Risky Biz News: After botched comms, there's now a timeline for the Azure mandatory MFA rollout
In other news: US government confirms Iran hacked Trump campaign; CISA to get a new fancy HQ; FAA prepares cyber rules.

This newsletter is brought to you by enterprise browser maker Island. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

After making a mess of its comms earlier this year in May, Microsoft has published a more detailed timeline about its plan to enforce multi-factor authentication for all users accessing Azure and other admin portals.
The company says that by October this year, MFA will be required to access the Azure portal, Microsoft Entra admin center, and Intune admin center.
Admins will receive emails and notifications in the Azure Service Health portal to enable MFA for their accounts or face losing access to their paid services.
Microsoft joins the ranks of AWS and Oracle as cloud services that require mandatory MFA to access admin accounts.
The mandatory MFA requirement will expand to other Microsoft admin resources in early 2025. Microsoft says it will slowly and gradually start enforcing MFA for accessing tools like the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Azure mobile app, and the Infrastructure as Code service.
It's nice having Microsoft lay down a plan in a properly worded blog post—as opposed to what happened back in May when it published a Tech Community note announcing "MFA for all Azure users" by July.
It took several days of complaints from panicking customers for the company to explain that the change affected only admin users accessing the Azure Portal.
This was Microsoft testing the upcoming October "mandatory MFA" requirement with a few customers via a gradual rollout phase—but also the perfect example of what happens when you botch corporate comms.
As for MFA options, Microsoft infrastructure supports all the modern options, such as passkeys, hardware security keys, the Microsoft Authenticator app, passkeys, and certificate-based authentication. If you have to, you can also use SMS one-time codes, although Microsoft would prefer you not.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Parcl frontend hack: Pocket Universe, a browser security extension for the cryptocurrency community, claims that a threat actor has hacked the website of the Parcl cryptocurrency platform and injected code that stole funds from users' wallets. No other third-party confirmation at the time of writing.
Boni ransomware attack: The Akira ransomware gang has hit Dutch supermarket chain Boni. [Additional coverage in WNL]
Flint ransomware attack: The beleaguered city of Flint, Michigan, is now dealing with a ransomware attack.
BVIEC cyber attack: A cyberattack has crippled the internal network of BVIEC, the main power company for the British Virgin Islands. The incident hit five days after tropical storm Ernesto devastated the islands and required the intervention of the British Royal Navy. BVIEC has been working almost non-stop to restore electricity lines to affected homes and is now also focused on rebuilding its IT systems. [Additional coverage in BVI News]
Oregon Zoo e-skimming incident: The Oregon Zoo says a web skimmer was planted on its official website, and a threat actor stole the credit card details of more than 117,000 customers.
General tech and privacy
Woman sues Google over scam app: A Florida woman has sued Google after she installed a malicious crypto-wallet app from the official Play Store and lost $5 million worth of assets. Maria Vaca says Google is liable for damages because the company failed to detect the malicious app and then took almost three months to remove it from its store. Vaca says Google failed to intervene and disrupt the scheme even if the company received a formal complaint from the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) on the day she was hacked. Vaca says she is one of five victims who lost funds because of the malicious app and Google's slow response. [Additional coverage in Law.com and The Block]
Tilda bows: Website builder Tilda has removed the website of Public Sociology Lab, a non-profit that publishes research on Russia's authoritarian government and its war in Ukraine and the Russian military. The UK and UAE-based company suspended the website at the request of Russian officials.
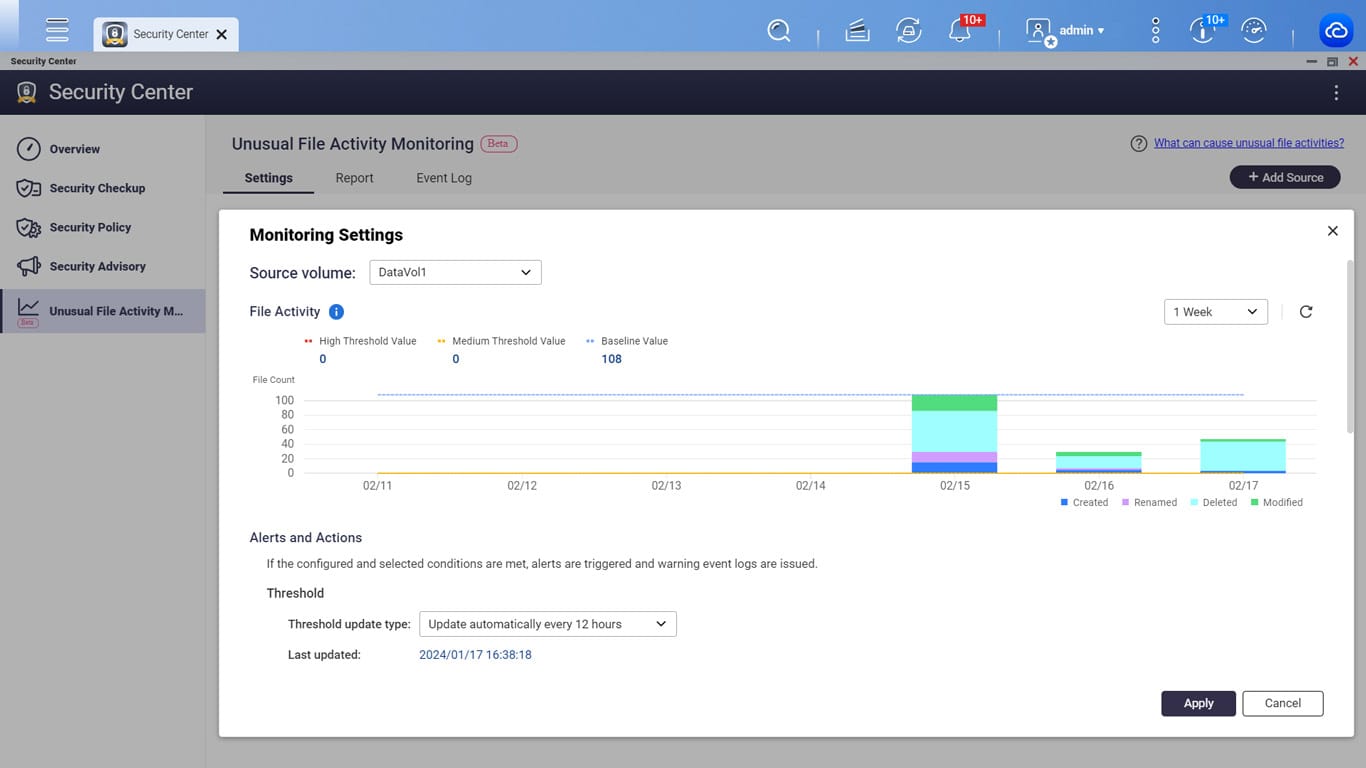
QNAP adds ransomware protection: Taiwanese company QNAP has released a new version of its NAS operating system that includes a security center. The new feature is designed to help users scan systems for malware. It also contains a feature that alerts NAS owners when suspicious file activity occurs, such as repetitive file encryption specific to ransomware attacks. If a ransomware attack is detected, the OS can interrupt the activity and back up the user's files.
Government, politics, and policy
US govt confirms Trump campaign hack: The US government has confirmed that Iranian hackers are behind the recent hack of the Trump presidential campaign. CISA, the FBI, and ODNI say they have "observed increasingly aggressive Iranian activity during this election cycle." The increased activity included cyberattacks against both campaigns and influence operations targeting the general public. The three agencies say they're working to bolster campaign security and disrupt the attackers.
New CISA HQ: The US government has awarded a $524-million contract to build new headquarters for the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. The new HQ will be funded through the Inflation Reduction Act and will be located at the St. Elizabeths West Campus in Washington, DC. The DHS created CISA in 2018 and currently operates out of Arlington, Virginia.
Aviation cyber rules: The Biden administration is working on adding cybersecurity requirements to new aircraft sold in the US. The Federal Aviation Administration is expected to publish the new rules this week. Aircraft manufacturers will be expected to bolster airplanes and their systems to cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities. [Additional coverage in CyberScoop]
The Pakistan Great Firewall: An organization representing the Pakistan IT industry says local companies are expected to lose $300 million due to the government's hurried and unannounced introduction of a national firewall system. The Pakistan Software Houses Association (P@SHA) says members have reported "prolonged internet disconnections and erratic VPN performance" due to the new firewall. Members say foreign customers have also expressed concerns that proprietary data and user privacy could be compromised due to the new firewall system. P@SHA has urged the government to reconsider its system, fearing a collapse of the local IT sector and one of the country's biggest exports.
Russia's white-hat hacker registry: The Russian government, the Interior Ministry, and the FSB are working to create a registry of white-hat hackers and their certifications. [Additional coverage in Vedomosti]
EU cuts FOSS funding: The European Commission has cut funding for the Next Generation Internet project that funds open-source software across the EU. The project has run since 2018 and has provided support to more than 400 FOSS projects. Both the Free Software Foundation Europe and the European Digital Rights non-profits have warned that the move puts the EU's software independence from the US at risk.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Brian A. Coleman, Senior Director at Pfizer for Insider Risk, Information Security, Digital Forensics Expert. Brian goes over all the Island features that have made the browser a favorite tool to secure older corporate apps, either by blocking insecure features or adding logging capabilities where they didn't exist.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Hacker who faked his own death sentenced: A US judge has sentenced a hacker to 81 months in prison for faking his own death to avoid paying child support. Jesse Kipf, from Somerset, Kentucky, was arrested last year on multiple hacking-related charges. Officials say Kipf was a prolific phisher and access broker who hacked companies and sold access to their networks. Kipf's victims included multiple government organizations and private companies, including the Marriott hotel chain. He also hacked the death certificate systems of Arizona, Hawaii, and Vermont—and successfully faked his own death in the last two.
ASIC takedowns: Australia's Securities and Investment Commission says it took down more than 7,300 phishing and investment scam sites over the past year since July of last year. The vast majority of sites offered access to fake investment platforms, usually promoted through social media. Officials called their efforts a game of whack-a-mole that is making a difference.
PWA app phishing: ESET warns about a new mobile phishing technique that targets both Android and iOS users and abuses progressive web apps (PWAs) to load phishing pages.
Malware technical reports
QWERTY Stealer: CyFirma researchers have published a report on the new QWERTY infostealer.
UULoader: CyberInt researchers look at UULoader, a new malware loader that launched in July and appears to have been developed by a Chinese speaker.
NUMOZYLOD: Google Cloud's security team has published an article on NUMOZYLOD, a malware strain also known as FakeBat, EugenLoader, and PaykLoader. The campaign they analyzed was linked to the UNC4536 group.
Msupedge: Symantec has a report on Msupedge, a new backdoor it found deployed on the network of a Taiwanese university. The backdoor was installed via a PHP-CGI vulnerability detailed in another section below—also abused by ransomware gangs, DDoS, and cryptomining botnets.
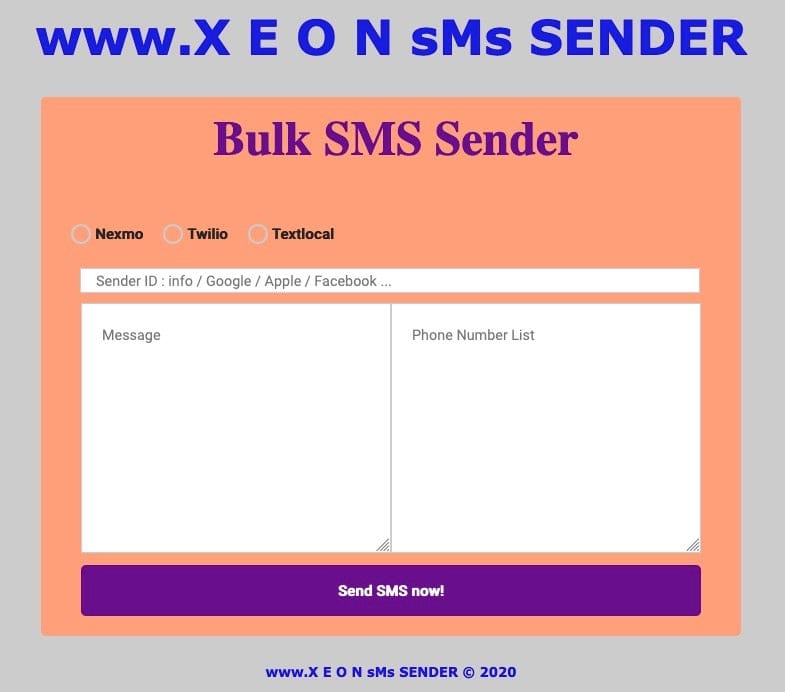
Xeon Sender: SentinelOne looks at Xeon Sender, a tool used by cybercrime groups to send SMS spam through nine different SaaS providers.
Sponsor Section
Learn more about choosing the best enterprise browser for your organization. Dive into features, top vendors, and what to consider when researching.
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
UAC-0020 (Vermin): A Russian cyber-espionage group is using spear-phishing campaigns on the topic of Russian prisoners of war to infect Ukrainian organizations with malware. The final payload in this campaign is a spyware named SPECTR and an exfil tool named FIRMACHAGENT. Ukraine CERT says the attack is the work of a group named UAC-0020 (Vermin). The group was first seen in early 2022, entered a dormancy period, and then came back with new operations this June. Ukraine previously attributed the Vermin group to Russian law enforcement forces operating out of the occupied region of Luhansk.
Blind Eagle (APT-C-36): Kaspersky has published an overview of some recent operations linked to South American APT group Blind Eagle.
"Since its inception, BlindEagle has been conducting persistent campaigns targeting entities and individuals, particularly in Colombia and other Latin American, countries such as Ecuador, Chile, and Panama. In the espionage campaigns we observed in May and June this year, the group primarily targeted individuals and organizations in Colombia, which accounted for 87% of the detected victims. These attacks involved entities across various sectors, notably government, education, health and transportation."
Lazarus Windows zero-day: A North Korean APT known as the Lazarus Group is behind a Windows zero-day (CVE-2024-38193) that was patched earlier this month. Security firm Gen Digital says the group exploited a bug in the Windows Ancillary Function Driver (AFD.sys) to elevate privileges on compromised systems. The zero-day was used to turn off Windows security features and install the FUDModule rootkit since at least June this year.
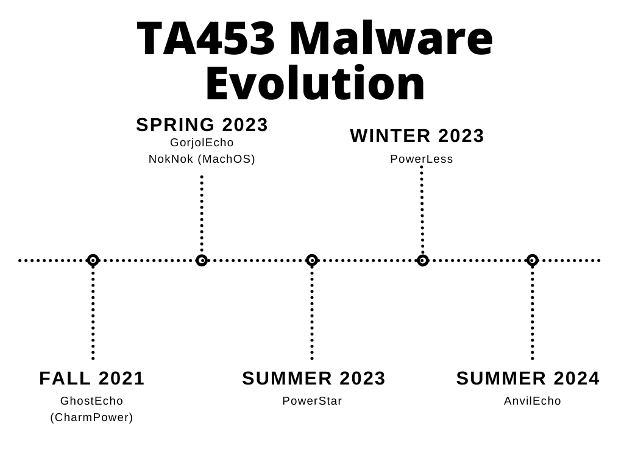
GreenCharlie: Recorded Future has published a report on GreenCharlie, also known as Mint Sandstorm, TA453, Charming Kitten, and APT42, the group that recently breached the Trump campaign.
TA453: An Iranian APT group has targeted a prominent Jewish religious figure with a fake podcast interview invitation. The incident took place in mid-July, and the attacker posed as the Research Director for the Institute for the Study of War (ISW). Proofpoint says the attack was carried out by a group known as TA453 or APT42. The incident stood out to researchers because the group premiered a new malware toolkit named BlackSmith.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Google winds down Google Play VRP: Google is ending a bug bounty program that paid security researchers for vulnerabilities found in popular Android apps. The Google Play Security Reward Program (GPSRP) will stop accepting new submissions at the end of the month, and the final rewards will be paid by the end of September. The program launched with a few participating apps in 2017, and Google opened it to all apps with over 100 million installs in 2019. According to Android Authority, Google shut down the program after a decrease in actionable bug reports.
PHP-CGI bug used in ransomware attacks: The TellYouThePass ransomware group is using a vulnerability in the PHP-CGI module to take over Windows PHP servers. The group has been exploiting the vulnerability (CVE-2024–4577) two days after it was initially revealed in early June. According to South Korean security firm S2W, the group has used the bug as initial access into corporate networks and then pivoted to other systems to deploy its ransomware. The same bug has also been exploited in the wild by DDoS and crypto-mining botnets.
Jenkins exploitation: CISA says multiple threat actors are exploiting a vulnerability in the Jenkins command-line component to hack and access corporate systems. The vulnerability (CVE-2024-23897) has been patched since January and exploitation has been taking place since March. Threat actors linked to attacks include a hacking group named IntelBroker and the RansomEXX ransomware group. The vulnerability has been identified as the entry point for the RansomEXX attack on C-Edge Technologies, a provider of financial software. The attack crippled the payment systems for more than 300 Indian regional and cooperative banks at the end of July. The bug has now been added to the CISA KEV database.
Log4Shell exploitation: DataDog has detected a new wave of attacks exploiting the Log4Shell vulnerability.
Kubernetes vulnerability: ARMO researchers have published a breakdown of CVE-2024-7646, a bug they found and helped patch in Kubernetes.
"A security issue was discovered in ingress-nginx where an actor with permission to create Ingress objects [...] can bypass annotation validation to inject arbitrary commands and obtain the credentials of the ingress-nginx controller. In the default configuration, that credential has access to all secrets in the cluster."
Azure Kubernetes attack: Mandiant researchers have discovered a TLS bootstrap attack in Microsoft Azure Kubernetes servers that can "read all secrets within the cluster."
Copilot Studio SSRF: Tenable researchers have found an SSRF vulnerability in Microsoft's Copilot Studio. The issue can allow access to potentially sensitive information regarding service internals with potential cross-tenant impact.
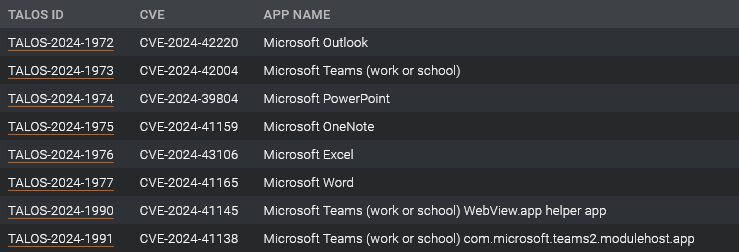
MSFT macOS app vulns: Cisco Talos has identified eight vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office applications for the macOS operating system. The vulnerabilities could allow threat actors to inject malicious code into Microsoft apps and hijack entitlements and user-granted permissions. Microsoft has fixed the bugs only in the Teams and OneNote macOS apps. The company did not fix the issues in Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook since it would cripple support for third-party add-ins.
Moodle security updates: The Moodle LMS has released patches for 16 vulnerabilities, including a severe SQL injection in the site admin.
VeraCrypt security updates: VeraCrypt has patched several security issues, including a fix for an XTS master key vulnerability.
Zabbix RCE: The Zabbix IT monitoring software has released a patch to fix an RCE vulnerability (CVE-2024-22116) with a rating of 9.9/10.
OBS unfixed bug: A maliciously crafted GIF with LZW compressed data may trigger a heap overflow bug in the OBS streaming software's image parser library. A fix is being prepared but no official fix is out.
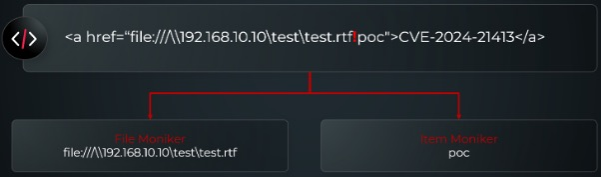
Outlook RCE: Morphisec has published a technical report on CVE-2024-38021, an RCE in Microsoft Outlook. This was patched in the July Patch Tuesday updates. The PoC is apparently extremely trivial.
"Despite Microsoft's efforts to patch the specific attack vector discovered in CVE-2024-38021, one vulnerability remains unpatched. We discovered that passing a simple file moniker still results in the local NTLM credentials being leaked, indicating that the patch does not fully address all potential security risks associated with moniker handling."
Infosec industry
New tool—Blinks: Security researcher Punit Sharma has released Blinks, a Burp Suite extension that automates active scanning with Burp Suite Pro and enhances its functionality. With the integration of webhooks, this tool sends real-time updates whenever a new issue is identified directly to a preferred endpoint. No more waiting for final reports.
New tool—HookChain: Sec4US founder and security researcher Helvio Junior has released HookChain, a new tool to evade EDR solutions.
New tool—Windows API Function Cheatsheet: Security researcher Tetsuo Nishiyama has published an updated Windows API Function Cheatsheet.
Threat/trend reports: DataDome, Malwarebytes, and QiAnXin [PDF] have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends.
New Phrack: The Phrack hacker e-zine issue 71 is now out! The e-zine returns after a three-year break. The last edition came out in October 2021.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine how the cybersecurity industry is very strange when compared to other professional fields, such as doctors and accountants.
In this discussion, Tom Uren and Patrick Gray talk about a US government policy initiative to cover cyber insurance gaps while also improving security across the economy. Lofty goals, but Tom wonders if it is a difficult way to address security gaps.
Risky Business is now on YouTube with video versions of our main podcasts. Below is our latest weekly show with Pat and Adam at the helm!





