Risky Biz News: Apple's WWDC 2024 security lineup
In other news: Ransomware gang goes after PHP servers; Chinese hackers breached 20k Fortinet devices; White House announces cybersecurity support for rural hospitals.

This newsletter is brought to you by Detection-as-Code company Panther. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

Apple is holding its yearly Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) this week in Cupertino, and the company has announced several security-related features on the first day of the event.
This year's biggest announcement is Private Cloud Compute, a new feature that will take user data and process it inside an encrypted cloud server. This feature will be used for new Apple AI services that require more processing power than is available on the user's device.
Apple says the data will be stored on servers that use custom-built hardware and run a custom operating system. Data is sent to PCC servers only with the user's approval, and Apple says that even its staff with administrative rights can't access or view it. Everything, of course, is wrapped in cryptographic protocols.
A technical description of this entire convoluted process is available here, and Apple says it will make PCC server software images available for security research.
All of this is to process data for Apple's AI-based features, which most users won't really bother that much, to be honest. AI is still creepy as hell and hasn't earned the consumers' trust so far.
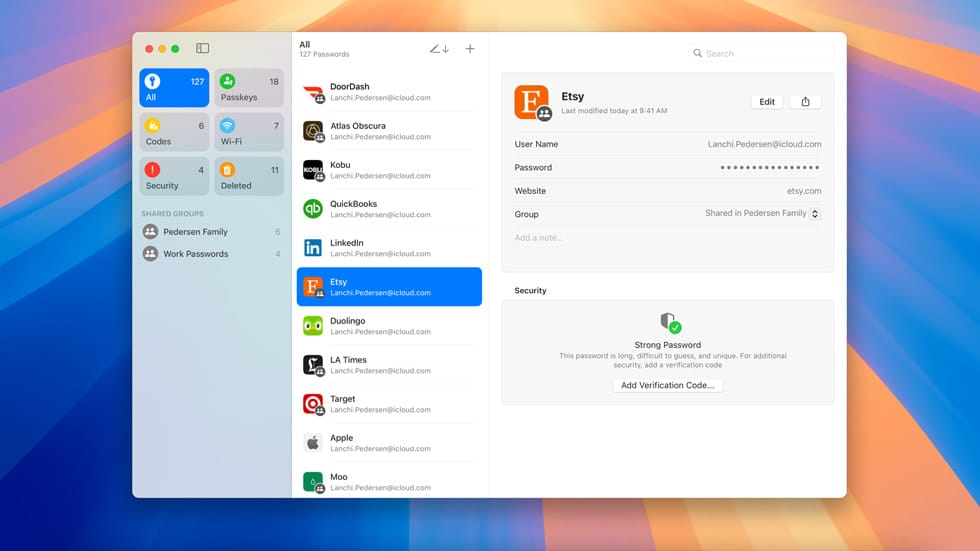
What normal users will love more is Apple's new and extremely originally-named app Passwords. This is just a regular password manager, which Apple described as an evolution of its older Keychain app.
Apple says Passwords will simplify retrieving and auto-filling data from Keychain, such as account passwords, passkeys, Wi-Fi passwords, and two-factor authentication codes. It will also start showing alerts for the user's credentials if they are known to be included in public breached data.
The app should be available for both iOS and macOS, and will be able to sync between devices—including from Windows via the iCloud for Windows app.
Another consumer-friendly feature added to iOS 18 this fall will be the ability to lock specific apps behind Face ID, Touch ID, or a passcode.
The feature is designed to stop threat actors with physical access to an unlocked or unprotected device from opening sensitive apps.
If that's not enough, users can also hide the app, so a snooper won't even know it's there.
The best thing about this feature is that while an app is locked or hidden, all its information won't appear in other places, like the file manager, search, and notifications.
Apple also announced support for satellite communications in the Messages app, which, in the event of an emergency, should allow users in remote areas to contact family or other help.
As a girl, it is a mini freakout moment when you don’t have wifi, network and are on low battery.
— Ash Arora (@0xashesonchain) June 10, 2024
Text your live location by using messages via SATELLITE, for free pic.twitter.com/vNSmM1XEYe
The Apple WWDC is taking place throughout the rest of the week until June 14. We'll add any new announcements to the web version of this newsletter as they come out.
Post-publication update:
- Apple will now let virtual machine users sign into iCloud and Apple ID.
- You can now mirror your iPhone on a macOS device, which opens the door for a million types of abuses.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Cleveland cyber-attack: The city of Cleveland shut down City Hall on Monday in the aftermath of a cybersecurity incident. No other details were provided. [Additional coverage in Cleveland.com]
23andMe breach: 23andMe is now under investigation in Canada and the UK for its October 2023 security breach.
UwU Lend crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $19.3 million worth of assets from the UwU Lend DeFi platform. The company says it detected the hack within minutes, but that was enough for the attacker to exfiltrate a large chunk of its funds. UwU Lend has paused all operations and has made an "offer" to the attacker to return the funds. [Additional coverage in CoinGape]
Niconico hack: Japanese video-sharing service Niconico has suspended operations in the aftermath of a cybersecurity incident. Its services have been offline since June 8, and the company is not sure when it will be able to resume operations. Niconico says it's unsure if any user data was compromised. [Additional coverage in Japan Today]
Netherlands MoD hack: The Dutch government says that a Chinese hacking campaign that breached its Ministry of Defense in February was far larger than it initially believed. Dutch officials say the group behind the attacks gained access to more than 20,000 Fortinet devices using a vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-42475. The group's attacks began in 2022 when the vulnerability was a zero-day and continued throughout 2023. More than 14,000 of the hacked devices were compromised when the vulnerability was still a zero-day. Officials say that after compromising the devices, Chinese hackers sifted through systems, deployed additional malware, and stole data from the most high-value victims.
Cylance hack: Cybersecurity firm BlackBerry has confirmed that a threat actor is selling data from its Cylance subsidiary. The company says the files were taken from a third-party platform and represent old Cylance information. The threat actor claimed to be in possession of more than 34 million PII data and emails for Cylance customers and employees. The incident is suspected to be connected to the larger Snowflake breach. Several of Snowflake's customers have had data put up for sale on hacking forums over the past week. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
Pure Storage hack: On the same note, also add Pure Storage to the list of Snowflake victims.
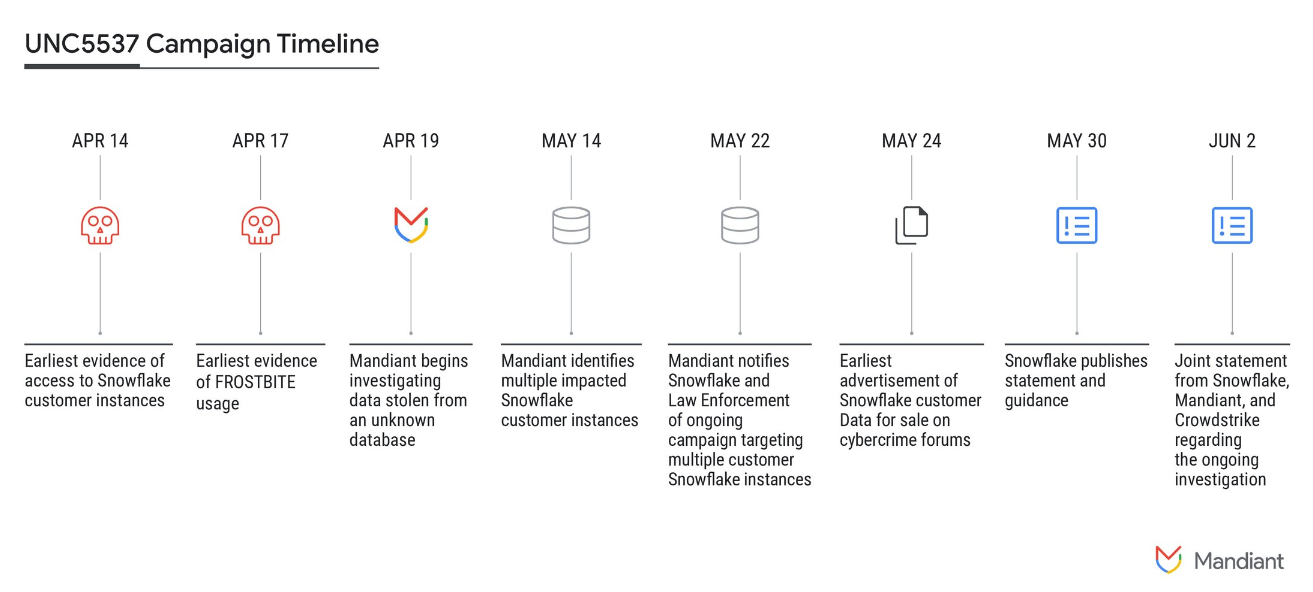
Snowflake hacks: Mandiant says it notified almost 165 companies that their Snowflake cloud accounts could have been compromised as part of a recent hacking and data extortion campaign. A hacking group named UNC5537 is behind the attacks. Mandiant says the group has used credentials for Snowflake accounts bought from underground markets to breach companies and steal their data. The group has used the hacks to extort companies or put their data for sale on hacking forums. Mandiant says the group has had success in cases where victims did not enable MFA for their Snowflake accounts.
General tech and privacy
AWS adds passkey support: AWS has announced support for FIDO2-compliant passkeys as one of its MFA options. The announcement comes as Amazon is making MFA a mandatory requirement for some AWS root accounts next month. Amazon says root users of standalone accounts (not managed through an organization) will be required to use at least one MFA solution starting July. The new requirement will be enforced for the root users of larger organizations later this year.
Chrome 126: Google has released version 126 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. Other changes in this release include the ability to extract text from PDFs, new memory resource-saving improvements, and support for tab groups on the iPad. Also, starting with this release, the Google Gemini Nano AI client is now built into the Chrome Desktop client itself—just to be sure users who value their privacy can't remove it! Long live sh***y unwanted and useless AI features!
Firefox 127: Mozilla has released Firefox 127. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest change is support for setting Firefox to auto-launch with Windows, which means no more Windows Startup tricks are needed anymore to achieve this. On the security side of things, Firefox will now auto-upgrade images, videos, and audio files from HTTP to HTTPS when possible.
Youtube embed apocalypse: Google is apparently running tests where it blocks YouTube video playbacks unless viewers are logged in. The measure will cripple YouTube content downloaders but also trillions of video embeds.
Mozilla removes anti-censorship add-ons: Mozilla has silently removed at least four Firefox add-ons from the Russian version of its add-ons portal. The Firefox add-ons were being used to bypass the Kremlin's internet censorship. Developers say Mozilla did not notify them of the removal, and it's unclear if this was done at the request of the Russian government. The use of tools to circumvent censorship is not illegal in Russia, but the Russian government has previously banned VPN services and protocols.
Government, politics, and policy
Europol now wants 5G/6G access: After European law enforcement agencies have argued for lawful access to encrypted instant messaging clients for a few years now, their demands have recently expanded. In a new report published this week, Europol has asked that lawful access should be considered for other technologies that use encryption, such as 6G, biometrics, DNS, the blockchain, and quantum computing.
"Collaboration with academia and private industry is essential for the creation of new tools to both serve law enforcement investigations without compromising the overall security of communications."
New disinformation center: Poland, Ukraine, and the United States have established a new center in Warsaw to counter Russian disinformation campaigns. The new center is named the Ukraine Communications Group and will be in Warsaw. The group will primarily address misleading narratives about Russia's invasion of Ukraine and expand from that to address the global disinformation environment.
Rural hospital support: The White House has announced a new initiative that will provide cybersecurity services at reduced prices for rural hospitals across the US. The program is supported by Google and Microsoft. Google will provide endpoint security advice to rural hospitals and nonprofit organizations at no cost. Some organizations will receive discounted pricing for communication and collaboration tools and security support. Microsoft will provide discounts of up to 75% for its security products for rural emergency hospitals. The White House says rural hospitals serve around 60 million Americans.
Annual FISMA report: US federal agencies have suffered more than 32,000 security incidents over fiscal year 2023, according to a new White House report [PDF]. More than a third of all incidents were caused by employees misusing their access to sensitive data. Phishing attacks were the second most reported incident category. CISA says that 99% of the incidents were "unsubstantiated or inconsequential events."
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Panther Senior Engineering Manager Nicholas Hakmiller on how the IT market is adapting to the cybersecurity skill shortage by training regular software talent in detection engineering, how AI is not there yet, and how Panther excels at spotting initial account compromise.

Cybercrime and threat intel
ShinyHunters disappears: DataBreaches.net reports that websites and Telegram channels for the ShinyHunters threat actor have gone down over the past few days.
PHP-CGI exposure: More than 458,000 PHP Windows servers are currently exposed on the internet and potentially vulnerable to being hacked. The servers are vulnerable to a security flaw (CVE-2024-4577) disclosed that can allow threat actors to hijack PHP servers using the CGI module on Windows. Attacks targeting the vulnerability began over the weekend after multiple proof-of-concepts were published online. While a patch has been released, exploitation is deemed trivial. One of the threat actors exploiting the vulnerability is the TellYouThePass ransomware gang.
Smishing Triad: Resecurity says that a notorious threat actor named the Smishing Triad has expanded operations and is now targeting Pakistani users. Researchers say the group appears to be using a database of stolen Pakistani data they acquired from the dark web. The latest telemetry suggests the group is sending between 50,000 and 100,000 spam SMS messages every day. The Smishing Triad operation has been active since mid-2023 and previously targeted users in the US, Europe, and the UAE.
Windows Search abuse: Trustwave has published details on a malspam campaign that abuses the Windows Search feature to deploy malware on targeted systems.
OTP bot market: Kaspersky has published an analysis on the market of OTP bots, tools widely used by cybercrime groups to bypass 2FA.
Threat/trend reports: Check Point, Forescout, RSM, and VulnCheck have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends. The most interesting of these studies is a report from US consulting firm RSM. The report found that chief technology officers are most often in charge of controlling a company's cybersecurity budgets. 42% of responding companies said their CTO was in charge of putting together the security budget, while CFOs and CEOs were in charge in 34% and 32% of cases. According to a different report, the annual cybersecurity budget is around $14.6 million. [More on this in CybersecurityDive]
Malware technical reports
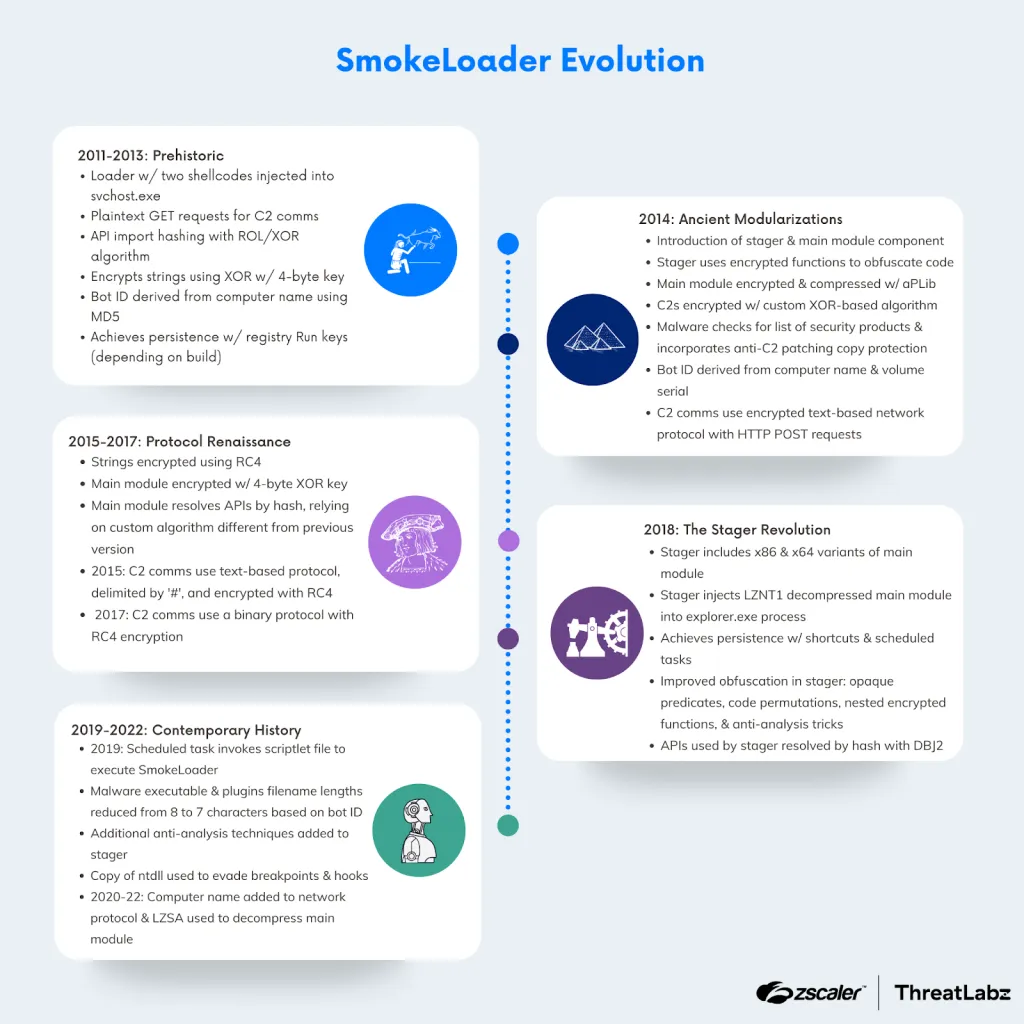
SmokeLoader: Zscaler has published a history of the SmokeLoader malware. The company was one of the security firms that helped law enforcement take down the botnet as part of Operation Endgame.
SSLoad: Intezer looks at SSLoad, a new malware loader available as a MaaS that launched earlier this year in April.
WARMCOOKIE: Elastic's security team has discovered a new Windows backdoor malware strain named WARMCOOKIE. Elastic linked the malware to a cluster it tracks as REF6127. The threat actor is spinning up new domains and infrastructure weekly to support new campaigns.
IcedID: The DFIR Report team has published a write-up about an October 2023 IcedId infection that led to a subsequent attack with the AlphV ransomware.
ValleyRAT: Zscaler researchers have published a report on ValleyRAT, a remote access trojan targeting Windows users. The malware was first seen last year and is commonly distributed via email campaigns.
"ValleyRAT is developed by a China-based threat group that continues to update the code including the ability to capture screenshots of an infected system and manipulate system events (which are common RAT features). ValleyRAT utilizes a convoluted multi-stage process to infect a system with the final payload that performs the majority of the malicious operations. This staged approach combined with DLL sideloading are likely designed to better evade host-based security solutions such as EDRs and anti-virus applications."
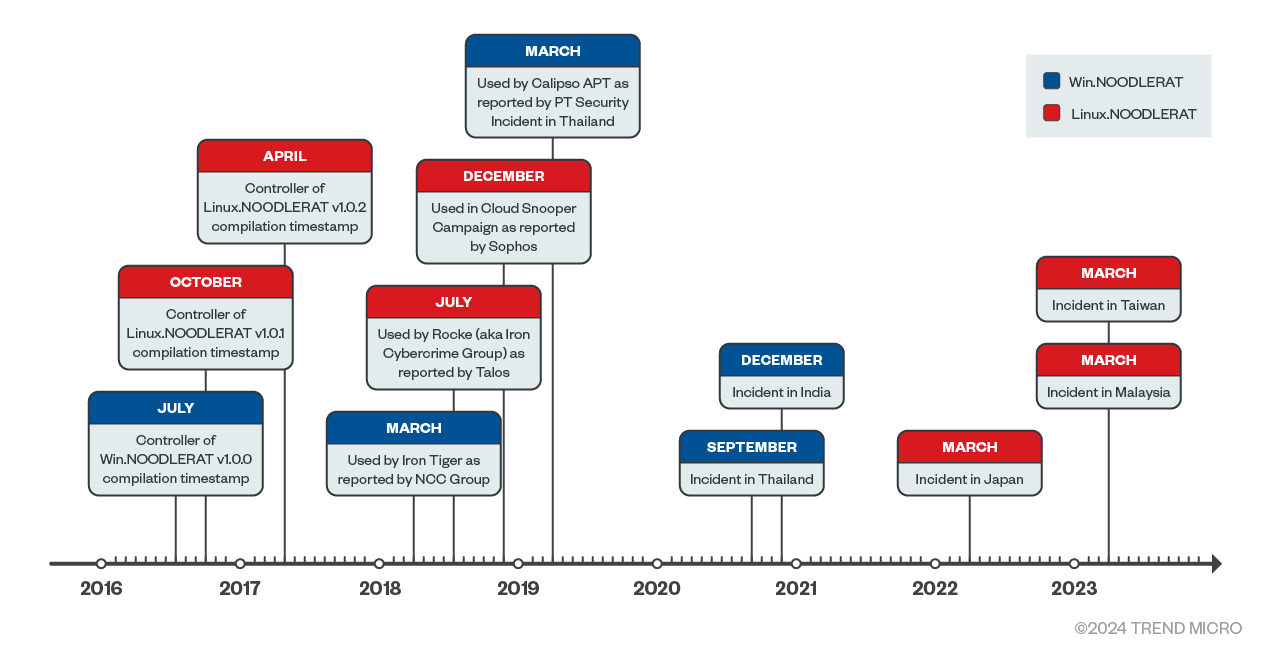
Noodle RAT: Trend Micro looks at Noodle RAT, a dual Windows and Linux remote access trojan used by Chinese APTs and cybercrime groups alike.
Sponsor Section
Today's podcast is brought to you by Detection-as-Code company Panther... and, in what we think is a first, they've released a detection-as-code graphic novel... called Guardians of Valora. It teaches the five key principles of Detection-as-Code... grab it now from panther.com."

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Pro-Russian Telegram disinformation in Africa: Social media research group Open Measures has discovered a concerted pro-Russian disinformation campaign taking place via Telegram and targeting African audiences. The campaign amplified narratives undermining UN missions and promoting Russian military involvement instead. The campaign targeted UN missions in Mali, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Central African Republic. Open Measures says many of the channels have direct or indirect links to the Kremlin-backed Wagner paramilitary group.
DPRK's SmallTiger malware: AhnLab has published a report on SmallTiger, a malware downloader used by two DPRK groups—Andariel and Kimsuky.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the June 2024 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Apple, Microsoft, Arm, Fortinet, SAP, Citrix, Kubernetes, JetBrains, Google Chrome, Firefox, Schneider Electric, Siemens, and Zoom. The Android Project, SolarWinds, VMware, F5, Cisco, Zyxel, Elastic, Fortra, Veeam, and Ruby on Rails released security updates last week as well. This month, Microsoft patched 51 vulnerabilities with no zero-days.
Arm zero-day: Chipmaker Arm has released firmware patches to fix an actively exploited zero-day in Mali GPU drivers. Tracked as CVE-2024-4610, the vulnerability impacts Bifrost and Valhall GPU architectures used with mobile and laptop devices. The company did not release details about the attacks.
Outlook RCE: Morphisec has published a detailed write-up on CVE-2024-30103, a remote code execution bug impacting Microsoft's Outlook email client the company patched in this month's Patch Tuesday. Morphisec says it will release a PoC at DEFCON in August.
Veeam PoC: The SummoningTeam has released a detailed write-up and PoC for a remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2024-29849) in Veeam backup solutions.
ZKTeco vulnerabilities: Kaspersky researchers have discovered 24 vulnerabilities in ZKTeco biometrics scanners.
- 6 SQL injection vulnerabilities;
- 7 buffer stack overflow vulnerabilities;
- 5 command injection vulnerabilities;
- 4 arbitrary file write vulnerabilities;
- 2 arbitrary file read vulnerabilities.
Apple bug bounty drama: Security researcher Dohyun Lee says Apple underpaid and downplayed a critical iOS and macOS vulnerability (CVE-2024-23282). Lee says he received only $5,000 for a bug that uses maliciously crafted emails to initiate FaceTime calls without user authorization. The researchers said the bug could be used to force users with Lockdown Mode to call attacks, exposing their identities. Lockdown Mode only blocks incoming calls but not outgoing ones.
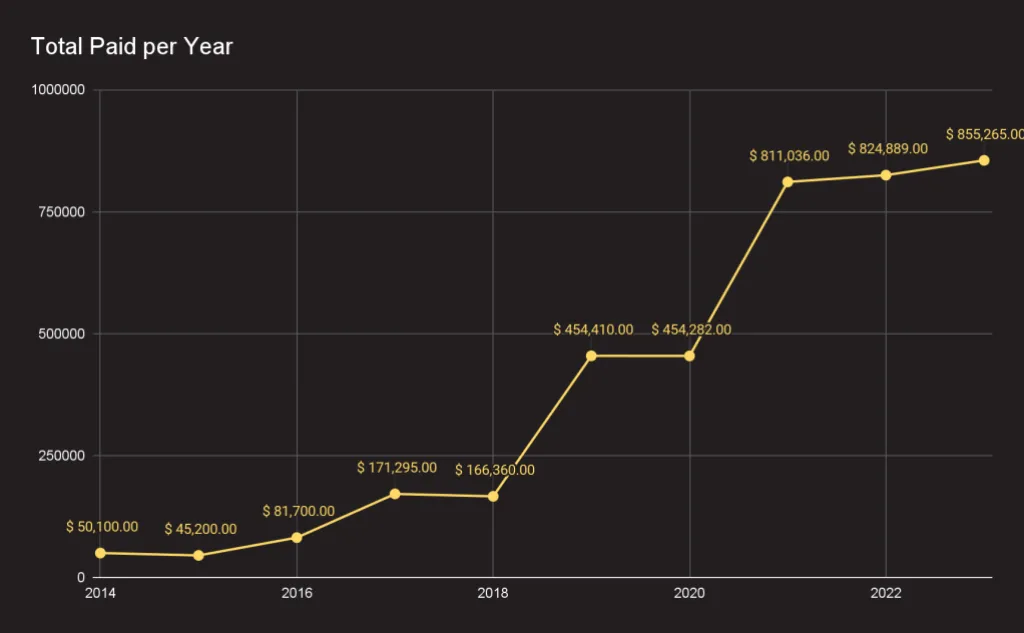
GitHub bug bounty program: GitHub says it paid over $4 million in rewards via its bug bounty program over the past decade. The program had its most successful year in 2023; when it paid out over $850,000 to researchers. The highest reward paid last year is a whopping $75,000 bounty, a sum larger than all the rewards paid in the program's first year.
Infosec industry
New tool—FreeSocks: Unredacted has open-sourced FreeSocks, a Shadowsocks proxy-based system for bypassing internet censorship. See blog post and GitHub repo.
New tool—MAT: German security firm SySS has open-sourced a tool named MAT (MSSQL Attack Tool) that can be used to pen-test MS-SQL databases.
New tool—Reset Tolkien: Security researcher Aethlios has published Reset Tolkien, a tool to crack and generate time-based tokens.
New tool—MDE_Enum: 0xsp Research and Development Labs has released MDE_Enum, a tool designed to extract and display detailed information about Windows Defender exclusions and Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) rules without Admin privileges.
Acquisition news: Fortinet is acquiring cloud security firm Lacework for an undisclosed sum.
DakotaCon 2024: Talks from the DakotaCon 2024 security conference, which took place in March, are available on YouTube.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how the use of cyber operations in Ukraine is informative, but the information is incomplete. Rather than clarifying the role of cyber operations in conventional warfare, there is still a lot of room for confirmation bias.




