Italy's market competition agency has fined TikTok €10 million for failing to implement content filtering controls. The agency says TikTok does not have a mechanism to monitor and block harmful content from reaching minors and vulnerable individuals. Officials say TikTok's recommendation algorithm often boosts harmful content.
Microsoft suspends more services in Russia: Microsoft has suspended additional cloud services in Russia following the latest round of EU sanctions. The company suspended access to its business intelligence and CRM products on March 20. The suspension impacts Microsoft PowerBI and Dynamics 365 platforms. Russian IT group Softline says Amazon and Google are also preparing similar moves. [Additional coverage in RBC]
Microsoft deprecated feature: Microsoft has deprecated support for certificates that use RSA keys with key lengths shorter than 2048.
IoT security specification: The Connectivity Standards Alliance, an industry group of IoT device makers, has published the first version of a new cybersecurity specification for modern IoT devices. According to the CSA, almost 200 companies contributed to the standard. This includes the likes of Amazon, Google, Arm, and Comcast.
Government, politics, and policy
NCSC SCADA guidance: The UK NCSC has published security guidance for OT/ICS organizations that are considering migrating SCADA infrastructure to the cloud.
More countries join anti-spyware effort: Six new countries have joined a US-led anti-spyware coalition. Finland, Germany, Ireland, Japan, Poland, and South Korea join a list of 11 other countries that promised to fight the proliferation and misuse of commercial spyware. The six new members joined the coalition at the third Summit for Democracy, held this week in Seoul, South Korea.
Russia sanctions WaPo cyber reporters: The Russian government imposed new sanctions last week on more than 200 Americans. The majority of sanctions target academics and defense contractors, but also several US journalists. Among the sanctions are four of the Washington Post's current and former cybersecurity reporters. They include Joseph Menn, Joseph Marks, Tim Starks, and Ellen Nakashima.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with George Glass, Senior Vice-President for Kroll's Cyber Risk business. George covers the company's latest report, a Kimsuky attack on ConnectWise ScreenConnect devices with a new malware strain named ToddlerShark.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Cybercrime compound raided: The Philippines National Police have freed hundreds of people who were forced to work against their will in a cybercrime compound in the city of Bamban. Officials say they freed 875 and detained eight individuals suspected of running the operation. Victims had their passports taken away and forced to carry out romance and cryptocurrency scams. Police said they acted on a tip from a Vietnamese national who managed to escape the facility at the end of February. [Additional coverage in the Manila Standard]
Lifelock pleads guilty: An Idaho hacker known as Lifelock has pleaded guilty to hacking the city of Newnan, Georgia, and a medical clinic in Griffin, Georgia.
Omnipotent extradition: The former administrator of a major hacking forum has asked UK authorities to deny his extradition to the US. Portuguese national Diogo Santos Coelho was arrested in the UK in early 2022 for allegedly running RaidForum, an infamous cybercrime marketplace where hackers leaked and traded hacked data. US officials claimed Coelho was the site's "chief administrator" and went by the hacker name of Omnipotent. According to The Guardian, Coelho was diagnosed with autism after his arrest and is now trying to block his extradition to the US claiming he will receive inadequate care. Coelho also claims that he was groomed and exploited by adults since the age of 14 into committing the alleged crimes.
LockbitSupp interview: In an interview with The Record, the administrator of the LockBit ransomware gang vowed to continue hacking—despite a recent takedown of the LockBit RaaS by EU and US authorities.
CREATE2 hacks: The research team at Check Point has published a report on how threat actors are abusing the Ethereum blockchain's CREATE2 function to hack and steal funds from user wallets.
"The attack method involves tricking users into approving transactions for smart contracts that haven't been deployed yet, allowing cybercriminals to later deploy malicious contracts and steal cryptocurrencies."
Operation PhantomBlu: Perception Point has published a report on Operation PhantomBlu, a malspam campaign distributing a version of the NetSupport RAT.
Spa F1 GP phishing: In one of the weirdest phishing campaigns you'll see, hackers are targeting users who plan to attend this year's Spa F1 GP.
Ransomware negotiations: KELA has published a report looking at how the Akira and BlackBasta gangs are conducting their extortions and negotiations.
Threat/trend reports: Akamai, Cado Security, Kaspersky, Proofpoint, Recorded Future, and Uptycs have recently published some interesting reports covering infosec industry threats and trends. The reports range from lateral movements in cloud environments to AI red-team use.
Malware technical reports
CryptoWire: South Korean security firm AhnLab has seen the old CryptoWire ransomware (circa 2018) being used in attacks. The ransomware is still the old version that uses a hardcoded encryption key, allowing victims to easily recover their files.
AsukaStealer: ANY.RUN has published an analysis of AsukaStealer, a possible evolution of the older ObserverStealer.
Mirai Nomi: Chinese security firm QiAnXin has published a technical analysis of Mirai Nomi, the latest variant of the Mirai botnet malware.
GCleaner: OALABS has published an analysis of a new version of the GCleaner loader, also known as NullMixer.
Sponsor Section
The Kroll CTI team observed a campaign using a new malware that appears to be very similar to BABYSHARK, previously reported to have been developed and used by the APT group Kimsuky (KTA082). Read more.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Earth Krahang: Trend Micro has linked Chinese cyber contractor i-SOON to a second Chinese APT group. The security firm says i-SOON operates two penetration teams that carry out offensive operations. It previously linked the first team to a Chinese APT named Earth Lusca and has now linked the second to a group named Earth Krahang. Trend Micro says Earth Krahang has been active since early 2022 and has primarily targeted government organizations across Southeast Asia. Data from i-SOON's internal network was leaked on GitHub in February.
"Our previous report suggests Earth Lusca might be the penetration team behind the Chinese company I-Soon, which had their information leaked on GitHub recently. Using this leaked information, we found that the company organized their penetration team into two different subgroups. This could be the possible reason why we saw two independent clusters of activities active in the wild but with limited association. Earth Krahang could be another penetration team under the same company."
Volt Typhoon: Five Eyes cybersecurity agencies have published a new factsheet on Volt Typhoon APT operations.
DEEP#GOSU: Securonix has published a report on DEEP#GOSU, a malware distribution campaign the company has linked to the Kimsuky DPRK APT group.
"The malware payloads used in the DEEP#GOSU represent a sophisticated, multi-stage threat designed to operate stealthily on Windows systems especially from a network-monitoring standpoint. It relied on both PowerShell and VBScript for its execution which interestingly enough used very minimal obfuscation. Each stage was encrypted using AES and a common password and IV which should minimize network, or flat file scanning detections."
Andariel: The Andariel North Korean APT group is abusing an open-source asset management platform to control and deploy malware on infected networks. Security firm AhnLab has spotted the group abusing the MeshCentral project in recent attacks across South Korea. Andariel is deploying the MeshCentral agent on infected networks and then using a custom server to deploy backdoors and other malware. AhnLab says the group abused the Innorix asset management software in a similar fashion throughout 2023.
UAC-0006: CERT-UA and Palo Alto Networks have published a report on UAC-0006, a threat actor behind attempts to install the SmokeLoader malware at Ukrainian organizations. [h/t Simon Tsui]
"The SCPC SSSCIP report documents 23 waves of Smoke Loader attacks from May through December 2023 based on our joint research. These campaigns have notably increased the threat level for accountants in Ukraine and represent the potential loss of 1 million hryvnias per week on average."
AcidPour: SentinelOne researchers have spotted a new variant of the AcidRain wiper. Russian military hackers used AcidRain during the 2022 Viasat hack to wipe satellite modems before the Ukraine invasion. SentinelOne has named the new version AcidPour and says it's more dangerous than the original. The main change allows AcidPour to run on Linux x86 platforms. SentinelOne and CERT-UA say the malware has been used in the wild but have not disclosed the names of any victims.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
DOD VRP: The US Department of Defense says it processed more than 50,000 bug reports via its vulnerability reward programs (VRP).
Rewards for AI plugins: Google will pay coders from $500 to $3,133.7 to develop AI-related plugins for its Tsunami network scanner.
USBGuard bypass: Pulse Security's Michael Fincham has published details on a new method to bypass USBGuard on Linux systems. Details went live after Gnome refused to acknowledge it as a security issue.
JSON smuggling PoC: CloudSEK researcher XSCorp has published proof-of-concept code for a new technique known as JSON smuggling. The new technique takes advantage of insignificant bytes in a JSON document to smuggle arbitrary files and is obviously inspired by old HTML smuggling trick.
Arm Mali GPU UAF: GitHub's Man Yue Mo has published a write-up on CVE-2023-6241, a use-after-free vulnerability in the Arm Mali mobile GPU.
Jenkins vulnerability: Trend Micro has published a technical report on CVE-2024-23897, a major bug in the Jenkins CLI component that allows attackers to hijack Jenkins installs. A similar older report is also available from Zscaler.
LoadMaster vulnerability: Rhino Security Labs has published a write-up on CVE-2024-1212, an unauthenticated command injection in the Progress LoadMaster load balancer. Progress Software patched the vulnerability last week.
WebGPU attack: A team of academics has published a paper [PDF] detailing side-channel attacks on web browsers that support the new WebGPU API. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
"Our attacks require no user interaction and work in a time frame that easily enables drive-by attacks while browsing the Internet. Our work emphasizes that browser vendors need to treat access to the GPU similar to other security- and privacy-related resources."
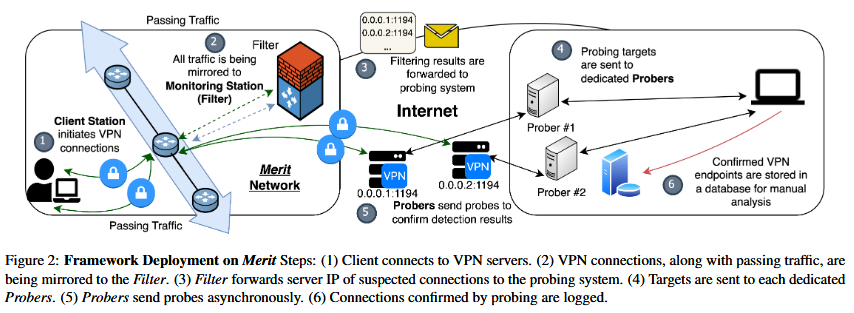
OpenVPN fingerprinting: A team of academics from US universities has discovered a way to fingerprint OpenVPN connections. The team says it identified three fingerprint types that can be used to block the protocol. The three methods use details such as byte patterns, packet size, and server responses. The team says their methods have an accuracy rate of 85% with "negligible false positive."
"Governments can also quickly adopt these fingerprints to track and block VPN usage during sensitive times, like political upheavals, when VPN connections are most vital to the free flow of information."
Infosec industry
Non-acquisition news: Airbus has pulled out of its deal to buy French cybersecurity company ATOS.
New tool—GTPDOOR scanner: Security researcher HaxRob has published a scanner to detect systems infected with the new GTPDOOR malware.
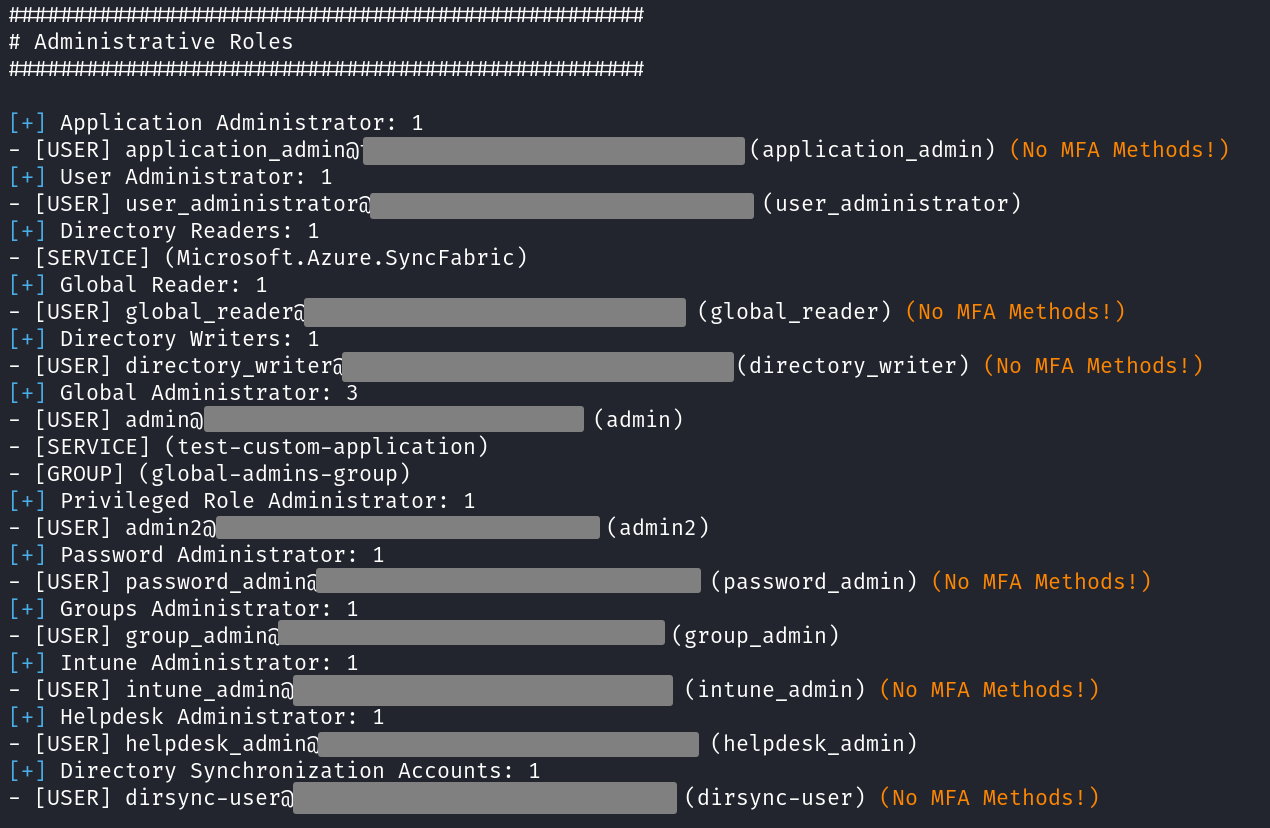
New tool—AzurEnum: German security firm SySS has open-sourced a tool named AzurEnum that can enumerate Microsoft Entra ID artifacts.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at Russia's recent leak of an intercepted German military discussion. From an intelligence point of view, the content of the discussion is only moderately interesting, but Russia decided to leak it in an attempt to influence European attitudes towards providing military aid to Ukraine.




