Risky Biz News: CISA to provide free security scans to public water utilities
In other news: Adobe, Google, Mozilla, and Microsoft patch zero-days; MGM Resorts suffers mysterious cyber incident; and Dutch football federation pays ransom to avoid player data leak.
This newsletter is brought to you by Red Canary, your Managed Detection and Response ally. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has announced it is providing free access to its official Vulnerability Scanning (VS) service to the operators of public US water and wastewater utilities.
The VS service has been running for years but has been previously available to federal civilian agencies only.
The service will help water utilities identify internet-exposed systems and see if they are vulnerable to known security bugs.
Water utilities that sign up will receive a weekly status report with details about exposed systems and vulnerabilities that will need to be patched. Based on the severity of identified vulnerabilities, CISA will rescan systems at various intervals to see if they've been patched properly and notify administrators again. More details here [PDF].
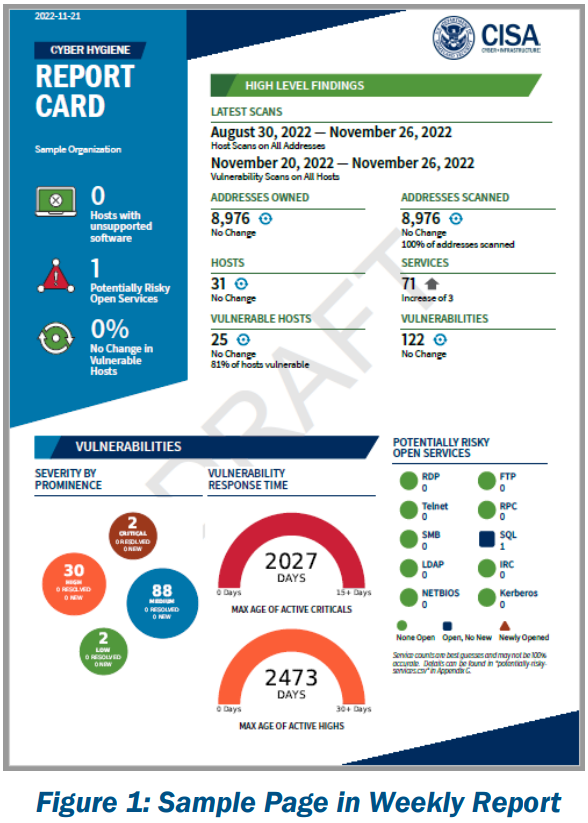

Opening up the VS service to public US water utilities is the latest CISA effort to help local critical infrastructure operators secure vulnerability systems.
In March, CISA launched the Ransomware Vulnerability Warning Pilot (RVWP) program, an effort to scan the networks of critical infrastructure entities and identify systems that are vulnerable to common entry vectors used by ransomware gangs.
CISA also runs the Cyber Hygiene Web Application Scanning service, which scans web apps for common misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
MGM Resorts incident: MGM Resorts says it is responding to a "cybersecurity issue" that forced the company to take down some of its IT systems. The incident has impacted the company's properties across the US. According to reports on social media, some guests couldn't access their rooms or use the hotel's bars, ATMs, and slot machines. The hotel chain's website was also down. [Additional coverage in Gizmodo]
arXiv DDoS attack: The arXiv e-print hosting service is dealing with a DDoS attack that has crippled the platform's email systems. The attack was conducted with only 200 IP addresses, with most being owned by a Chinese ISP. arXiv says the attacker initiated more than one million email change requests over a short period of time, which required the platform to block the attacker's IP range.
Telegram DDoS attack: The Anonymous Sudan fake hacktivist group launched a series of DDoS attacks against Telegram after the service took down their official channel.
KNVB ransomware attack: The Dutch football (soccer) association has paid an undisclosed ransom to the Lockbit ransomware gang to prevent the leak of sensitive player data online. The incident took place in April this year when LockBit breached the federation's network and stole hundreds of gigabytes of data. Officials say the stolen files contained sensitive information about registered players, including minors. Stolen data included ID and passport scans, salary details, and even medical information.
Free Download Manager supply chain attack: The website of the Free Download Manager application has redirected some of the app's Linux users to a malicious package as far back as 2015. Not all users were redirected to the malicious download, but those that did received a version of the app containing the Bew backdoor. Russian security firm Kaspersky says it contacted the app's maker, but they have yet to receive a reply about the site's compromise.
Twitch incident: Two Twitch extensions named Pando and Stream Alerts TV were compromised and used to post spam and profanity across Twitch streams over the weekend. The two extensions were created by CVS Gaming. The company says it disabled both extensions when it learned of the abuse and rolled out a fix to patch the bug exploited by the spammers. [Additional coverage in Dot Esports]
General tech and privacy
ICANN to open new generic TLD: ICANN is taking applications for new gTLDs. Let's go! More file extensions as domain names!!! Let's do it!
No Topics in Vivaldi: The Vilvadi browser has disabled the Topics API (Privacy Sandbox) in its Chromium-based browser.
WhatsApp cross-platform messaging: Meta is testing a beta version of WhatsApp with cross-platform messaging capabilities, allowing users to message users on other platforms. The feature is meant to comply with the new EU Digital Markets Act (DMA). [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
Chrome 117: Google has released version 117 of its Chrome browser. See here for security patches and webdev-related changes. Major changes include the deprecation of TLS SHA-1 server signatures and the sandboxing of the network service on Linux and ChromeOS to improve security.
Unity adds runtime fee: Game engine maker Unity plans to add what it calls a "runtime fee" that will cost game developers $0.2 per game install, per month. The move is expected to cripple many gaming studios, especially in the mobile market.
Government, politics, and policy
Council of Europe calls for spyware investigations: The Council of Europe says it is seeing mounting evidence that spyware is being used for illegal surveillance across Europe and in violation of human rights. The Council—which is not part of the EU and works as a separate and independent body—has called on the governments of Poland, Hungary, Greece, Spain, and Azerbaijan to investigate their use of the Pegasus and similar spyware in politically motivated cases. Officials have also called on the governments of Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands to clarify how they also use spyware and what mechanisms they have in place to oversee its use.
Smaller fines in the UK: The UK's cybersecurity agency and data protection agency have signed a memorandum of understanding meant to encourage hacked companies to cooperate with the NCSC. The ICO has promised reduced fines for companies that report breaches and collaborate with the country's main cyber agency. The fine reduction will vary based on each company's cooperation and engagement levels with the NCSC.
NCSC's ransomware report: The UK NCSC has published a report on the evolution of the ransomware ecosystem and the cybercrime ecosystem that supports it. The report says that criminal gangs have easy access to ransomware code and that companies should not focus on detecting ransomware variants. Instead, they should focus on maintaining good cyber hygiene to avoid getting breached, starting with using MFA and good password policies. An excerpt below.
"More recently, some groups conduct data theft and extortion only, without deploying ransomware. Accordingly, cyber criminals will now use whichever approach they believe most likely to yield payment, deploying ransomware attacks to disrupt logistics companies that need the data to function, but favouring extortion-only attacks against healthcare services (where patient privacy is paramount)."
CISA's OSS roadmap: CISA has published a roadmap of its goals for securing the open-source software ecosystem. The plan includes partnerships with federal agencies, open-source software (OSS) consumers, and the OSS community. Other goals include increasing CISA's visibility in OSS usage, setting up open-source program offices (OSPOs), and promoting the use of software bill of materials (SBOMs).
New hunt-forward mission: US CyberCom has successfully conducted its second hunt-forward mission in Lithuania, where it helped the local government hunt for malware on internal networks. CyberCom staff was previously deployed in Lithuania in May 2022 to help hunt for malware on national defense systems. This is CyberCom's 50th mission since the agency started sending hunt-forward missions to help foreign governments back in 2018.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Red Canary Principal Readiness Engineer Gerry Johansen about the need to prepare and drill IR plans in advance and why that's just as important as the IR playbook itself.
Cybercrime and threat intel
Football Leaks hacker sentenced: A Portuguese court has sentenced the hacker behind the Football Leaks scandal to a suspended prison sentence of four years. Rui Pinto was convicted on nine of 90 charges related to hacking the email accounts of soccer stars and soccer clubs. The hacked information was shared between 2015 and 2018 on a website named Football Leaks and with sports journalists across Europe. Pinto's leaks exposed tax evasion and financial trickeries used by Europe's top clubs and the rape allegations made against Cristiano Ronaldo. Pinto is still facing 377 privacy and hacking-related offenses in a second case that got underway earlier this year and may still spend years in prison.
CSAM sextortions: The FBI IC3 has published a public service announcement warning about online groups targeting minors and extorting them to record CSAM material. The FBI particularly mentioned the names of such groups, such as "676, 764, CVLT, Court, Kaskar, Harm Nation, Leak Society, and H3ll."
Prohqcker phishing operations: Silent Push has an analysis of the phishing infrastructure of a threat group known as Prohqcker, which they've linked to several smishing operations targeting American banks and the Australian Tax Office.
Remcos campaign in Colombia: Check Point says it identified a massive phishing operation that has targeted more than 40 Colombian companies with the Remcos RAT over the past two months.
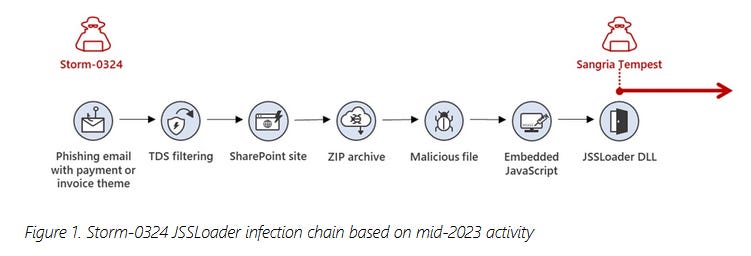
Storm-0324: Microsoft says a threat actor named Storm-0324 (DEV-0324, Sagrid, TA543) is conducting phishing operations via Microsoft Teams. The group's campaigns began in July this year and are using an open-source tool named TeamsPhisher. The tool allows threat actors to send messages with malicious attachments to organizations that allow Teams external communications. Microsoft says Storm-0324 operates as an initial access broker and has been seen selling access to compromised corporate networks to ransomware gangs. One of the group's recent collaborators has been the Clop (Sangria Tempest) ransomware group.
Malware technical reports
CatDDoS botnet: Chinese security firm QiAnXin has discovered a new Mirai-based botnet named CatDDoS. The botnet was set up this month and uses n-day vulnerabilities to compromise devices. Targeted devices include Linksys routers, Apache Hadoop servers, and the ExifTool app.
Hook: Fox-IT looks at how the ERMAC Android banking trojan evolved into the Hook strain.
"Hook had a relatively short run. It was first announced on the 12th of January 2023, and the closing of the project was announced on April 19th, 2023, due to 'leaving for special military operation.' On May 11th, 2023, the actors claimed that the source code of Hook was sold at a price of $70.000. If these announcements are true, it could mean that we will see interesting new versions of Hook in the future."
MidgeDropper: Fortinet's security team has discovered a new malware dropper named MidgeDropper that is currently being distributed through various malspam campaigns.
OriginBotnet: The same Fortinet team also discovered a new loader family named OriginBotnet. It is currently used to deploy the RedLine infostealer as a second-stage payload. With Emotet and Trickbot on a hiatus and Qakbot down following a law enforcement takedown, the loader will certainly have customers.
RomCom RAT: K7 Computing has a report on the RomCom RAT, a remote access trojan developed by the group behind the Cuba ransomware.
Cuba ransomware: Kaspersky has a report on the Cuba group and its operations, involving its ransomware strain and other tools. One of the most interesting findings was that Kaspersky discovered a possible rebrand attempt from Cuba to V is Vendetta.

Sponsor Section
Timing and response plans could mean the difference between an attempted attack or a full-blown compromise. Red Canary's Incident Response & Readiness Guide arms security teams with the blueprint for a modern and effective incident response plan.

APTs and cyber-espionage
Ballistic Bobcat: An Iranian APT group known as Ballistic Bobcat (aka APT35, Charming Kitten, TA453, PHOSPHORUS) has breached 34 companies across the world using a new backdoor named Sponsor. Thirty-two of the companies are located in Israel, while the other two are from Brazil and the UAE. Security firm ESET says the group developed the backdoor in 2021, shortly after CISA published an advisory detailing the inner workings of its previous backdoor named PowerLess.
Redfly: A suspected Chinese cyber-espionage group named Redfly has compromised a national power grid of an Asian country earlier this year. The intrusion lasted six months, and Redfly obtained login credentials and compromised multiple computers on the operator's network. Broadcom's Symantec division says the attackers used a version of the ShadowPad remote access trojan, and Redfly infrastructure overlaps with groups that other security firms track as APT41, Brass Typhoon, Wicked Panda, Winnti, and Red Echo.
Confucius: Chinese security team Antiy has published a report on the Android malware and campaigns of the Confucius suspected Pakistani APT.
BlueShell exploitation: South Korean security firm says it is seeing APT groups mount campaigns that exploit the BlueShell vulnerability.
RFA DPRK series: Radio Free Asia Korean has a three-part video series on how North Korean hackers operate.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Patch Tuesday: Yesterday was the September 2023 Patch Tuesday. We had security updates from Adobe, Microsoft, Chrome, Cisco, Zoom, Asus, Siemens, and SAP. The Android Project, Apple, QNAP, VMWare, NVIDIA, Jenkins, Kubernetes, GitLab, and Drupal, released security updates last week as well.
Microsoft zero-days: This month, Microsoft's Patch Tuesday included 66 fixes, including two zero-days tracked as CVE-2023-36761 (info disclosure in Word) and CVE-2023-36802 (EoP in Microsoft Streaming Service Proxy).
Chrome and Firefox zero-day: Google and Mozilla have released security updates for the Chrome and Firefox web browsers to patch an actively exploited zero-day, tracked as CVE-2023-4863. Both companies credited CitizenLab and Apple's security team for discovering and reporting the vulnerability. While not officially confirmed, the zero-day appears to be connected to the BLASTPASS attack that CitizenLab disclosed last week. BLASTPASS are two iOS zero-days that were used to install the NSO Group's Pegasus spyware on iPhones without user interaction. The new zero-day suggests the existence of a browser-based delivery mechanism that most likely exploits the WebP image format.
Adobe zero-day: Also in this Patch Tuesday, Adobe fixed a zero-day (CVE-2023-26369) in Adobe Acrobat and Reader. No details on exploitation.
WP plugin vulnerabilities: Wordfence researchers have found SQLi and XSS vulnerabilities in the Slimstat Analytics WordPress plugin. More than 100,000 are believed to be affected. A security update has been available since the end of August.
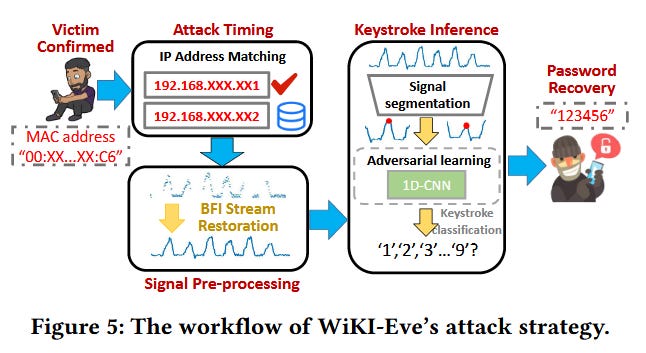
WiKI-Eve attack: A team of Chinese and Singaporean academics has put together WiKI-Eve, a new WiFi attack that can eavesdrop on keystrokes on modern smartphones. The attack exploits a new feature named BFI (beamforming feedback information) that was added in WiFi 5 and which lets access points accurately pinpoint a device's location for better signal quality. Since BFI data is sent in cleartext over WiFi, an attacker in a victim's vicinity can recover this data and potentially infer finger movements on a screen. Researchers say their WiKI-Eve works best with numerical passwords, but alpha-numerical passwords can also be guessed, but with a lower accuracy.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine how AI can help cyber criminals and scammers.




