Risky Biz News: Konfety gang creates an alternate reality for its mobile ad fraud
In other news: Kasperksy winds down US business; Ukraine detains fraud group stealing from dead soldiers; SSD accuses Sonicwall of hiding a security flaw.

This newsletter is brought to you by asset inventory and network visibility company runZero. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

A Russian cybercrime group named Konfety has orchestrated a massive ad fraud operation that found and utilized a novel way to disguise its malicious apps and ad traffic.
The group's operations were discovered by researchers from HUMAN Security, a company specialized in detecting bot attacks and advertising fraud.
HUMAN says the Konfety group operates out of Russia and poses as an ad network company behind an advertising SDK named CaramelAds.
To make their SDK look legitimate, the Konfety gang built and uploaded more than 250 Android apps on the official Google Play Store. These apps have simplistic functionality, are based on similar template, and they use the CaramelAds SDK in their code.
These apps are used for a cloak-and-dagger type of attack, where they represent the front of the operation.
HUMAN's security researchers say they also discovered "evil twins" of the same apps that are distributed outside the Play Store, either through malvertising, click-baiting, or unwanted drive-by downloads.
The "evil twin" apps also contain the CaramelAds SDK, but they perform ad fraud by surreptitiously loading and playing video ads on infected devices.
These malicious apps spoof the app and advertising publisher IDs of the legitimate apps listed on the Play Store to trick legitimate networks that the traffic is legitimate and is coming from the "clean" version of the apps.
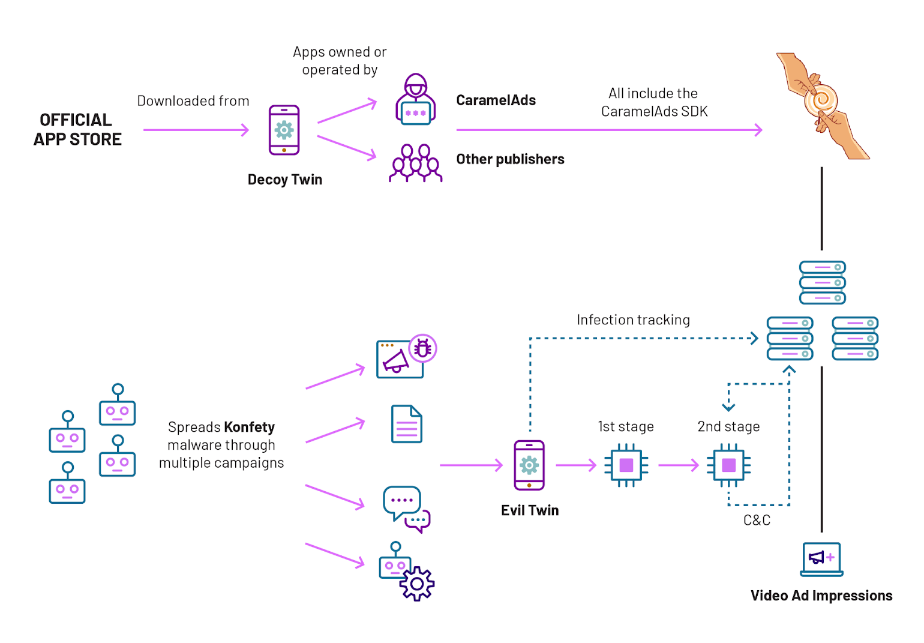
The technique is novel and is the result of past actions from Google and others who cracked down on ad fraud apps uploaded on the Play Store.
HUMAN says that at its peak, the Konfety gang was making around 10 billion requests to load video ads per day on targeted video advertising platforms, generating huge losses in revenue.
The security firm says the Konfety gang has switched the video ad platforms it abuses after it understood it was under observation.
The group's "clean" apps are still available on the Play Store. A list is available here. It is advised that users remove the apps since they can be easily turned into malicious versions within an update and abused to perform other malicious actions, such as installing other apps or stealing a user's data.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Minterest crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $1.4 million worth of assets from crosschain lending protocol Minterest. The hack took place over the past weekend and employed a flash loan attack. Minterest paused transactions to patch its platform and notified law enforcement.
LI.FI crypto-heist: Hackers have stolen nearly $10 million worth of assets from LI.FI, a cryptocurrency platform that interconnects all major blockchains and protocols. The attacker allegedly used an exploit that drained funds from users who granted LI.FI access to their wallets. The company has urged users not to interact with its apps and revoke approvals for some of its smart contracts. According to blockchain security firm PeckShield, the attacker used a variation of an older exploit that was used to hack LI.FI in March 2022 for around $600,000.
BaumankaLeaks: Pro-Ukrainian hacktivist group Cyber Resistance has hacked and leaked data from the Military Training Center (MTC), a division inside the Bauman Moscow State Technical University (BMSTU). The leaked data contains operating manuals of key Russian air defense systems and the personal data of more than a hundred young air defense/missile defense officers. Cyber Resistance claims the officers are responsible for defending the skies over Moscow and the Kremlin. Ukrainian reporters claim that some of these officers were also stationed at the Khmeimim airbase in Syria, from where Russia launched attacks on Syrian hospitals and the city of Allepo against civilian targets. [Additional coverage in InforNapalm]
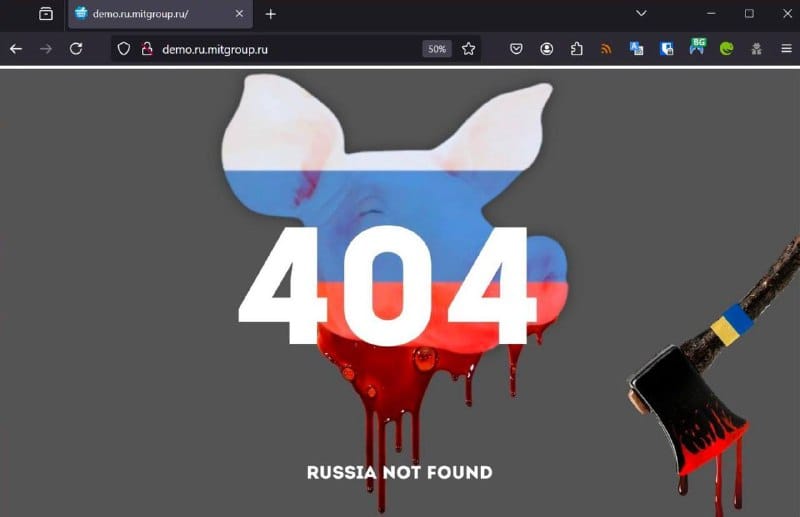
GUR's pig-head defacements: Ukraine's Defence Intelligence Main Directorate (GUR) claims it defaced more than 100 websites associated with the Russian government and companies involved in its war effort. GUR hackers replaced web pages with an image of a pig's head and the text of "404 Russia Not Found." The image of a cut-off pig's head is often used to relay a death threat in acts of intimidation. [Additional coverage in the Kyiv Independent]
General tech and privacy
EDPB audits: The European Data Protection Board has launched audits to inspect the safety and privacy of AI and messenger systems.
Trump shooter phone: The FBI says it managed to gain access to the phone of Thomas Matthew Crooks, the individual who tried to assassinate former US President Donald Trump over the weekend.
The irony of the decade: Zoom, the company that makes video conferencing software for geographically distributed teams and remote workers, is mandating a return to the office for its employees. This is being enforced by an exec who will continue to work remotely. [Additional coverage in Fortune]
Windows 11 checkpoint cumulative updates: Microsoft is introducing a new concept called checkpoint cumulative updates for Windows 11. The new update system will launch later this year with Windows 11 version 24H2. A checkpoint cumulative update will allow users to receive features and security updates through smaller update packages. These updates will only contain the changes since the previous checkpoint instead of replacing entire portions of the OS. Microsoft says this system saves time, bandwidth, and hard drive space. Besides Windows 11, the new update system will also be available for the new Windows Server 2025 OS.
"Previously with Windows 11, version 21H2, we introduced smaller downloads to Windows devices by doing range reads to only download and install binary differentials missing on the device. These binary differentials are computed against the RTM version of the binaries. When Windows 11 24H2 cumulative update is released as a checkpoint, the binary differentials in subsequent cumulative updates are generated against the version of binaries in the latest checkpoint instead of the RTM version. Therefore, these differentials are smaller and faster to apply on devices that have already synced to the latest checkpoint cumulative update."
Government, politics, and policy
Russia formally threatens YouTube: The Russian government has sent a formal letter to Google ordering the American company to unban over 200 channels they were previously using to push propaganda. The letter comes days after local media reported that Russia built a YouTube clone, began throttling traffic to the site, and was preparing to fully block the site by September.
Info warriors on US submarines: The US Navy will continue its test pilot program of embedding information warfare officers on submarines. It is now expanding the practice from its East Coast fleet to the Pacific. [Additional coverage in NextGov]
Correction on an earlier piece: On July 10, we featured a piece from The Record with a poor description that claimed that Cyber Command was phasing out its CNMF unit. Cyber Command was only phasing out CNMF's project that published malware on VirusTotal. The unit is just fine. They're now primarily working on Under Assessment, a new project where they share the same malware samples with cybersecurity partners privately. We apologize for the error. Words are hard.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Rob King, Director of Security Research at runZero, about keeping up with the stream of vulnerabilities in the KEV list and OT devices and runZero's research into the SSH protocol.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Ukraine detains fraud group stealing from dead soldiers: Ukrainian authorities have arrested five suspects accused of stealing funds from dead soldiers. Officials say the group operated out of the city of Dnipro and had access to a forensic medical examination bureau. The suspects used their access to steal the personal belongings of soldiers who died on the front, break into phones, access bank accounts, and steal money. Officials say the group stole at least $36,000 from 20 victims. They also sold some of the stolen items online.
Russians charged for Coins.ph hack: Philippine authorities have filed charges against two Russian nationals for stealing $5.8 million worth of assets from local cryptocurrency platform Coins.ph. Officials have named the suspects as Vladimir Evgenevich Avdeev and Sergey Yaschuck. The two worked as consultants for the platform and are believed to have used their access to steal the funds. The two suspects are still at large. [Additional coverage in PhilStar]
Russian hacker convicted: A Russian court has convicted a resident of Mari El for using malicious code to hack and obtain credentials from foreign servers.
SEXi rebrand: The SEXi ransomware group has apparently rebranded as APT INC, continuing the trend of ransomware gangs using the most idiotic names ever.
NullBulge: Sentinel One's Jim Walter has published a profile on NullBulge, a new threat actor that recently leaked data from Disney.
"NullBulge is a low-sophistication actor, targeting an emerging pool of victims with commodity malware and ransomware. The group's invasive targeting of AI-centric games and applications poses a threat to those working with such technologies and highlights an intriguing area of focus for threat actors. [...] Groups like NullBulge represent the ongoing threat of low-barrier-of-entry ransomware, combined with the evergreen effect of infostealer infections."
Squarespace DNS hijacks: Paradigm and Metamask researchers have published a post-mortem of the DNS hijacks that targeted Squarespace domains that had been recently migrated from Google Domain. We covered this topic in our Monday newsletter. The researchers say Squarespace mitigated the migration loophole.
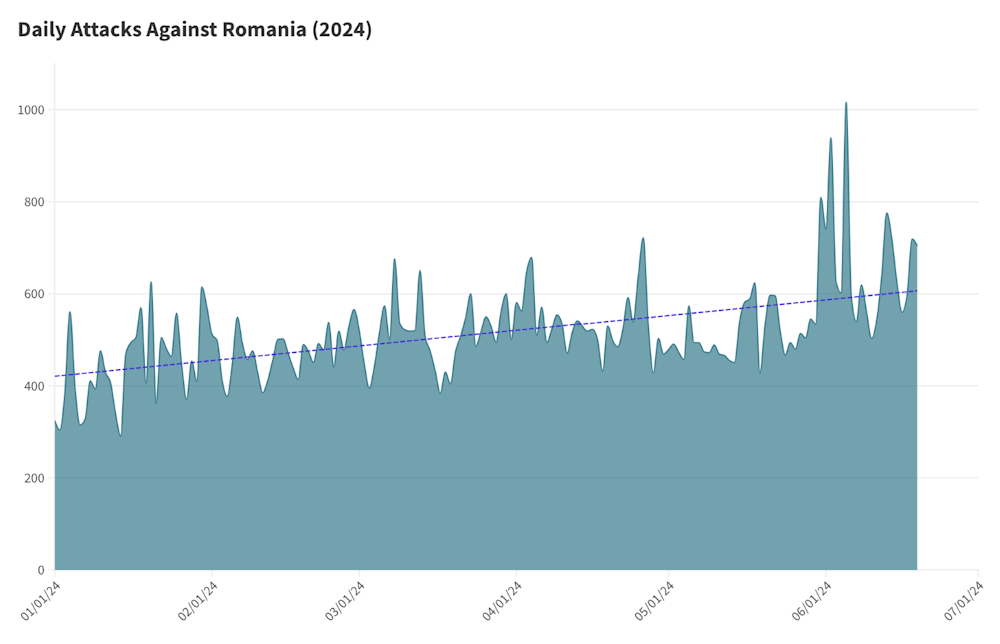
DDoS attacks targeting Romania: Netscout says that Romania has become an increasing target for geopolitical DDoS attacks. The attacks have been steadily rising since the start of June after Romania announced it would donate a Patriot missile system to Ukraine. The groups behind the attacks are pro-Kremlin threat actors such as CyberDragon, NONAME057(16), and Cyber Army of Russia. Similar upticks in DDoS attacks were also observed in Sweden and Moldova after both countries showed public support for Ukraine.
Backdoors in Russian push-button phones: A Russian security researcher has found pre-installed backdoors in the firmware of Digma push-button feature phones sold on the Russian market. The backdoor allegedly allows a remote threat actor to intercept and send SMS messages from an infected phone. The researcher who found the backdoor previously told Risky Business that they believe the phones are being used for an online service that provides virtual phone numbers. [Additional coverage in Kommersant]
Facebook malvertising epidemic: Trustwave has discovered a massive malvertising campaign abusing Facebook ads to deliver the SYS01 infostealer.
Octo Tempest/Scattered Spider adds new ransomware: Microsoft's security team says that the Octo Tempest and Oktapus group, also known as Scattered Spider, has adopted two new ransomware strains for its intrusions, such as RansomHub and Qilin. The group was previously an affiliate for the now-defunct AlphV/BlackCat RaaS.
AWS-themed npm malware: DevSecOps firm Phylum has discovered two AWS-related npm packages that contained malicious code.
"We have reported these packages for removal, however the malicious packages remained available on npm for nearly two days. This is worrying as it implies that most systems are unable to detect and promptly report on these packages, leaving developers vulnerable to attack for longer periods of time."
Threat/trend reports: Check Point, Cloudflare, NextDLP, ReliaQuest, Spamhaus [PDF], and the Linux Foundation have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
Malware technical reports
BadPack: Palo Alto Networks looks at the BadPack Android trojan.
"BadPack is an APK file intentionally packaged in a malicious way. In most cases, this means an attacker has maliciously altered header information used in the compressed file format for APK files. These tampered headers are a key feature of BadPack, and such samples typically pose a challenge for Android reverse engineering tools."
Killer Ultra: BinaryDefense researchers have published a report on Killer Ultra, a tool used by malware gangs to disable EDR, AV, and other security tools. According to BianryDefense, one of the tool's most avid users is the Qilin ransomware gang.
Sponsor Section
Senior Sales Engineer Ali Cheikh demonstrates the runZero platform to Risky Business host Patrick Gray. runZero is a cyber asset management tool that combines active scanning, passive discovery, and API integrations to discover IT, OT, and IoT assets (both managed and unmanaged) across your network, including cloud, mobile, and remote environments.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Lazarus money laundering: The Lazarus North Korean hacking group has allegedly laundered stolen cryptocurrency funds through Cambodian payments firm Huione Pay. The platform was outed last week by blockchain company Elliptic as a major money laundering hub for criminal gangs and online scammers. The same report linked the platform to the Cambodian royal family. According to a new Reuters report, Lazarus laundered at least $150,000 of stolen crypto through Huione Pay. In the meantime, cryptocurrency platform Tether has frozen $29 million worth of assets linked to the platform while it investigates the money laundering allegations.
DPRK's MiroTalk clone: Security researchers have found a boobytrapped version of the MiroTalk macOS app that appears to be part of a DPRK malware operation. The encased malware was a version of BeaverTail.
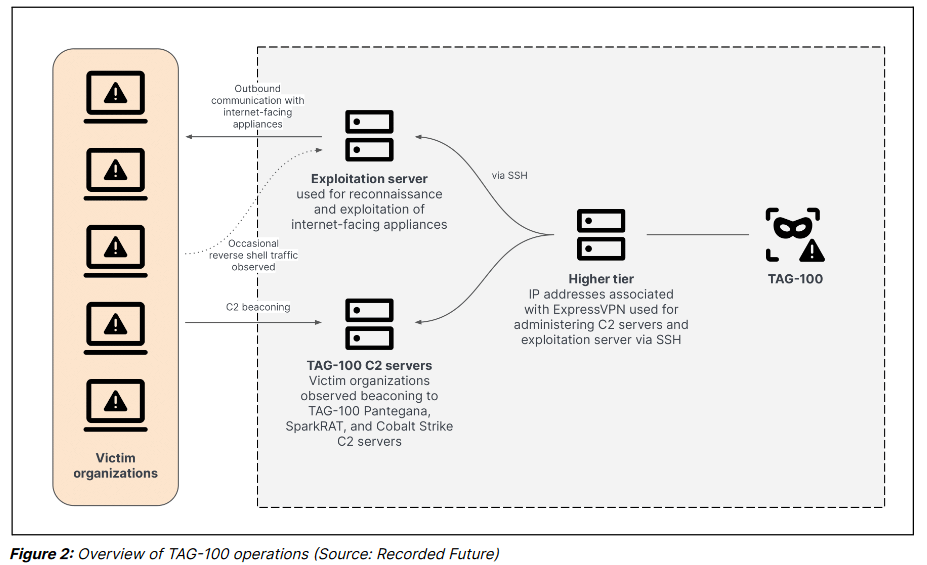
New TAG-100 group: Recorded Future has discovered a new APT group targeting internet-facing appliances for cyber-espionage operations. Named TAG-100, the group has targeted a wide array of networking gear such as Citrix NetScaler, F5 BIG-IP, Zimbra, Microsoft Exchange, SonicWall, Cisco ASA, Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect, and Fortinet FortiGate. Recorded Future says the group has successfully compromised organizations in at least ten countries, including two Asia-Pacific intergovernmental organizations.
Void Banshee's zero-day spree: An APT group named Void Banshee is behind attacks exploiting a recently disclosed Microsoft zero-day tracked as CVE-2024-38112. The attacks were independently spotted and reported to Microsoft by both Check Point and Trend Micro. Check Point says the zero-day has been exploited in the wild since January 2023. The zero-day can be used to execute files through the disabled Internet Explorer using MSHTML. Trend Micro says Void Banshee has used the zero-day to deploy the Atlantida infostealer on targeted systems.
MirrorFace recent activity: JPCERT/CC says that an APT group they are tracking as MirrorFace has expanded operations over the past year. The actor's initial targets were think tanks, universities, media, and political organizations, but it has now shifted to going after manufacturers and research institutions since last year. The group's main tools are the LODEINFO and NOOPDOOR backdoors.
Doppelganger switches support: After far-right, anti-EU, and anti-NATO party Rassemblement National lost the recent French election, Russian disinfo group Doppelganger has now switched its target. Recent disinformation campaigns are trying to prop up the far-left party La France Insoumise, according to French observers.
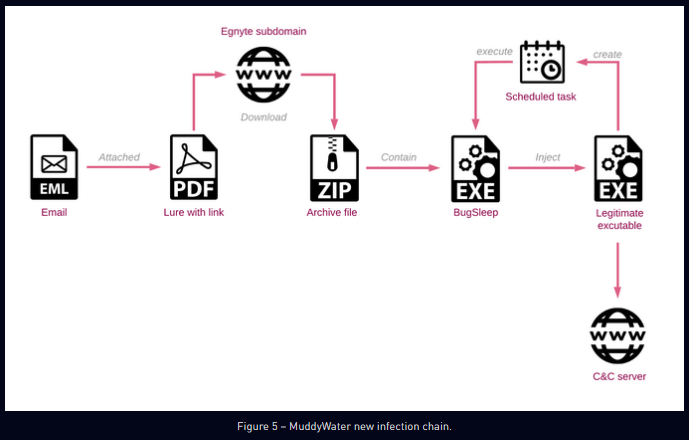
MuddyWater's BugSleep: Iranian APT group MuddyWater has significantly increased its operations targeting Israel since the beginning of the Israel-Hamas war in October 2023. According to a new Check Point report, the group's latest phishing campaigns deliver a new backdoor strain named BugSleep. Besides Israeli targets, the group's phishing campaigns have also targeted organizations in Turkey, Azerbaijan, Portugal, India, and Saudi Arabia. Sekoia has spotted the same malware, which it tracks as MuddyRot.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Major WP plugin vulnerability: The WPScan team has discovered a major vulnerability in a popular WordPress plugin named Profile Builder and its commercial version, Profile Builder Pro. The vulnerability allows threat actors to gain admin access without having any kind of account on the site. The vulnerability received a severity score of 9.8/10.
Synology vulnerabilities: Claroty has published more details on a Synology BC500 IP camera vulnerability that can be used to pivot from WAN to internal LANs. The vulnerability was used at the Pwn2Own Toronto hacking contest last year and was patched this June.
Collateral Damage exploit: Two security researchers have released Collateral Damage, a kernel exploit for the Xbox SystemOS. As the researchers say, this is not a jailbreak. It's an exploit on SystemOS, a VM where local Xbox apps run. It's an exploit designed for developers of apps for Xbox One and Xbox Series consoles.
HugeGraph exploitation: Threat actors are exploiting a recently patched vulnerability in order to hijack Apache HugeGraph database servers. Tracked as CVE-2024-27348, the vulnerability received a 9.8/10 severity rating and was patched in April. The attacks began a month after researchers published a scan script and PoC on GitHub.
GeoServer exploitation: CISA says threat actors are exploiting a recently patched vulnerability in GeoServer installations. The attacks are exploiting one of two remote code execution bugs the GeoServer team patched at the start of the month. Attacks began a week after proof-of-concept code was publicly shared on GitHub. GeoServer is an open-source software server written in Java that provides the ability to view, edit, and share geospatial data.
Microsoft CVD disaster: ZDI's Dustin Childs has published a comprehensive critique of Microsoft's vulnerability disclosure program that has consistently failed to treat researchers properly, fix bugs in time, pay bounties, and even communicate properly with bug hunters over the past year. It's actually a pretty bleak reading and something I can also confirm from our coverage of various Microsoft bug reports over the past year.
Sonicwall hidden security bug: Vulnerability disclosure platform SSD has accused Sonicwall of secretly patching a major security flaw in its SMA100 security appliances. SSD says SMA100 appliances contained a vulnerability in a feature called Classic Mode that could have been abused for RCE attacks on authenticated users. The security firm claims Sonicwall removed Classic Mode from SMA100 devices last November without telling users of the possible threat. Sonicwall didn't include the removal in patch notes, didn't assign a CVE for the bug, and did not warn customers still using older firmware. SSD has now released a write-up and exploit code.
SharePoint RCE POCs: Security researcher Nguyen Jang has published POCs for three Microsoft SharePoint remote code execution bugs (CVE-2024-38023, CVE-2024-38024, and CVE-2024-38094).
Infosec industry
New tool—RateMy8K: Cloud engineer City Hallin has launched a Mastodon bot named RateMy8K that tracks and posts about new SEC 8-K filings.
New tool—Gigaproxy: Sprocket Security has open-sourced Gigaproxy, a proxy system for pen-testing engagements that can rotate IPs using mitmproxy, AWS API Gateway, and Lambda.
Acquisition news: British open-source intelligence firm OSINT Industries is in talks to acquire its French rival OSINTracker. [Additional coverage in Intelligence Online]
Kaspersky shuts down US business: Russian security firm Kaspersky will begin to wind down its US business starting on July 20. The company has already begun laying off US employees at the start of July, according to a Twitter account named KasperSekrets. The company is winding down US operations exactly a month after the Biden administration banned sales of Kaspersky software in the US on June 20. Kaspersky vowed to fight the ban in US courts, but its latest move suggests it does not anticipate a positive outcome. [Additional coverage in Zero Day]
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq discuss Shashank Joshi's notes from a recent Oxford Cyber forum. Topics include the role of zero-days and who is ahead when it comes to offensive cyber operations.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about how South Korean internet regulations inadvertently encouraged a large ISP to hack their own customers to cut down on torrent traffic.
Abhishek Agrawal is the CEO and co-founder of Material Security, an email security company that locks down cloud email archives. Attackers have been raiding mailspools since hacking has existed, and with those mailspools now in the cloud with services like o365 and Google Workspace, guess where the attackers are going?




