Risky Biz News: FCC adopts SIM-swapping and port-out protections
In other news: Russia blocks Shadowsocks protocol; Google launches new Titan security keys; and a crypto threat actor specializes in exit scams.
This newsletter is brought to you by Gigamon. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Spotify:
The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has adopted new rules designed to protect US consumers from SIM-swapping attacks and port-out scams.
Under the new rules, US wireless providers are required to use "secure methods of authenticating a customer" when they request porting a SIM card to a new device (aka SIM swapping) or their phone number to a new carrier (aka port-out).
The Commission did not specify what the "secure methods" should be, and it appears the agency is leaving this up to each of the US carriers and their own internal procedures.
In addition, the FCC says wireless carriers have to immediately notify customers when a SIM swap or port-out operation has been requested.
The Commission hopes the notification will help victims spot a malicious request when it takes place and prevent attackers from gaining control of a user's phone number.
Both SIM-swapping and port-outs have been extensively and repeatedly used by a wide range of threat actors to hijack access to a user's phone number.
Threat actors typically use this temporary access to request password resets for the victim's online accounts, change passwords, gain control of the accounts, and then steal bank or cryptocurrency assets.
Individuals who fell victim to SIM-swapping and port-out attacks range from regular nobodies who lost their cryptocurrency savings to former Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey, who had his account hijacked to promote links to various crypto-scams.
SIM-swapping and port-out scams have also been widely adopted by professional cybercrime and ransomware groups, which typically use them to hijack low-level employee accounts and then pivot to internal networks.
Two of the most prolific groups to do so are Lapsus$ and Scattered Spider, both of which have used SIM-swapping and port-outs as the core element of their intrusions.
Back in February 2022, the FBI put out a public service announcement warning about the rise of SIM swapping and these exact same scenarios, and in August this year, the DHS Cyber Safety Review Board asked both the FCC and the FTC "to mandate and standardize best practices to combat SIM swapping."
The FCC's new rules were first proposed in July and have been adopted after a period of public comments. The FCC has opened the newly passed rules for new public comments to give telcos a way to "further harmonize" the requirements if they need to.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
NTMC leak: Bangladesh intelligence agency NTMC has left a sensitive database exposed on the internet and leaked the personal details of an unknown number of citizens. The leaked data contained more than 120 data points for each citizen, ranging from real names to Twitter IDs, criminal records, and phone call records. Discovered by Viktor Markopoulos of CloudDefense.AI, the researcher says he reported the database to Bangladesh officials, but the server was never secured. Instead, it was wiped and replaced with a ransom demand, presumably in an automated attack. [Additional coverage in Wired/non-paywall]
Ransomware gang reports victim to SEC: The AlphV ransomware gang has reported one of its victims to the US Securities and Exchange Commission for failing to report its security breach via a 10-K form. The reported company is MeridianLink, a digital lending service provider for the financial industry. MeridianLink has confirmed the incident but has not commented on AlphV's actions. [Additional coverage in DataBreaches.net]
Toyota ransomware incident: Japanese carmaker Toyota has confirmed that a ransomware group breached its financial services division and is now threatening to leak stolen documents on the dark web. The company confirmed the hack after the Medusa ransomware gang listed Toyota on its leak site, demanding a $8 million payment. The breach allegedly took place at Toyota's financial division in Germany. [Additional coverage in BleepingComputer]
General tech and privacy
ETSI open-sources TETRA code: ETSI, the organization behind the TETRA communications protocol, has decided to open-source the code behind its protocols and algorithms after researchers found a series of backdoors in its code in July this year. [Additional coverage in Zero Day]
New protestware: Researchers at DevSecOps company ReversingLabs have discovered new protestware packages on the npm portal containing messages of peace related to the conflicts in Ukraine, Israel, and the Gaza Strip. One of these is owned by Israeli DevSecOps company Snyk.
EFF complains to the FTC: The EFF has filed a complaint with the FTC asking the agency to crack down on e-commerce portals like Amazon and AliExpress. The EFF says the two companies and others are still selling Android TV set-top boxes infected with malware—even after such reports have been public for months. The EFF says it also notified CISA Director Jen Easterly of the issue since the backdoored devices represent a supply chain risk for the US consumer market.
Meta pushback: Meta is pushing against US lawmakers who are trying to make the company protect kids on its platform. The company is now pushing for legislation that would have app store makers verify the age of kids and require parental approval for the installation of dangerous apps. I mean, Meta is not innocent here, but they're not wrong either. [Additional coverage in the Washington Post/non-paywall]
New Titan security keys: Google launched two new Titan security key models that can store up to 250 unique passkeys. The new models will replace Google's current line-up of USB-A and USB-C Titan keys. Besides USB ports, both models will also support NFC connectivity. As part of the product launch, Google says it will also be providing 100,000 of its new Titan keys to high-risk users for free. This includes campaign workers, activists, and journalists.

Government, politics, and policy
ASD ACSC annual report: Australia's Cyber Security Centre has published its annual Cyber Threat Report for the year. The report covers 1,100 cyber security incidents from Australian organizations. The ACSC says that of these, 127 were extortion-related incidents, with 118 involving ransomware. The report also highlights that one in five critical vulnerabilities was exploited within 48 hours. As for nation-state activity, foreign actors focused on critical infrastructure and intelligence collection, with a special focus on the AUKUS partnership on nuclear submarines and other advanced military capabilities.
EU rejects client-side CSAM scanning: A key committee in the European Parliament has voted against the EU's plan to force internet companies to scan user communications for child sexual abuse material (CSAM). In a smashing 52-2-1 vote, the Committee on Civil Liberties, Justice, and Home Affairs ruled against the introduction of client-side scanning and age verification mechanisms.
Russia blocks Shadowsocks protocol: Russian telecommunications watchdog Roskomnadzor has ordered internet service providers to block the Shadowsocks tunneling protocol. Shadowsocks is the latest internet protocol added to the country's VPN blocklist, which the agency silently started enforcing earlier this year. It is one of the 49 protocols Russia is currently attempting to block. The full blocklist leaked online last week after the Ministry of Transport sent a document about the ban to its subordinates. Other protocols included on the list include the likes of WireGuard, OpenVPN, IPSec, and IKEv2. [Additional coverage in The Moscow Times]
Harry Coker nomination: The Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee advanced the nomination of Harry Coker for the role of White House National Cyber Director. Coker's animation passed in a 9 to 6 vote. Coker is set to replace Chris Inglis, who left the post in February. [Additional coverage in The Record]
Biden campaign CISO: The Biden camp is looking for a CISO to help it safeguard the US President's re-election attempt. [Additional coverage in SecurityWeek]
Sponsor section
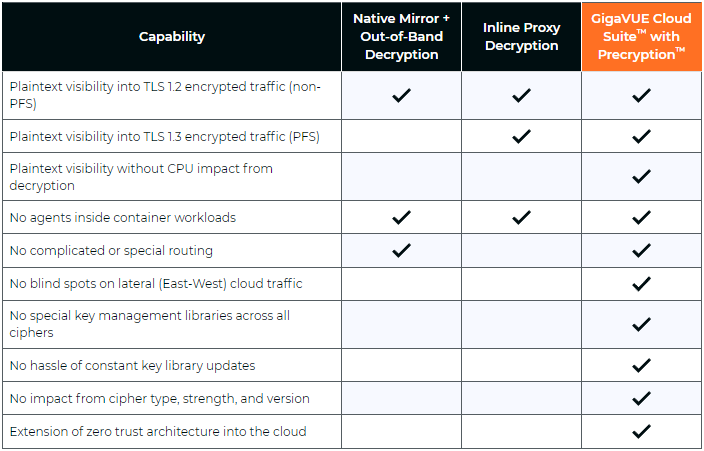
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Tom Uren talks to Ryan Mahoney, Product Director at Gigamon. The TLS 1.3 encryption standard makes passive network monitoring inside your network difficult without break-and-inspect contortions. But Gigamon has what they call a "precryption" solution!
Cybercrime and threat intel
Exit scam group: Blockchain investigator ZachXBT has found traces that a single threat actor has orchestrated exit scams at six different cryptocurrency projects. The group is believed to have stolen more than $16.2 million worth of crypto assets from early investors in their projects. So far, the group has been tied to rug pulls at the Lendora Protocol, Magnate, Solfire, Hash DAO, Kokomo, and Snowflake.
Phishing gang detained: Police from Czechia and Ukraine have detained members of a phishing gang believed to have stolen more than €8 million from victims. Four suspects were arrested in Czechia and six in Ukraine. According to Europol, the group operated from call centers in Ukraine and carried out vishing attacks, mainly targeting Czech victims. The group's tactics involved tricking victims into thinking they were hacked and moving funds to safe accounts controlled by the gang.
LockBit and CitrixBleed: CyFirma and security researcher Kevin Beaumont have published reports on LockBit and the group's exploitation of the CitrixBleed vulnerability.
KEV update: CISA has updated its KEV database with five new vulnerabilities that are currently being exploited in the wild. The list includes the three zero-days. The first is CVE-2023-36584, a Windows zero-day patched last month. The second and third are older bugs in Sophos firewalls and Oracle Fusion servers that have recently been spotted being abused in the wild.
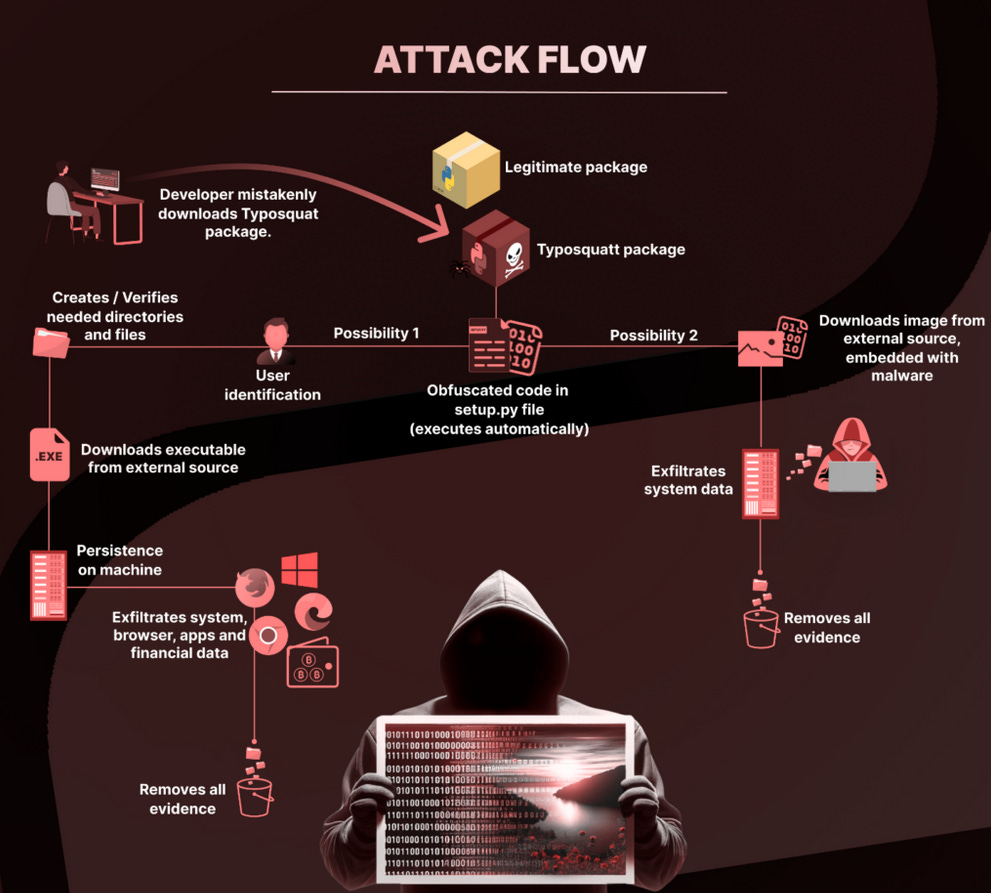
PyPI campaign: DevSecOps company Checkmarx has discovered a threat actor who, for the past six months, has uploaded 27 malicious packages to the PyPI repository. Checkmarx says the packages typosquatted the names of legitimate libraries in order to trick developers into accidentally installing them. The libraries contained code meant to gain reboot persistence on infected hosts and collect and exfil user data to a Discord channel.
Chang Way: Bridewell security researcher Joshua Penny has published an analysis of Chang Way Technologies, a bulletproof hosting provider operating from Hong Kong. According to Penny, the service has hosted infrastructure for the BlackByte ransomware, the 404 traffic distribution system, multiple Android bankers, and initial access brokers.
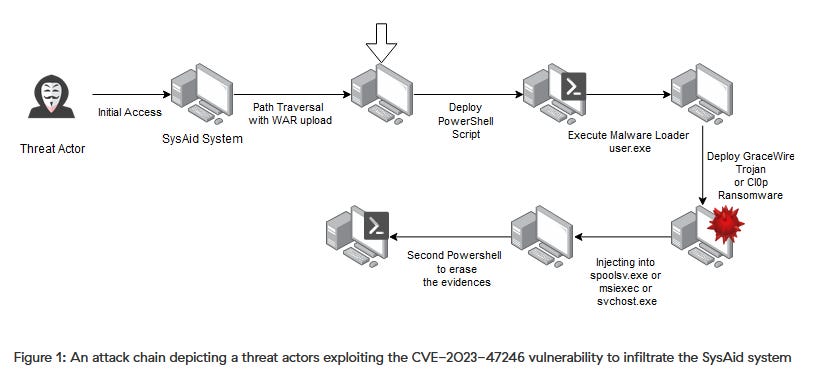
SysAid attacks: Zscaler has published its own analysis of Clop's campaign targeting SysAid servers. The campaign started last week, and it's still ongoing.
FBI yearly warning: The FBI has published its yearly alert, advising consumers to be wary of scams ahead of the holiday shopping season.
Scattered Spider: Together with CISA, the FBI also released a security advisory with TTPs used by the Scattered Spider (Starfraud, UNC3944, Scatter Swine, Muddled Libra) group in recent intrusions. These include posing as IT tech support staff, MFA prompt-bombing, SIM swapping, and deploying the AlphV ransomware on hacked networks.
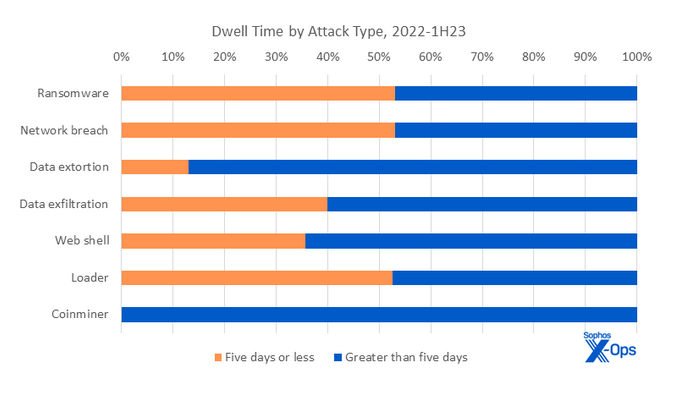
Threat reports: Avast, Chainguard, WithSecure, Guidepoint, Trellix, Wiz, and Sophos have published threat reports. The most interesting conclusion is Sophos' observation that dwell times are going down, in line with what Secureworks reported last month.
Malware technical reports
Rhysida ransomware: CISA and Fortinet have published write-ups on Rhysida, a new RaaS that launched back in May and has significantly ramped up operations.
Royal ransomware: CISA has updated its analysis of the Royal ransomware and added information about the gang's potential attempt to rebrand as Blacksuit.
Elevator: Lumen's Black Lotus Labs has discovered a new Linux malware strain named Elevator. The malware abuses the Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) to escalate privileges to kernel access on already compromised Linux servers and secure persistent access for the attacker.
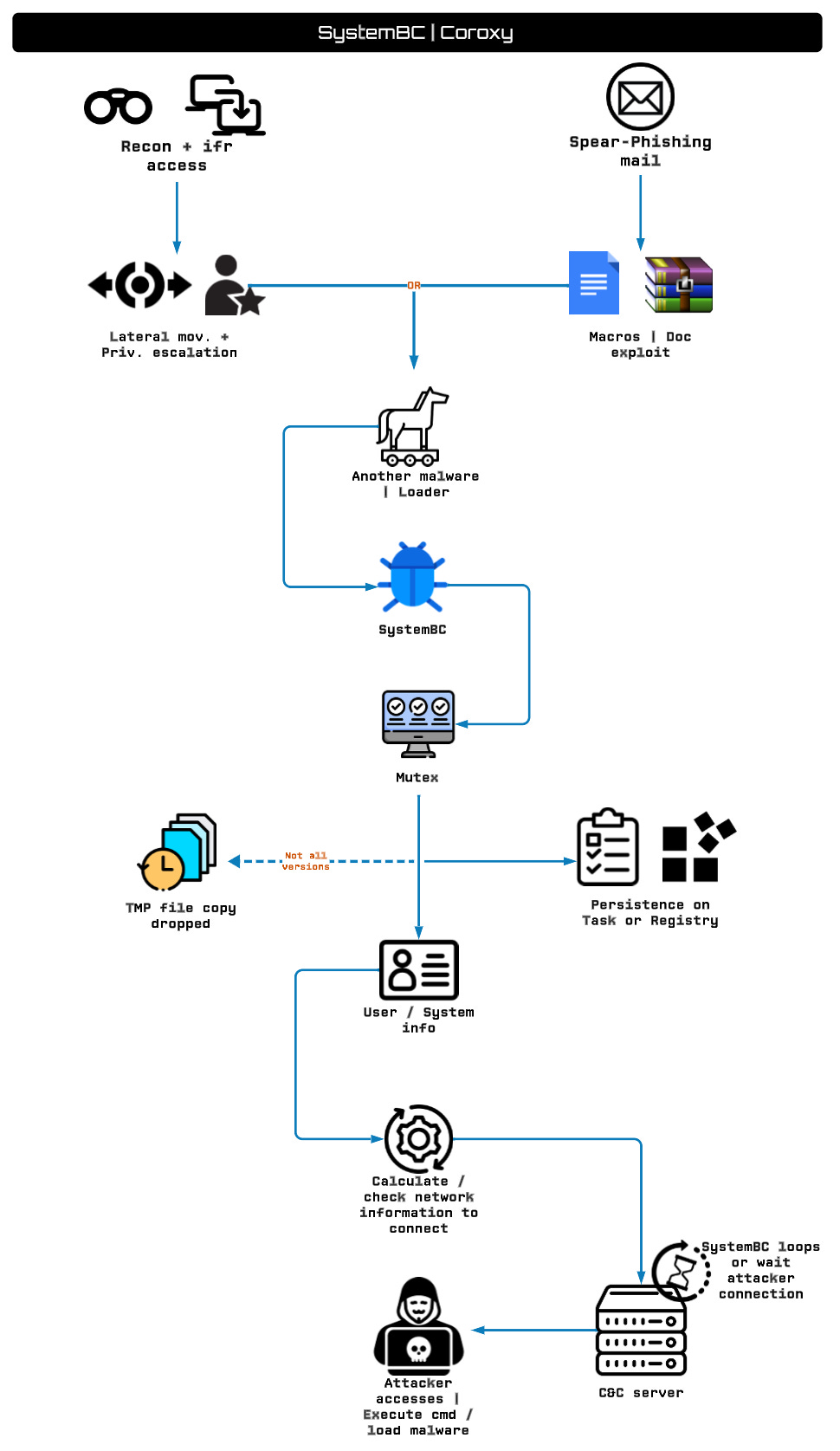
SystemBC: One eSecurity researcher Aaron Jornet has published an analysis of SystemBC (Coroxy, DroxiDat), a proxy malware bot often also used as initial access by other cybercrime groups. Many of these groups include ransomware gangs, such as Cuba, Darkside, Conti, Ryuk, Avaddon, BlackBasta, 8Base, Rhisida, Vice Society, Maze, Egregor, Hive, and Play.
Sponsor Demo
Brought to you by Gigamon Precryption, a visibility solution for encrypted traffic across virtual machine (VM) or container workloads. Perform advanced threat detection, investigation, and response across the hybrid cloud infrastructure. To learn more, please visit gigamon.com/precryption
APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Raccoon Security: Censys has discovered that Russian company Raccoon Security is the cybersecurity arm of NTC Vulkan, a private firm contracted by the Russian Ministry of Defense to develop offensive cyber weapons. NTC Vulkan was sanctioned by both the US and the EU.
Sandworm: Security researcher Monty has put together a list of recent Sandworm TTPs.
BlueNoroff's macOS malware: South Korean security researcher Sakai has published an analysis of a new strain of macOS malware employed by North Korean hacking group BlueNoroff.
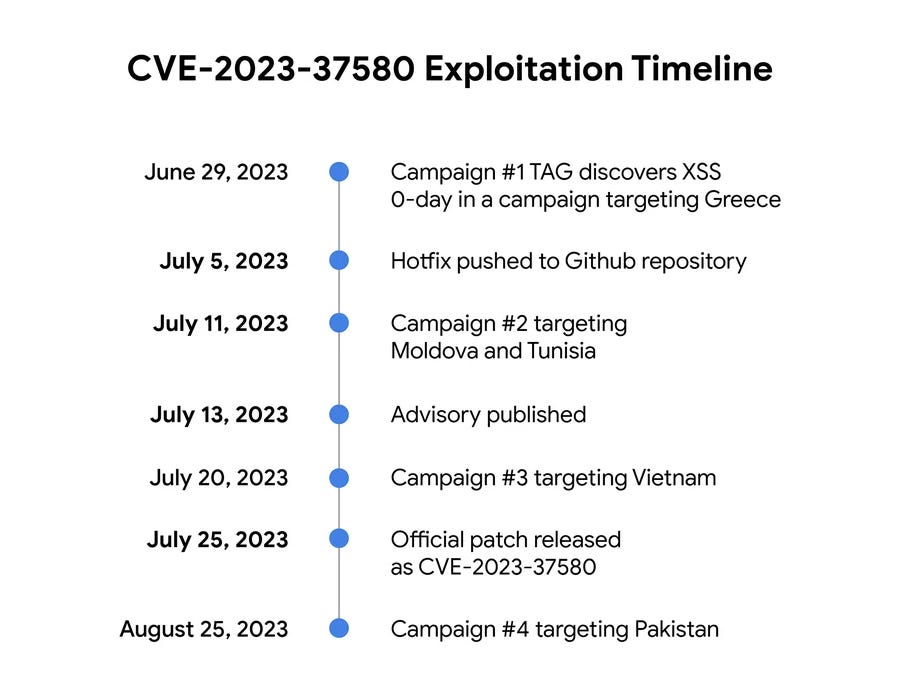
Zimbra zero-day attacks: Google's TAG security team has published additional details about a zero-day (CVE-2023-37580) in the Zimbra email server it saw exploited in the wild in June. While Google did not make a formal attribution, TAG researchers say the first attacks used an email-stealing tool used in the past by a Chinese APT group named TEMP_Heretic. Google says that once Zimbra patched the zero-day, another threat actor named Winter Vivern also started exploiting the bug in its operations. ESET previously classified Winter Wivern as a Belarus-aligned threat actor. All in all, Google TAG says it saw the Zimbra zero-day used across four separate campaigns targeting organizations in Greece, Moldova, Tunisia, Vietnam, and Pakistan.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
M365 misconfigurations: The research team at Reco has reminded the world that Microsoft has still not fixed one of its major issues—that when disabling a user account for an employee who left an organization, access tokens remain active. Org admins must manually trigger the "Sign out inactive users automatically" option in their backends.
Google Workspace abuse: Bitdefender has found a way to expand access from a single machine to an organization's Google Workspace environment. The method exploits the Google Credential Provider for Windows. Google was notified but declined to release a fix.
Reptar vulnerability: Intel has released security updates for all its CPU models to fix a vulnerability that can be abused to elevate privileges and crash systems. Named Reptar (CVE-2023-23583), the bug was discovered by Google security researcher Tavis Ormandy. The researcher says exploiting the bug puts the CPU in a so-called "glitch state" where normal operational rules are suspended, and attackers can perform actions they normally couldn't.
WP Fastest Cache vulnerability: Automattic's WPScan team has discovered a severe SQL injection vulnerability in the WP Fastest Cache plugin. The vulnerability can be used to hijack unpatched websites. WP Fastest Cache is one of the most popular WordPress plugin, installed on more than one million sites.
CrushFTP unauth RCE: Converge security researchers have discovered and helped patch an unauth RCE vulnerability in the CrushFTP file-transfer software. Tracked as CVE-2023-43177, the vulnerability was patched in August. More than 10,000 CrushFTP servers are currently available online, making this a huge attack surface that can be exploited.
ActiveMQ exploitation: Security firm VulnCheck has published a new method of exploiting an Apache ActiveMQ vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-46604. The vulnerability has been exploited in the wild since mid-October to deploy the HelloKitty and TellYouThePass ransomware on unpatched servers. The new exploitation method allows threat actors to execute attacks from memory and remain undetected by security solutions. There are currently more than 11,000 internet-facing ActiveMQ servers.
Typos research: NCC Group division Fox-IT scanned the internet for typos in reserver HTTP responses and found that they are quite common.
"Our research concludes that typos alone are insufficient to identify malicious servers. Nevertheless, they retain potential as part of a broader detection framework."
VMWare auth bypass: VMWare says its Cloud Director Appliance is vulnerable to an authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2023-34060). The company says it's still working on a patch and has released temporary mitigations that can be used to safeguard appliances. The vulnerability has received a severity rating of 9.8/10.
Cisco security updates: Cisco has released or updated five security advisories for various products.
WhatsApp security audit: NCC Group has audited Auditable Key Directory (AKD), a library used by Meta for WhatsApp's cryptographic algorithms.
"The review was performed remotely by 3 consultants over a two-week period with a total of 20 person-days spent. The project concluded with a retest phase a few weeks after the original engagement that confirmed all findings were fixed."
StackOverflow leaks: According to a software developer named Matan H., there are thousands of API keys and tokens that have been accidentally posted on StackOverflow. Most have probably been revoked by now, but this shows a trend with programmers who still fail to sanitize their code when asking for help online.
Infosec industry
New tool—IISHelper: PwC UK has open-sourced an IDA Pro plugin named IISHelper to aid with the analysis of native IIS modules.
Clorox CISO departs after hack: Clorox chief information security officer Amy Bogac is departing her role in the aftermath of a ransomware attack that crippled the company's operations in August this year. Bogac served as the company's CISO for two and half years before she departed at the end of last week. In SEC filings, Clorox said it expects sales to drop by $356 million as a result of the incident. [Additional coverage in Bloomberg/non-paywall]
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about International Humanitarian Law, aka the Rules of War in cyberspace. These rules don't really make sense in cyberspace, but despite that, Tom and The Grugq think talking about them (and other norms of behavior) is still worthwhile.




