Risky Biz News: Law enforcement disrupts six malware botnets
In other news: Check Point patches zero-day; ISP loses 600,000 routers in data-wiping attack; Poland's secret surveillance program deemed illegal.

This newsletter is brought to you by SpecterOps, the experts in Attack Path Management. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

A coalition of law enforcement agencies orchestrated the largest cybercrime takedown to date and seized servers and domains used by six of the world's largest malware botnets.
Named Operation Endgame, the takedown specifically targeted the botnets of "malware loaders," a type of malware that infects systems and then rents access to other cybercrime groups.
Europol says the coalition specifically targeted these botnets because of their role in helping deploy ransomware as part of their "host rental" business model.
The list of disrupted botnets includes some of the biggest players on the cybercrime scene:
- Bumblebee
- IcedID
- Pikabot
- Smokeloader
- SystemBC
- Trickbot

Besides seizing servers and domains associated with the botnets, authorities also detained four suspects (1 in Armenia and 3 in Ukraine) and searched 16 locations for further evidence (1 in Armenia, 1 in the Netherlands, 3 in Portugal and 11 in Ukraine).
German police have also issued international arrest warrants for eight other suspects, pictured below, involved in the Smokeloader (first image, first row) and Trickbot botnets. The eight are now on the EU's most-wanted list.

Officials estimate that the six botnets collectively made around $75 million (€69 million) from renting access to their infrastructure.
"The suspect's transactions are constantly being monitored and legal permission to seize these assets upon future actions has already been obtained."
Law enforcement agencies from 20 countries participated in the takedown, along with a long list of cybersecurity for-profit and non-profit organizations: Bitdefender, Cryptolaemus, Sekoia, Shadowserver, Team Cymru, Prodaft, Proofpoint, NFIR, Computest, Northwave, Fox-IT, HaveIBeenPwned, Spamhaus, and the DIVD.
Officials are now in the process of contacting affected victims, and, here, HaveIBeenPwned will play a crucial role, along with national CERTs.
"Many of the victims were not aware of the infection of their systems. The estimated financial loss these criminals have caused to companies and government institutions amounts to hundreds of millions of euros."
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
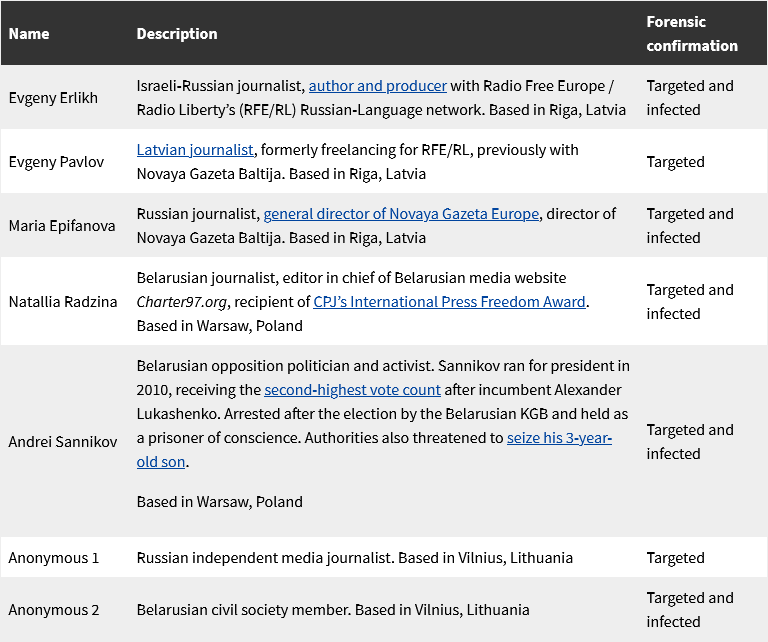
New Pegasus cases in Europe: Access Now and CitizenLab have found traces of the Pegasus spyware on the phones of seven Russian and Belarusian-speaking independent journalists and activists across Europe. Compromises date as far back as August 2020, but most of the infections took place after Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Investigators say that five of the seven compromises appear to have been carried out by a single NSO Group customer.
Seattle Public Library ransomware attack: A ransomware attack has crippled the activity of the Seattle Public Library. The incident took place over the weekend and brought down the library's online catalog, WiFi networks, and public computers. The library reverted to using paper forms for lending out books, CDs, and DVDs. The incident is still ongoing, and the library has no estimated time for resolution. The Toronto Public Library was hit by a similar ransomware attack last October and officials needed more than four months to recover.
BBC breach: A threat actor has gained access to one of the BBC's cloud servers and stole data from the company's Pension Scheme. The BBC says the breach took place last week and impacted 25,000 of its current and former employees. Exposed data includes names, insurance numbers, dates of birth, and home addresses.
pcTattletell shuts down: US spyware vendor pcTattletale has shut down operations after a recent hack, according to a statement from its founder. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
First American incident: First American, the second largest title insurance company in the US, said in an SEC filing this week that hackers stole the personal data of almost 44,000 individuals in a security breach at the end of last year.
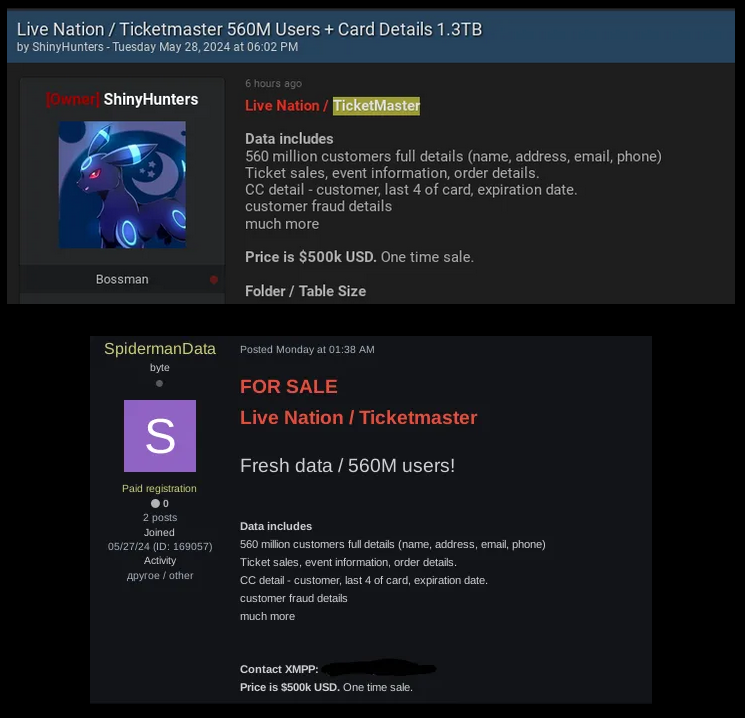
TicketMaster alleged leak: A threat actor claimed over the weekend to have breached TicketMaster and was selling some of the company's user data. There's apparently some drama related to the whole thing, from a "stolen hack" to "attention whoring" accusations. For now, the authenticity of the data has not been confirmed. Personally, I find this whole thing exhausting.
General tech and privacy
Tax on foreign software: The Russian government is considering introducing a special tax on companies that continue to use foreign software—or at least software from the super mean Western democratic countries, yadda, yadda, yadda. [Additional coverage in TASS]
Microsoft TLS server authentication: Microsoft plans to deprecate TLS server authentication certificates with 1024-bit RSA keys by the end of the year.
iOS secure enclaves: According to a report from The Information, iOS 18, coming later this year, will support secure enclaves thanks to its new M2 and M4 chips.
PQC traffic protections: Around a fifth of all Cloudflare traffic now features post-quantum cryptographic protections. Adoption of PQC protections has skyrocketed since the end of last year when it was hovering around 1-2%.
Activision wins lawsuit against cheat provider: Activision has won a lawsuit against EngineOwning, a company that makes cheats for Call of Duty games. The judge awarded Activision a default judgement of $14.4 million and has ordered EngineOwning to stop making cheats and turn over its website to Activision. In a forum post, the EO devs didn't seem to care. [Additional coverage in The Verge]
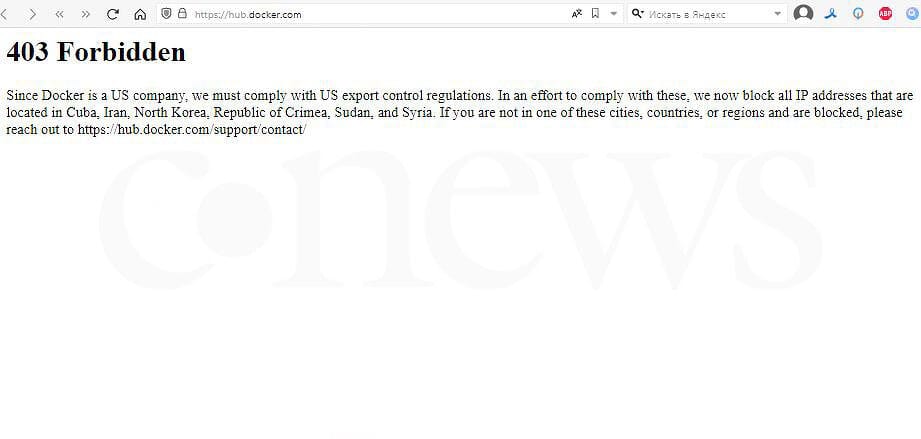
Docker Hub blocks in Russia: Docker is now blocking access to its Docker Hub image repository for Russian users—in accordance with Western sanctions. [Additional coverage in Cnews.ru]
Government, politics, and policy
DMCA exemption for AI safety: The US Senate Intelligence Committee has asked the US Copyright Office to add an exemption to the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) to allow for good-faith security research related to AI safety.
NFT warning: The US Treasury Department has published a report on the impact of NFTs on the financial ecosystem and warned the tokens are highly susceptible to fraud and money laundering. Duuuh!!! Welcome to 2020!
NSA zero trust guidance: The NSA has issued another one of its zero trust model guides.
False Claims Act and cybersecurity: Eric Geller has published a piece in The Record on how the US Justice Department is using the Civil War-era False Claims Act to go after government contractors that lie about their cybersecurity posture, hoping this will trigger a change and contractors will start investing in their own cybersecurity.
ECHR on Polish surveillance: The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) has ruled that a Polish surveillance law violates the European Convention on Human Rights. The court ordered Poland to change the legislation—passed by the former Law and Justice (PiS) government in 2016 and described at the time as "anti-terrorism measures." The ECHR ruled that Poland's secret surveillance program violated the personal privacy of its targets and did not provide an avenue of appeal. The court also found the program did not undergo reviews by an independent body and was subject to political influence. Poland's current government welcomed the court's decision and said it would change the law. The former Polish government extensively used spyware to surveil opposition parties, prosecutors, and reporters. [Additional coverage in Notes from Poland]
Cybersecurity education in the EU: The EU's cybersecurity agency ENISA has published a guide on how member states can assess the maturity levels of their cybersecurity training at the primary and secondary school levels.
Israel's cyber-espionage of the ICC: A report in The Guardian claims Israel has been engaged in a decade-long operation to hack, surveil, and intimidate members of the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Justin Kohler, VP of the Bloodhound team at SpectreOps about 'attack paths', the ways that malicious actors maneuver through Active Directory to elevate their privileges. They discuss how and why they arise and what you can do about them.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Dutch Fappening suspect sentenced: A Dutch court has sentenced a 40-year-old man to a year in prison for stealing and sharing private photos of Dutch celebrities. Officials say the man used social engineering to hack the iCloud accounts of 43 women, some of which were sports and TV celebrities in the Netherlands. The hacks took place between 2014 and 2019, and some of the photos were leaked online. The man must also pay compensation to some of the victims. [Additional coverage in NHD]
Japanese man arrested for AI ransomware: Japanese authorities have arrested a 25-year-old man for allegedly creating ransomware using generative AI tools. According to the Yomiuri Shinbun, Ryuki Hayashi from the city of Kawasaki used his phone and computer to access AI coding tools, bypass safety restrictions, and generate the ransomware code. Officials say there are no reports of damage caused by the ransomware. Hayashi also confessed to his crime and said he only wanted to make money. [h/t DataBreaches.net]
Pig-butchering arrests in India: Indian authorities have arrested five suspects on charges of trafficking unwitting job seekers into Southeast Asian scam compounds. The group targeted young people with alluring jobs in exotic locations, but applicants were sent to scam call centers based in Laos, Thailand, and Cambodia. One of the five people arrested is the bodybuilder and social media influencer Balwant 'Bobby' Kataria, who allegedly advertised jobs on his YouTube and Instagram channels. The Indian government says it rescued and repatriated over 400 nationals who were duped and trapped in scam compounds across Southeast Asia. [Additional coverage in The Record]
STAAR hackerman: US authorities have issued an arrest warrant for an 18-year-old student for launching cyberattacks that disrupted the STAAR online exams in the state of Texas. Officials claim Keontra Lamont Kenemore used his school-issued Chromebook to order DDoS attacks on the STAAR portal. The attacks disrupted online tests for almost 25,000 Texas students across two days. Kenemore allegedly confessed to ordering the attacks when confronted by school staff. [Additional coverage in the Houston Chronicle]
911 S5 botnet admin arrested: US authorities have charged and detained a Chinese national for running the 911 S5 proxy botnet. YunHe Wang, 35, was arrested for his role in infecting systems with malware and redirecting malicious traffic through victims' computers. Together with two other Chinese nationals, Wang infected more than 19 million devices from 2014 through July 2022. Officials say the group made almost $100 million from renting access to the 911 S5 botnet throughout the past years. The 911 S5 service shut down in July 2022 after hackers breached the service and leaked user data. The service was in the process of attempting a comeback when it was disrupted by the FBI, which seized servers and domains. Officials say the 911 S5 botnet facilitated cyber-attacks, large-scale fraud, child exploitation, harassment, and bomb threats. According to the FBI, commercial VPN solutions that used the 911 S5 infrastructure include MaskVPN, DewVPN, PaladinVPN, ProxyGate, ShieldVPN, and ShineVPN. Wang and his accomplices were also sanctioned by the US Treasury earlier this week.
Malware campaigns: AhnLab covers three malware campaigns spreading various forms of malware, such as XWorm, Orcus RAT, and XMRig.
Telesquare exposure: IoT search engine Censys is seeing more than 3,300 Telesquare routers exposed on the internet. A PoC for a recent Telesquare vulnerability was published online earlier this month.
Okta cred stuffing alert: Identity provider Okta says it detected credential-stuffing attacks targeting the cross-origin authentication feature in its Customer Identity Cloud (CIC). The company says the earliest attacks began on April 15 this year. Okta has notified customers and published guidance on how customers can protect their CIC services.
Piano scam: Proofpoint is seeing a wave of email scams using the lure of a "free piano" to trick victims into paying an advanced shipment fee. Most of the messages target students and faculty at colleges and universities in North America. I honestly can't believe something like this is working in 2024.
StackOverflow campaign: Threat actors are answering questions on Stack Overflow with links to malicious Python packages in an attempt to infect users with infostealers. According to Sonatype's Ax Sharma, the campaign started last week and the malicious package has been downloaded more than 250 times already. The malicious Python libraries appear to be part of a larger cluster of activity dating back to mid-2023.
Water Sigbin: Trend Micro has published a report covering recent changes in the campaigns of the Water Sigbin (8220 Gang) crypto-mining operation, which has now adopted Atlassian Confluence exploitation.
FlyingYeti disruption: Cloudflare has shut down accounts on its platform used by a Russian threat actor known as FlyingYeti (UAC-0149) to launch phishing attacks on Ukrainian users and organizations.
Fake update campaigns: The fake browser update malware delivery campaigns are still going strong, delivering stuff like BitRAT and Lumma Stealer.
Threat/trend reports: BVP, Cloudwards, Sophos, Trend Micro, and Veracode have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
Malware technical reports
Infostealers overview: Both Elastic and DarkOwl have published reports looking at the engineering side of modern-day infostealers.
Ov3r_Stealer: Romania's cybersecurity agency DNSC has published a technical report on the Ov3r_Stealer infostealer. It's in Romanian, but you can Google Translate through it.
Cuckoo: Kandji has published a follow-up report on the Cuckoo infostealer, a malware strain they first documented last month.
AllaSenha: Security firm Harfang has published a report on AllaSenha, a new version of the AllaKore RAT that is currently being used in the wild to target the users of Brazilian banks.
CryptoChameleon: SilentPush analyzes CryptoChameleon, a popular phishing kit designed to target cryptocurrency users.
RedTail: Akamai says the RedTail cryptomining gang has weaponized a recent Palo Alto VPN exploit in its attacks. The report also looks at the recent changes in RedTail's code.
"The attackers have taken a step forward by employing private cryptomining pools for greater control over mining outcomes despite the increased operational and financial costs. This mirrors tactics used by the Lazarus group, leading to speculation about attack attribution."
Merry-Go-Round: HUMAN has published a report on Merry-Go-Round, an ad fraud operation that uses a novel technique to open multiple tabs and load additional ads when users visit a web page part of their network.
"At its peak, Merry-Go-Round—so named for the carousel of domains the pop-unders cycle through—reached 782 million bid requests a day. This operation is still active; today, Merry-Go-Round accounts for roughly 200 million bid requests a day, and the threat actors behind both rings continue to attempt to adapt their attack, adding new domains and subdomains to both rings. This operation is unique in its level of sophistication and obfuscation; the threat actors took pains to both conceal the rings (removing referrer information in between each domain in the cycle) and to maximize their profit (requesting as many as a hundred ads on each domain in the cycle)."
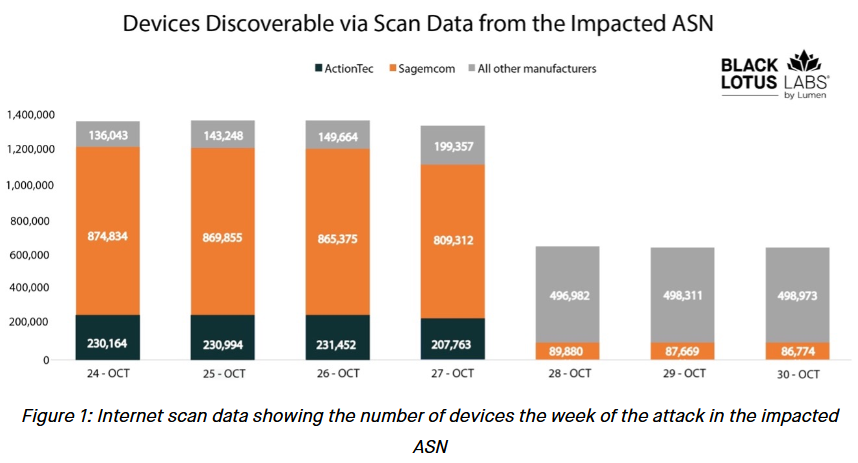
Chalubo wipe incident: Researchers from Lumen's Black Lotus Labs have discovered that a malware strain named Chalubo wiped more than 600,000 routers at the end of last year. Almost all of the affected devices were ActionTec and Sagemcom routers belonging to the internet service provider. Lumen says the malware is typically used to build DDoS botnets, and it's unclear if the attack was intentional. The company says there was no overlap between the malware's infrastructure and known APT and state-sponsored groups. Details from the Lumen report and posts on Reddit and DSLReports suggest the affected ISP might be Windstream.
Sponsor Section
Justin Kohler, VP of Product at SpecterOps, shows how BloodHound Enterprise can be used to find and fix Active Directory (mis)configurations that could let attackers easily own your entire enterprise.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Andariel: AhnLab looks at a campaign from the Andariel APT group targeting South Korean companies with the Dora RAT.
LightSpy's macOS malware: ThreatFabric looks at LightSpy, a macOS spyware strain used by the LightSpy APT group. The malware is also known as F_Warehouse.
LilacSquid: Cisco Talos researchers have published a report on a new APT group they are naming LilacSquid. The group has been active since 2021 and has used malware tools such as InkLoader, InkBox, and PurpleInk. Talos does not attribute the group to any state.
APT41: Natto Thoughts looks at APT41's reconnaissance techniques and tools.
BlueDelta (APT28): Recorded Future has published a report on a cyber-espionage campaign carried out by Russian APT group BlueDelta that primarily targeted Ukrainian and European organizations with a tangent to Russia's war in Ukraine. The final payload in this campaign was the Headlace infostealer. The campaign started in late 2023 and is ongoing.
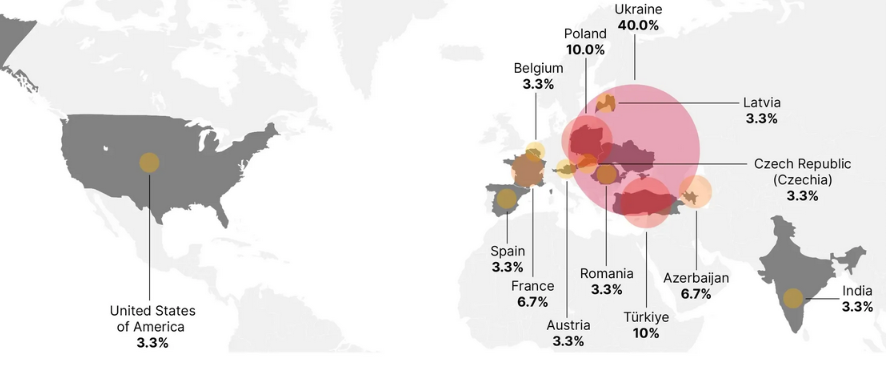
The DC Weekly disinfo network: Disinformation experts from NewsGuard have linked a network of over 150 fake local news websites to John Mark Dougan, a former American law enforcement officer who fled the US during a legal investigation and is now living in Moscow. The websites try to mimic the names and looks of legitimate US local news sites but publish Russian propaganda. NewsGuard says the sites typically publish content about Russia's invasion of Ukraine, but they have recently started switching to supporting Donald Trump ahead of the upcoming US election.
Meta disrupts influence operations: Social media company Meta says it took down more than 500 Facebook and Instagram accounts operated by Israeli political marketing firm STOIC. Meta says the company used AI-generated comments to praise Israel and criticize campus protests and antisemitism. The comments were published on posts from international media outlets, government agencies, and other public figures. The takedown was one of the multiple influence networks Meta took down in the first quarter of the year. It also took down influence networks based in Iran, Bangladesh, Croatia, and China. [More in Meta's report/PDF].
OpenAI disrupts influence operations: OpenAI has shut down accounts used by five threat actors to generate artificial content for online influence operations. This is the first time that OpenAI has moved to disrupt influence operations abusing its service. The disruptions targeted old and new threat actors alike:
- A previously unreported operation from Russia, which we dubbed "Bad Grammar," operating mainly on Telegram and targeting Ukraine, Moldova, the Baltic States, and the United States.
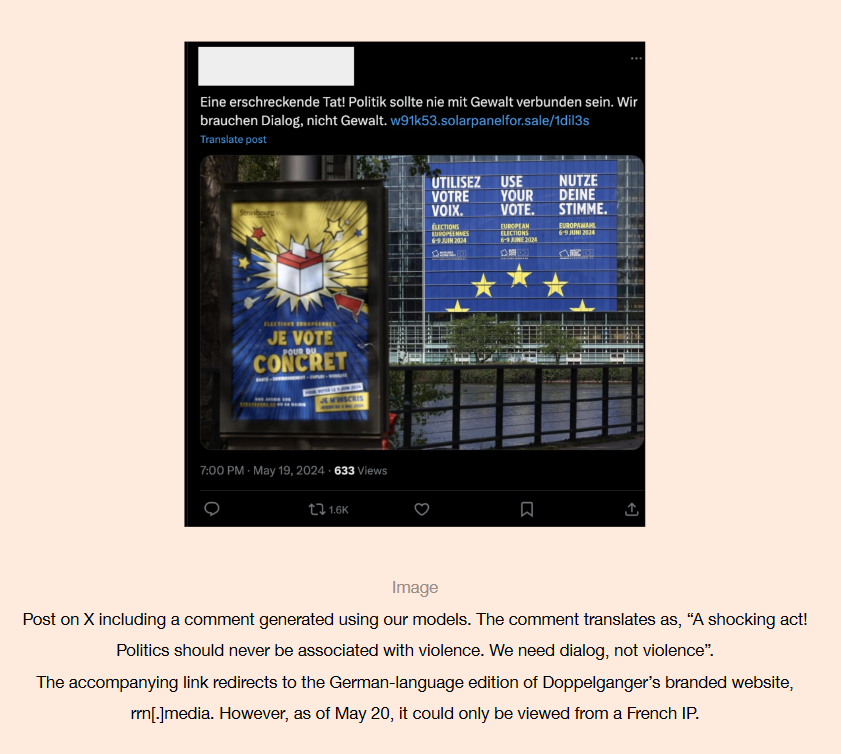
- A persistent Russian threat actor posting content about Ukraine across the internet, known as "Doppelganger."
- A persistent Chinese threat actor posting content across the internet to praise China and criticize its critics, known as "Spamouflage."
- A persistent Iranian threat actor posting web content that supported Iran and criticized Israel and the US, known as the International Union of Virtual Media (IUVM).
- A commercial company in Israel called STOIC, generating content about the Gaza conflict, and to a lesser extent the Histadrut trade unions organization in Israel and the Indian elections.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Check Point patches zero-day: Check Point has released a security update to patch a zero-day exploited in its VPN and security appliances. Tracked as CVE-2024-24919, the vulnerability is an information disclosure that allows threat actors to retrieve data from the Check Point appliance. Security firm Mnemonic says it observed threat actors use the vulnerability to enumerate and extract password hashes, including the accounts used to connect to Active Directory. Mnemonic says the earliest attacks date to April 30, a full month ahead of the patch. The attacks are related to a security advisory Check Point released earlier this week, where it warned about mysterious attacks on its VPN products. WatchTowr Labs has published a technical write-up on the bug here.
"We have observed threat actors extracting ntds.dit from compromised customers within 2-3 hours after logging in with a local user. mnemonic links this vulnerability to the activity described in our blog about the misuse of Visual Studio Code for traffic tunneling. CVE-2024-24919 was in that case used to extract user information which the threat actor then used to move laterally in the network."
Eclipse ThreadX vulnerabilities: HN Security has found three vulnerabilities in the Eclipse ThreadX real-time operating system—formerly known as the Microsoft Azure RTOS (before it was transferred over to the Eclipse Foundation).
SharePoint XXE: Trend Micro's ZDI has published a write-up of CVE-2024-30043, an XXE patched in Microsoft SharePoint servers this month.
Ivanti Landesk LPE: Security researchers at Mantodea have found a vulnerability in the Ivanti LanDesk software that could be abused to achieve local privilege escalation via arbitrary code execution. Tracked as CVE-2024-22058, the issue was patched this week.
Telerik server auth bypass: Progress Software has released a security patch to fix an authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2024-4358) in the Telerik Report Server. [h/t Screaming Goat]
"Although we have not received any reports that this vulnerability has been exploited, it is important to review your Report Server’s users list for any new Local users you have not added at {host}/Users/Index."
ASUS security updates: ASUS has released a firmware update for several router models to fix a vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-0401.
TeamCity security updates: JetBrains has released security updates for its TeamCity servers to address several vulnerabilities.
MinMax CMS backdoor: The MinMax CMS from Taiwanese company MinMax Digital Technology contains a hidden administrator account with a fixed password that cannot be removed or disabled. Tracked as CVE-2024-5514.
XZ-Utils update: The XZ-Utils library has released another version (5.6.2) to remove additional code from the hidden backdoor (CVE-2024-3094) that was inserted in its project years ago. Similar updates will most likely follow since it's hard to untangle all that code in one quick release.
AWS CloudTrail bypasses: DataDog researcher Nick Frichette has found two bypasses in AWS' CloudTrail auditing and logging tool.
"We determined that non-production AWS API endpoints could be used for permission enumeration without logging to CloudTrail. Since our initial public disclosure of this technique, we’ve collaborated closely with AWS to illustrate how adversaries could leverage this method to stealthily assess the privileges of compromised credentials. As a result of this partnership, AWS has classified this technique as a security issue and is actively remediating instances of it."
iOS/macOS PoC: Security researcher Meysam Firouzi has released a PoC for CVE-2024-27804, a vulnerability in the AppleAVD service that can crash systems.
Netflix bug bounty program: Netflix says it has now awarded more than $1 million to security researchers via its bug bounty program. Netflix launched the program in 2016, received more than 5,600 submissions, and awarded 845 payouts.
NIST backlog update: The US National Institute of Standards and Technology says it hired a new contractor to help the agency deal with the backlog of unprocessed entries in the National Vulnerability Database. NIST staff slowed down the pace of new NVD entries in mid-February, citing a need to re-organize and the increasing volume of vulnerabilities. The agency now says it expects the backlog to be cleared by the end of the fiscal year. A report published this month found that 93% of all vulnerabilities added to the NVD database over the last three months lacked metadata and other information. The contractor is Maryland-based cybersecurity company Analygence. [h/t Patrick Garrity]
Infosec industry
PHDays 2024: Talks from the Positive Hack Days 2024 security conference, which took place last week, are available on YouTube. PHDays is Russia's largest cybersecurity conference, and all the talks are in Russian.
Acquisition news: Internet infrastructure company Cloudflare has acquired BastionZero, a company specializing in remote access services.
New tool—BadDNS: Black Lantern Security has open-sourced BadDNS, a subdomain takeover detection tool.
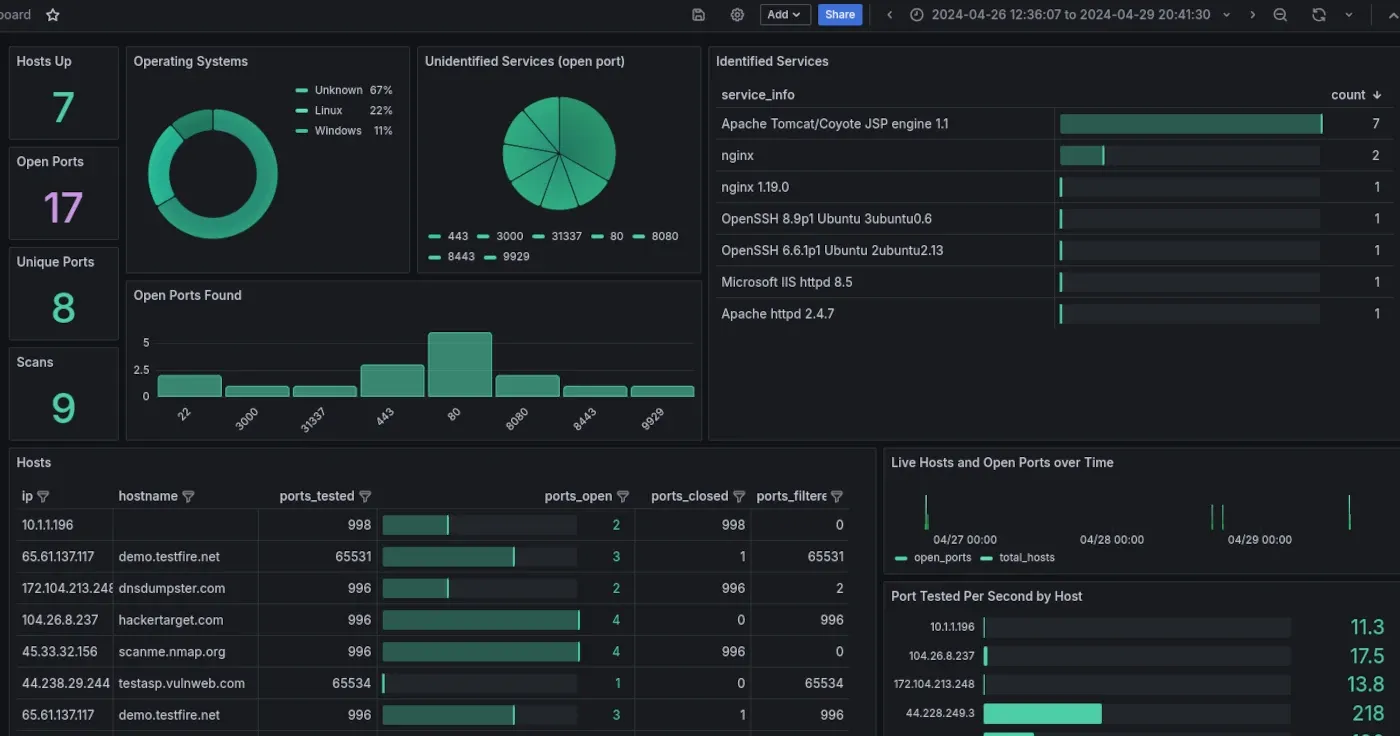
New tool—nmap-did-what: Security firm Hacker Target has released nmap-did-what, a tool to create Grafana dashboards to visualize nmap scan results.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about the role of the state in tackling ransomware, why action has been slow and ineffective, and what it will take to truly change the situation.




