Risky Biz News: Edge adds new sandbox escape protection
In other news: Data breach impacts 43 million French citizens; E-Root admin sentenced to 3.5 years in prison; BlackByte ransomware returns.

This newsletter is brought to you by Kroll. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Microsoft has developed a new security protection for its Edge web browser.
The new feature—which has no official name—aims to stop sandbox escape attacks.
The Microsoft Edge security team explains how the new protection works at a higher technical level in a blog post here.
In a super simplified explanation—the new protection works by crashing the JavaScript rendering process when an attacker tries to escape the sandbox (where a website's code is executed) and then pivot to a more high-privileged internal browser component.
It basically crashes the Renderer Process when attackers try to mess with MojoJS settings—MojoJS being the component that allows Chromium processes to talk and interact with each other.
The new feature is scheduled to roll out to all Edge users with the release of version 123 later this week.
The new protection has also been added to the Chromium open-source browser, although it's unclear when it will reach Chrome, Opera, Vivaldi, and the other Chromium-based browsers.
This marks the Edge team's second major contribution to the Chromium codebase (they had plenty, but we're only talking about the big ones). Google recently added a JITless mode to Chrome after Edge first pioneered and tested the tech back in 2021.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
France Travail cyberattack: Hackers have breached France's unemployment agency and stolen the personal data of nearly 43 million people. The breach affected anyone who used the agency to find a job or seek financial aid. The breach took place in February this year. The agency says hackers didn't access any financial information. [Additional coverage in Le Monde]
IMF breach: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has disclosed a security breach that impacted 11 email accounts. The IMF says it discovered the hack on February 16 and has since resecured the compromised users. The organization says the investigation is still ongoing and did not formally attribute the intrusion.
Mozaic crypto-heist: The Mozaic cryptocurrency platform says that a former developer stole $2 million worth of assets from its accounts. Mozaic claims the former developer compromised a core team member and stole the private keys of a security module. They used the keys to steal funds from a fail-safe vault mechanism before it was set to be phased out. Mozaic revoked access to its systems for all employees as it investigates the hack. The company says 90% of the stolen funds have been frozen at third-party platforms and are likely to be returned.
General tech and privacy
McDonald's IT outage: McDonald's restaurants and some online services were down on Friday in what the company described as an IT outage at a third-party provider. Similar IT outages also hit Tesco and Sainsbury on the same day. Sainsbury blamed it on a software update.
Microsoft shenanigans: Microsoft is injecting popups into the Chrome browser in an attempt to get users to switch to Edge and Bing. The popups are appearing on Windows 10 and 11. This is the second time they have shown up after Microsoft pulled off the same stunt last year and called it "unintended behaviour." [Additional coverage in 9to5Google]
Cloudflare stats: Cloudflare has lost 22% of domains hosted on its infrastructure after Freenom stopped managing the .tk domain space. More than 12.6 million .tk domains have now been nulled and stopped revolving, according to Netcraft. Other domains that disappeared with the Freenom shutdown include .cf and .gq.
Twitter loses brand safety seal: After an influx of malicious ads redirecting users to crypto-scams for months and months, Twitter has lost its Brand Safety certification from the TAG ad-tech industry group.
Gab goes after fReE sPeEcH: Gab, a far-right social media platform that billed itself as the platform of free speech, has announced plans to start moderating its content.
"After facing a barrage of threats, doxxing, and other unhinged behavior over the past few weeks I've come to the conclusion that these subversive mentally ill people don’t deserve the freedom of speech, they deserve to be committed. [...] Threats and harassment are not protected by the First Amendment and they aren’t protected by Gab's terms of service. In the past we have been far too forgiving and lenient with giving people second, third, and fourth chances to change their behavior. That ends now."
Government, politics, and policy
Russia's presidential election: Rostelecom CEO Mikhail Oseevsky claimed that Ukraine's military intelligence service GUR tried to destroy Russia's electronic voting system. GUR called the statement propaganda and proceeded to mock him on their Telegram channel.
Rostelekom blocks SIP: Rostelekom is blocking the SIP protocol on its Russian network. In a letter to affected customers, the company claimed it acted on orders from the Russian Federal Security Service. The block has affected telephony services at smaller companies all over Russia.
US cybersecurity budget: The Biden administration has requested $13 billion to fund cybersecurity programs across multiple US federal agencies. CISA is set to receive $3 billion under a budget proposal for the 2025 fiscal year. The budget proposal includes $394 million for CISA's Joint Collaborative Environment (JCE), a program that allows private sector entities to work on joint CISA projects. It also allocates $116 million for new CISA staff and technology to support the agency's new cyber incident reporting program (CIRCIA). The White House’s budget proposal is unlikely to pass Congress but experts say it proves the administration’s dedication to improving cybersecurity across the US. [Additional coverage in FederalNewsNetwork and CyberScoop]
US Cyber Trust Mark: The FCC has formally adopted a voluntary cybersecurity labeling scheme for internet-connected devices. Named the US Cyber Trust Mark, the program was announced by the White House in July of last year. It allows vendors to apply a special shield logo on their devices if they meet basic cybersecurity requirements. Criteria include having unique and strong default passwords, receiving security updates, and restricting access to their management interfaces.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with George Glass, Senior Vice-President for Kroll's Cyber Risk business. George covers the company's latest report, a Kimsuky attack on ConnectWise ScreenConnect devices with a new malware strain named ToddlerShark.

Cybercrime and threat intel
E-Root admin sentenced: US authorities have sentenced the administrator of the E-Root cybercrime marketplace to 42 months in prison. Moldovan national Sandu Boris Diaconu was arrested while trying to leave the UK in May 2021 and was extradited to the US last October. Officials say he ran a network of sites called E-Root where threat actors sold more than 350,000 user account credentials.
Telco manager SIM swapper: A former manager of a New Jersey telco has pleaded guilty to participating in SIM swapping attacks. Jonathan Katz admitted to using his manager credentials to change SIM details for customers. Katz was allegedly paid in Bitcoin for each SIM swap. Authorities identified Katz after tracing threat actor transactions to his personal account.
US recovers pig butchering funds: The US Justice Department has recovered $2.3 million worth of cryptocurrency stolen through pig-butchering romance scams.
Onerep profile: Infosec reporter Brian Krebs has published a profile on Onerep, a service that claims to be able to remove people's data from more than 200 websites. While the company bills itself as a US-based business, Krebs found the site was operated out of Belarus and Cyprus. He also found links between Onerep and tens of people-searching services.
Threat/trend reports: Some infosec reports covering industry threats and trends came out from BlackBerry, F5 Networks, CPX, and ResearchAndMarkets.
New npm malware: Thirty malicious npm packages were discovered last week. Check out GitHub's security advisory portal for additional details.
Azure Batch abuse: Stephan Berger describes how a threat actor has abused Azure Batch for hidden crypto-mining operations.
Synapse ransomware claims: As first spotted by CyFirma's Kaushík Pał, the developer of the new Synapse ransomware has released a demo on hacking forums in an attempt to prove his encrypter is the fastest ransomware to encrypt files to date.
BlackByte returns: The BlackByte ransomware gang has resumed activity after a five-month hiatus. The group has returned with a new look and a new dark web leak site. Its previous site had been dormant since October of last year. The gang has listed a new victim, a California-based wastewater utility.
Malware technical reports
Pipedream framework: Security researcher Diablohorn has published an analysis of Pipedream (Incontroller), a framework for attacking OT networks.
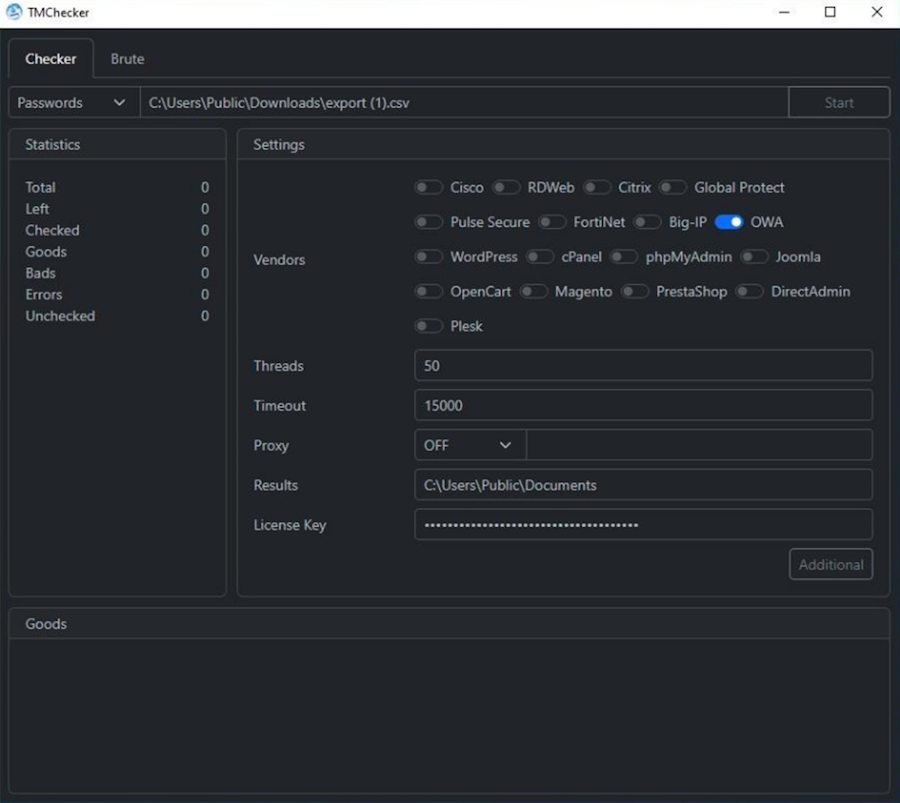
TMChecker: Resecurity has a report out on TMChecker, a tool designed to attack remote-access services and popular e-commerce applications. The tool can carry out brute-force attacks or can check the validity of compromised credentials. Currently, it supports 17 different platforms, from Joomla to Pulse Secure and from FTP to RDP.
Azorult: Netskope researchers analyze one of the recent malspam campaigns using HTML smuggling to deliver the Azorult infostealer.
Nikki Stealer: CyFirma researchers look at Nikki Stealer, a new infostealer that was developed by a threat actor named Sk4yx. The same individual also developed the older Crow Stealer and has a long history of website defacements.
GlorySprout: Malware analyst RussianPanda has published a blog post on GlorySprout, a new infostealer that was put up for sale on hacking forums earlier this month. GlorySprout appears to be a clone of the more popular Taurus Stealer.
SnakeKeylogger: Cisco's Splunk team looks at the SnakeKeylogger. This is the .NET version that's been in the wild since November 2020. There's also a Python one with the same name going around.
LESLIELOADER: Kroll's security team has discovered a new malware loader used in campaigns in the wild. The malware is named LESLIELOADER and is written in the Go programming language. Kroll researchers believe the malware was based on top of an open-source project published on GitHub in June last year.
BunnyLoader 3.0: A new Malware-as-a-Service named BunnyLoader is making a name for itself in the cybercrime underground. The service launched in September last year and has already reached version 3.0. Its developer claims it redesigned 90% of the code. According to Palo Alto Networks, the malware now includes modules for stealing keystrokes, credential theft, clipboard hijacking, and fileless loading. There's also a DDoS module and an update to the C&C comms feature.
StopCrypt ransomware: SonicWall researchers have published an analysis of a new variant of the StopCrypt ransomware.
RA World: Fortinet analyzes RA World, a rebranded version of last year's RA Group RaaS platform. A similar report is also available from Trend Micro.
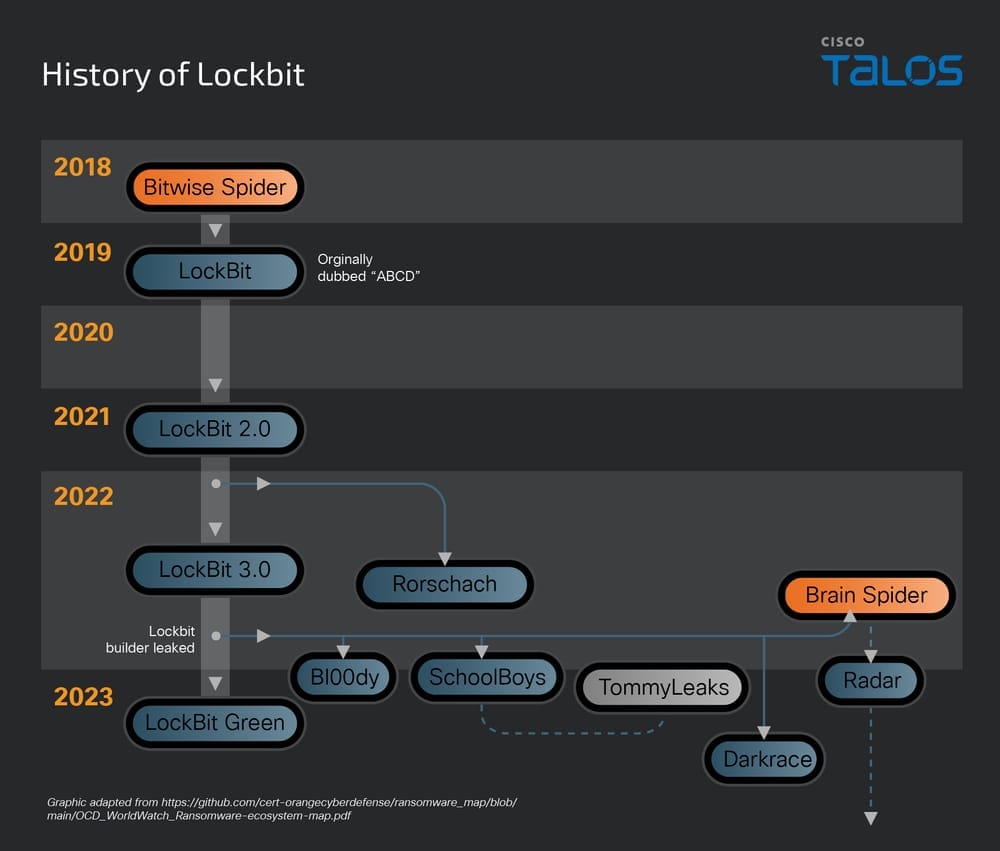
LockBit ransomware: Cisco Talos looks at the history of the recently disrupted LockBit ransomware gang and how the company anticipates the group is gonna regroup and come back online.
"Talos has intelligence that Lockbit is still accepting affiliates into their program."
A report on LockBit post-takedown activity is also available from ThreatMon.
Sponsor Section
The Kroll CTI team observed a campaign using a new malware that appears to be very similar to BABYSHARK, previously reported to have been developed and used by the APT group Kimsuky (KTA082). Read more.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Konni: South Korean firm Genians has published a report on Konni APT operations targeting cryptocurrency organizations.
Kimsuky: Qihoo 360 researchers look at a recent Kimsuky APT malware strain designed to steal user data from Naver Whale web browsers.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
NIST support letter: The infosec community is gathering in support and signing an open letter that asks Congress to allocate more resources to NIST in order to properly manage the NVD, the National Vulnerability Database. We covered all the recent NIST NVD issues in our last edition.
EOL WP plugins: Security firm miniOrange has retired two plugins that contain major security flaws. The plugins allow unauthenticated attackers to grant themselves admin rights by updating a user password. The miniOrange Malware Scanner and the miniOrange Web Application Firewall were removed from the WordPress plugin index, but they are still installed on more than 10,000 websites.
5Ghoul impact: SANS ISC researchers have looked at the impact of the 5Ghoul vulnerabilities three months after their disclosure. 5Ghoul is a collection of 14 vulnerabilities in 5G modems from Qualcomm and MediaTek. They impact more than 710 modern smartphone models. Three months later, SANS ISC says some devices are still waiting for patches—which is not a real surprise if you're familiar with the hardware ecosystem and the Android space.
QNAP exposure: There are more than 8,500 QNAP NAS devices exposed on the internet that are vulnerable to a recently disclosed vulnerability. Tracked as CVE-2024-21899, the vulnerability allows attackers to bypass authentication and take over the device. Proof of concept code was published online, but no exploitation has yet been observed. QNAP released patches for affected devices on March 9.
GoAnywhere security updates: Fortra has published a security update for its beleaguered GoAnywhere MFT.
Infosec industry
New tool—uBlacklist: GitHub user Laylavish has put together uBlocklist, a huge blocklist for the uBlock Origin ad-blocker that can block websites known for using AI-generated content.
New tool—BlueSpy: TarLogic has open-sourced a tool named BlueSpy, a proof of concept for exploiting vulnerabilities in Bluetooth headsets and eavesdropping on private conversations.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at recent efforts to disrupt ransomware gangs and discuss what could make these efforts more effective.




