Risky Biz News: Most of 2023's top exploited vulnerabilities were initially zero-days
In other news: State Dept disinfo center faces shutdown; US to back controversial UN cybercrime treaty; Google Cloud to issue cloud CVEs.

This newsletter is brought to you by Kroll. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
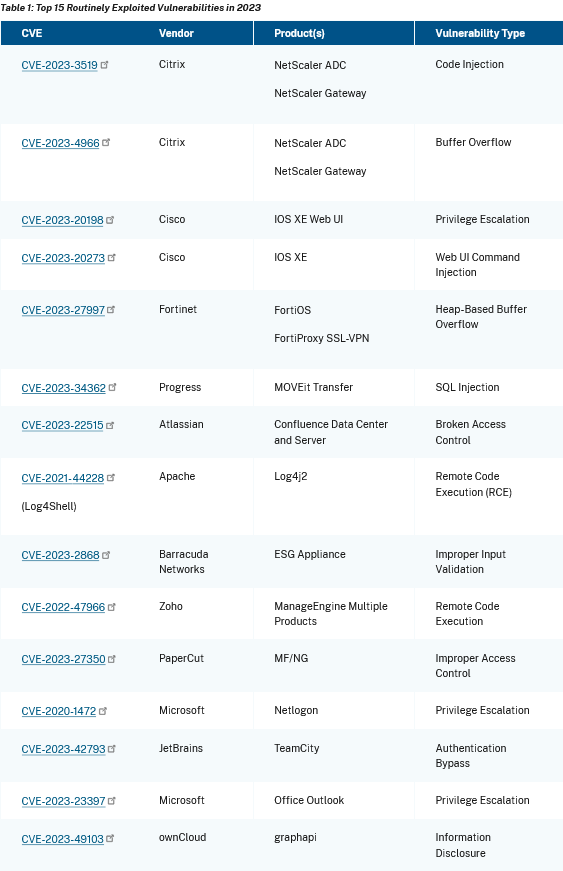
Ten of the 15 most frequently exploited vulnerabilities last year were initially zero-days, CISA said in a joint report published with cybersecurity agencies from Five Eyes countries on Tuesday.
This includes ifamous zero-days, such as the one that forced Barracuda to tell customers to replace all ESG appliances, the zero-day used in the MOVEit hacking spree, and the CitrixBleed vulnerability.
Because zero-days dominated last year's Top 15, 2023 marks the first time CISA's Top Exploited Vulnerabilities list is dominated by new CVEs.
CISA's past reports were known to include many old CVEs, showing that, at the time, threat actors had preferred tried-and-tested exploits over newer bugs.
Last year's Top 15 also shows a very obvious trend toward the exploitation of enterprise and network perimeter devices.
All the Top 15 vulnerabilities are related to enterprise software.
CISA's list complements another recent report from Google's Mandiant division that found that of the 138 vulnerabilities disclosed last year, 70% were first exploited as zero-days—before patches were available.
A conclusion that can be drawn from both reports is that threat actors are investing in exploit development more than they have in the past, hoping to go on massive hacking sprees before patches are available.
The reasoning behind this is simple. Shoddy companies running old hardware and software have been compromised several times already. As a threat actor, you're looking for new hunting grounds, and these are the companies that typically patch their stuff. Zero-days are how you catch these companies off guard.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Ahold Delhaize cyberattack: Retail store giant Ahold Delhaize says that a cybersecurity incident has disrupted operations of its US IT network. The online stores of the company's US brands were offline over the weekend. The company says it's still investigating the incident. EU operations are not affected. Ahold Delhaize is one of the world's largest retailers, with around $87 billion in annual revenue. Its US brands include Food Lion, Stop&Shop, and Hannaford.
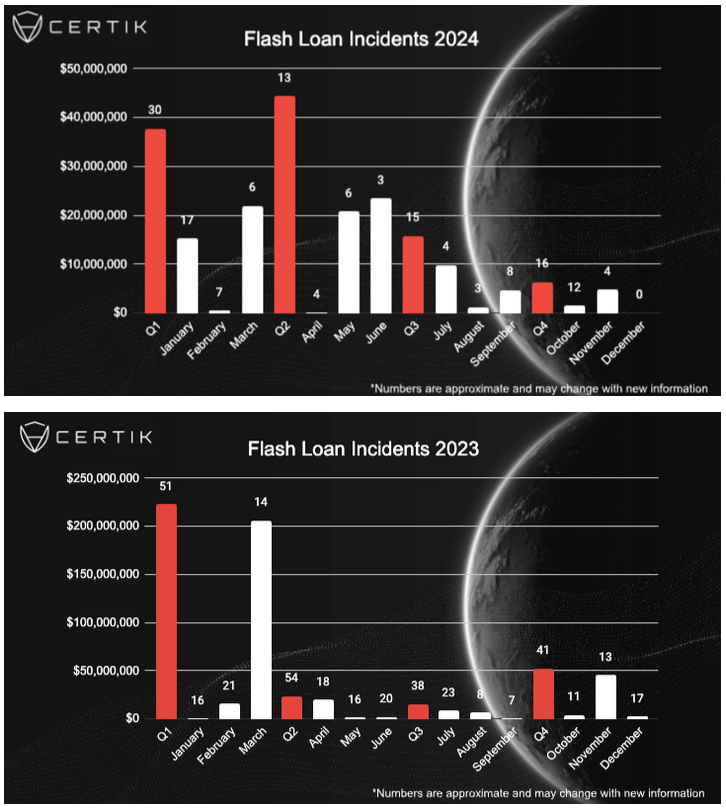
DeltaPrime crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen an estimated $4.8 million worth of crypto assets from the DeltaPrime crypto brokerage platform. According to blockchain security firm CertiK, the attack combined two vulnerabilities to execute flash loan attacks and steal Arbitrum and Avalanche tokens from the platform's wallets. DeltaPrima has confirmed the hack and says it contained the incident. CertiK researchers say flash loan attacks have declined, accounting for only $104 million in losses, compared to $313 million last year.
General tech and privacy
Chrome 131: Google has released version 131 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. The biggest changes in this release include support for the new quantum-resistant ML-KEM algorithm, OCR support for the browser's PDF reader, and the distrust of Entrust certificates.
OpenID is now an ISO/IEC standard: The OpenID Connect specification has finally been published after 10 years and is now also an ISO/IEC standard.
Twitter algorithm: New research claims that Twitter modified its algorithm to promote content from Republicans and Elon Musk ahead of this year's US Presidential Election. The change appears to have taken place around mid-July. [Additional coverage in The Conversation]
TikTok changed its algorithm to favor conservatives: Citing internal sources, The Information reports that TikTok modified its algorithm and loosened moderation practices to promote conservative topics and appeal to the Trump campaign. The change occurred while Republican lawmakers were pushing a bill to ban TikTok in the US. The news comes after a WaPo report claimed that tweets from Republicans and US conservatives were receiving more views on Twitter compared to Democrats.
Meta cuts price for ad-free tier: Meta has reduced the price for its EU subscription—which allows users to use the platform without seeing ads or being tracked by the company.
"From today, we will reduce the price of the monthly subscription from €9.99 to €5.99/month on the web, or from €12.99 to €7.99/month on iOS and Android. Each additional Facebook or Instagram account will be charged at €4/month on the web and €5/month on iOS and Android."
Microsoft expands AccountGuard to Africa: Microsoft has expanded the AccountGuard service to African countries. The service provides extra protection for sensitive user accounts involved in political campaigns, think tanks, NGOs, and journalists. The program will initially be available in Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa. Microsoft plans to expand it to Ghana and other countries in the future.
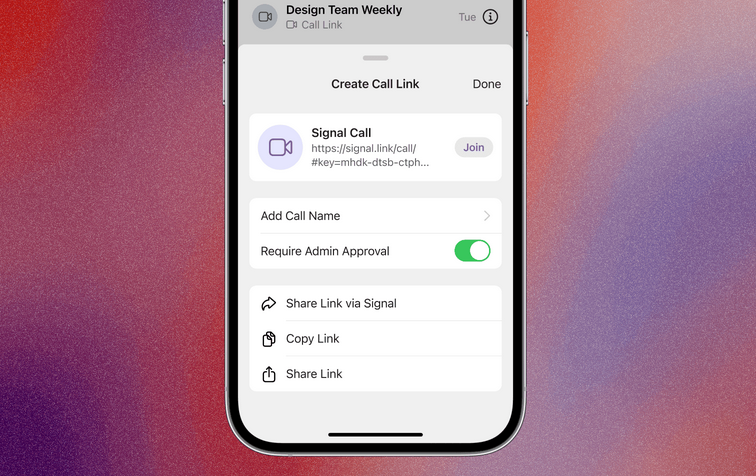
New Signal feature: Signal is rolling out "Call Links," a new feature that allows multiple users to easily join a secure group video call just by clicking a link—similar to Google Meet's link generator. This is an improvement over the old system, where users had to join the same Signal group before initiating a group call.
Government, politics, and policy
GEC impending shutdown: The US Congress has not extended the mandate of a US State Department office that hunts down and exposes foreign disinformation campaigns. The Global Engagement Center is scheduled to cease operations after its current seven-year mandate lapses on December 23. One of the office's biggest critics has been Elon Musk, who accused it of trying to shape social media content after the center exposed Russian and Chinese info ops on Twitter. The center has a yearly budget of $61 million and around 130 employees. [Additional coverage in the WSJ]
US backs controversial UN cybercrime treaty: The US government will support a controversial UN cybercrime treaty. The treaty has been put forward by the Russian government and has been heavily criticized for promoting a wide surveillance regime under the guise of protecting against cybercrime. Digital rights groups have warned the treaty gives authoritarian regimes the power to harass critics located abroad. US officials believe the treaty has positives, such as new legal frameworks to pursue cybercriminals and CSAM offenders. A vote is scheduled for this week, and the treaty needs approval from two-thirds of UN members to be ratified. [Additional coverage in Politico]
Fixed rewards for bug bounty work: The Russian government is considering establishing a fixed rewards bracket for Russian bug bounty programs. The bracket would mandate that organizations pay certain amounts of money to researchers who find vulnerabilities in their systems. The bracket would apply to any bugs found in critical infrastructure and government agencies. Bug rewards would range from around $300 to $10,000. The project is currently in the proposal phase but has already received backing from major Russian security companies. [Additional coverage in Kommersant]
No troll farms here; move along: Romanian intelligence service SRI says there are no troll farms located inside the country's borders, but it is aware of social media accounts that are trying to denigrate candidates ahead of the country's presidential election in December. The SRI responded to an inquiry from the Romanian Parliament after USR candidate Elena Lasconi accused independent runner Mircea Geoana of using troll farms to attack her online. There are also reports that the PSD candidate Marcel Ciolacu, and main favorite, is also using online trolls to boost their online presence.
Sponsor Section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with George Glass, Senior Vice-President for Kroll's Cyber Risk business. George covers the company's latest report, a Kimsuky attack on ConnectWise ScreenConnect devices with a new malware strain named ToddlerShark.

Arrests, cybercrime, and threat intel
Hacker trial in France: ZDNet France is reporting on the trial of Rayan K., a 20-year-old from Paris who is accused of hacking Pass Navigo, the Ile-de-France Mobilités public transport service, in November last year.
GoIssue: SlashNext looks at GoIssue, a new toolkit advertised on hacking forums for harvesting public GitHub data and then automating phishing attacks against GitHub users.
SocEng: Russian security firm FACCT has published a report on SocEng, a new phishing toolkit targeting Telegram and WhatsApp accounts.
ZIP concatenation malspam: Threat actors are using a technique known as ZIP concatenation to bypass security tools and deliver malware. The technique involves merging multiple archives into a new one. Perception Point says the technique works because some security tools only scan the main archive and don't decompress the smaller archives contained within. ZIP concatenation is different from re-archiving a malicious file multiple times but works on the same principles.
SEO malware clusters: Trend Micro and Japanese researchers have published a report analyzing malware clusters linked to several SEO malvertising campaigns. The work received the Best Paper Award at this year's IEEE Conference on Dependable and Secure Computing conference.
UK winter heating scams: UK police say that scammers are seen texting British residents posing as government agencies to lure victims on malicious sites with the promise of receiving new heating subsidies. The new scams exploded after the UK government cut winter heating subsidies for pensioners in September. Officials have warned residents not to enter any personal or banking information on links they receive via SMS.

Malware technical reports
New Android adware: Dr.Web researchers have discovered a new strain of Android adware inside apps on the official Play Store. The adware works by loading remote ad-laden websites when users start the infected apps. The malware's novel feature is using DNS requests to retrieve the URL where users need to be redirected. Dr.Web says it found the malware in apps that have been downloaded more than 2.1 million times.
Ymir ransomware: Kaspersky looks at a new ransomware strain named Ymir that appears to be installed after victims were previously infected with an infostealer.

Sponsor Section
Kroll has investigated many different tactics that threat actors use to steal consumer data on e-commerce sites. These types of attacks can be especially damaging for organizations that are responsible for storing customers' personal and financial information that is collected during transactions. Read more about Kroll's prevention tips and security best practices.

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
AI info-ops research: A report from the Institute for Strategic Dialog looks at how threat actors used AI for propaganda and disinformation during the recent US Presidential Elections.
Turla: Intel471 has published a report on how to hunt for new Turla TTPs.
Kasablanka's LodaRAT: Rapid7 has published a report on a new version of LodaRAT, a malware strain linked to the Kasablanka APT group.
Volt Typhoon rebuilds botnet: Chinese APT group Volt Typhoon has rebuilt its KV Botnet ten months after US authorities took down the botnet's infrastructure in late December of last year. SecurityScorecard says the group has rebuilt the botnet by targeting old Cisco RV routers and Netgear ProSAFE routers. Both device types were a core part of the botnet's first iteration. Volt Typhoon first attempted to rebuild its botnet days after the US takedown, but that initial attempt failed. The Chinese group has used the botnet to disguise the origin of its attacks, most of which target US critical infrastructure.
Melofee evolution: Chinese security firm QiAnXin has discovered a new version of the Melofee backdoor specifically designed to infect RHEL 7.9 systems. The malware has been historically associated with Chinese cyber-espionage group APT17. QiAnXin claims it found evidence the malware connected to infrastructure operated this year by Indian APt group SideWinder—however, researchers believe this is a false positive.
"Does this imply that Melofee has circulated among multiple organizations, becoming a cross-group tool rather than being exclusive to a single group? We believe this is unlikely. The IP address 91.195.240.123 is a parking IP provided by domain registrar NameSilo. Labeling it as malicious likely constitutes a false positive."
New DPRK APT macOS malware: Jamf has discovered new macOS malware samples linked to North Korean hacking operations that were built with Google's Flutter app framework.
WIRTE: A Hamas-affiliated APT group has expanded operations beyond cyber espionage and is now conducting data-wiping attacks against Israeli entities. Check Point says it found evidence that connected the WIRTE group's older malware to SameCoin, a data wiper deployed across Israel in February and October this year. The company says the group is one of the very few Hamas cyber groups that has remained active through the Israeli-Palestine conflict.
TA455 Dream Job campaign: ClearSky Cyber Security research identified a campaign named "Iranian Dream Job," in which the Iranian threat actor TA455 (Charming Kitten) targeted the aerospace industry by offering fake jobs. The campaign distributed the SnailResin malware, which activates the SlugResin backdoor. ClearSky says other security vendors misattributed the campaign to North Korea.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Google Cloud to issue CVEs: Google says it will now issue CVE identifiers for vulnerabilities reported in its Google Cloud service. The company says it will issue CVEs only for critical bugs, even if no customer action is required and patches are installed automatically. Google Cloud joins AWS and Microsoft as the third major cloud vendor to issue CVEs for cloud vulnerabilities.
Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktop vulnerabilities: watchTowr Labs has identified a vulnerability that can be exploited for remote code execution attacks against the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktop client. The vulnerability exploits a deserialization bug in a feature that allows Citrix admins to record virtual desktop sessions. A threat actor only has to send an HTTP payload to a misconfigured Citrix endpoint that handles the session recording feature. Citrix appears to have released patches without notifying the researchers. The company claims attackers must be authenticated to execute an attack, while watchTowr claims the attack can be unauthenticated. Proof-of-concept code has been released on GitHub this week.
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the November 2024 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Microsoft, Chrome, Ivanti, Citrix [1, 2], Fortinet, SAP, Intel, AMD, Zyxel, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Rockwell, and Zoom. The Android Project, Firefox, Cisco, NVIDIA, Veeam, Okta, ASUS, Synology, and QNAP released security updates last week as well.
Microsoft Patch Tuesday: This month, Microsoft patched 89 vulnerabilities (excuse the mess in there, the API was spewing garbage entries), including two actively exploited zero-days. Seeing who reported the two zero-days, it's very likely the two were used in state-sponsored attacks.
- CVE-2024-43451 - NTLM Hash Disclosure Spoofing Vulnerability (via ClearSky)
- CVE-2024-49039 - Windows Task Scheduler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (via Google TAG)
D-Link EoL stuff again: After last week, D-Link told some NAS owners to replace old devices because of a newly disclosed vulnerability, the company has now told the same to the owners of DSL-6740C modems.
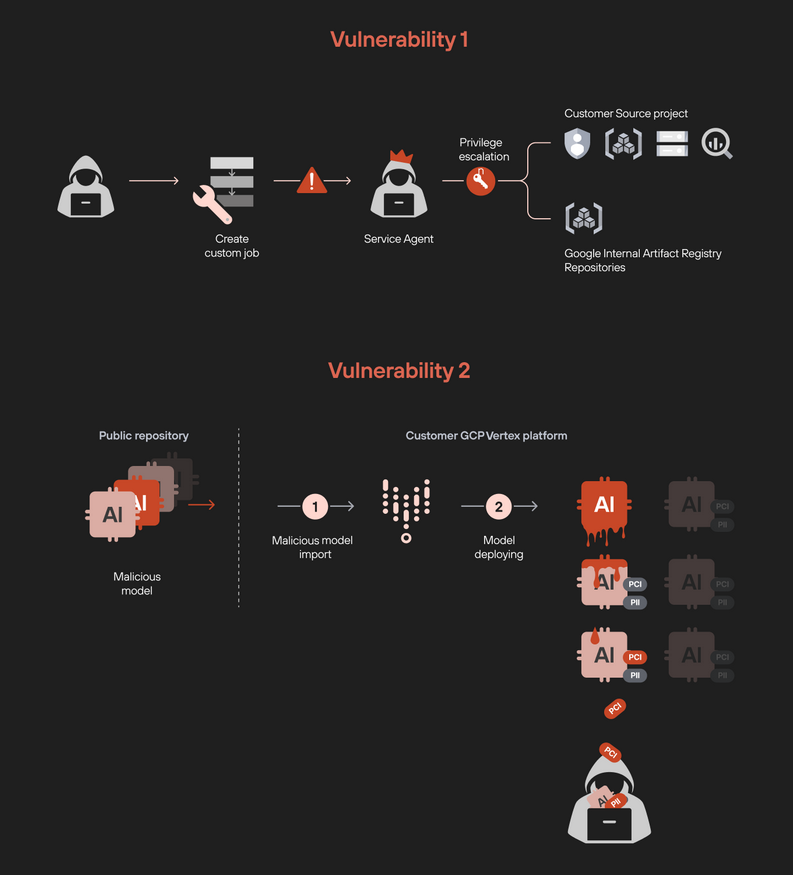
Vertex AI vulnerabilities: Palo Alto Networks researchers uncovered two vulnerabilities in Google's Vertex AI platform. These vulnerabilities could have allowed attackers to escalate privileges and exfiltrate models.
Infosec industry
Trustwave and Cybereason announce merger: Cybersecurity and managed security services Trustwave has announced plans to merge with EDR provider Cybereason.
Threat/trend reports: Check Point, Pakistan Telecommunication Authority [PDF], and Panaseer have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
New tool—Bjorn: French security researcher Fabien (infinition) has released Bjorn, a network scanning and offensive security tool for the Raspberry Pi.
New tool—KexecDDPlus: Orange's security team has released KexecDDPlus, a tool to exploit the KsecDD driver through LSASS and Server Silos.
BlueHat 2024 videos: Talks from Microsoft's BlueHat 2024 security conference, which took place at the end of October, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how ungoverned spaces on Telegram result in increasingly toxic and antisocial communities.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about the Snowflake hack after the person allegedly responsible was arrested in Canada. Telegram is involved at all sorts of levels and Tom wonders if this crime would have occurred if Telegram didn't exist.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!




