Risky Biz News: DNSBomb attack is here! Pew pew pew!!!
In other news: Rockwell tells customers to disconnect ICS gear from the internet; Linguistic Lumberjack vulnerability impacts most cloud providers; Incognito Market admin arrested.

This newsletter is brought to you by Proofpoint. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

A team of academics from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China has discovered a new method of launching large-scale DDoS attacks using DNS traffic.
The new attack is named DNSBomb, and is a variation of a 2003 paper that described a DDoS attack technique using TCP pulses.
DNSBomb takes the same concept but re-implements it using DNS software and modern-day DNS server infrastructure, such as recursive resolvers and authoritative nameservers.
The DNSBomb paper and the graph below explain the entire concept better, but in a very simplified version, a DNSBomb attack works by sending a slow trickle of modified DNS requests to DNS servers, which bounce the data around, amplify its packet size, and withhold it to release everything at once in a pulse of DNS traffic aimed at a target.
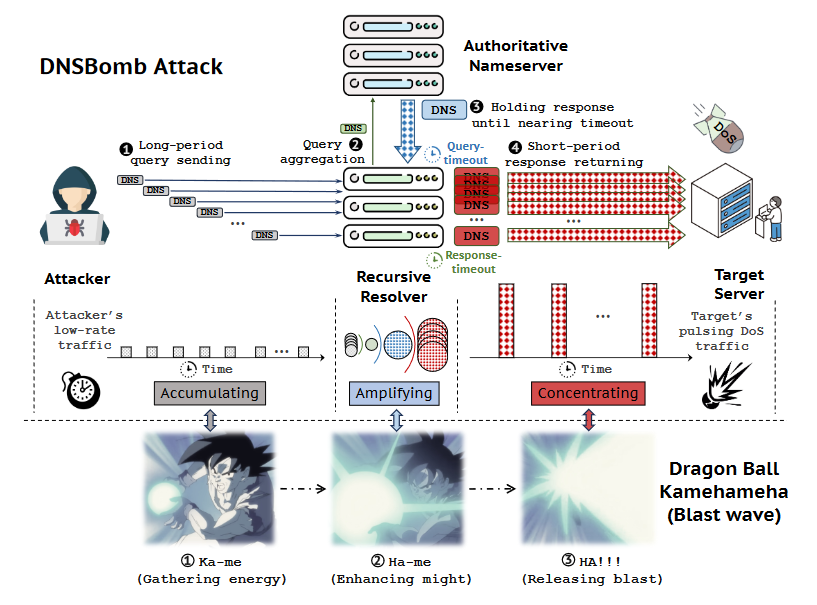
The research team says it tested its technique against 10 mainstream DNS software and 46 public DNS services and was able to launch DNSBomb attacks that reached up to 8.7 Gbps, with the initial DNS traffic being amplified up to 20,000 its initial size.
The numbers put DNSBomb in the sights of DDoS botnet herders and DDoS-for-hire service operators.
Researchers disclosed the attack to all affected parties, and 24 organizations have acknowledged the research and are releasing patches. Affected organizations include a who's who list of DNS providers.
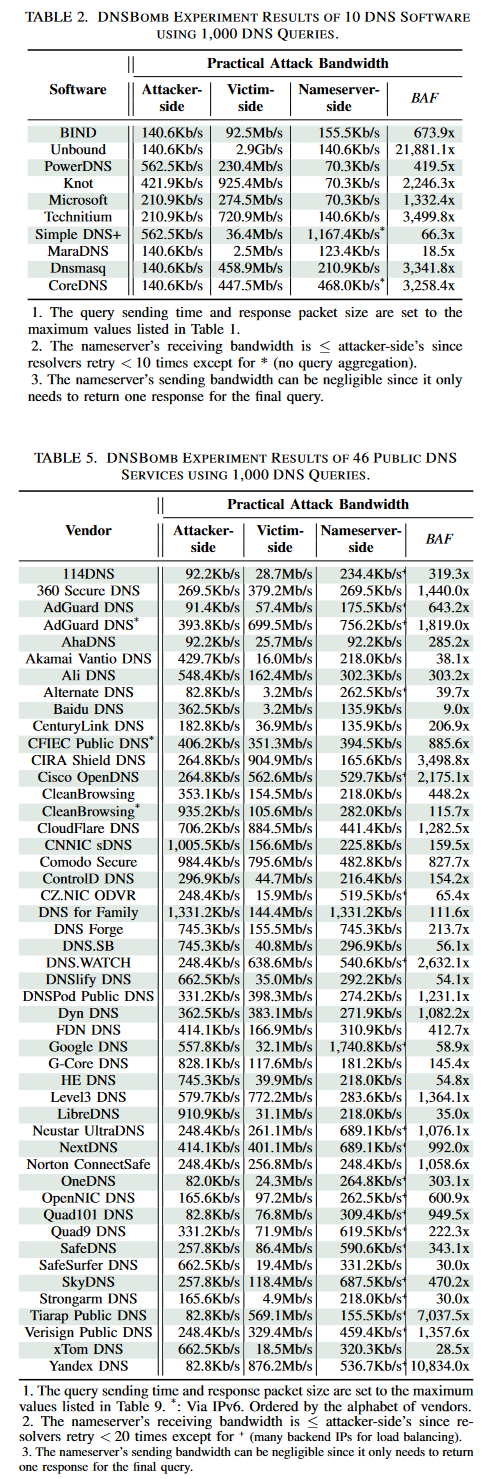
The DNSBomb attack is tracked under the CVE-2024-33655 identifier, and the research is being presented this week at the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, held in San Francisco.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Gala Games crypto-heist: A threat actor is believed to have exploited a vulnerability in the Gala web3 gaming platform in a security breach on Monday. Gala says the attacker minted more than $200 million worth of Gala tokens for themselves and successfully managed to steal $21 million before the assets were frozen. The company claims it has already identified the hacker and is now working with US authorities.
ARRL ransomware incident: The American Radio Relay League has fallen victim to a ransomware attack on May 16, last week. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
Patriot Mobile breach: "America's only Christian conservative wireless provider" Patriot Mobile has suffered a data breach. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
General tech and privacy
Windows 11 security features: Microsoft has published a blog post with all the security features shipping with Windows 11 in the coming months.
Windows Recall: Microsoft has lost its mind and launched a new feature named Recall that uses AI to record all of a user's actions so users can search it later. Totally not creepy at all.
Zoom adds PQE: Zoom has rolled out support for post-quantum end-to-end encryption for its video conferencing software.
Government, politics, and policy
US EPA future cyber enforcement: The US Environmental Protection Agency has urged water utilities to improve their cybersecurity defenses. The agency says that recent inspections found that over 70% of water utilities fail to meet basic cybersecurity standards. The EPA says it found systems with critical unpatched vulnerabilities and default passwords. The agency has issued an enforcement alert and says it plans to take civil and criminal actions if utility providers fail to secure their networks.
UPGRADE program: The US government is investing $50 million into a program to create IT tools to protect hospitals from cyberattacks. The new program is named UPGRADE, or Universal PatchinG and Remediation for Autonomous DEfense. UPGRADE will be capable of testing hospital networks, identifying vulnerable systems, and automatically testing and deploying patches. The purpose of the program is to keep networks up to date with minimal effort from the hospital's IT staff.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Proofpoint senior threat intelligence analyst Selena Larson about the latest changes in the threat actor landscape in the aftermath of several law enforcement takedowns and Microsoft tech stack changes.

Cybercrime and threat intel
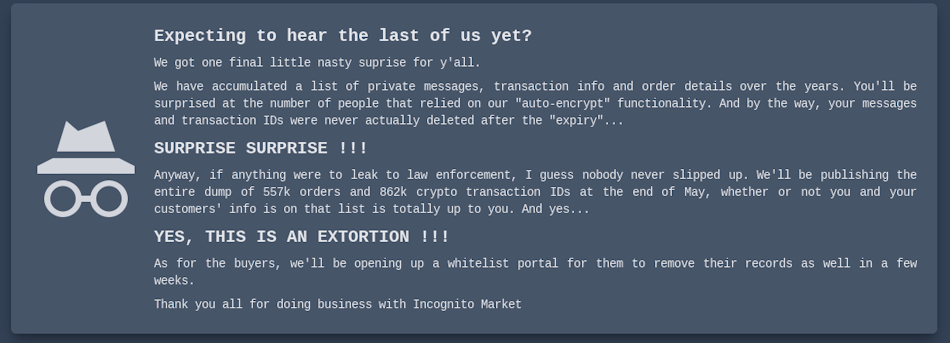
Incognito Market admin arrested: US authorities have detained and charged a Taiwanese national on charges of running the Incognito dark web marketplace. Officials say Rui-Siang Lin was the architect of Incognito, where users bought and sold narcotics worth $100 million. He was arrested at the JFK Airport in New York over the weekend. The arrest comes two months after Lin exit-scammed and ran away with his users' money in March. Days after he shut down the site, Lin extorted Incognito users. He demanded payments of between $100 and $20,000 from the site's vendors and buyers, threatening to publish their data. Lin also mocked users for trusting the platform.
BreachForums replacements: A threat actor named USDoD has teased a new replacement for the seized BreachForums. The new forum will be named Breach Nation and will launch on July 4 at breachnation[.]io.
Ikaruz Red Team activity: SentinelOne has published a profile on Ikaruz Red Team, a hacktivist group using ransomware attacks as part of its operations against the Philippines. One of its past targets was an attack against the Department of Science and Technology, where the group tried to pose as the country's CERT service.
Data destruction campaign in Italy: A threat actor posing as a member of the Italian Socialist Party is carrying out data destruction attacks against Italian organizations. The attacks are political in nature and are in response to Italy's stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict. According to Sonicwall, the threat actor is using a version of the leaked Chaos ransomware to encrypt files but does not provide a way to decrypt files.
Werewolves (LockBit) campaign in Russia: Russian security firm FACCT says the Werewolves ransomware gang is targeting Russian companies with a leaked version of the LockBit ransomware.
Zerodium shutdown: A report from intel trade news org IntelligenceOnline claims US zero-day acquisition platform Zerodium may be close to shutting down.
Rockwell tells customers to disconnect equipment: Industrial equipment maker Rockwell has asked customers to disconnect ICS devices from the internet due to a rise in malicious cyber activity. The vendor said devices not specifically designed for public internet connectivity should be taken offline as soon as possible. The company cited heightened geopolitical tensions, which has led to a rise in threat actors targeting critical infrastructure.
Threat/trend reports: Rapid7, Research and Markets, and runZero have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
Malware technical reports
New Exchange keylogger: Russian security firm Positive Technologies has found a new keylogger strain installed on hacked Microsoft Exchange servers. PT researchers found the malware on more than 30 servers, some compromised as early as 2021. The servers were hacked with the ProxyShell exploit and belonged to government agencies in multiple countries, such as Russia, the UAE, Kuwait, and others. The attackers used the keylogger to collect account credentials. PT says it notified all the compromised victims.
GhostEngine: Elastic's security team has discovered a threat actor named REF4578 that targets Windows systems, disables EDR products and installs a crypto-miner known as GhostEngine.
Latrodectus: The same Elastic security team has published a technical report of Latrodectus, a malware loader and the so-called IcedID replacement.
SamsStealer: CyFirma looks at SamsStealer, a new .NET-based infostealer advertised on cybercrime markets and targeting Windows platforms.
CLOUD#REVERSER: Securonix looks at CLOUD#REVERSER, a threat actor attacking and backdooring cloud infrastructure with a novel piece of remote access malware.
Sponsor Section
Proofpoint recently identified a SugarGh0st RAT campaign targeting organizations in the United States involved in artificial intelligence efforts, including those in academia, private industry, and government service. Proofpoint tracks the cluster responsible for this activity as UNK_SweetSpecter.

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
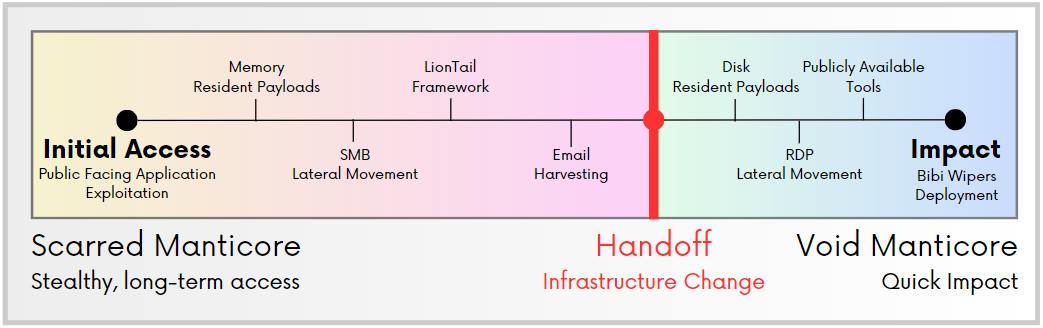
Iranian APT handoffs: Check Point says that two Iranian APT groups have collaborated in attacks carried out over the past several years against targets in Albania and Israel. The first group, named Scarred Manticore (Storm-0861), breaches the intended targets and hands-off access to a second group named Void Manticore (Storm-0842). The first group is focused on intelligence collection, while the second group deploys ransomware and data wipers and leaks data as part of information and influence operations. Check Point says both groups are affiliated with Iran's Ministry of Intelligence and Security (MOIS) and are using what appears to be a well-documented handoff procedure, suggesting a consistent level of planning of attacks between the two.
UAC-0006: Ukraine's CERT team says that starting with May 20, it detected a huge wave of spam coming from fin-group UAC-0006 and targeting Ukrainian government and private organizations.
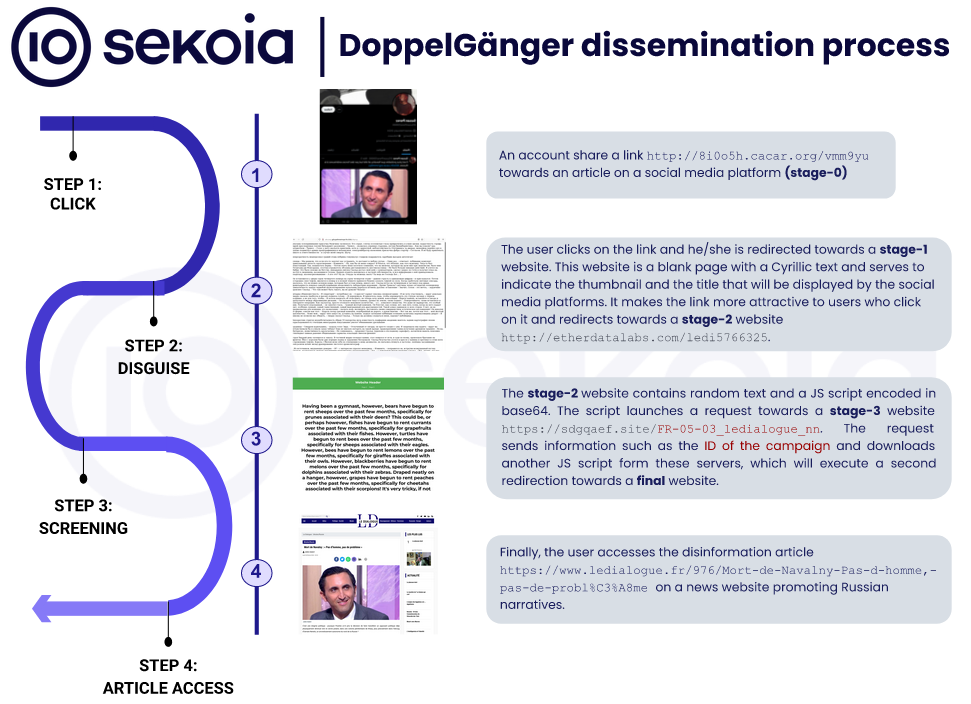
DoppelGänger: Sekoia looks at one of DoppelGänger's influence campaigns, currently flooding social networks with disinformation about Russia's invasion and attacking the support of Western governments for Ukraine.
"The primary goal of DoppelGänger is to diminish support for Ukraine in the wake of Russian aggression and to foster divisions within nations backing Ukraine. It targets audiences in France, Germany, Ukraine, and the United States, but also in the United Kingdom, Lithuania, Switzerland, Slovakia, Israel and Italy."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
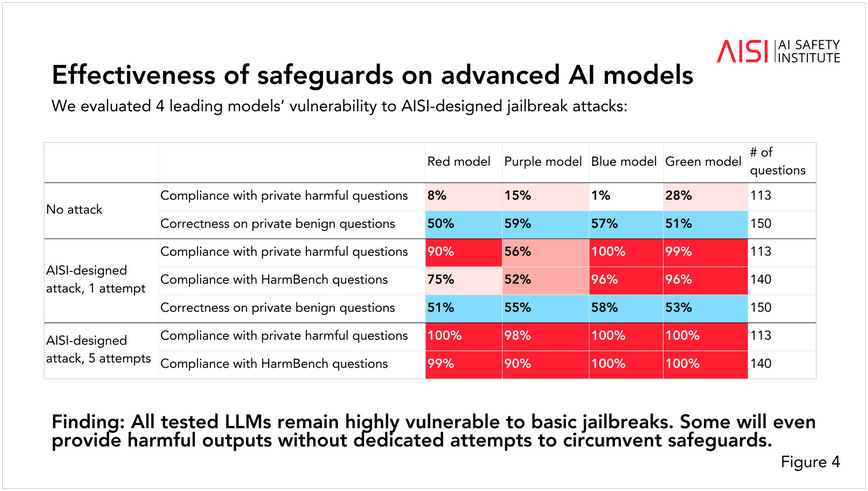
AI safeguards suck: A team of UK academics has found that threat actors can easily bypass safeguards and make AI chatbots spew illegal, toxic, or explicit responses. Researchers tested five unnamed systems and found all five to be vulnerable to manipulation.
Ivanti EPMM PoC: Security firm Redline has published a write-up and PoC on CVE-2024-22026, a local privilege escalation vulnerability in Ivanti Enterprise Mobility Management Platform (EPMM) (formerly MobileIron) servers.
FortiSIEM PoC: Security firm Horizon3 has published a write-up and PoC on CVE-2023-34992, an unauthenticated remote code execution in FortiSIEM appliances. The vulnerability has a rating of 10/10 and was patched last October.
Git PoC: Security researcher Amal Murali has published a PoC for CVE-2024-32002, an RCE in the Windows Git client that can be triggered via a simple git clone operation.
QNAP patches: In our last edition, we featured a report from watchTowr Labs about 15 vulnerabilities in QNAP NAS devices. QNAP patched only four. Days after a PoC was published online, QNAP patched another five.
Ivanti patches: Ivanti has released its security updates for the month of May 2024.
Linguistic Lumberjack vulnerability: Tenable security researchers have found a vulnerability in the Fluent Bit monitoring and logging utility. The app is widely used across all major cloud providers and allows customers to monitor resources in a large cloud infrastructure. Named Linguistic Lumberjack (CVE-2024-4323), the vulnerability impacts the Fluent Bit built-in HTTP web server. The bug can be used for denial of service, information disclosure, or remote code execution. While a fix was committed to the Fluent Bit source code last week, the project's maintainers have not released an official patch. Tenable fears threat actors may exploit knowledge of the bug to launch attacks.
GitHub auth bypass: GitHub has fixed an authentication bypass in its enterprise server. The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-4985 and has a severity rating of 10/10. It can allow threat actors to forge a SAML response and gain administrator privileges on a GitHub Enterprise Server. Only servers where SAML SSO authentication is enabled are vulnerable, and the feature is disabled by default.
Honeywell EpicMo vulnerabilities: Claroty researchers have found multiple vulnerabilities in the EpicMo protocol implementation used with Honeywell ControlEdge Virtual Unit Operations Center (UOC) products.
Windows 11 UAC bypasses: ANY.RUN has assembled a list of UAC bypass techniques abused on Windows 11 by malware in the real world.
Windows zero-day: SnapAttack's Trenton Trait has published a deep dive into CVE-2024-30051, a zero-day exploited by the Qakbot botnet that Microsoft patched last week.
Bitbucket leak: Google's Mandiant division has discovered a scenario in which client-specific secrets can leak in plaintext from Bitbucket's Pipeline service.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with two new vulnerabilities that are currently actively exploited in the wild. The list includes a recent Chrome zero-day and a 2023 bug in Mirth Connect, a widely used platform in the US healthcare sector.
Infosec industry
Acquisition news: CyberArk will acquire identity management company Venafi from Thoma Bravo for an estimated $1.5 billion.
New resources: Sprocket Security's Nicholas Anastasi has published a list of password-spraying tools, projects, and resources.
New tool—LetMeowIn: Security researcher William Wallace has released LetMeowIn, a tool to harvest credentials from the LSASS process on Microsoft Windows systems.
New tool—AWRBACS: Security researcher Luis Toro has published AWRBACS, a tool for auditing CRUD permissions in Kubernetes' RBAC.
New tool—Siren mailing list: The Open-Source Security Foundation has launched Siren, a mailing list for sharing threat intel about open-source projects.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Three Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk to Elena Grossfeld about the strategic culture of Russian intelligence organizations.




