Risky Biz News: EU sanctions Russian cybersecurity firms
In other news: India arrests CoWIN hackers; Australia appoints first National Cyber Security Coordinator; one of the Twitter hackers gets five years.

This newsletter is brought to you by application allowlisting software maker Airlock Digital. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
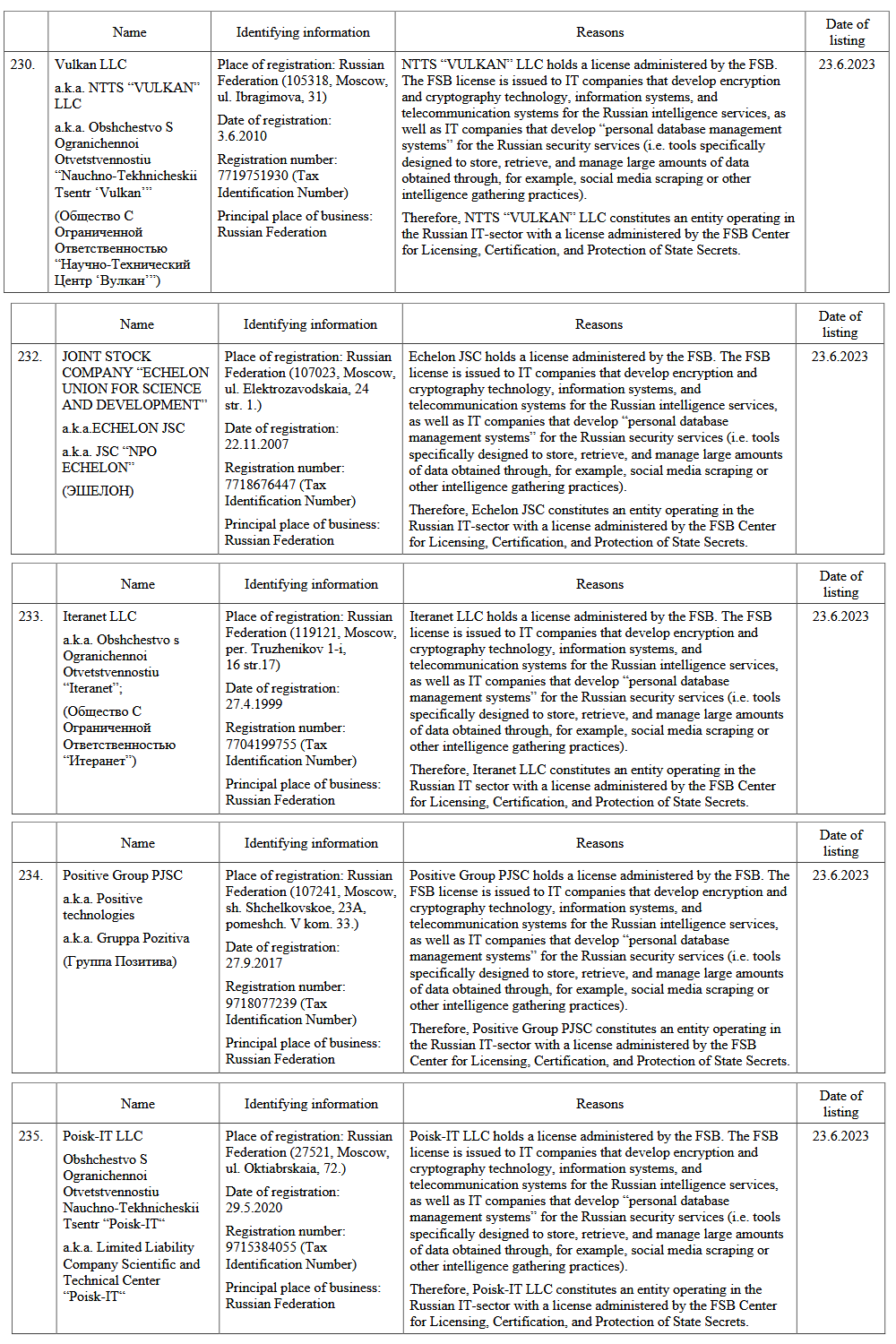
The European Union has issued its 11th package of sanctions against Russia for its invasion of Ukraine. Issued last Friday, the sanctions list was expanded with 71 individuals and 33 entities, including five Russian cybersecurity and IT companies such as Positive Technologies, NTC Vulcan, Echelon, Iteranet, and Poisk-IT.
EU officials say the companies provide IT services to support the activity of Russian intelligence services, such as developing hacking tools and data collection and analysis.
The biggest name on the list is Positive Technologies, one of Russia's largest cybersecurity companies. This is the second time the company has been sanctioned. It was also sanctioned by the US Treasury in April 2021 for providing hacking tools to the FSB and using its security conference as an FSB and GRU recruiting hub.
In a statement provided to Russian media on Friday, the company says the recent EU sanctions don't impact its business, which primarily caters to the former USSR territory. The company's EU business has been slowly dying since the 2021 sanctions and Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The company also closed down its Czech (Brno) and UK (London) offices in February this year.
The second most recognizable name on the EU's newest sanctions list is NTC Vulkan (the Scientific and Technical Center Vulkan). If the name sounds familiar, that's because the company was at the center of the VulkanLeaks earlier this year.
Documents stolen and leaked by a whistleblower from the company's internal network revealed how Vulkan had been contracted to develop offensive cyber weapons for the Russian Ministry of Defense.
The leaks exposed information about Amezit (communications interception and influence platform), Scan-AS (adversary network mapping utility), and Krystal-2B (training platform for IO/OT operations). More on these leaks from Mandiant, Sekoia, and Trustwave.
Besides Russian IT and cybersecurity companies, last week's sanctions also targeted Russia's military sector, individuals and entities involved in forced deportations and adoption of Ukrainian children to Russia, as well as Russian journalists spreading propaganda and false narratives about the war.
The full list of sanctioned entities is available here [PDF] (h/t Stefan Soesanto).
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
SolarWinds SEC case: SolarWinds says some of its current and former executives have received a Wells notice from the US Securities and Exchange Commission in connection to the company's 2020 security incident. A Wells notice is a letter the SEC sends to companies when the agency is planning to bring an enforcement action against them. SolarWinds says the SEC may fine or bar some executives from serving as officers or directors of public companies.
Battle.net DDoS attacks: ActivisionBlizzard's Battle.net client has been targeted with an hours-long DDoS attack that has prevented many of its users from connecting and playing the company's games (i.e., Diablo, Call of Duty, Overwatch, etc.). The attack took place on the same day one of the Call of Duty WSOW qualifiers was supposed to take place. They were postponed, but for unrelated reasons—CoD stats were not tracking correctly, so the qualifiers would have been based on incorrect results. Too bad the attackers didn't find out about it.
American Airlines & Southwest Airlines incident: Both American Airlines and Southeast Airlines have disclosed security incidents at a third-party vendor that exposed the information of their pilots.
General tech and privacy
DRACO Stream Cipher: Academics have developed a new stream cipher named DRACO. It was developed by ERNW Research in cooperation with the Universität Mannheim and the Universität Siegen, and has recently been presented at FSE 2023 in Kobe, Japan.
KasperskyOS: Russian cybersecurity firm KasperskyOS has previewed the first version of KasperskyOS, a new "hack-resistant" mobile operating system the company has been developing for the past years. Demoed at a business conference held in Sankt Petersburg earlier this month, the first version of the OS is equipped with basic applications for calling, SMS messaging, an address book, and a settings panel. Kaspersky says it's currently working on adding a Chromium-based web browser and support for a camera, Wi-Fi, and NFC features. The company says it's still looking to partner with a vendor to produce a smartphone, which will be made available on Russia's internal market as a replacement for devices from Western companies, such as Apple. [Additional coverage in RIA]
DuckDuckGo browser: Privacy-focused search engine DuckDuckGo has launched a Windows browser. The company launched a browser for macOS last year.
New Tor Browser out: Version 12.5 of the Tor Browser is out, with a bunch of UI improvements, including a redesigned visualization of the Tor circuit.
Government, politics, and policy
Australia's National Cyber Security Coordinator: The Australian government has named its inaugural National Cyber Security Coordinator. Air Marshal Darren Goldie will lead the government's national cyber security policy and coordinate responses to major cyber incidents. He is named to a new position established in February this year by the Australian government in response to the Optus and Medibank incidents last year.
Russia goes after web hosts: Russian telecommunications watchdog Roskomnadzor has ordered 12 foreign web hosting companies to open offices in Russia or risk fines or even access blocked to their infrastructure. The list includes the world's largest web and cloud hosting companies, such as AWS, DigitalOcean, GoDaddy, HostGator, DreamHost, Bluehost, Hetzner, WPEngine, Network Solutions, Ionos, FastComet, and Kamatera.
US Cyber Force: The Senate Armed Services Committee is formally exploring the idea of creating a dedicated Cyber Force as a branch of the US military. A provision has been added to the 2024 National Defense Authorization Act calling for an assessment of creating a dedicated Cyber Force branch. This is the first regulatory step towards the creation of an eight US uniformed military branch—after the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, Coast Guard, National Guard, and Space Force. [Additional coverage in DefenseScoop]
Cybersecurity of genomic data: US NIST has released the initial public draft of the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) for Genomic Data. The document provides basic guidance to help organizations manage cybersecurity risks for systems that process genomic data. The agency will be taking public comments on the document until July 17, 2023.
Water and wastewater security: NIST has also started the regulatory process for creating basic guidelines for managing cybersecurity risks in the water and wastewater sector. We'll probably hear more on this in the coming months or years. This usually takes a while.
EU Product Liability Directive: The EU is reviewing the EU Product Liability Directive, a law it adopted 30 years ago, to take into consideration the complex supply chains of today's manufacturing landscape.
"The proposed rules also ensure that consumers are compensated for defective products manufactured outside the EU. The proposal alleviates the burden of proof for victims under certain circumstances and obliges manufacturers to disclose information where plausible claims for compensation are made."
Sponsor section
In this sponsored Soap Box podcast Patrick Gray talks to Airlock Digital co-founders Daniel Schell and David Cottingham about living off the land.
The recent Volt Typhoon report out of Microsoft chronicled the adventures of a Chinese APT crew in US critical infrastructure. But one of the most fascinating aspects of the Volt Typhoon campaign was that the attackers almost exclusively used so-called living off the land techniques.
So the question becomes – what can you do about an attacker in your environment who has privilege and isn’t using malware?
Cybercrime and threat intel
India arrests CoWIN hackers: Indian authorities have arrested two brothers for accessing and stealing information from India's COVID-19 vaccination scheduling platform. Officials say the duo used their mother's nurse credentials to access the country's CoWIN platform. The collected information was used to build a Telegram bot that returned the personal details of Indian citizens based on a phone number. The arrests contradict an earlier statement from the Indian government that claimed the CoWIN database was not hacked and the Telegram bot was only showing information from other third-party breaches. Officials also said they received help from Telegram, which is odd because the company has made a name for itself by hosting all types of criminal channels and rarely cooperating with authorities. [Additional coverage in the Indian Express]
PlugWalkJoe sentenced: A US judge has sentenced 24-year-old UK national Joseph James O'Connor to five years in prison over his role in the 2020 Twitter hack. Known online under his hacker pseudonym of "PlugwalkJoe," O'Connor is one of four detained hackers who broke into Twitter's backend in July 2020. The group used their access to post tweets promoting a cryptocurrency scam to 130 high-profile Twitter accounts. Tweets were posted on the official accounts of Apple, Uber, Bill Gates, Elon Musk, Joe Biden, and Barack Obama, to name a few. He was also found guilty of conducting SIM-swapping attacks and stealing $794,000 from a US-based cryptocurrency company. The US is seeking $2 million in forfeiture and O'Connor will get credit for 28 months already served.
Monopoly Market admin charged: The US has charged Croatian and Serbian national Milomir Desnica with running the Monopoly dark web marketplace. Desnica was arrested in November 2022 in Austria and extradited to the US. The Monopoly Market served as a drug trading marketplace on the dark web. It was taken down by German authorities in December 2021. Intelligence collected during the takedown was used to detain 288 drug traders in May this year, part of Operation SpecTor. Europol called it its most successful operation against dark web marketplaces so far.
Nigerians extradited for IRS claims fraud: Four Nigerian men were detained and extradited to the US to face charges of fraud. The DOJ says the quartet used the stolen identities of US citizens to file false and fraudulent tax returns with the IRS.
Apple state-sponsor attack notifications: Apple has sent out a new wave of threat notifications, the type of notifications the company sends out when its users have been attacked using spyware or state-sponsored-linked malware. Social media reports suggest some victims are based in Jordan.
Cyberattack prevented in Romania: Romania's intelligence service SRI and the DIICOT anti-terrorist division say they thwarted a cyberattack planned by a Romanian national. The attack was meant to disrupt the second meeting of the European Political Community, which was held in Moldova at the start of the month. The summit hosted the heads of state from 45 European countries and primarily focused on the war in Ukraine and Moldova's plan to join the EU. [Additional coverage in HotNews]
Brothel tracking app dismantled: South Korean police have arrested 15 suspects who built and operated a mobile app used by more than 6,400 brothels across the country. The app was used to collect and index the phone numbers and personal information of brothel visitors. It was used by brothel owners to track customers, their sexual preferences, and potentially identify police stings. South Korean police say the app collected the information of millions of customers. Police also linked the app's database to a series of criminal schemes that extorted brothel visitors. [Additional coverage in 1Gan]
FBI seizes BreachForums clone: The FBI has seized an underground cybercrime forum going by Breached[.]vc. The forum was created by Pompompurin, the admin of BreachForums, and served as a backup to the main site. Authorities seized the original BreachForums and detained Pompompurin earlier this year. They seized this backup and other domains owned by Pompompurin last week in a follow-up action. Big rops to the FBI graphics department, who added a handcuffed version of Pompompurin's avatar to the seizure banner. Btw, this domain is different from breachforums[.]vc, another BreachForums clone run by ShinyHunters that is still active. A history of BreachForums is also available on the CyberInt blog.

New npm malware: Fifteen new malicious npm packages were discovered last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for more details.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with six new vulnerabilities that are currently being actively exploited. The list includes recently patched vulnerabilities from VMWare, Zyxel, and Apple. The Apple bugs include two zero-days exploited during Operation Triangulation. The Russian government claimed the zero-days were exploited by the NSA to spy on Russian government officials, foreign diplomats working in Russia, and Kaspersky employees.
Zero-Day Shop: CyFirma researchers have identified a new underground cybercrime marketplace named the Zero-Day Shop that sells access to a wide selection of compromised and backdoored servers, such RDPs, email servers, cPanel installs, and WordPress sites. The site launched in April and is currently advertised via Telegram.
Malware technical reports
RDPCredentialStealer: ThreatMon researchers have published a report breaking down RDPCredentialStealer, a malware strain designed to extract credentials entered by users during RDP sessions.
PindOS: DeepInstinct has documented a new strain of a JavaScript-based dropper named PindOS that is currently used to install Bumblebee and IcedID on infected systems.
SmokeLoader: Embee researchers have published a tutorial on decoding SmokeLoader using Procmon.
JokerSpy: Elastic's security team says that a macOS backdoor discovered by Bitdefender earlier this month has been used in an attempt to hack a cryptocurrency exchange based in Japan. The company is a major trader in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other common cryptocurrencies—but remained unnamed in Elastic's report. The malware is named JokerSpy and contains advanced backdoor capabilities. Elastic says the malware was used together with several custom and open-source macOS reconnaissance and hacking utilities as part of an intrusion they are attributing to a threat actor named REF9134.
Trigona ransomware: Trend Micro has a breakdown of the Trigona ransomware Linux and Windows versions.
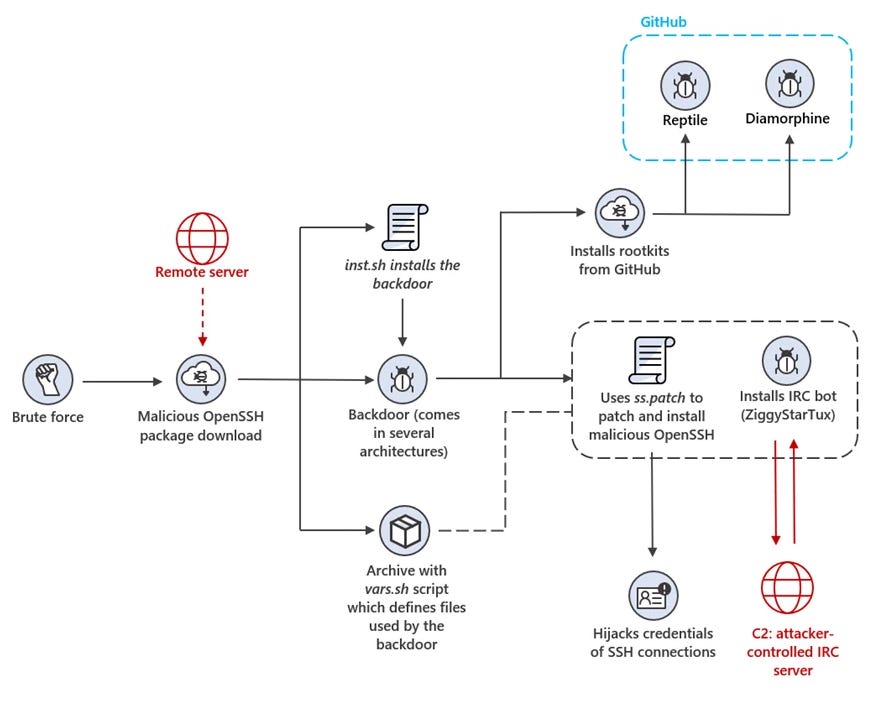
Cryptomining botnet: Microsoft has discovered a criminal operation backdooring Linux and IoT devices and deploying a crypto-miner. The group gains access to systems via brute-force attacks and deploys backdoored versions of OpenSSH and two open-source rootkits for future access. Infected devices are then controlled via an IRC bot. Microsoft says it traced the campaign to a user named Asterzeu on the CardingForum[.]cx cybercrime forum.
Risky Business Demo
Airlock Digital is one of this newsletter's supporters and this week's featured sponsor. Airlock Digital CEO David Cottingham held a product demo with Patrick Gray, the host of the main Risky Business podcast, showing how Airlock's allow-listing product works.
APTs and cyber-espionage
Ukraine sees surge in cyberattacks: Russia has ramped up its cyber operations targeting Ukraine in the aftermath of Kiyv's counteroffensive, White House Deputy National Security Adviser Anne Neuberger said last week at the FT Cyber Resilience Summit in Washington. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Trellix Cyberthreat Report: Trellix has released its Q1 2023 Cyberthreat Report. According to the company's detection data, 79% of nation-state threat activity is linked to China. The most active groups are Mustang Panda and UNC4191.
Kimsuky: AhnLab has published a report on a recent Kimsuky operation that unfolded in May. The campaign leveraged malicious CHM files, and unlike past campaigns that used documents on North Korea-related topics, this attack used a variety of lures and subjects.
OceanLotus: Chinese researchers at Th0r Security have published an analysis of recent OceanLotus campaigns.
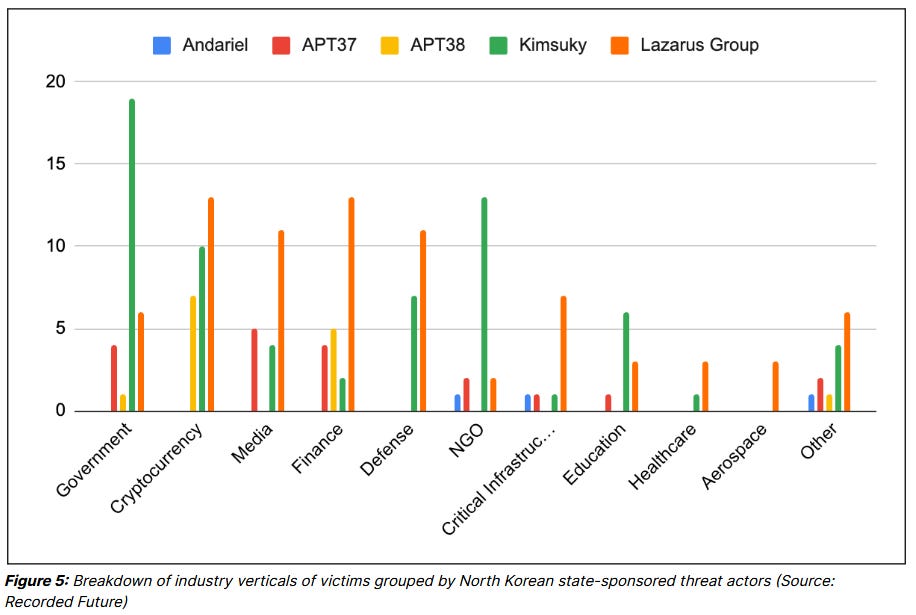
North Korea cyber: Recorded Future has analyzed data from 273 cyberattacks attributed to North Korean state-sponsored groups. The data shows what industry vertical and geographical region each APT group is specialized in and focuses on.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
RepoJacking research: Almost 37,000 GitHub repositories are vulnerable to repojacking, according to a scan of 1.25 million projects conducted by Aqua Security. Repojacking is a class of attacks where threat actors hijack legitimate projects by registering retired project names or old usernames that have been freed up. This allows threat actors to gain the ability to load code in legitimate projects and their respective upstreams. Aqua researchers say that by extrapolating the results of their study to GitHub's entire project base, they believe that the true number of projects vulnerable to repojacking might be in the millions.
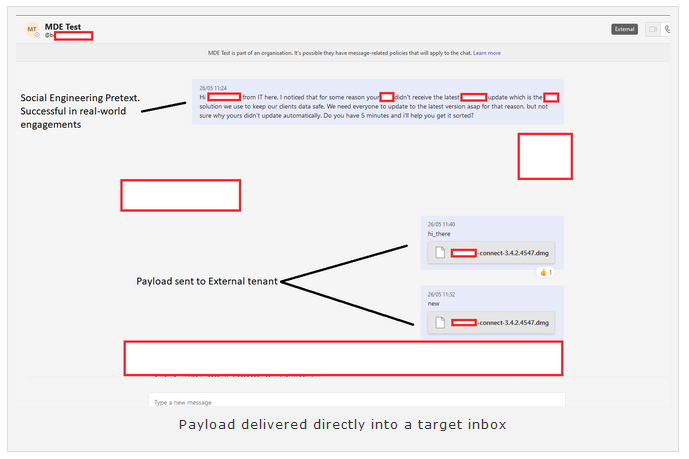
Microsoft Teams IDOR: JUMPSEC researchers have discovered an IDOR vulnerability in the Microsoft Teams service that can allow a malicious actor to introduce malware into an organization's Teams service. The researchers say the vulnerability bypasses the Microsoft Teams client-side security controls that prevent external tenants from sending files to an organization's members. JUMPSEC says it reported the issue to Microsoft, but the company declined to release a patch.
Infosec industry
Tool update—ZMap: ZMap v3 is out.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at three different state operations that have recently been outed and what these operations tell us about how these states are behaving.




