Risky Biz News: Attackers are on the hunt for the new UNIX CUPS RCE
In other news: Three Iranians indicted for Trump campaign hack; UK train station WiFi hacker detained; Microsoft re-adds Recall to Windows 11.

This newsletter is brought to you by Zero Networks. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Threat actors are scanning the internet for UNIX systems that are exposing their printing ports in an attempt to exploit a set of four vulnerabilities in the CUPS printing component.
The vulnerabilities were discovered by Italian security researcher Simone Margaritelli earlier this year and were disclosed at the end of last week.
They impact CUPS, the Common UNIX Printing System, an open-source component to allow UNIX systems to function as print servers.
The four bugs are part of an exploit chain that can allow an attacker to deploy a malicious printer, have the printer indexed by a victim's CUPS server, plant malicious code on the CUPS server (UNIX system) inside a PPD file, and have the malicious code from the PPD file executed when a user launches a print job via the attacker's (malicious) printer.
The exploit chain is in this order: CVE-2024-47176, CVE-2024-47076, CVE-2024-47175, and CVE-2024-47177.
Besides Margaritelli's write-up explaining how the four bugs work, other analyses on the four are also available via Akamai, Rapid7, Elastic, Tenable, Qualys, DataDog, and AquaSec.
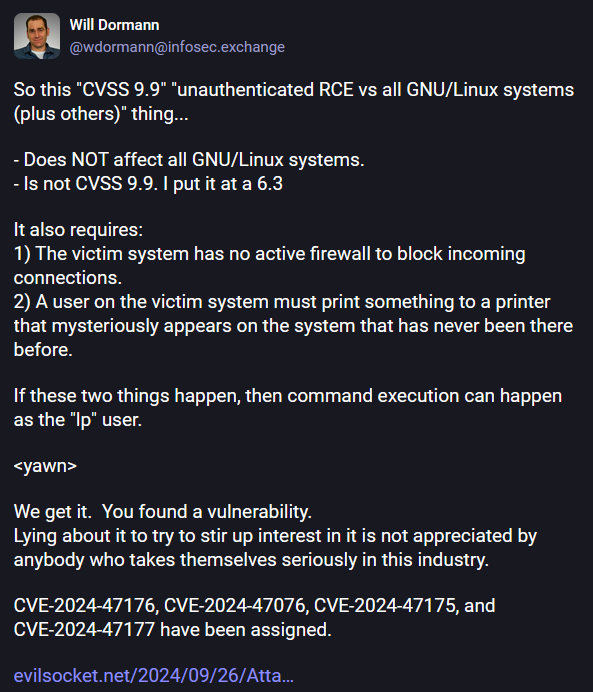
The bugs got a lot of attention and were extremely over-hyped over the past week after Margaritelli posted about them on Twitter before patches were released.
Let's just say they are not as bad as they were made up to be. They don't impact all Linux distros (only a few, actually), they're only exploitable in very limited scenarios, and the 9.9 CVSS score should have been lower. Yes, they're bad bugs that are easy to exploit, but they're not the Linux world-ending kind (like Heartbleed, for example).
But regardless of their severity and all the weird conditions needed to exploit the bugs, threat actors don't care.
After Margaritelli and others published proof-of-concept code at the end of last week, threat actors began scanning the internet for UDP port 631, which is the port on which the CUPS server listens for new printers announcing their presence.
If this port is exposed on the internet, then bad things are about to happen to your CUPS server in the coming days.
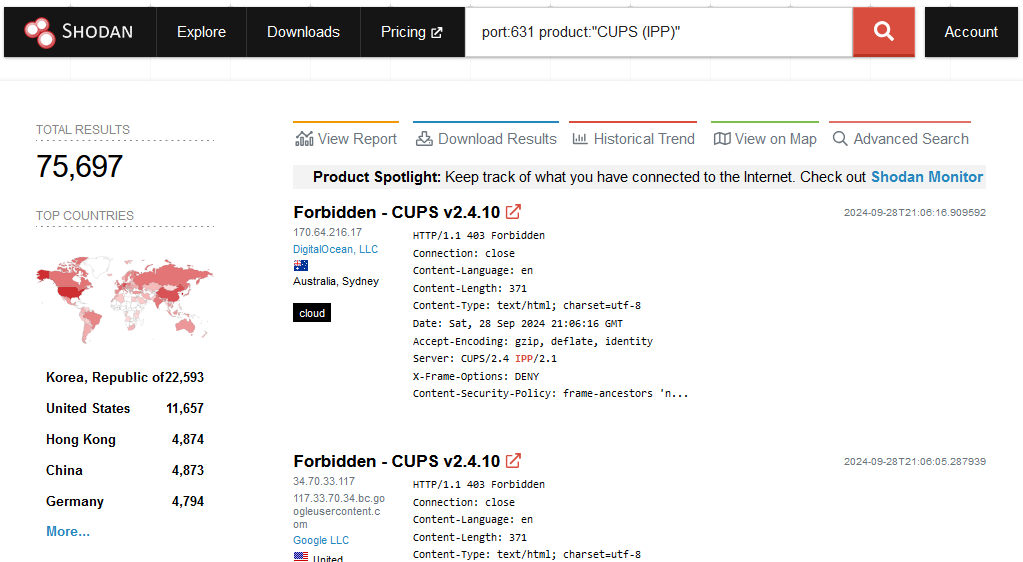
Even if CUPS ships disabled by default on most distros, according to Shodan, there are currently over 75,000 systems running CUPS exposed over the internet, which is quite an attractive piece of pie if you're an attacker. Other scans have these numbers at over 107,000, but they could be even bigger than this.
Mitigating the vulnerability should be pretty easy. Just disable, remove, or update CUPS. You shouldn't be running that anyway.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Diehl Defence hack: North Korean hackers have breached German arms maker Diehl Defence in a security breach that took place earlier this year. The hack took place after Diehl employees opened malicious PDF files for lucrative job offers at US arms companies. Google's Mandiant division attributed the attack to a North Korean APT group known as APT43 (Kimsuky). North Korean hackers appear to have targeted the company after Diehl signed a contract with the South Korean military for its new Iris-T air-to-air missiles. [Additional coverage in Spiegel/English coverage in MSN]
Dutch police breach: Hackers have stolen the work details of more than 65,000 Dutch police officers. The Dutch Minister for Justice and Security said no personal data was included in the stolen files. Officials say they are still assessing if undercover officers are at risk following the hack. [Additional coverage in NOS]
IDF leak: Pro-Palestinian hacktivist group Handala Hack has leaked more than 60,000 emails from Israel's Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The leaked data contains the inboxes of former Israeli Minister of Foreign Affairs and IDF Chief of General Staff Gabriel Ashkenazi. The group also claims to have the emails of former Israeli Defence Minister and retired Army General Benny Gantz. Although Handala Hack poses as a hacktivist group, several security firms have linked the group to Iranian intelligence. [Additional coverage in CyberDaily]
Kuwait hospitals cyberattack: A suspected ransomware attack has taken down IT systems at multiple hospitals across Kuwait. The incident has impacted cancer control centers, health insurance, and administrative systems. Kuwait's Health Ministry is restoring systems from backups, and no ransomware group has yet to take credit for the attack. [Additional coverage in KUNA]
AFP cyberattack: A cyberattack has impacted IT systems at French news agency Agence France-Presse (AFP). The incident impacted a system responsible for delivering news services to customers. AFP says its normal newsroom operations were not impacted. The agency says it reported the incident to France's cybersecurity agency.
Onyx crypto-heist: Hackers have stolen $3.8 million worth of crypto-assets from DeFi platform Onyx. The attacker used an exploit that was a variant of a bug used to hack the platform in November of last year. The bug impacted "empty market" protocols that are used when launching new trading pools. [Additional coverage in CoinTelegraph]
Bedrock crypto-heist: Cryptocurrency project Bedrock has lost $2 million worth of crypto-assets following an exploit in one of its smart contracts.
General tech and privacy
Irish DPA fines Meta: Ireland's data protection agency has fined Meta €91 million ($101.5 million) for storing some users' passwords in plaintext. The fine is for a Marchattacker'sdent. Yes, it took them five years to issue a fine.
Meta's Russian problem: Meta has some explaining to do in regards to its EU personnel.
LibGen court ruling: A US court has ordered the LibGen book piracy portal to pay $30 million in copyright infringement damages to book publishers. [Additional coverage in TorrentFreak]
Arch Linux and Valve collab: Valve has announced an official collaboration with Arch Linux to sponsor some of its critical projects. Valve's SteamOS is based on Arch, so this makes a lot of sense.
Cloudflare Project Alexandria: Cloudflare announced Project Alexandria, an effort that provides "credits" to open-source projects that they can later use to acquire Cloudflare services for free.
Microsft re-adds Recall to Windows: Microsoft has re-engineered and added privacy and security upgrades to Recall—a controversial feature that takes screenshots of the user's screen and uses AI to search through old activity. The company first announced Recall earlier this year but was forced to abandon its initial plans after fierce public criticism. Security experts slammed the company for not allowing users to remove the feature and leaving screenshots unprotected on disk. The new Recall will ship with Windows 11 later this year as an opt-in component that will be disabled by default. It will still be able to take screenshots of everything a user does, but now that content is encrypted, and the encryption keys are stored inside a PC's TPM. Microsoft says users will be able to view past Recall screenshots only after they authenticate using Windows Hello biometric credentials. Content from password and credit card fields will not be stored, and users can now filter out specific apps or websites from being screenshotted. And the best part—Microsoft is now letting users remove Recall entirely if they don't want the feature present on their systems.

Government, politics, and policy
Discord close to getting banned in Russia: Russian internet watchdog Roskomnadzor has added Discord to its registry, a first step in formally blocking access to the service within Russia's borders. [Additional coverage in Kommersant]
US gives up on Cyber Force: The Pentagon has asked this week US lawmakers to shut down an independent assessment analyzing if the US military needs to establish a separate cyber branch. The assessment was a necessary formal step in establishing a separate US Cyber Force. Multiple US think tanks had advocated for a unified new branch just for cyber operations. They argued that having separate cyber units in each military branch is an ineffective solution when it comes to recruiting and retaining talent. According to The Record, the Pentagon killing the assessment instead of Congress came off as a big surprise on Capitol Hill.
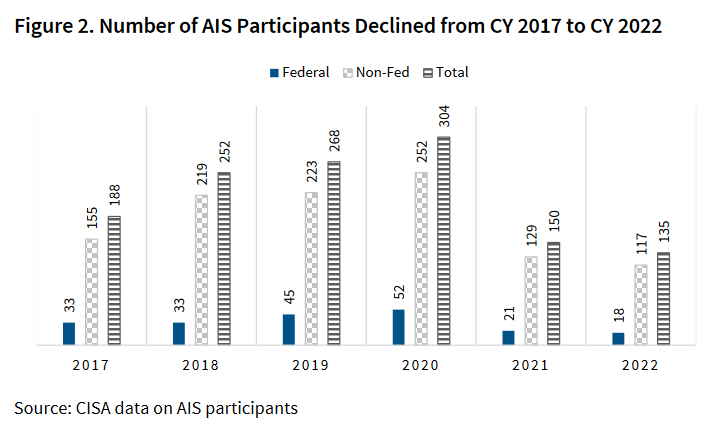
CISA cyber information sharing problems: The number of participants in CISA's cyber information-sharing program has drastically decreased to numbers lower than in 2017 when the program was first established. Only 270 organizations participated in the Automated Indicator Sharing (AIS) program in 2022, compared to the 376 organizations active in 2017. The number of indicators also declined from nearly 9.5 million in 2021 to only 413,000 in 2022. The report blamed the sudden fall in shared IOCs on a federal system that was moved to a new federal agency and stopped sharing data because of "unspecified security concerns." The DHS Inspector General says the reduction in participants and shared data is preventing CISA from responding to threats in real-time. It also labeled AIS as ineffective and "a potential waste of taxpayer funding." [See more in the DHS OIG report/PDF]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsored interview, Tom Uren talks to Benny Lakunishok, CEO and cofounder of ZeroNetworks, about network microsegmentation, why it is important, how to do it, and what the NSA gets wrong about it.

Cybercrime and threat intel
UK train stations WiFi hacker detained: The British Transport Police has detained a man on suspicion of hacking the WiFi networks at 19 train stations across the UK. The suspect allegedly reconfigured the WiFi networks to redirect travelers to a page with Islamophobic messages and a list of terrorist attacks that had taken place across the UK and Europe. Officials have identified the man as an employee of Global Reach Technology, a company that provides WiFi services to Network Rail stations.
UK man arrested in hack-to-trade scheme: US authorities have charged a UK national for hacking five US companies in hack-to-trade criminal scheme. Robert Westbrook allegedly stole non-public corporate earnings reports and used the data to trade on the stock market in advance. He earned more than $3.75 million in illicit profits ahead of official announcements. Westbrook was arrested last week in the UK, and the US is seeking his extradition.
New npm malware: Forty-two malicious npm packages were discovered and taken down last week. Check out the GitHub security advisory portal for more details.
REF6138 abuses gambling APIs: The Elastic security team has discovered a novel Linux botnet that appears to be abusing APIs for gambling sites to launder its illegal profits. Tracked as REF6138, the botnet emerged in March of this year and is mainly made up of hacked Apache web servers. Elastic says servers are infected with different malware strains for hidden crypto-mining and DDoS attacks. One of the botnet's unique features is a script that automatically places bets on gambling APIs with the minted cryptocurrency. Researchers believe the feature is a new technique that's being tested for laundering crypto-mining proceeds.
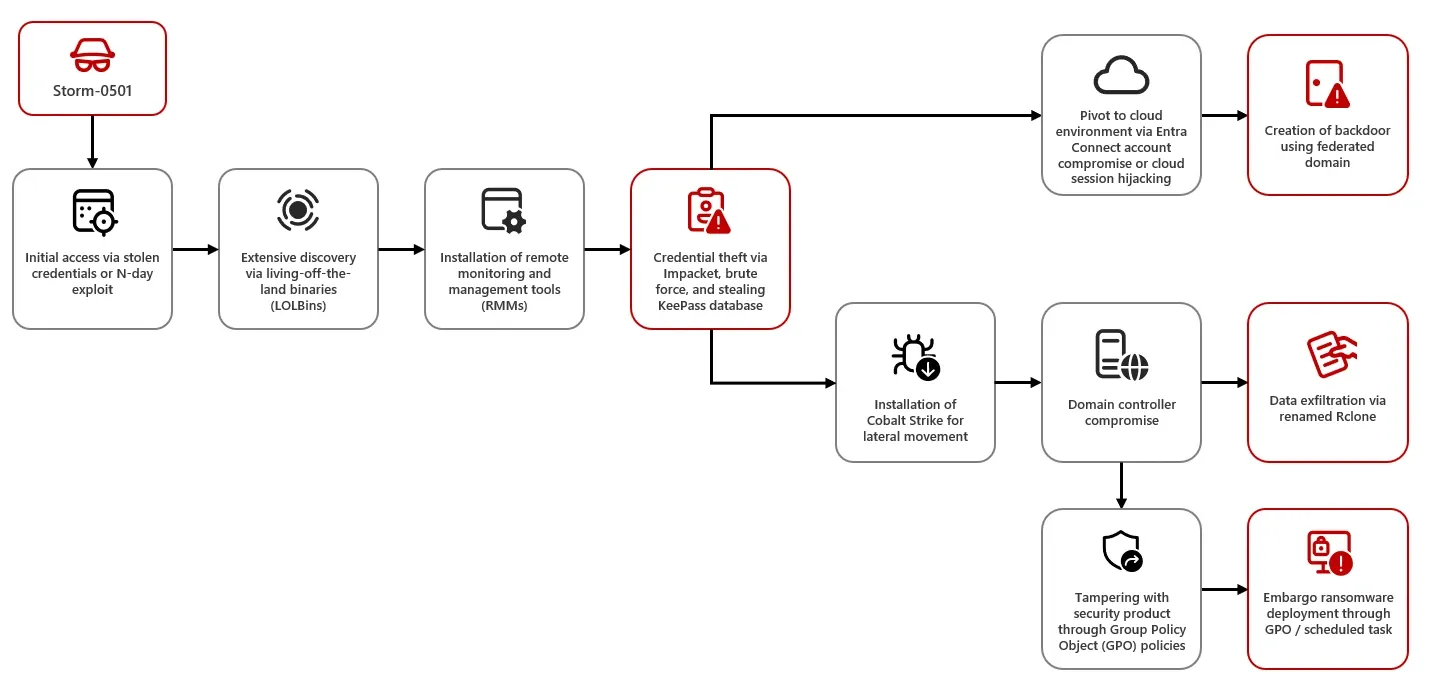
Storm-0501 goes after hybrid cloud environments: Microsoft's security team says that a threat actor tracked as Storm-0501 is now targeting hybrid cloud environments. The group breaches local networks and then pivots to a company's cloud environment, where it leaves backdoors for future access. Storm-0501 emerged in early 2021 and deployed the Sabbath (54bb47h) ransomware in its first attacks. The group eventually became an affiliate for other larger RaaS platforms and is currently using the Embargo ransomware for its operations.
Malware technical reports
Rast ransomware: QiAnXin has published an analysis of Rast, a new ransomware strain that's been observed in attacks against Chinese companies. As the name suggests, the ransomware is written in the Rust programming language. The group has been active since December 2023.
Sponsor Section
Founded in 2019, Zero Networks is a unified zero-trust platform for network segmentation, identity segmentation, and secure remote access. Zero Networks' microsegmentation module is automated, agentless, and segments all network assets to stop lateral movement and block ransomware with a firewall and just-in-time MFA.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Transparent Tribe: CyFirma tracked and exposed new infrastructure linked to the Transparent Tribe (APT36) group by leveraging common OSINT techniques.
Old African info-ops: BindingHook has a good summary of Russian info-ops in Libya that took place in the late 2010s.
Iranian ops: US and UK authorities have published an alert on how Iranian threat actors are targeting personal instead of work accounts to hack their targets.
US charges Trump hackers: The US government indicted three Iranian nationals for the alleged hack of the Trump campaign earlier this year. The hack was part of a larger four-year hacking campaign that also targeted members of Congress, former White House, and senior government officials. The Justice Department says Iran launched the campaign in retaliation for the killing of Iranian general Qasem Soleimani by the Trump administration in 2020. The three suspects are named Masoud Jalili, Seyyed Ali Aghamiri, and Yasar Balaghi. Jalili was also sanctioned by the US Treasury, and the State Department is also offering a $10 million bounty for information on other Iranian threat actors trying to meddle in the 2024 US election.

Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Cloudflare VIP VRP: Cloudflare has launched a second bug bounty program on top of its public one. This one is a VIP invite-only program.
Hidden GFW filtering: Assetnote researchers have found a secret behavior of the Chinese Great Firewall that manipulates DNS responses if domains contain blacklisted or blocked keywords. Researchers say this undocumented behavior could be abused to perform DNS poisoning attacks.
JupiterX theme vulnerabilities: French security firm LEXFO has found two vulnerabilities in the extremely popular JupiterX WordPress and WooCommerce theme. The vulnerabilities include an authentication bypass and a remote code execution issue that can allow attackers to take over affected sites. Exploitation requirements include a form with a file upload field. JupiterX is the eight most-sold item on the ThemeForest marketplace, with more than 178,000 sales.
Zimbra RCE: Project Discovery security researchers have discovered a vulnerability in the Zimbra email platform that can be used to take over unpatched servers. Tracked as CVE-2024-45519, the vulnerability impacts the PostJournal service and allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands on affected Zimbra installations. The Zimbra team patched the bug in a security update at the start of September.
VLC security update: VideoLAN has released a patch for the VLC media player to fix a vulnerability that could allow attackers to execute code via a maliciously crafted MMS stream.
iOS Screen Time bypass: Security researcher Patryk Kowalski has published details of a now-patched bypass of the iOS Screen Time parental control system. The bug could have been abused to retrieve the Screen Time password and disable the feature.
Infosec industry
New tool—HackerNews for AI Papers: HuggingFace's Ahsen Khaliq has created a HackerNews-like interface for new AI papers.
New tool—Sigmalite: RunReveal has open-sourced Sigmalite, a Sigma rules evaluation engine. The code is also on GitHub.
New tool—RansomGuard: A security researcher known as Windy Bug has released RansomGuard, a filesystem mini-filter driver designed to stop ransomware from encrypting files through the use of the filter manager.
New tool—PolyTracker: Trail of Bits researchers have released PolyTracker, a tool for understanding how computer programs handle your data. The research paper is here.
Tool update—Slack Watchman: Security researcher PaperMtn has updated their Slack Watchman tool to be able to retrieve data from Slack workspaces while unauthenticated.
RomHack 2024: Live streams from the RomHack 2024 security conference are available on YouTube.
Acquisition news: Visa has acquired AI-based fraud detection company Featurespace.
Threat/trend reports: OpenText, Red Canary, Securonix, and SkyQuest have recently published reports and summaries covering various infosec trends and industry threats.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about new reports saying that Russia is creating new cyber groups made up of cyber criminals.
In this podcast, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about the possibility of deterring Volt Typhoon, the Chinese group that is compromising US critical infrastructure to enable future disruption operations in the event of a conflict with the US. Tom thinks it is not possible to deter Volt Typhoon, but things might work the other way. If the US can neuter Volt Typhoon and take away the PRC's magic cyber bullet, it could make conflict less likely.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!






