Risky Biz News: Brazilian police arrest Grandoreiro malware gang
In other news: Romanian government hit by ransomware attack; Ukraine's GUR wipes Russian company; and US goes after Volt Typhoon infrastructure.

This newsletter is brought to you by enterprise browser maker Island. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:
Brazil's Federal Police has detained five members of Grandoreiro, a malware gang specialized in stealing funds from banking customers with a custom-built banking trojan.
The group has been active since 2019 and is believed to have stolen at least $3.9 million from customers at banks in Brazil, Mexico, and Spain.
Brazilian officials say Spanish financial institution CaixaBank identified the Grandoreiro members and worked with Interpol and Spanish police to get them detained.
Besides the five arrests, officials raided 13 homes and also seized funds and physical assets owned by the group.
According to reports from ESET, Trustwave, and Zscaler, Grandoreiro is a malware strain written in Delphi designed to target Windows systems.
It operated by showing popups, manipulating browsers, and capturing keystrokes in order to collect the credentials and cookies needed to access a victim's bank and other online accounts.

Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
GUR hack in Russia: One of Ukraine's military intelligence agencies says it hacked and wiped servers at IPL Consulting, a Russian company that provides IT services for Russia's industrial sector. Officials from Ukraine's Defence Intelligence Main Directorate (GUR) say they wiped more than 60TB of data from dozens of servers and databases. GUR officials say they also worked with a group of "unknown cyber volunteers in Russia" to cripple the infrastructure of Akado-Telekom, an ISP used by the Putin administration, the FSB, the FSO, the Moscow local administration, and Sberbank.
SOMESING crypto-heist: A threat actor has stolen $11.5 million worth of crypto assets from SOMESING, a blockchain-based karaoke platform. The company says it investigated the incident and found no evidence that its staff was involved in any malicious activity. SOMESING says it reported the hack to South Korean law enforcement.
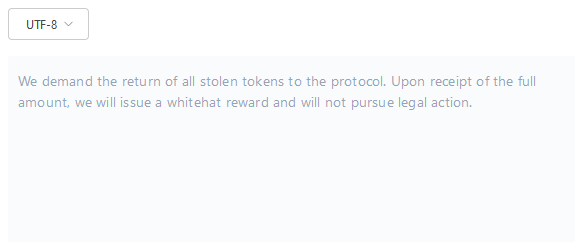
Goledo Finance crypto-heist: Cryptocurrency platform Goledo Finance lost $1.7 million worth of assets in a hack on January 28. The company blamed the loss on a flash loan attack. In a blockchain transaction, Goledo asked the hacker to return the stolen funds for a white hat reward.
Smartmatic legal case: Voting machine maker Smartmatic claims that the president of far-right TV network One America News (OAN) was in possession of a spreadsheet containing passwords of Smartmatic employees. Smartmatic claims OAN President Charles Herring and the network "may have engaged in criminal activities" to obtain the spreadsheet. In a lawsuit filed against OAN, the company says Herring sent the spreadsheet to one of Donald Trump's campaign lawyers in 2021. Smartmatic believes the passwords were used in attempts to access voting systems across the US to prove voter fraud during Trump's 2020 lost election. [Additional coverage in CNN]
Schneider Electric ransomware incident: Energy equipment maker Schneider Electric has fallen victim to a ransomware attack. The incident took place on January 17 and primarily impacted the company's Resource Advisor cloud platform. According to BleepingComputer, the Cactus ransomware group is behind the attack, and they are believed to have stolen terabytes of corporate data.
Romanian govt ransomware incident: A ransomware gang has breached and stolen 250GB of data from the IT systems of Romania's Chamber of Deputies, the country's lower house of Parliament. The Knight ransomware group took credit for the attack in a now-deleted post on their dark web leak site. The group claimed it obtained copies of government contracts, salary information, and copies of national IDs for Romania's top politicians. Romanian officials confirmed the incident for local media after the gang posted national ID copies for the country's prime minister and one of its opposition leaders. [Additional coverage in Hotnews.ro and News.ro]

General tech and privacy
Italy finds ChatGPT violates GDPR: Italy's data protection agency has found that OpenAI's ChatGPT system violates the EU's GDPR regulation. The agency issued a temporary ban against ChatGPT in March of last year, alleging that OpenAI was unlawfully collecting user data. Officials have given the company 30 days to file a formal counterclaim before they make a final ruling and impose a fine.
Major IT outage in Russia: A major IT outage took place on Tuesday, January 30, across the Russian internet space due to a DNSSEC error at Russia's .ru national domain registrar. According to Russian tech experts, the outage was likely caused by a government's attempt to create its own national DNS system, separate from the international one.
Android app security update: Google has introduced a new feature for Android app makers that will allow developers to prompt users to update outdated app versions. Google says it introduced the feature after noticing that more than 50% of Android users respond to Play Store prompts. The new system is meant to complement Android's app auto-update and in-app update systems.
Government, politics, and policy
New cybercrime penalties in Italy: The Italian government is working on a law that will raise penalties for cybercrime offenses to between two and 12 years. Harsher penalties will be applied if the cyberattacks affect national security and involve the use of force or public officials. Cybercriminals who cooperate with police can have their sentence reduced by up to two-thirds. Italy's current legislation includes jail terms between one and eight years. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
Farm and Food Cybersecurity Act: US lawmakers have introduced the Farm and Food Cybersecurity Act, new legislation designed to strengthen cybersecurity practices across the US agricultural sector.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Bradon Rogers, Chief Customer Officer at enterprise browser Island, on how a modern enterprise browser solution like Island can be used to replace, complement, or enhance some enterprise security tools or technology stacks.
Cybercrime and threat intel
ISIS cyber sanctions: The US Treasury Department has sanctioned an Egyptian couple for providing cybersecurity training to ISIS leaders and supporters. US officials say the couple ran the Electronic Horizons Foundation, an online platform also known as Afaq [PDF]. The Afaq site hosted tutorials on how to set up secure computers, how to securely donate cryptocurrency to ISIS, and provided a platform for secure conversations. The Afaq portal shut down in March 2022 in the aftermath of a cyberattack.
Vastaamo hack: In the trial of Julius Aleksanteri Kivimäki, the hacker who extorted victims of the Vaastamo healthcare provider, Finnish authorities claim to have found a way to trace his Monero transactions. Authorities have not released any technical details, and the method still remains unclear. [Additional coverage in CoinTelegraph]
"As per the Finnish police, the hacker received payments in Bitcoin and sent the funds to an exchange that was not compliant with Know Your Customer (KYC) guidelines before swapping for Monero and then transferring the funds to a dedicated Monero wallet."
Sosa profile: Infosec reporter Brian Krebs has published a profile on Noah Michael Urban, the 19-year-old from Florida believed to be a member of the Scattered Spider gang. Urban was detained earlier this year.
Former FSB officer trial delayed: The trial of a former FSB officer accused of taking bribes from hackers has been delayed. The former officer from the city of Perm was accused of taking a $1 million bribe from a hacking group to arrange their release from prison and dismissal of their criminal case. He was detained in September 2023.
Major BTC seizure: German authorities have taken custody of more than €2 billion worth of Bitcoin from one of the operators of movie2k.to, a now-defunct movie piracy portal. The funds were voluntarily transferred to officials by the site's programmer, who's been in pre-trial detention since 2019. In 2020, he also handed over control of the site's domain to authorities. Other movie2k.to admins are still at large and are believed to have similar Bitcoin holdings as the staff were early adopters of the cryptocurrency. [Additional coverage in DerSpiegel]
DarkNetLive scandal: A Darkdot article claims that DarkNetLive—the last standing news sites covering the dark web—has been secretly acquired in November 2022 by Incognito, a darknet drug marketplace. Darkdot claims Incognito has been using the news site to suppress criticism and steer public perception in their favor.
DarkGate via Teams: AT&T's AlienLabs is seeing Microsoft Teams phishing campaigns distributing DarkGate-infected files.
GitHub spam campaign: Code hosting platform GitHub is seeing a rise in cryptocurrency spam after threat actors have found a loophole in the company's defenses. The trick revolves around posting crypto-spam in GitHub commits and issue trackers and then immediately deleting the messages. Project owners receive the spam via email, but because the original content was deleted, they can't report it.
Greatness PhaaS: Trustwave researchers have seen a rise in phishing pages created via the Greatness Phishing-as-a-Service portal.
Phishing kit ecosystem: Guardio Labs looks at the phishing kit ecosystem that's currently flourishing on Telegram channels.
Yahoo Boys: A report from the Network Contagion Research Institute looks at how groups of scammers across West Africa—sometimes referred to as Yahoo Boys—have slowly switched from email financial fraud to social media-enabled sextortion schemes. The report looks at the underground scene that sells sextortion manuals, common tactics and patterns, and how some of these criminals/groups often brag about successful sextortions online without fear or shame. [Additional details in NCRI's report/PDF]

Malware technical reports
Trigona ransomware: The DFIR Report team has published a report on typical Trigona ransomware infections, which typically end up with file encryption with 3h.
CrackedCantil: ANY.RUN researcher Lena Y. has published a report on CrackedCantil, a malware strain distributed via cracked and pirated software. The malware appears to work as a downloader for various other threats.
Ermac: IBM's Trusteer team has published a report on Ermac, an Android banking trojan active since September 2022.
Sponsor Section
Island is an enterprise browser that embeds access policies, data protection, and security controls to create a safe environment that works on unmanaged as well as managed endpoints. Take a look at Island's essential features below [PDF].

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Volt Typhoon secret takedowns: The US government has taken steps to disable hacking infrastructure used by a Chinese cyber-espionage group named Volt Typhoon. Discovered in early 2023, the group has been linked to intrusions at US government agencies and critical infrastructure operators. Although not confirmed, the secretive takedown most likely targeted KV, an IoT botnet operated by the Volt Typhoon group. [Additional coverage in Reuters]
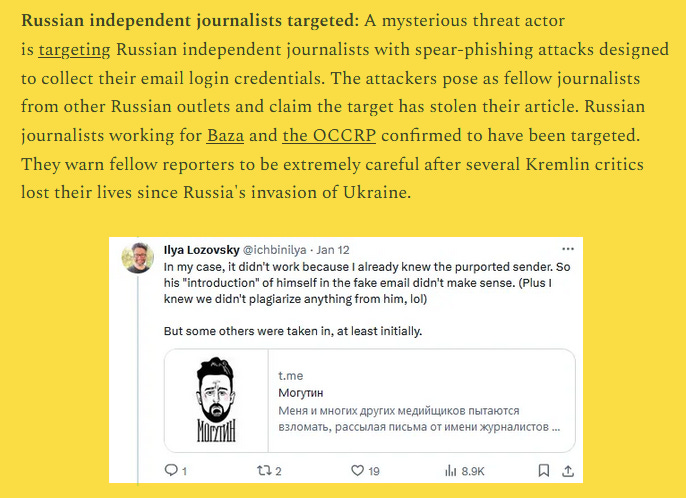
Russian APT: Security firm Cluster25 says the Russian government is most likely behind a spear-phishing campaign that targeted independent journalists and Russian dissident movements inside and beyond the nation's borders. The campaign took place and was spotted earlier this month by Russian journalists from Bellingcat and The Bell. It consisted of a spear-phishing campaign that attempted to install shells on victims' computers. Details below from our January 15 edition.
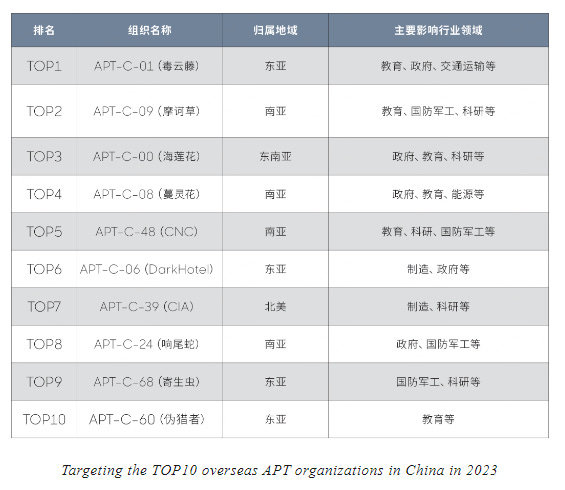
China's 2023 APT report: Chinese security firm Qihoo 360 claims that the CIA was the seventh most active APT group in China last year. Qihoo tracked 135 APTs last year, including 46 new groups. The company says that DarkHotel (APT-C-06) and Parasite (APT-C-68) were the two cyber-espionage groups that used the most zero-days last year. [Full report/PDF]
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
Chrome zero-day details: South Korean firm Theori has published a technical breakdown of CVE-2023–2033, a Chrome zero-day that was exploited in the wild and patched in April 2024.
Hitron zero-days: The operators of the InfectedSlurs botnet have used six zero-days in DVRs from South Korean company Hitron Systems. According to internet infrastructure company Akamai, the zero-days were used to infect the Hitron DVRs with DDoS malware. Patches for all six zero-days were released on January 30.
Jenkins exposure: More than 45,000 Jenkins servers are currently exposed on the internet and are vulnerable to attacks with a flaw in the application's CLI component. Tracked as CVE-2024-23897, the vulnerability was discovered by SonarSource researchers and patched last week. It has a severity rating of 9.8/10 and allows attackers to retrieve cryptographic keys, delete files, or run malicious code. Proof-of-concept code has been published online, and early scanning activity has already been observed.
Ivanti patches delayed: Enterprise software maker Ivanti has delayed crucial patches meant to fix two zero-days in its Connect Secure VPN devices. Ivanti released temporary mitigations for its customers at the start of the month and promised to have firmware updates by January 22. More than a week later, Ivanti has yet to release the updates and to provide an explanation for its delay. Tracked as CVE-2023-46805 and CVE-2024-21887, the two zero-days have been exploited in the wild by a Chinese APT group named UTA0178 since early December of last year.
Android OEM issue: Meta's Red Team X has found that several major Android OEMs sign their APEX modules with private keys from the Android project's public source code repository. Researchers say the issue could have allowed threat actors to forge updates for APEX, a file format used to ship Android system components. Meta says most vendors have fixed the issue in December 2023 security updates—tracked as CVE-2023-45779.
Tor security audit: The Tor Project published its recent security audit for the source code of the Tor network and its browser.
Splunk security updates: Splunk has released security patches to fix three vulnerabilities in its products.
Infosec industry
New tool—White Phoenix web version: CyberArk has released a web version of White Phoenix, a tool that can be used in some limited cases to recover files that have been encrypted using intermittent encryption.
New tool—PolEx: DoyenSec has open-sourced a tool named PolEx, a Visual Studio Code extension to analyze Infrastructure as Code (IaC) architectures and the points where a web application and the underlying infrastructure intersect.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how the war in Ukraine is showing how useful mobile devices are in a war. Using them is risky, but those risks need to be managed.




