Risky Biz News: Russia wants its own CISA
In other news: Google patches Pixel zero-day; Black Basta ransomware gang had a secret Windows zero-day for three months; Ukraine arrests bot farm operators linked to smishing attacks on its soldiers.

This newsletter is brought to you by Detection-as-Code company Panther. You can subscribe to an audio version of this newsletter as a podcast by searching for "Risky Business News" in your podcatcher or subscribing via this RSS feed. On Apple Podcasts:

The Russian government is holding private talks on establishing a dedicated cybersecurity agency, similar to the role CISA plays in the US.
Talks are in early stages but a RIA Novosti report suggests the initiative has support from Russia's private sector.
The Russian government has recently passed or started working on several cybersecurity-related initiatives.
These include larger fines for data breaches, mandatory incident reporting, legalizing vulnerability research, and banning the use of Western software in critical infrastructure on the grounds of national security.
Currently, the enforcement of Russia's cybersecurity regulations fall on multiple agencies, such as the FSB, FSTEC, Roskomnadzor, the Ministry of Digital Affairs, and Russia's Central Bank.
Breaches, hacks, and security incidents
Wichita ransomware attack: A month after falling victim to a ransomware attack, the city of Wichita says it has now restored almost all of the affected servers. [Additional coverage in GovTech]
Tile hack: A threat actor has hacked Tile, a vendor of Bluetooth trackers. The company says the intruder stole names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, and Tile device ID numbers. According to 404 Media, the hacker also managed to gain access to several internal systems, including one used to process law enforcement assistance requests. The hacker told reporters that while they managed to gain access to this tool, they have not abused it.
Aldi skimmer incident: Grocery store Aldi says it found skimmers installed on payment card terminals at five of its stores in California and New Jersey. The company couldn't determine when the devices were installed.
Russia airports targeted: Ukrainian hackers have launched DDoS attacks on Russian airports, causing some flights to get delayed, per UkrInform.
Loopring crypto-heist: A threat actor has exploited the 2FA mechanism of Loopring smart wallet to compromise and steal from customer accounts. The attacker is believed to have stolen at least $5 million worth of assets from customer wallets. Loopring has suspended its 2FA service and is working with law enforcement to track down the hacker.
General tech and privacy
Microsoft deprecates DirectAccess: Microsoft is deprecating DirectAccess, a VPN-like technology that allows users to connect to intranet computers. The feature will be removed in a future version of Windows 11. Microsoft has urged customers to move to its new Always On VPN feature. Always On VPN is available for Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 and subsequent releases.
Safety-Critical Rust Consortium: The Rust Foundation and eight other organizations have launched a new initiative named the Safety-Critical Rust Consortium. The new project will advocate and create guidance for the responsible use of the Rust programming language in safety-critical software, such as industrial equipment and the automotive industry. The Consortium has promised to release any tools and guidance under an open-source license to ensure easy and broad adoption. Founding members also include Toyota, OxidOS, and AdaCore.
Adobe reverses course: Adobe has changed course on a recent ToS change that "granted itself" the right to access and use customer data for its AI models. After a wave of criticism from some of the world's top creators, the company is now rolling out a new ToS that specifically clarifies that it will not use any customer data to train its AI.
Google Chrome complaint: European privacy organization noyb has filed a complaint with Austria's data protection agency against Google for its new Privacy Sandbox technology. Noyb says Google is tricking users to enable Privacy Sandbox by falsely advertising it as an ad privacy feature.
Oracle shuts down ad business: Oracle has shut down its ad business after generating only $300 million in fiscal year 2024, down from $2 billion two years ago. [Additional coverage in AdWeek]
Verisk shuts down: Data broker company Verisk has shut down a division that collects driver behavior data and sells it to car insurance companies. According to The Record, Verisk is one of the several data brokers that buy driver behavior data from car manufacturers and resell it to insurers. The company most likely shut down its product after the FTC announced a future crackdown on the misuse of car and driving data.
Meta attacks researchers: Social media Meta has harassed and discredited a team of researchers from one of Brazil's top universities who found fraudulent ads on its platforms. This is the latest incident where Meta was caught attacking academics who were studying abuses on its platform. In 2021, Meta banned NYU researchers from its platforms while they were investigating disinformation campaigns on the platform. [Additional coverage in Nucleo]
Mastodon and BlueSky scrape: A start-up named Maven, founded by an ex-OpenAI executive, is scraping Mastodon and BlueSky posts. There is no way to opt out or to have posts deleted. The posts are used to show content to the company's social media app. More than 1.12 million Mastodon posts have been scraped so far. The company said it scraped the posts as a temporary solution while it implemented its ActivityPub integration. It promised to delete the data after being criticized by Mastodon users.
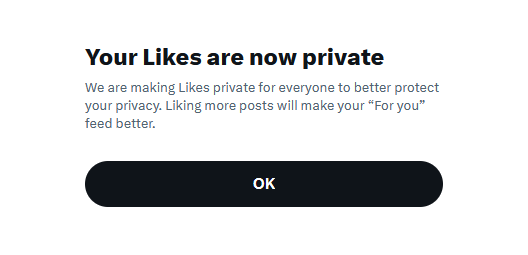
Twitter likes are now private: Twitter has made user likes private, a feature that has been requested for more than a decade. RIP to all the moments when we caught politicians liking pr0n on the site.
Government, politics, and policy
New Western sanctions: The US government has issued new sanctions against Russia this week. The sanctions target Russia's military and financial sector, and they have an IT-related component.
"To implement this policy, Treasury, in consultation with the Department of State, has issued a new determination under Executive Order (E.O.) 14071, which prohibits the supply to any person in the Russian Federation of (1) IT consultancy and design services; and (2) IT support services and cloud-based services for enterprise management software and design and manufacturing software. The determination will take effect on September 12, 2024."
Russia sanctions back: The Kremlin has extended its ban on Russian government agencies and critical organizations from using IT security services from "unfriendly" countries. The new ban will enter into effect on January 1, 2025, when the previous one was set to expire. [Additional coverage in SecurityLab]
Microsoft inquiry: ProPublica has published the story of Andrew Harris, a former Microsoft security engineer set to testify before the House Homeland Security Committee this week in a Congressional inquiry into recent Microsoft hacks. Harris says he warned the company about security issues with the ADFS SSO feature but was ignored. He accused the company of putting its own profits ahead of customer security, which several other infosec experts have also said in the past. Microsoft Vice Chair and President Brad Smith will have to answer this and much more on Thursday. His prepared testimony is here. The committee meeting will be live-streamed on YouTube and available via the video below.
Sponsor section
In this Risky Business News sponsor interview, Catalin Cimpanu talks with Panther Senior Engineering Manager Nicholas Hakmiller on how the IT market is adapting to the cybersecurity skill shortage by training regular software talent in detection engineering, how AI is not there yet, and how Panther excels at spotting initial account compromise.

Cybercrime and threat intel
Conti arrest: Last week, Dutch officials announced the arrest of a Conti member in Kyiv. Ukraine's Cyber Police has now also confirmed the arrest and said the suspect provided crypting services to both Conti and LockBit groups.
Russian bot farm operators detained: Ukrainian authorities have arrested two individuals who ran mobile bot farms. The two suspects used Ukrainian SIM cards to register more than 15,000 social media accounts and sold access to the accounts through the dark web. The Ukrainian SBU says Russian intelligence bought access to some of these accounts to spread pro-Kremlin propaganda and send smishing messages to Ukrainian soldiers.

Desjardins arrests: Canadian authorities have arrested three individuals believed to have hacked the Desjardins Group, the country's largest credit union. The hack took place in 2019, and hackers stole the personal data of 4.2 million customers and 173,000 businesses. Authorities have named two of the suspects and said they also issued an arrest warrant for a fourth suspect. [Additional coverage in the CBC]
Disgruntled IT employee sentenced: Singaporean authorities have sentenced a former employee of IT company NCS to two years and eight months in prison. Officials say Kandula Nagaraju wiped over 180 NCS servers in March 2023, months after he was fired for poor performance. He was arrested later in 2023 after NCS tracked down the attack to the laptop of Nagaraju's roommate, also a former NCS employee. [Additional coverage in ChannelNewsAsia]
Hacker-for-hire scandal: The California State Bar has accused a Los Angeles lawyer of trying to hire Israeli hackers to break into the emails of a judge and rival attorney. Michael Libman concocted the scheme with another lawyer named Paul Paradis after a judge canceled a settlement in a class action lawsuit against the California Department of Water and Power. Another lawsuit found that Paradis had secretly represented both of the parties in the class action lawsuit. The judge canceled the settlement and ordered Libman to return $1.65 million he received as attorney fees in the case. The California State Bar claims Libman and Paradis wanted to use a hacker to get the judge's emails hoping to find evidence to get the ruling annulled and keep their attorney fees. The scheme was uncovered after Paradis turned FBI informant. [Additional coverage in the Daily Journal]
Variston development: Spanish surveillance vendor Variston is considering leaving the offensive security field after losing most of its staff earlier this year.
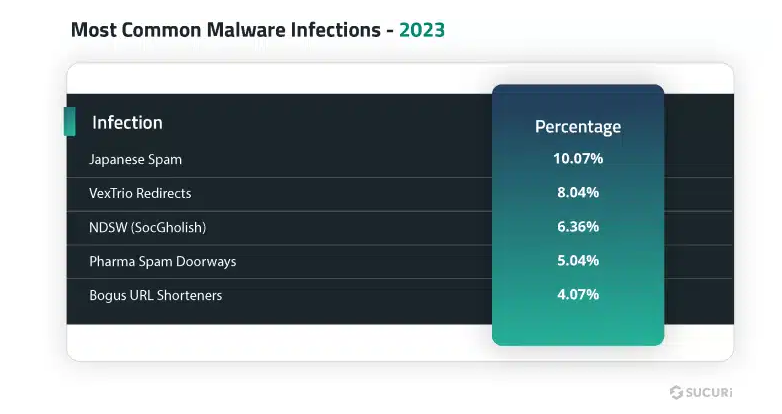
Threat/trend reports: Bitdefender, CyFirma, GuidePoint Security, Sophos, Sucuri, ProtectAI, and VulnCheck have recently published reports covering infosec industry threats and trends. The most interesting of these reports is the Bitdefender one, which found that roughly 70% of infosec researchers often work on the weekends to address security issues at their employer/customers.
Qilin RaaS: Equinix threat intel analyst Will Thomas has published an analysis of the Qilin ransomware operation, the group behind the recent attack on Synnovis, a lab service provider for UK hospitals. The attack delayed transplant surgeries and blood transfusions at affected hospitals.
Pro-Kremlin DDoS attacks: A bunch of pro-Kremlin groups have turned their sights on Canadian websites, carrying out several DDoS attacks on Canadian ISP Telus already.
DDoS attacks on the EU election: The CyberVandals research group says it did not see widespread coordinated DDoS attacks from pro-Kremlin groups during the recent EU elections.
Brazil cyber ecosystem: Google's Mandiant division has published a threat report on Brazil, the groups that target the country, and its famous underground cybercrime ecosystem.
"Since 2020, cyber espionage groups from more than a dozen countries have targeted users in Brazil; however, more than 85% of government-backed phishing activity is concentrated among groups from the PRC, North Korea, and Russia."
UNC3944: The same Mandiant team has also published a report on UNC3944 (0ktapus, Octo Tempest, Scatter Swine, or Scattered Spider). The report focuses on the group's general techniques and its recent pivot to targeting and stealing data from accounts on SaaS applications.
Scam group exposed: Security firm Netcraft has spotted financial and technical infrastructure linked to a scam group engaging in pig-butchering and advanced fee fraud that made at least $45 million worth of crypto from their operations.
Networking equipment fails: CERT-FR has published a report (only in French for now) on all the recent vulnerabilities in networking and enterprise equipment exploited over 2023 and the start of 2024. It's a long list. Le French sigh!
Docker group: DataDog has published a report on a new series of attacks on Docker systems exposing their API. The company says the campaign was carried out by the same group behind the Spinning YARN operation from earlier this year.
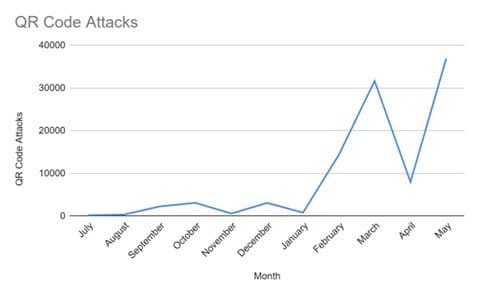
QR code phishing attacks: Check Point says that QR code phishing, also known as quishing, is rapidly becoming one of the most prevalent threats today.
CISA fraud alert: CISA has put out a warning that phone scammers are posing as its staff to extract payments from American companies. The agency says this is part of a larger trend where threat actors pose as US government employees to drive their scam success rates.
Russian crypto scams: Russian security firm FACCT warns of a new trend in social engineering tactics targeting Russian crypto owners. The new tactic uses ENS domains that are based on the Ethereum blockchain to host ephemeral phishing infrastructure.
Olympics scams are coming: Proofpoint says it identified 338 fraudulent websites purporting to sell tickets to the Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games. The company has worked with French police to take some of them down.
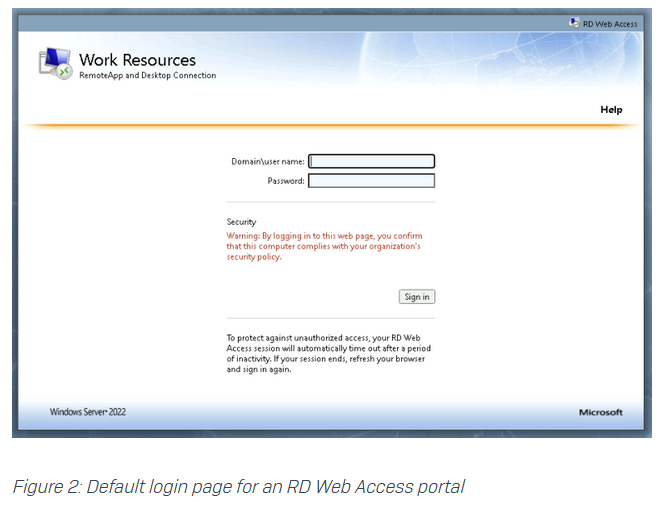
RD Web Access abuse: Security firm Sophos says it responded to multiple incidents since the start of the year where threat actors gained access to an organization via their RD Web Access portals. RD Web Access is one of the four components of the Microsoft Remote Desktop service. It allows users to authenticate via a web portal before connecting to their remote host. Sophos says the intrusions were linked to portals that didn't use MFA.
Malware technical reports
Bondnet: South Korean firm AhnLab says the Bondnet crypto-mining botnet is still alive seven years later after being first spotted in 2017 by GuardiCore.
BadSpace: G Data researchers analyze BadSpace, a new backdoor that is currently distributed via hacked websites pushing fake browser updates.
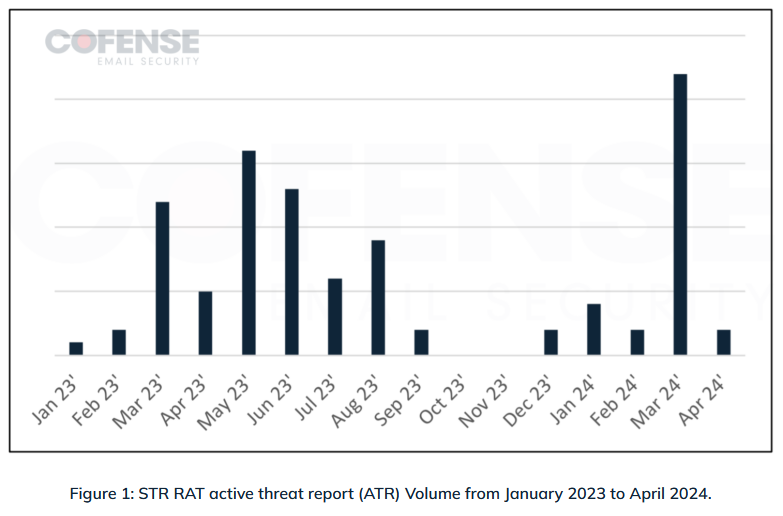
STR RAT: Cofense researchers have analyzed the recent activity and recent campaigns delivering STR RAT, a lesser-known remote access trojan that's been around since 2020.
Sponsor Section
Today's podcast is brought to you by Detection-as-Code company Panther... and, in what we think is a first, they've released a detection-as-code graphic novel... called Guardians of Valora. It teaches the five key principles of Detection-as-Code... grab it now from panther.com."

APTs, cyber-espionage, and info-ops
Matriochka: The French government has published a report on Matriochka, a pro-Russian social media influence campaign that tried to discredit Western news media, public figures, and fact-checking organizations. Matriochka accounts impersonated their targets, aiming to discredit their trustworthiness while also spreading Russian interests. The campaign has been active since September of last year, and its main objective has been to propagate and amplify anti-Ukrainian narratives. French officials say disinformation posted on Twitter was initially posted on Russian Telegram channels, suggesting the content was initially set up for Russian-speaking audiences and then repurposed for Western audiences.
"VIGINUM believes that this campaign undermines the reputation of French mainstream media and official institutions. Since the start of the large-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the Russian influencing mechanism has regularly targeted fact-checkers and used extensive resources to discredit analysis from Western media outlets."
AridViper: Palestinian APT group AridViper has recently used trojanized apps to target Android users in Egypt and Palestine. According to ESET, the apps were infected with the AridSpy spyware and were distributed using third-party sites.
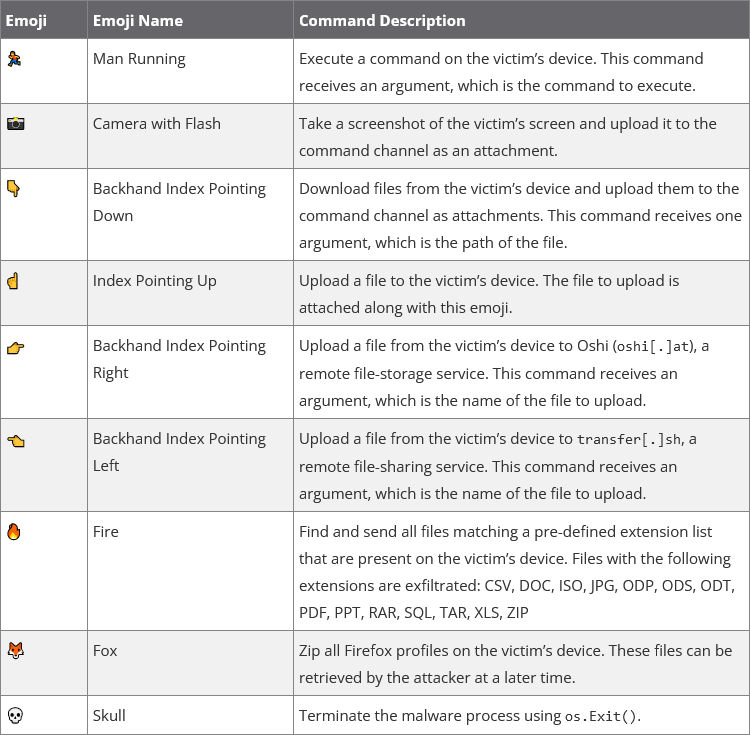
UTA0137 and DISGOMOJI: Security firm Volexity has discovered a suspected Pakistani APT group engaging in cyber-espionage against Indian government entities. The group's main toolkit is DISGOMOJI, a malware strain designed to target Linux servers. The malware uses a Discord channel as its command-and-control server and emojis as commands to control infected systems. Volexity tracks the new group as UTA0137.
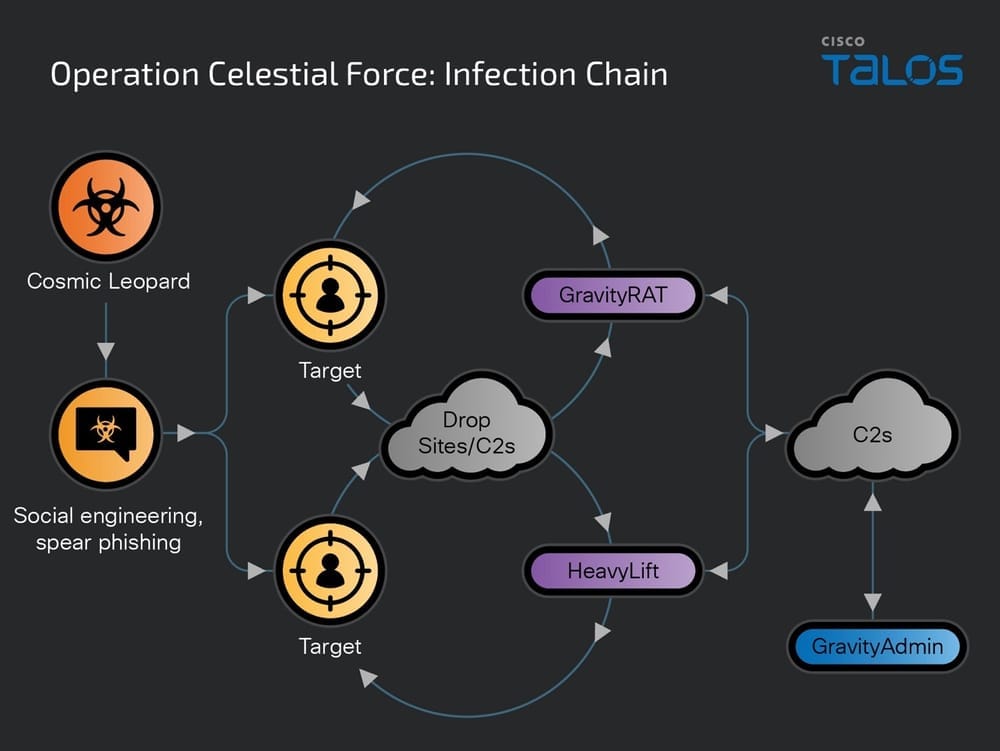
Cosmic Leopard: Cisco Talos has discovered a new Pakistani APT group focused on espionage and surveillance of Indian targets. Cisco says the Cosmic Leopard group has been active since 2018 and operates a malware platform named GravityAdmin. The group uses the platform to manage infections with the GravityRAT on Android and the HeavyLift malware on Windows. Researchers say some Cosmic Leopard TTPs overlap with another Pakistani APT group named Transparent Tribe.
Vulnerabilities, security research, and bug bounty
ENISA is a CNA: The EU cybersecurity agency ENISA has been approved as an official CVE Numbering Authority (CNA). The agency can now assign CVE identifiers to vulnerabilities found or reported to its staff.
Windows zero-day abused by ransomware: Symantec researchers have found evidence to suggest that the Black Basta ransomware was in possession of a Windows zero-day. Researchers say they found an exploit for a vulnerability in the Windows Error Reporting Service (CVE-2024-26169) that was dated before Microsoft's official patch. The zero-day would have allowed the gang to elevate privileges on compromised systems. Symantec says it found exploits for the bug compiled a full three months before Microsoft's patch.
Google Pixel zero-day: Google has released a security update for its Pixel smartphones to fix a zero-day vulnerability exploited in the wild. The company described the vulnerability (CVE-2024-32896) as an elevation of privilege in the Pixel firmware. Google patched two other Pixel zero-days in April, which were used by forensic firms to unlock phones without a PIN.
Weak Fortinet password: German security firm G Data has discovered that Fortinet firewalls use weak password hashes to secure backup files. Tracked as CVE-2024-21754, the vulnerability can be exploited to decrypt backup files and read a device's login credentials. Fortinet released a patch earlier this week to address the issue. G Data says Fortinet backup files are often sent via email and can be intercepted and decrypted by threat actors. The company has urged Fortinet customers to apply the patch as soon as possible.
HTTP/2 Rapid Reset PoC: Russian DDoS mitigation firm Qrator Labs says threat actors are sharing proof-of-concept (PoC) code for the HTTP/2 Rapid Reset DDoS attack.
Apple bug PoC: CertiK SkyFall researcher Wang Tielei has published a PoC for CVE-2024-27801, a bug impacting the NSXPC component in Apple's macOS and iOS. The bug impacts all component versions since its release a decade ago. Apple patched the vulnerability in May. [h/t ScreamingGoat]
"This vulnerability could have potentially allowed malicious apps to gain unauthorized access to system services or steal user data from certain third-party applications, particularly those with architectures similar to Telegram. Our proof-of-concept attack demonstrated how a malicious app could steal chat history (such as pictures) from Telegram and transfer it to a remote server."
Ivanti EPM SQLi PoC: Horizon3 has published a detailed write-up and a PoC on CVE-2024-29824, an SQL injection in the Ivanti EPM, an enterprise endpoint management solution. No attacks were observed in the wild just yet.
Sonatype Nexus PoC: A security researcher has published a write-up and PoC for an unauthenticated path traversal vulnerability (CVE-2024–4956) in the Sonatype Nexus Repository artifact manager. Sonatype patched the vulnerability in May.
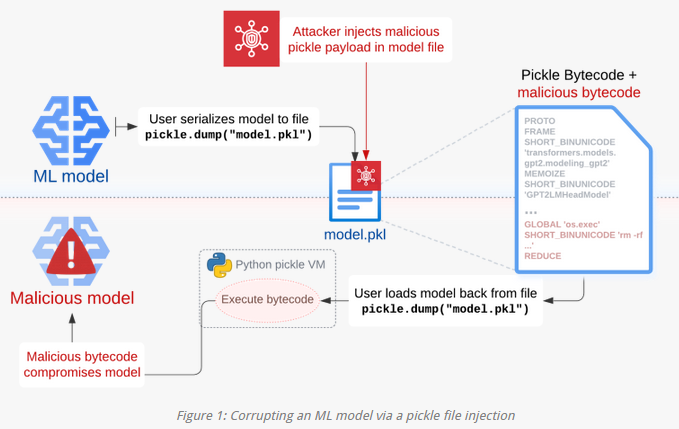
Pickle attack techniques: Security research company has published research on Sleepy Pickle, a new technique to exploit Pickle, the (pkl) file format used to package and distribute ML models.
Infosec industry
Google CTF: Google's security team has launched its yearly Capture The Flag contest.
New tool—Fancy Cryptography: Databricks security engineer Steve Weis has compiled a list of companies that use non-standard cryptography setups.
New tool—YetiHunter: Cloud security firm Permiso has open-sourced a tool named YetiHunter that can search for signs of compromise in a company's Snowflake accounts.
New tool—SusScanner: AWS has open-sourced SusScanner (Sustainability Scanner), a tool to validate AWS CloudFormation templates against AWS best practices.
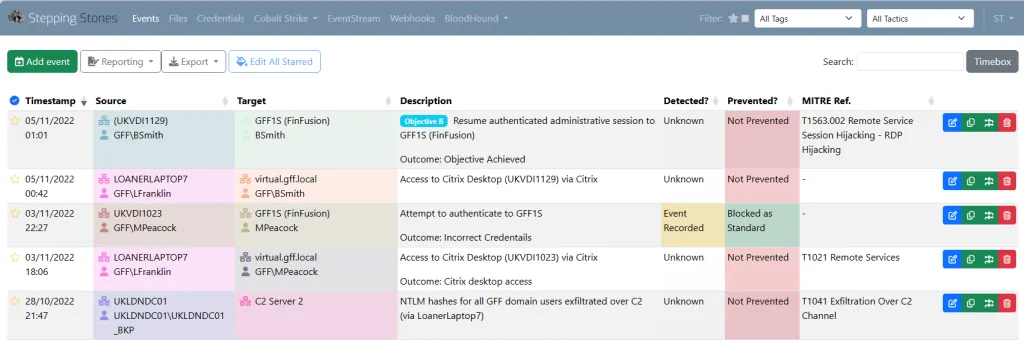
New tool—Stepping Stones: The NCC Group has open-sourced a tool named Stepping Stones that can help red teams with record keeping, situational awareness, and reports.
Risky Business Podcasts
In this edition of Between Two Nerds, Tom Uren and The Grugq talk about how the use of cyber operations in Ukraine is informative, but the information is incomplete. Rather than clarifying the role of cyber operations in conventional warfare, there is still a lot of room for confirmation bias.




