Risky Biz News: CISA releases HBOM framework
In other news: Crypto platform Mixin hacked for $200 million; the UK is also conducting hunt-forward missions; and Google open-sources BinDiff.
This newsletter is brought to you by Stairwell. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency released on Monday the first version of the Hardware Bill of Materials (HBOM), a framework meant to mitigate supply chain risks for hardware/physical products.
The framework is inspired and is meant to be a complement to SBOM, a similar framework that CISA has been pushing to software vendors since the Log4Shell incident in late 2021.
Under the new HBOM framework, hardware vendors are expected to produce an HBOM file that will contain information on all physical components used in a product.
Information on the component's parent company, hardware makeup, physical attributes, firmware, serial numbers, age, and country of origin or assembly will be included.
The US government hopes the new HBOM framework will help US companies untangle and keep better track of their supply chains amid fear of Chinese tampering with equipment sold in the West. The framework's release comes a month after the South Korean government started a countrywide investigation seeking to identify smart equipment that may contain Chinese backdoors. The investigation began after the government found malicious code found in the chips of weather-measuring instruments made in China and used by the Korean Meteorological Administration.
Cycuity CEO Andreas Kuehlmann argues that HBOM is also crucial in tracking the impact and spread of hardware-based vulnerabilities, such as CPU-related vulnerabilities like Meltdown and Spectre. He often likened an HBOM to the ingredients list found on all edible products today.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Mixin crypto-heist: Cryptocurrency platform Mixin has suspended operations after hackers stole almost $200 million from its wallets. Mixin says the hack took place after the attackers gained access to its cloud infrastructure. The company says it's now working with blockchain security firm SlowMist and Google's Mandiant division to investigate the incident. The Mixin theft is currently this year's largest crypto-heist.
HTX crypto-heist: The HTX cryptocurrency exchange has lost $8 million worth of Ether after a hacker gained access and emptied one of its hot wallets. The company says the stolen funds represented only a small fraction of the $3 billion user funds it is holding. Previously known as Huobi, HTX says it plans to cover user losses from its own pockets.
OpenSea API leak: NFT marketplace OpenSea is notifying customers and asking them to rotate their API keys. OpenSea says it is rotating keys after a security breach at one of its vendors. The incident appears to be related to a similar "vendor incident" that took place at blockchain company Nansen.
Fort Lauderdale BEC scam: The city of Fort Lauderdale in Florida lost $1.2 million in a BEC scam after an employee sent the funds to a scammer pretending to work for a local construction firm. Officials say the scammer pretended to be one of the companies building the city's new police headquarters. The incident took place on September 14, and the wrong transaction was discovered six days later. [Additional coverage in StateScoop]
Insolvency after ransomware attack: A major UK logistics operator, KNP Logistics, has filed for administration and will fire roughly 730 employees after a ransomware attack impacted its operations and market position earlier this year. [Additional coverage in the BBC]
New Iran govt hack: A hacktivist group named "Uprising till Overthrow" claims it hacked the network of Iran's Ministry of Science and unmasked the government's purge of the Iranian academic sector. The group says it breached 500 computers and stole more than 20,000 documents. The files allegedly show the government's crackdown on students who participated in last year's Mahsa Amini protests, as well as the firing and hiring of more than 15,000 pro-regime professors and university staff following the same protests. [Additional coverage in Iran International]
CardX data leak: Thai payments provider CardX has disclosed a security breach that exposed the personal information of customers who applied for cash cards and personal loans. The incident took place on September 15, and the company shut down operations a week later to upgrade its systems.
BORN Ontario hack: An Ontario healthcare organization says hackers have stolen the personal details of 3.4 million people who sought fertility, pregnancy, and child healthcare services from the company. BORN Ontario says the breach impacted the personal data of everyone who requested its assistance over the last 13 years, between January 2010 and May 2023. The organization blamed the incident on the Clop criminal group and linked it to the MOVEit hacking spree that took place earlier this year. [Additional coverage in TechCrunch]
MOVEit victim count passes 2K: The number of companies impacted by Clop's MOVEit hacking spree has formally surpassed 2,000, according to security firm Emsisoft. So far, the Clop gang is believed to have gained access to the personal data of more than 62 million people. US government contractor Maximus disclosed the largest breach, with 11 million users impacted.
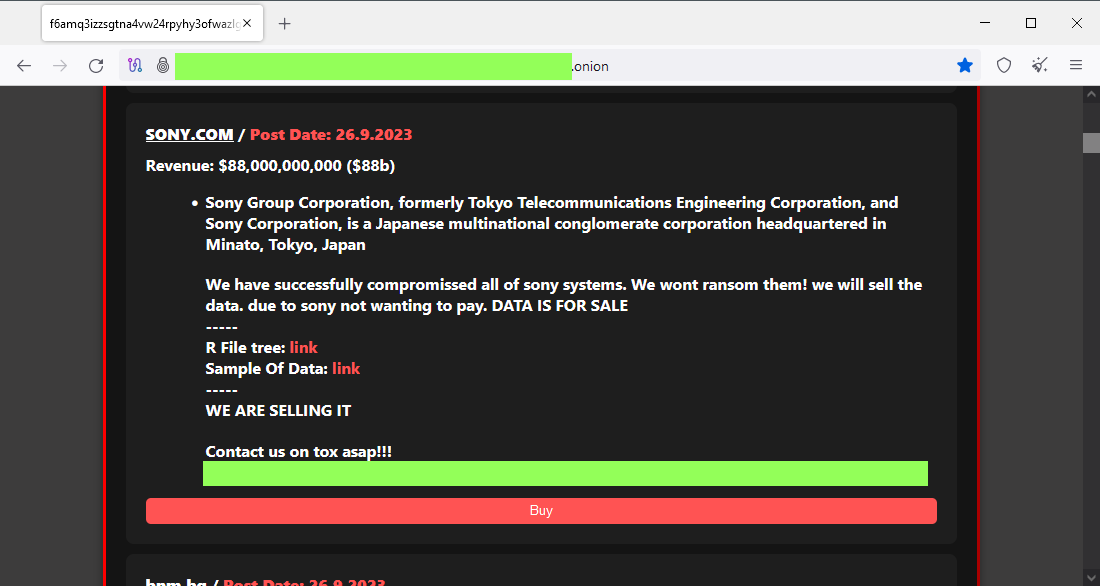
Sony ransomware attack: The RansomedVC ransomware group claims to have breached Japanese company Sony. The group is now selling the company's data on the dark web after the company allegedly declined to pay the ransom. Sony has yet to confirm the breach, and it remains unclear if the breach is authentic, as all evidence released so far has only been screenshots. [Additional coverage in Kotaku]
General tech and privacy
Patreon privacy update: Patreon is preparing a privacy policy update that will make its users' contributions and support public by default for anyone to see.
New Windows 11 security features: Microsoft has a rundown of the new security features landing in Windows 11 next month.
Firefox 118: Mozilla has released Firefox 118. New features and security fixes are included. The biggest change is that Firefox now supports built-in translations, similar to Chrome. All translations are done locally, via language packs, and not in the cloud. Not all languages are supported by default.
Government, politics, and policy
UK hunt-forward missions: The UK National Cyber Force (NCF) has conducted hunt-forward missions where its staff have aided foreign governments in scanning networks and investigating cybersecurity incidents. In an interview, Lt. Gen. Tom Copinger-Symes, deputy commander of the United Kingdom's Strategic Command, says the missions were modeled after similar operations carried out by US Cyber Command over the last few years. The official did not say how many missions the UK has conducted nor in which countries. This month, Cyber Command said it carried out its 50th mission since the agency started sending hunt-forward missions overseas in 2018.
Russian bans: WhatsApp and YouTube have apparently dodged bans in Russia pending government investigations. [Additional coverage in Interfax]
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Stairwell Principal Reverse Engineer Silas Cutler about Akira's recent server leak and attacker infrastructure.
Cybercrime and threat intel
UN-ASEAN-China collaboration: China, the United Nations, and ASEAN are joining forces in an effort to crack down on the local Asian scam call center problem. [Additional coverage in SCMP]
FSB agent detained: Russian authorities have arrested an FSB officer from the city of Perm for taking a bribe from a hacking group to arrange their release from prison and dismissal of their criminal case. The bribe was 100 million rubles, representing more than $1 million. The officer was detained in April this year, and his detention has been extended until November. The name of the criminal gang who paid the bribe is unknown. The gang was detained in February 2022, and it is not related to the REvil and Infraud arrests that took place at the time (likely related to this US case). [h/t Oleg Shakirov; Additional coverage in Kommersant]
C0met: The Shadow ransomware gang has now rebranded to C0met, according to Russian security firm FACCT.
ShadowSyndicate: Security researchers from Group-IB have discovered a major group named ShadowSyndicate that operates as an initial access broker and partner for multiple ransomware operations. The group has been active since July 2022 and has worked with ransomware operations such as Quantum, Nokoyawa, AlphV, Royal, Clop, Cactus, and Play. The group has been seen operating servers all over the world and using malware such as IcedId, Matanbuchus, and Cobalt Strike during its intrusions.
Smishing Triad: A Chinese-speaking cybercrime group known as the Smishing Triad has been spamming UAE citizens after carrying a similar campaign targeting US users earlier this year.
Malware technical reports
Xenomorph: Mobile security firm ThreatFabric has discovered new versions of the Xenomorph Android banking trojan that have been updated to target US banks. Android malware targeting US banks is extremely rare, primarily because of Android's smaller userbase in the US. The targeting of US banks follows a recent trend observed in the Android malware ecosystem. Previous Android banking trojans that have recently targeted US users include the likes of Octo, Hydra, and Hook.
HijackLoader: Alpine Security has another report on HijackLoader, a loader first spotted in the wild this month by Zscaler.
Lu0Bot: ANY.RUN looks at Lu0Bot, a Node.js infostealer first spotted in February 2021 and still used in the wild.
ZenRAT: Proofpoint takes a deep dive into ZenRAT, a remote access trojan distributed via fake installation packages for the Bitwarden password manager.
MoneyMessage ransomware: SecurityScorecard's Vlad Pasca has a technical breakdown of the MoneyMessage ransomware strain.
Hive ransomware: The DFIR Report team has a breakdown of a recent Hive ransomware intrusion.
New ransomware: Fortinet looks at two new ransomware versions named Retch and SHO.
Sponsor Demo Section
Stairwell's Mike Wiacek demonstrates Stairwell's file analysis and threat detection platform to Risky Business host Patrick Gray. Stairwell helps you monitor and analyze every executable file in your organization, automatically collecting crucial intelligence and providing your security team with in-depth visibility and detections.
APTs and cyber-espionage
NSA backdoors: Chinese security firm Xitan Laboratory has published a write-up on "five remote control backdoors" allegedly used by the NSA to breach the Xi'an Northwestern Polytechnical University in June of last year. The five backdoors are NOPEN, FireJet, SecondDate, CunningHeretic, and StoicSurgeon.
AtlasCross: Chinese security firm NSFOCUS has discovered a new APT group named AtlasCross that has been running spear-phishing operations aimed at infecting its victims with the DangerAds and AtlasAgent malware. The company didn't attribute the attacks to any state but said the campaign was interesting because it spoofed US Red Cross operations.
STARK#VORTEX: A Russian APT group named STARK#VORTEX (UAC-0154) is targeting members of the Ukrainian military using malware hidden inside drone manuals. The campaign took place in August and attempted to infect Ukrainian military employees with the MerlinAgent malware.
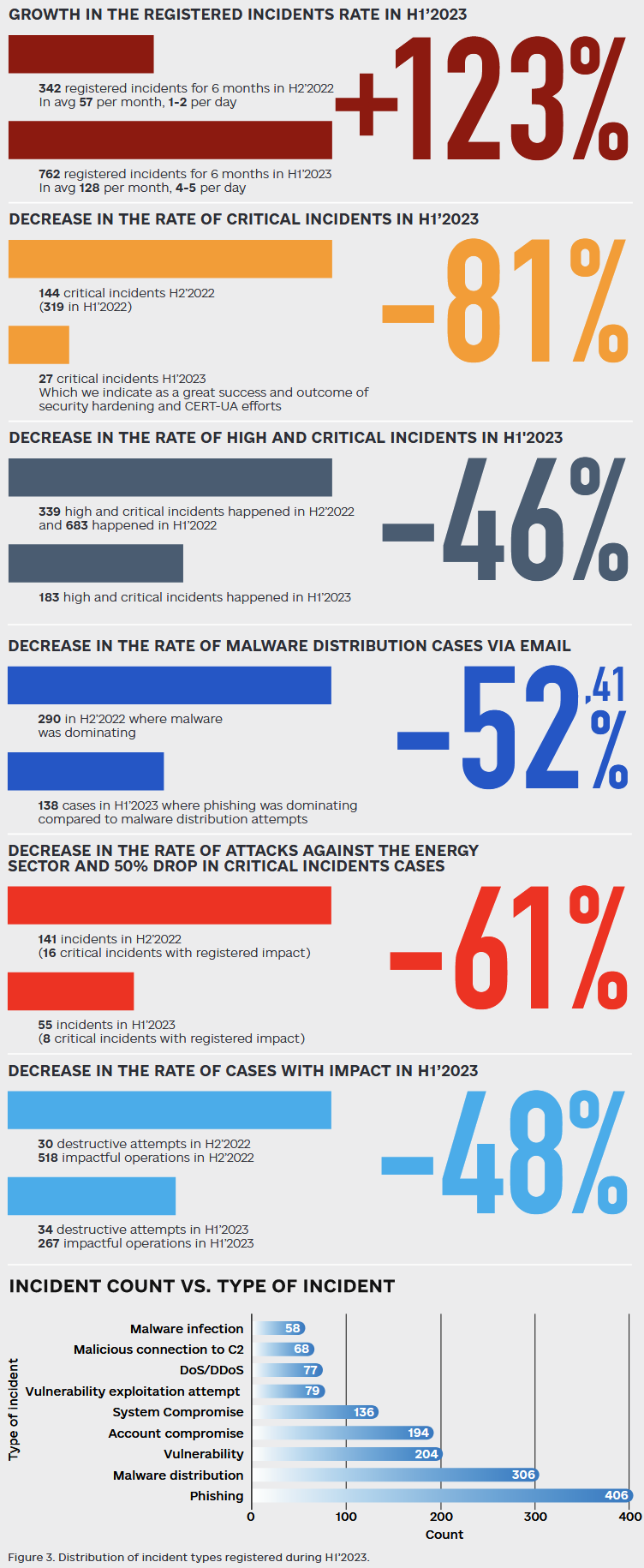
Russian APT activity in Ukraine: Russian cyber-activity in Ukraine has intensified in the first half of the year, but attacks have shifted from malware deployment attempts to phishing operations. Most attacks have targeted government bodies, while many operations also targeted the media sector in order to plant fake news and disinformation in official outlets. Russian hackers are revisiting past victims to obtain new information and targeting email servers to gain access to sensitive communications. Other operations have also targeted Ukrainian law enforcement agencies investigating Russian war crimes. [More in the SSSCIP's report]
"In 2023, the most active groups were UAC-0010 (Gamaredon/FSB), UAC-0056 (GRU), UAC-0028 (APT28/GRU), UAC-0082 (Sandworm/GRU), UAC-0144 / UAC-0024 / UAC-0003 (Turla), UAC-0029 (APT29/SVR), UAC-0109 (Zarya), UAC-0100, UAC-0106 (XakNet), UAC-0107 (CyberArmyofRussia)."
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Openfire exploitation: Threat actors are deploying ransomware, cryptominers, and backdoors on Openfire RTC instant messaging servers. The attackers are exploiting an authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2023-32315) that was patched back in May. Although patches have been available for months, thousands of servers are still unpatched and reachable online.
WinRAR zero-day analysis: SecureLayer7 has published a breakdown of CVE-2023-38831, a recent WinRAR zero-day exploited in the wild.
Chrome vulnerability analysis: GitHub's security team has published an analysis of CVE-2023-3420, a type confusion in Chrome's V8 engine.
SharePoint RCE: StarLabs researchers have published an analysis of an RCE exploit chain (CVE-2023–29357 & CVE-2023–24955) in SharePoint servers they used earlier this year at Pwn2Own Vancouver, a hacking contest where the team came second.
JetBrains TeamCity security update: JetBrains has released a security update for TeamCity on-premise CI/CD servers to fix an authentication bypass vulnerability that can allow attackers to run malicious code and take over customer systems. All versions of TeamCity on-premise servers are affected by the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-42793. TeamCity Cloud is not affected, according to JetBrains. Exploitation is expected, but Rapid7 says attacks have not yet started, primarily because of a lack of a functional PoC. A write-up of the bug is available from the SonarSource team that found it.
Libwebp bug: The Libwebp vulnerability at the core of a recent Chrome zero-day that was exploited in the wild to install the Pegasus spyware now has its own identifier as CVE-2023-5129. Also, a rare 10.0 CVSSv3 severity rating as well.
PPLFault protections: Elastic's security team looks at new experimental Windows features meant to protect the Windows Code Integrity subsystem and make it harder for malware to tamper with Anti-Malware processes and other important security features. This type of feature is expected to block attacks such as PPLFault and GoldFault.
Infosec industry
BinDiff goes open-source: Google's Christian Blichmann has open-sourced BinDiff, a tool used to compare the structure of binary files. The tool has been free to use since 2016, but its source code was still private.
New tool—RedPersist: BGA security researcher Mert Daş has open-sourced RedPersist, a tool for gaining persistence on Windows systems through nine different methods.
Sophos closes Naked Security: British cybersecurity firm Sophos has closed down its cybersecurity blog Naked Security. Naked Security launched in 2007 and featured articles from journalists like Graham Cluley, Paul Roberts, Paul Ducklin, Chester Wisniewski, and many more. The news comes a year after Kaspersky also closed down its ThreatPost publication.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq examine how US and UK strategies to use cyber power differ but are in some ways mirror images of each other.




