Risky Biz News: $922 million worth of crypto-assets stolen in the first half of 2023
In other news: CISA launches CyberSentry platform; Sweden becomes fifth EU state to advise against use of Google Analytics; and hackers leak data of 1,100 French magistrates.
This newsletter is brought to you by asset inventory and network visibility company runZero. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
More than $922 million worth of cryptocurrency assets were stolen in the first half of 2023 across a total of 185 security incidents, blockchain security firm SlowMist reports.
The number is less than half compared to the first half of 2022, when hackers stole $2 billion worth of crypto across 187 incidents.
Almost half of the funds stolen this year were taken from NFT, DeFi, and cross-chain bridge platforms, which lost $487 million across 131 incidents.
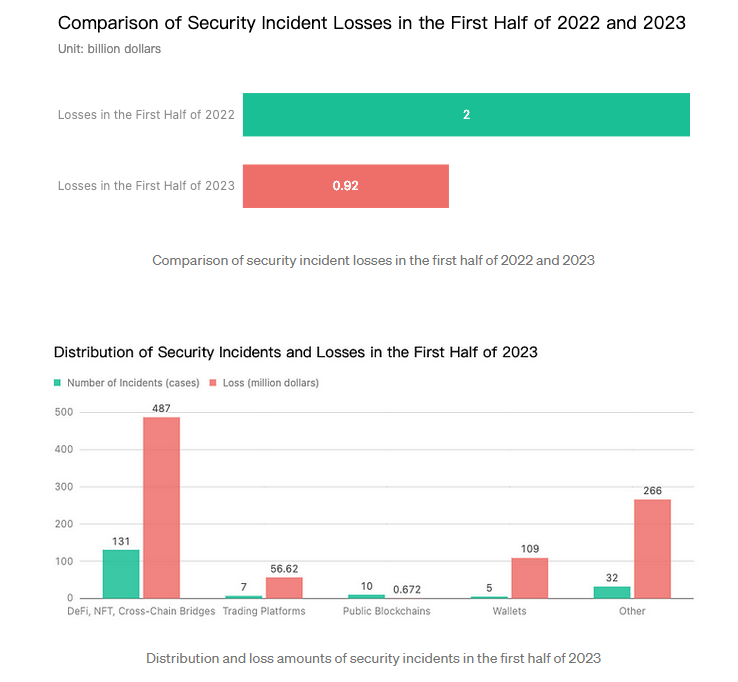
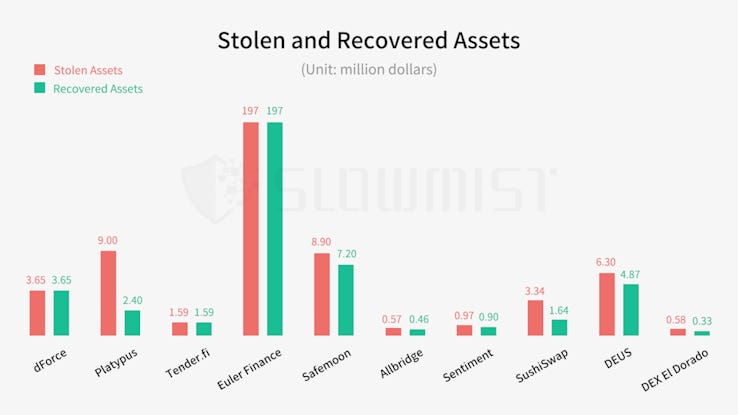
The year's largest hack so far was the Euler Finance incident, where the platform lost $197 million. The hacker eventually returned most of the stolen funds in one of the ten incidents where attackers returned stolen crypto.
Cryptocurrency users lost more than $3.8 billion worth of assets in 2022, according to a report published in February by Chainalysis. It's unclear why this year saw fewer funds stolen compared to last year. It's definitely not because crypto-platforms are more secure, that' for damn sure.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Indian bank fined for major hack: The Reserve Bank of India has fined the AP Mahesh Cooperative Urban Bank the lowly sum of $80,000 for getting hacked and losing $1.5 million of customer funds. The bank was breached in January 2022 after hackers gained full access to the bank's network following a successful phishing attack. The Hyderabad police found the bank at fault for the breach after it failed to implement basic cybersecurity measures. They initially wanted to charge the bank's management with criminal negligence but lacked the legal framework to do so and instead wrote the RBI. Six men, including two Nigerians, were detained in connection to the hack. [Additional coverage in The Times of India]
French Ministry of Justice leak: A hacking group named KromSec has leaked the personal data of 1,120 employees of the French Ministry of Justice. KromSec says it carried out the hack and subsequent leak in response to the protests that have hit France following the police killing of Nahel Merzouk. The group says they obtained the data after hacking the ministry's Drupal CMS. [Additional coverage in ZDNet]
Microsoft denies Anonymous Sudan hack: Microsoft has denied that the hacktivist group Anonymous Sudan obtained the account information of more than 30 million users. The company put out a statement after the group claimed in a Telegram post to have breached Microsoft servers and stolen emails and passwords for 30 million users. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
General tech and privacy
IVPN drops port-forwarding after abuse: IVPN will drop support for its port-forwarding feature by September 30 this year. The feature allows remote users to access computers hidden behind IVPN's network. The company says the feature has seen large-scale abuse and was used to share "objectionable materials." IVPN is the second major VPN provider to drop support for port-forwarding after Mullvad announced a similar move at the end of May. IVPN says that Mullvad's announcement drove a wave of new customers to its service, which increased risks for the company from both law enforcement and data centers.
Google changes privacy policy: Google has changed its privacy policy to let its users know that any publicly-available information may be scanned and used to train its AI models. It's funny that Google's legal team thinks its privacy policy is stronger than copyright law. Hilarious!
Twitter paywalls TweetDeck: After spectacularly shooting itself in the foot over the weekend and crashing the main site and TweetDeck for all its users, QAnon and neo-nazi hell-hole Twitter has launched a new TweetDeck version on Monday. The catch? After 30 days, only Blue users will be able to access it.
Twitter's ever-growing spam problem: BleepingComputer's Ax Sharma has a rundown of Twitter's latest problem—spambots pushing adult content. And yes, they are everywhere!
Instagram Threads goes live: Meta has released a preview version of its Twitter competitor, named Instagram Threads. The app is already available for download in some EU countries. A formal launch is scheduled for July 6.
EU deems Meta's GDPR approach illegal: The European Court of Justice has ruled in a case between Meta and Germany's Federal Cartel Office, concluding that Meta's interpretation of the EU's GDPR regulation is illegal. The court sided with the German agency, which ruled in 2019 that Meta was bypassing GDPR privacy protections by taking data collected by various of its services without proper user consent and merging it behind the scenes. The aggregated data allowed Meta to continue tracking German and EU users for its advertising business. The court's ruling effectively bars the company from engaging in the behavior going further. [See CJEU court ruling (PDF) and TechCrunch and noyb coverage]
Sweden cracks down on GA use: The Swedish data protection agency has fined two local companies for their use of the Google Analytics service and has recommended against future use of the tool. A €1 million fine was handed out to Swedish telco Tele2 and a €25,000 fine to local online retailer CDON. The fines were handed out because companies allowed Google Analytics to collect data on Swedish citizens and transfer it to the US. Sweden becomes the fifth EU member state to fine or recommend against the use of Google Analytics after Austria, Denmark, France, and Italy.
FarCry source code leak: The code of the FarCry 2004 game has mysteriously popped up online. The source of the leak is currently unknown. No word from Ubisoft on the leak. [Additional coverage in EuroGamer]
KEM API coming to Java: OpenJDK is gonna get an API for key encapsulation mechanisms (KEMs), an encryption technique for securing symmetric keys using public key cryptography. The API will be post-quantum cryptography ready. It will ship with OpenJDK 21—see full list of planned features on Nicolai Parlog's blog.
"KEMs will be an important tool for defending against quantum attacks. None of the existing cryptographic APIs in the Java Platform is capable of representing KEMs in a natural way. Implementors of third-party security providers have already expressed a need for a standard KEM API. It is time to add one to the Java Platform."
Firefox 115: Mozilla has released Firefox 115. New features and security fixes are included.
Government, politics, and policy
US Marines triples cyber jobs bonuses: The US Marines Corps has tripled the signing bonuses for recruits who enlist in cyber and crypto operations. The bonus is now $15,000, up from just $5,000, the sum first announced last year. The new cyber bonus is now the largest enlistment bonus in the Marines Corp after it was the smallest in the previous years. [Additional coverage in DefenseNews]
"The military occupational specialties eligible for the bonus are cyberspace warfare operator (1721), communications intelligence/electronic warfare operator (2621), electronic intelligence/electronic warfare analyst (2631), cryptologic language analyst (2641) and intelligence surveillance reconnaissance systems engineer (2651), according to the October 2022 administrative message and the Corps' index of specialties."
US Navy simplifies cyber roles: The US Navy has added a new job classification for its officers active in the cyber domain. The newly introduced maritime cyber warfare officer role will allow officers to operate in offensive and defensive cyberspace operations only. The new role effectively removes any signals intelligence and electronic warfare responsibilities from its IT specialists and cryptologists. The US Navy is expected to fill 300 of the new maritime cyber warfare officer roles [Additional coverage in NextGov]
FTC proposes ban on fake reviews: The US Federal Trade Commission has proposed a rule that will make it illegal for companies to use fake or paid reviews to boost product sales and deceive consumers. The new rule also prohibits companies from hiding negative reviews and hijacking feedback posted on one product to appear on another item. The proposed rules also address the hidden social media influencer market. Companies will be banned from either providing or using services that sell fake likes, fake followers, or fake views.
CISA CyberSentry: The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has launched a new threat detection and monitoring platform named CyberSentry. The platform is run by CISA staff and is provided free to all critical infrastructure operators. It will allow CISA to hunt for malicious cyber activity on critical infrastructure networks and then provide collective mitigations and recommendations to all participating organizations.
Sponsor section
This week's sponsor is RunZero. In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to RunZero's CEO Chris Kirsch about how the company has evolved from offering an active scanning product to one that can now discover assets on OT and cloud environments using both active and passive scanning approaches:
Cybercrime and threat intel
Neo_Net: A threat actor named Neo_Net has stolen hundreds of thousands of euros and compromised the personal information of thousands of victims. The threat actor's success comes from running smishing operations targeting Spanish-speaking countries over the past two years. Neo_Net has greatly expanded operations and is now renting out phishing panels, Android trojans, and has even launched a successful Smishing-as-a-Service portal named Ankarex. Researchers believe the threat actor is based in Mexico.
Crysis+Venus campaign: AhnLab researchers have spotted the threat actor behind the old Crysis ransomware deploy versions of the Venus ransomware in new attacks they have conducted. The intrusions were linked to compromised RDP servers being used for initial access.
Malware technical reports
Diicot cryptomining botnet: Chinese security firm Antiy and China's CERT team have published a joint technical analysis on the Diicot crypto-mining botnet that has recently hit a bunch of Chinese cloud service providers. Reports on the same group are also available from Cado Security, Akamai, and Bitdefender.
Sponsor Demo
RunZero (formerly Rumble Network Discovery) is one of this newsletter's four main supporters and this week's featured sponsor. The company's main product is its network discovery and asset inventory platform, which can be used to find any managed and unmanaged assets inside a customer's network. To learn more, please check out this runZero product demo below:
APTs and cyber-espionage
Patchwork's Spyder: QiAnXin has published an analysis of Spyder, a new backdoor used by the Patchwork APT, a variant of its previous WarHawk backdoor.
APT31: APT-doxing group IntrusionTruth has published a new report that maps how former employees of Chinese company Wuhan Xiaoruizhi have moved on to work for other companies across China. IntrusionTruth previously claimed Xiaoruizhi acted as a front company for the APT31 Chinese cyber-espionage group.
"Now, we may never know what happened at Xiaoruizhi at the end of 2019 that caused APT31 to pursue a mass career change. Perhaps Xiaoruizhi had simply served its time as an APT front and the powers that be needed to move APT31 into different administrative structures."
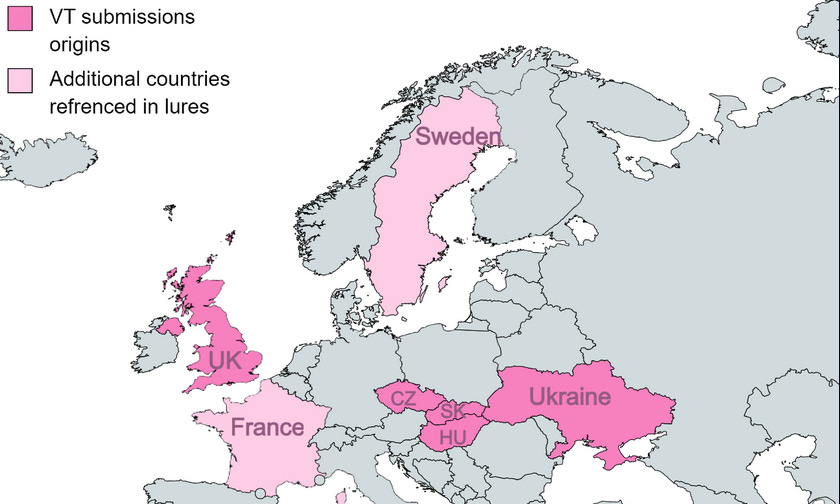
SmugX: Chinese cyber-espionage group RedDelta (Mustang Panda) has continued its persistent targeting of Foreign Affairs ministries and embassies across Europe. Security firm Check Point says the new attack represents a larger trend within the Chinese espionage ecosystem that has been slowly shifting its attention to European entities. The new operations are a continuation of RedDelta campaigns initially reported back in December 2022 by BlackBerry and Recorded Future. The attacks were spotted in countries such as Sweden, France, Ukraine, Czechia, Slovakia, Hungary, and the UK. Just like last year, the final malware payload deployed on infected systems was the good ol' faithful PlugX backdoor—a malware strain used by tens of Chinese APT groups for more than a decade.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Mastodon security update: A major security vulnerability will be disclosed this Thursday. Most Mastodon servers will receive a patch two days before, on Tuesday.
IBM i DDM vulnerability: Silent Signal researcher Zoltan Panczel has published details on an unauthenticated RCE in the DDM service of the IBM i relational database system (CVE-2023-30990). The bug was patched on June 30, last week.
CISA KEV update: Last week, CISA added two 2016 (Windows, Firefox), two 2019 (D-Link), and six 2021 (Samsung) vulnerabilities to its KEV catalog. The vulnerabilities were identified as missing from KEV after a cross-reference analysis between KEV and other exploited vuln DBs. The analysis was done by Nucleus Security's Patrick Garrity, who eventually reported them to CISA.
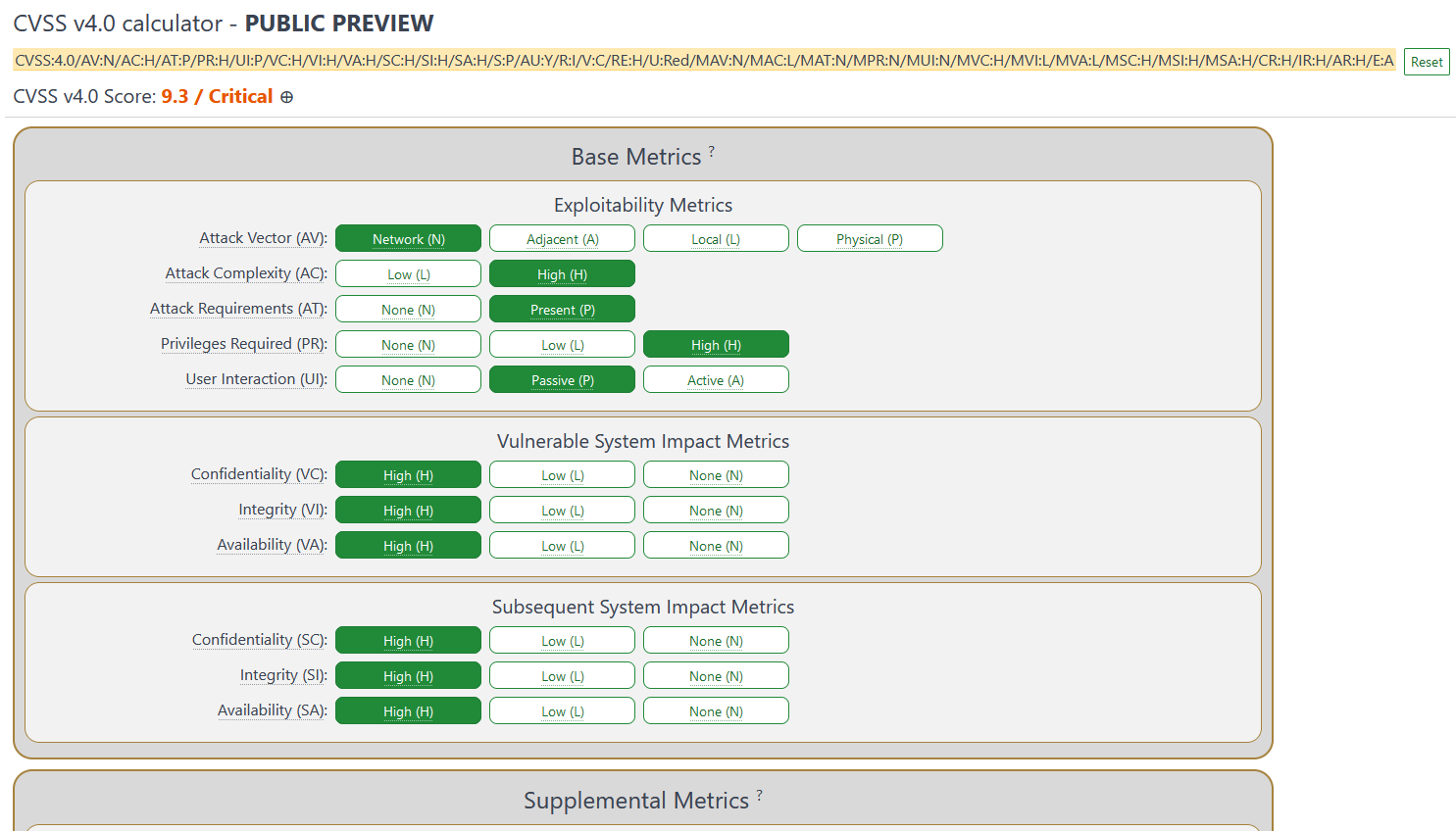
CVSSv4 CVE calculator: A first preview version of the CVSSv4 CVE score calculator is out and available for testing. The calculator will be live until the end of July 2023, when FIRST will close the public feedback period and prepare for the official CVSSv4 launch later this year.
Voice authentication attack: A team of academics from the University of Waterloo in Canada has discovered an attack technique that can successfully bypass voice authentication security systems typically used by banks. The system works by detecting typical markers found in deepfake audio that give it away as being computer-generated. The new attack removes these markers to allow threat actors to authenticate without being detected. The research team says their attack can successfully bypass voice authentication security systems with up to a 99% success rate after only six tries.
Infosec industry
IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 2023 videos: Talks from the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy 2023 conference, which took place at the end of May, are now available on YouTube.
New tool—npm manifest confusion checker: Software engineer Felix Pankratz has released a tool to check if npm packages are vulnerable to manifest confusion attacks.
New tool—TeamsPhisher: Alex Reid, a member of the US Navy's read team, has released a tool named TeamsPhisher that facilitates the delivery of phishing messages and attachments to Microsoft Teams users whose organizations allow external communications.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq look at the EU's proposed media freedom act and how one of its goals is to protect journalists from spyware.




